The risk of corrosion on stainless steel most often appears after welding work or after finishing processing of the part mechanically (emery tools, sandblasting, etc.). The essence of the damage received by the metal is the disruption of the chromium oxide layer, as a result of which the iron is “bare” and becomes unprotected. Therefore, every impact on stainless steel must be “neutralized” by passivation and chemical etching.
Stainless steel pickling. Indications. Etching methods.
Stainless steel often requires surface treatment to achieve the desired aesthetic or performance properties. Treatment with shot blasting and sandblasting devices is limited due to the high probability of hardening. Modern production uses etching of stainless steel, after preliminary thermal or mechanical treatment. The complexity of this process, compared to conventional black, low-alloy steels, is explained by the presence of a chromium oxide film that acts as a protective barrier. It is this that forms hard scale that does not interact well with reagents. Technological influences may cause color changes on the surface. These include welding, soldering, and other operations involving high temperatures. Iridescent tarnish can be removed by etching. For different chemical compositions of stainless steel, individual pickling methods and compositions have been developed, taking into account the influence of the steel elements, to achieve maximum results.
The predominant
methods of etching stainless steels are alkaline and acid, which can be intensified by electrolysis or proceed without it.
Reasons why processing is important
During the manufacture of numerous structures using stainless steel as the main material, welding methods are actively used due to the functioning of an electric arc in an inert gas environment.
Despite the formation of relatively smooth and strong seams, they are characterized by the presence of an unattractive appearance, resulting in the need to treat stainless steel welds. Thus, the place of the welded joint is characterized by the presence of a mirror color, while the area near the seam is yellow and its many shades.
In the case of the formation of a pattern in the form of scales, the presence of small black stripes is noted in the resulting grooves. After a certain period of time, there may be a risk of rust forming in these areas.
Phenomena of this nature are a consequence of exposure to excessively high temperature conditions, which results in overheating in the welding area. When high temperatures are present, alloying elements burn out with simultaneous depletion, which results in a change in color and an increase in the degree of vulnerability to external factors.
At the end of the process, a film is formed, which is characterized by a low level of resistance to aggressive environmental influences, which leads to the gradual development of corrosion at the treatment site.
Acid etching
The maximum effect of etching stainless steel with acids is achieved by sequential interaction of the stainless steel surface in baths with two types of acids - sulfuric and nitric. The sequence of stages is as follows
- Degreasing, removal of large snags, scale
- Pickling in a sulfuric acid bath (concentration 10-12%) or sulfuric acid bath (8% sulfuric acid, 4% hydrochloric acid). In this case, corrosion of scale and roughness on the surface occurs. The ideal temperature for the process is between 60 and 80 degrees Celsius. Monitoring this parameter is important for process control. The duration of treatment depends on the steel grade, the presence of a controlled ratio, and the concentration of acids. If the bath is depleted, pitting corrosion may occur. For example, steel with 18% Cr, 8% Ni requires 23 to 45 minutes of pickling in a sulfuric acid bath. Reducing the processing time by half can be achieved if this operation is carried out in a controlled atmosphere.
- Rinsing with plenty of running water
- Immersion of the workpiece in a bath filled with a solution of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid (10 - 20, 1-2 weight percent, respectively). At a bath temperature of 60–70 degrees, the treatment time is 7–15 minutes.
- Repeated rinsing with large volumes of water
The presented method is basic and has many variations. Etching in one nitrate bath with an admixture of hydrofluoric acid increases the etching time to 30 minutes. Sodium fluoride can act as a substitute for hydrofluoric acid. Increasing the concentration of hydrofluoric acid to 10% allows the process to be carried out at low temperatures, avoiding preliminary immersion in sulfuric acid.
Reducing the etching time in sulfuric acid can be achieved by adding no more than 5% sodium chloride. This move gives the desired effect in 15 minutes, but at the same temperature, about 80 degrees Celsius.
Be careful: if it is necessary to carry out the procedure in a room with insufficient aspiration, replace the components of the second stage of etching. Acids produce harmful fumes when etching. A solution of ferrous sulfate (7%) and hydrofluoric acid (2%) is proposed as a replacement.
To correctly select the acid etching method, you need to know and take into account the state of the oxide film on the surface of stainless steel.
Appearance can tell you about the composition of the film. The green color of the scale indicates a high content of chromium oxides. Accordingly, the action of acidic environments will be difficult and will require more time. Intermediate mechanical cleaning between two baths is recommended if descaling is difficult.
Mechanical grinding
Stainless steel is characterized by the presence of a high level of corrosive properties, which determine its active use in environments where liquids are often used. Although products made from such material are in active contact with water and are subject to preliminary welding, their appearance does not change significantly over time. This feature can be traced as a result of the use of certain processing principles.
Among the main processing options, it is customary to highlight mechanical grinding of stainless steel after welding. During this process, the top layer of the oxide component that forms at the welding site and represents a weak point in the entire structure is eliminated. Distinct color transitions and existing irregularities in the weld joint are also eliminated.
This process is characterized by the following sequence:
- eliminating waves in the area of the metal seam by using a thick grinding wheel and grinder, as well as leveling out any bulges present;
- using petal circles for the functioning of the grinder; the main goal of such elements is to carry out work more accurately, along with longer process times and consumption of materials, which is especially important for large-scale work;
- the use of a specially designed equipment complex in the form of a grinding machine, the result of which is a one-color matte coating;
- mandatory use of a respirator to reduce the risk of abrasive dust and metal particles entering the respiratory tract that are in the air during work.
Etching with ready-made pastes
Modern industry offers a variety of stainless steel pickling pastes . Their main purpose is local processing of welds, the consequences of changes in the uniformity of surface coloring under the influence of temperature. The principle of working with such pastes is simple and can be used even in small workshops.
- Apply the paste in a thick layer up to 2 cm, using a brush
- Exposure 60-90 minutes
- Water jet rinsing
Mechanical method of processing welds
You can remove color transitions and other visual defects using a felt wheel for an angle grinder and GOI paste. Moreover, it is better to use an angle grinder with a speed controller.
By the way, you can make a felt circle of the required diameter yourself. To do this, you can use old felt boots.
Apply GOI paste to the felt wheel and begin polishing. In this way you can achieve very good results.
By the way, instead of a felt wheel, you can also use Scotch Brite wheels or polishing muslin wheels. They allow you to achieve even better results than with felt.
Alkaline etching
Treating the surface of stainless steel with molten caustic soda is called alkaline etching. It should be noted that during this process the oxide film is destroyed, while the chemicals do not react with the metal. An increase in temperature promotes corrosion of the oxide film, improving the quality of the treated surface. Rapid cooling in liquid also helps to improve the treated surface.
It is almost impossible to achieve 100% results with this type of processing. Residual films from chromium oxides, nickel and iron oxides are possible on the metal. Among the recommendations for final finishing of such defects is a short-term treatment in a nitrate bath.
Treatment of stainless steel seams after welding
- Log in to reply to this topic
#1 nadar
- Top
- Insert nickname
#2 e233
- Top
- Insert nickname
#3 HUMBLE
How is the weld seam treated after argon welding, for example, railings made of stainless steel pipes to give it a civilized appearance? The abrasive method will not work in this case as it will leave scratches. Polishing is also not suitable, there are unpolished places left, and you can’t get anywhere.
The pickling paste is used to restore stainless steel surfaces damaged during welding, casting, cutting and blowing. The paste removes welding oxides, chromium-depleted metal layers, micro-slag particles and other components that can cause local corrosion.
Compared to classic etching pastes, the blue paste emits 70% less nitrogen fumes when used. Thanks to its flowing consistency and blue color visible on the metal surface, the paste ensures high performance and economical use.
This paste can be used for etching standard steel grades 304 (08Х18Н10), 321 (08Х18Н10Т) and 316 (03Х17Н14М3). The paste is applied to the metal that has cooled to room temperature (10 - 30°C). Etching time - 90 min at 10°C; 45min at 20°C; and 20 min at 30°C. https://z-master.su/p. cts_id=58000008
Welding of all types of metal in SAMARA -
- Top
- Insert nickname
#4 blazen79
- Top
- Insert nickname
#5 HUMBLE
How is the weld seam treated after argon welding, for example, railings made of stainless steel pipes to give it a civilized appearance? The abrasive method will not work in this case as it will leave scratches. Polishing is also not suitable, there are unpolished places left, and you can’t get anywhere.
Welding of all types of metal in SAMARA -
- Top
- Insert nickname
#6 blazen79
Attached images
- Top
- Insert nickname
#7 MIHA75
- Participant
- Messages: 841
- City: N. Tagil
- Top
- Insert nickname
Alkaline etching methods
The following methods are distinguished:
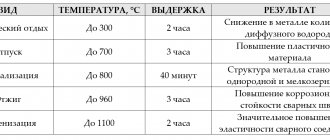
- Aging in soda. The sodium nitrate content should range from 20-40%, heated to a temperature of 460-500 degrees Celsius. Etching in such an environment lasts for 15 minutes. Some austenitic grades of stainless steel are prohibited from being heated above 450 degrees. This can lead to intergranular corrosion. This is followed by a rinsing step in a large amount of water, followed by a 5-minute immersion in a sulfuric acid bath and up to 10 minutes in a nitrate bath.
- Known in England since the first half of the 19th century, the etching method is combined with passing an electric current through the part being etched. At a current density of 11 A/m2, 15 seconds is sufficient. This reaction rate is associated with the electrolysis process. The release of sodium and hydrogen at the cathode contributes to the reduction of oxides. The reduced metal is deposited on the surface. This type of etching allows you to obtain degreased metal, characterized by purity and uniformity. This method uses soda. Variations are possible with the composition and addition of calcium chloride. This method is used for etching flat, rod blanks, and drawn products.
- Treatment with sodium hydrides is based on reduction by exposing the metal to sodium and hydrogen. The presence of sodium hydride is achieved by the interaction of hydrogen and sodium, which is in a molten state. A cylinder without a bottom plane is placed in molten caustic soda. The top plane has a hole. Sodium is poured into this hole, it reacts on the surface of the bath. A stream of hydrogen is passed through a spot of sodium on caustic soda. A hydride is formed and diffuses throughout the bath. Achieving the required concentration of 1-2% sodium hydride occurs within controlled threshold values. In the absence of an air separation product, dissociated ammonia is used. The parts are heated in such a bath to 400 degrees Celsius. Stainless steels show good pickling results with this technique and duration of 4-17 minutes. After etching, it is recommended to thoroughly rinse the parts. If necessary, carry out additional treatment in a nitrate bath. Given the high cost of this method, its obvious advantage is the fact that the metal does not interact with the etchant. Metal losses are minimal. Lower process temperatures reduce coolant costs and reduce operational safety.
There are certain rules that must be followed for any of the presented methods. Among them, priority is the treatment of the metal surface before etching, removal of the oxide film, and degreasing. The etching process is no less important.
Reasons for processing
In the manufacture of various stainless steel structures, methods of welding metals with an electric arc in an environment of inert gases are used. To do this, use a tungsten non-consumable electrode and a supply of pure argon to protect the weld pool from interaction with the environment. You can also create a seam using semi-automatic machines, where an arc burns between the tip of the wire and the product. A mixture of argon and carbon dioxide is supplied from the burner nozzle. The wire is pushed by a special mechanism, the speed of which is adjusted depending on the thickness of the metal and the current strength.
Although the seams are strong and even, they have an unattractive appearance and therefore need to be processed. The junction itself may have a bluish-mirrored hue. The peri-suture zone is often yellow. With a scaly pattern, black marks may be visible in the grooves. And over time, such places even rust.
All this happens due to overheating in the welding zone. High temperatures from an electric arc promote burnout of alloying elements and deplete this area. As a result, it changes color and becomes more vulnerable to external influences. The film formed on the surface has little resistance to an aggressive environment, therefore, when it comes into contact with working fluids at chemical plants, it becomes a weak point and becomes covered with corrosion.
Heated towel rails sometimes rust at the welding points due to the presence of a small electrical voltage in the pipes, which interacts with the material of the product and continues to weaken the weld. This also happens due to the wrong choice of stainless steel for a specific type of product. For example, instead of grade 304, which is rich in chromium, manufacturers use stainless steel 201, which is cheaper, but whose composition replaces chromium with manganese. It is difficult to distinguish them visually, but with prolonged work in contact with liquids, this will appear as red spots. Therefore, the correct choice of steel grade and subsequent processing of stainless steel is the key to a long, attractive appearance of the product.
Bath materials
Choosing the right material for making etching baths is a difficult task for chemists and materials scientists.
- ceramic coated
- glass covered brick
- wood, lead-coated concrete
- rubber derivatives
- Certain grades of stainless steel for acid baths.
The content of nitrogenous acid with impurities of hydrofluoric or hydrochloric acid allows the use of the same materials. The only exceptions are lead as a coating, ceramics with a high silicon content, due to their interaction. It is quite possible to use steel in alkali baths, monitoring the progress and intensity of electrolysis in close proximity to the material. Under certain conditions and acid content, its temperature, and nature, it is possible to use stainless steel grades for pickling tanks. Such, for example, as 8Х18Н8М or 10Х20Н25М4.
From the information provided in this review, we can conclude that the processing mode, the chemical composition of the bath, the need for additional mechanical processing, and the use of electrolysis should be determined based on specific initial conditions (steel grade, state of the oxide film, technological capabilities) and regulated in the context of the expected final result .
How to remove weld marks on stainless steel parts
Stainless steel is often used in the manufacture of sealed containers and piping elements, and even parking racks.
At the same time, stainless steel parts have a characteristic mirror surface, which makes them more attractive compared to products made from ordinary steel.
However, due to overheating, areas with discoloration almost always form at the welding site, which spoils the entire appearance of the finished product. Therefore, welds require special processing.
You can achieve the ideal result in different ways. In this review we will look at the most popular ones: mechanical and electrochemical.
We also recommend that you read an informative article that talks about soldering stainless steel batteries .
Stainless steel pickling
Pickling stainless steel is an important process that ensures the removal of the top layer of material and restoration of the original state. The bottom line is that after certain work is carried out, defects in the form of welds, oxides and scales can form on the surface of the stainless steel, which can significantly spoil the appearance of the material, as well as worsen the operational and aesthetic properties. A distinctive feature of steel is the presence of an oxide-chrome film, the purpose of which is to protect the top layer. It is because of this that the above defects arise, which are difficult to interact with reagents. If such troubles occur, you can correct the situation by using a special procedure - etching stainless steel.
Safety precautions
Before starting work on cleaning welding joints on stainless steel, you must make sure that the workplace and special clothing are ready. Be sure to check the equipment. You can begin work only with all the protective equipment necessary for a welder.
Periodically, the employee is required to undergo training and instructions on compliance with fire safety rules. Information about briefings is displayed in the work log under the employee’s signature.
Primary requirements:
- You cannot be distracted while processing welding seams;
- There should be no flammable objects in the room;
- Effective ventilation;
- The equipment can only be moved after the power supply has been turned off;
- Only serviceable equipment may be used;
- When carrying out a chemical or electrochemical method, it is necessary to ensure proper disposal of the products.
Stainless steel pickling procedure
Chemical and electrochemical treatment or etching is considered one of the best ways to clean the top layer of stainless steel. This procedure perfectly cleans the steel surface from welds, eliminates various types of deformations, and also helps strengthen the structure of the alloy after heat treatment. In addition to cleaning properties, the procedure ensures the restoration of the passive layer of steel, which is necessary to protect the alloy from structural destruction at elevated temperatures.
The essence of cleaning 12x18n10t steel is the chemical interaction of the top layer with a concentrated acid solution. Typically, hydrochloric or sulfuric acid is used, after which a mixture of molten alkali is used. The acid cleaning process has two stages: first of all, the metal is treated with a basic acid composition, and finally the alloy is kept in a bath with a solution of nitric acid.
When processing stainless steel, you should strictly follow the stages of the technological process. The container with the solution in which the alloy is placed should process only the upper layers of the metal, further eliminating existing damage. It is not recommended to allow changes in the macrostructure of stainless steel, as iron may lose its original properties.
Treatment of stainless steel seams
Stainless steels are actively used in industry for the manufacture of containers and pipelines for aggressive liquids. In everyday life, kitchen utensils and beautiful heated towel rails are made from this metal. The mirror surface has an attractive appearance, and the product can serve for a very long time. But to achieve such an effect on the finished structure, it is necessary to properly process the stainless steel welds. If this is not done, the weld areas will turn yellow and black, or they may even rust. Why is this happening? What mechanical and chemical processing methods are there?
Application of etching
The etching process is widely used in production during the cleaning of the upper layers of steel from welds, scale, oxides and rust. It is used when searching for internal defects by removing the top layer of the workpiece or to study the structure of the metal.
This procedure cleans the material, thereby increasing the adhesion of the top layer. This is necessary for the successful connection of a metal workpiece with another surface, after which a paint, enamel, galvanic layer or other protective coating is applied.
This type of processing not only ensures quick cleaning of the workpiece, but also creates a specified pattern on the top layer of metal. Using etching, you can cut out a channel of any thickness or create a complex image. Processing of large workpieces and rolled products is also possible. You can easily adjust the processing depth down to microns, making it possible to process surfaces with complex areas and small grooves. The procedure is used to carry out analysis that determines the formation of intercrystalline corrosion in stainless steel.
In addition, this process is widely used during the processing of carbon, low-alloy and high-alloy steels, non-ferrous metals and titanium. This technology is indispensable when processing small metal parts, watch gears. It is used to manufacture semiconductor chips and printed circuit boards in electronics. This processing method ensures the formation of a conductive channel on the microcircuits. In aircraft manufacturing, etching plays an important role, since through this process the thickness of metal sheets is reduced, thereby reducing the weight of the aircraft. This operation also plays a big role in applying drawings and inscriptions. Etching produces a relief image created by destroying a metal surface according to specific patterns. In everyday life, the operation helps clean the pipeline.
Mechanical grinding
The good corrosion properties of stainless steel contribute to its extensive use in environments where liquids are used. Such products last longer than mild steel. And the shine and mirror appearance of the surface allow you to install structures in prominent places, improving the overall design of the room or facade. External railings and ramps, parking racks, and various heated towel rails are made from stainless steel. Despite contact with water and welding work on the products, all these elements retain their beautiful appearance. This is achieved through several types of processing.
One of them is mechanical grinding, which removes the top oxide layer on the weld, which is the weak point of the structure, and also eliminates color transitions and irregularities in the weld joint. This process occurs in the following sequence:
- Using a grinder and a thick grinding wheel, the waves of the metal seam and its convexities protruding beyond the general plane of the surface are erased. This way you can quickly smooth out the seam, but the grinder leaves behind rough grooves from the abrasive and overheated areas with dark spots.
- To remove these defects more carefully, you can use petal wheels for an angle grinder. The process will take a little longer, and more consumables will be spent for a large volume of work, but the risks will remain smaller.
- Next, a grinding machine called Rebir is used. It has a straight shape, an electric motor and a handle to hold it. Petal circles (KSL) are put on the end, but their arrangement differs from the circles on the grinder. Thanks to the wide structure of the sandpaper pieces, it is possible to apply more pressure to the workpiece and cover a wide area. KSLs come in different calibers depending on the amount of abrasive used. To process stainless steel after welding, first use “40” and then “zero”. This eliminates all grooves from previous tools. The coating becomes monochromatic and matte.
Work should be carried out in a respirator, since dust from the abrasive and particles of removed metal float in the air. The grinder must also protect his eyes, for which he wears clear glasses. Stainless steel heats up from friction with grinding wheels, so the worker must wear gloves to avoid burns. As an analogue of manual grinding, sandblasting units are used, where sand granules are supplied under air pressure, removing the top oxide from the metal. This is used in enterprises with a large turnover of products. It is not advisable to install such equipment at home.
Etching methods
The following types of processing are used at home and at production sites:
- Acid cleaning;
- Electrolytic cleaning;
- Cleaning with pastes.
Acid etching
The best results when processing stainless steel are obtained by keeping the top layer of stainless steel for a long time in a container of acids made from sulfur and nitrogen. How this process happens:
- The initial stage is considered to be degreasing the top layer of steel, followed by cleaning of burrs and burns;
- Next, etching occurs in sulfuric acid baths. During the process, the acid composition eats away surface roughness, scale and burrs. The best temperature during corrosion is 60-80 degrees Celsius. It is important to control this parameter during the process. The duration of etching depends on the acid concentration (10-12%) and the marking of the steel. It is worth being more careful, since depletion of the acid bath leads to the formation of pitting corrosion on the metal surface. For example, steel containing chromium (18%) and nickel (8%) will require 20-40 minutes of treatment in a sulfuric acid bath. It is possible to reduce the time of this procedure several times. To do this, you need to control the atmospheric level.
- The next step is to wash the workpiece in a large amount of liquid.
- Next, you should immerse the workpiece in a bath filled with nitrate solution. The procedure takes from 5 to 15 minutes, taking into account the bath temperature of 50-70 degrees Celsius.
- The final stage is repeated rinsing with running water.
Treatment of stainless steel welds after welding
Content:
- Reasons why processing is important
- Mechanical grinding
- Polishing stainless steel after welding
- Gels and acids for processing
- Interesting video
In modern conditions of development of the industrial complex, it is expected that stainless steel will be actively used to create pipelines and form containers for further interaction with aggressive liquids. In everyday life, products made from this metal are ubiquitous, namely all kinds of accessories in the form of household utensils and other household items.
A characteristic feature of stainless steel is its attractive mirror surface and long service life. However, it should be noted that to create such an effect, you must first properly treat the stainless steel seam after welding. Otherwise, there will be black and yellow spots on the weld area with subsequent potential rust.
In view of this feature, the question arises of how to clean stainless steel after welding and how to properly organize the processing of stainless steel after welding.
Electrochemical method for processing welds
To remove color transitions, you can also use the so-called electrochemical method.
To do this, you will need a transformer (power supply) that produces 30 V and 1.5A, and an aqueous solution of citric acid (2 tsp food grade citric acid per 0.5 l of water).
The author also uses a homemade electrode, onto the end of which he places a small piece of felt.
One contact from the transformer is supplied to the workpiece (part), the second is connected to the electrode. We wet the felt in a solution of citric acid and treat the welding area.
Thanks to these two processing methods, it is possible to achieve an aesthetic appearance at the weld site.
Of course, this is a painstaking process that requires perseverance and patience, but the result is worth it. A weld on stainless steel will have a beautiful mirror surface on which corrosion will not form.
You can watch the video on our website for details on how to remove weld marks on stainless steel parts.