The exact chemical composition of steel 14Х17Н2
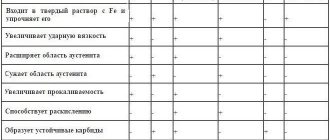
The operational and technical characteristics of products made from this material, as well as its chemical composition, are specified in the GOST 5632-72 standard. The alloy includes 9 elements.
The main ones:
- Chromium
- Nickel
Minor:
- Silicon
- Manganese
- Copper
- Titanium
- Carbon
- Phosphorus
- Sulfur
You can see the exact percentage of substances in the table and diagram below.
| Cr | Ni | Si | Mn | Cu | Ti | WITH | R | S |
| from 16 to 18 | 1,5 – 2,5 | less than 0.8 | less than 0.8 | less than 0.3 | up to 0.2 | 0,11 – 0,17 | up to 0.03 | less than 0.025 |
Analogs
Foreign labeling of some countries is fundamentally different. So in the main countries producing this brand:
| a country | Name |
| USA | 431 |
| Germany | X20CrNi72; X22CrNi17 |
| France | Z15CN16-02 |
| England | 431S29 |
Properties of steel 14Х17Н2
This alloy has excellent technical characteristics. It is very reliable and durable. Products made from this material are widely used in various areas of modern industry.
The specific gravity of this metal is 7750 kg/m3. Its heat treatment is carried out as follows:
- hardening at temperatures up to 1020oC,
- processing in oil,
- holiday when the thermometer readings are about +700oC,
- air cooling.
The initial forging temperature reaches 1250 oC, the final temperature - 900oC. The cross section reaches 350 mm. The hardness of the material is HB 10 -1 = 228 - 293 MPa.
Critical temperature marks:
- Ac1 = 720
- Ac3(Acm) = 830
- Ar1 = 700
Machinability is possible in the quenched and tempered state. The material is difficult to weld, so welding must be done with preheating and further heat treatment. It should be taken into account that the alloy is prone to temper brittleness.
Material characteristics
The use of rolled metal can be found in the following cases:
- Creation of working and guide blades for turbines. Such items bear a serious responsibility, and the stable operation of the entire unit will depend on their type. The blades are subjected to rapid rotation, and external factors in the form of gas or hot steam create additional stress. Even in a calm state, condensation can accumulate on the surface, which will begin to destroy ordinary metal.
- Manufacturing of fasteners. This includes bolts, nuts, pins, studs and others. These components also play a key role, and the reliability and safety of the entire structure will depend on their strength.
- Production of bushings. These components are found in car suspensions, so they must withstand not only force pressure, but also repel water after rain, withstand high temperatures in summer and low temperatures in winter, and serve without deformation. Bushings are also allowed to be installed in other mechanized devices.
- Release of shafts. Such spare parts transmit torque from one link of the mechanism to another. There are also negative factors here in the form of friction, pressure, temperature and others.
Such items can be used in various fields, and, in part, they can be classified as a universal type. Even a share of medical devices and instruments are made from this rental product. As for properties, the characteristics of 14Х17Н2 are as follows:
- stainless steel surface;
- ability to work at T = up to +400 °C;
- resistance to static and dynamic influences;
- low level of deformation.
It is difficult to find an alloy that could meet similar parameters. Therefore, it is valued at all manufacturing enterprises.
Technical characteristics of the most common products made of steel 14Х17Н2Н2
Steel bars
During the first stage of processing, they are hardened with oil at temperatures from +975° to +1040°C. Then it is released in air with thermometer readings from +275° to +350°C. In the second step, I harden the product with oil at a temperature of 1000°-1030°C, then tempering in air follows again, but at 620°-660°C.
Such rods have a cross-section of up to 60 mm. Their proof strength varies from 635 MPa to 835 MPa. The maximum tensile strength is 1080 MPa. Indicators of relative elongation after rupture vary from 10% to 16%, narrowing - from 30% to 55%.
Hot rolled and cold rolled steel sheets
They are hardened in water or in air at a temperature of 960°-1050°C. Tempering of transverse samples occurs in air at 275°-350°C.
The conditional yield strength of these sheets is 882 MPa. The tensile strength reaches 1078 MPa. The relative elongation after rupture is about 10%, but no narrowing occurs.
Steel forgings
These parts are manufactured using two methods.
First:
The product is quenched with oil at a temperature of 980° - 1020°C and tempered in air at 680° - 700°C. Its cross-section can reach up to 1000 mm. The yield strength is 637 MPa. Tensile strength – 784 MPa. The relative elongation after rupture reaches twelve percent, and the part narrows to 30%.
Second:
The forging is quenched with oil at 1000° - 1030°C. Then it undergoes a double tempering in an oven or in air at a temperature of 665° to 675°C. The cross-section of such parts reaches 100 mm. The yield strength conventionally reaches 540 MPa. Tensile strength – 690 MPa. Elongation after rupture can reach up to 15%, and narrowing up to 40%.
Heat treatment features
This procedure is necessary to improve the sample of the material. As a result of such work, processes occur that can change the properties of the workpiece. In this case, both ordinary blanks and finished parts can be processed. Heat treatment of steel 14Х17Н2 always follows one scenario:
- hardening in a furnace 980-1020 °C;
- tempering in oil up to 680-700 °C;
- outdoor cooling.
This process imparts hardness to the alloys and adds wear resistance, which is a very important indicator, since the material can be used to create complex technical devices or massive structures. The essence of this method is gradual heating with further sharp cooling, and this is done in several approaches.
It should be noted that during hardening there is a chance of defects occurring: overheating, burnout, oxidation, cracks, etc. To avoid such troubles, you must strictly follow all the rules of heat treatment.
Price
When determining the price of a product, the content of alloying components, capital investments in manufacturing, the complexity of the work, the equipment used, and additional materials are taken into account. Steel production is becoming more complex due to:
- the duration of cooling of the workpiece and the final part to obtain the required structure;
- evacuation, which removes unwanted gaseous substances, reducing fragility, flake content and the rate of aging of the material;
- the use of nickel in steel 14Х17Н2, which is manufactured in the form of sheets and is classified as semi-finished products;
- weak chemical interaction, which leads to increased consumption of composition components;
- high consumption of oxygen, which is used for oxidation, which increases the rate of chemical reactions and improves the interaction of components.
Subsequent heat treatment is necessary to impart certain qualities to the steel. This process also leads to additional costs that affect the cost of the final product:
- quenching with cooling in oil;
- the need to create a part of a certain size, which leads to metal cutting;
- the use of high-strength tools for machining the material.
All costs are justified from the point of view of manufacturability, the possibility of obtaining an alloy with established properties, and a wide range of applications. The price per kg of 14Х17Н2 is 150-180 rubles. Its exact value is determined based on the order volume and product shape.
Return to content
Stainless steel products 14Х17Н2
The company's catalog presents the following range of stainless steel:
- metal circles;
- rods calibrated in a wide dimensional grid;
- steel strips of different widths;
- pipes of all categories.
The cost of rolled metal depends on the processing technology, composition and form of release.
Thus, ground pipes require an additional stage of cleaning and grinding, so the price of such a product will be more expensive. If necessary, the company's technology department will help you select the desired alloy option and carry out preliminary calculations so that you can use the optimal raw material option for the production process. To select and purchase products made from stainless steel 14Х17Н2, go to the catalog.
Decoding
The name of the alloy indicates the main components that determine the qualities of the metal. Their concentration in the composition is also given. Decoding steel 14Х17Н2 allows you to obtain information:
- 14 – 14% carbon;
- X17 – 17% chromium;
- H2 – 2% nickel.
The elements missing in the name are present in much smaller quantities; they give the metal certain characteristics.
Return to content
Getting the structure
Grade 14x17n2 refers to chromium-nickel steel of the austenitic-ferritic class. This is a complex structure that highly alloyed steels acquire with elements such as nickel, chromium, and silicon. A carbon content of 0.14-0.17% positions these steels as medium carbon. If we can draw an analogy in terms of strength, then reinforcement of strength classes 1-3 is made from unalloyed steels with this carbon content.
But ultimately, the properties for which this alloy is valued are determined by its structure. If during smelting the conditions of melt homogeneity, absence of inclusions, and slow cooling must be ensured, then the product receives additional properties during quenching and tempering.
All possible methods of processing 14x17n2 steel have been determined through scientific research and described in strict sequence in the brand book; the requirements for carrying out the processes are set out in GOSTs.
Steel forgings
To produce forgings from steel grade 14Х17Н2, two methods are used:
- Quenching in an oil bath at 970-1025 degrees, tempering in air up to 670-705 degrees. The cross-section of forgings can reach 1 m. Operating parameters include yield strength - 638 MPa, tensile strength - 785 MPa, elongation - 12%, contraction - 30%.
- Quenching in an oil bath at 990-1035 degrees, tempering in two stages at 665-680 degrees. The cross-section of the forgings does not exceed 0.1 m. Characteristics: yield strength – 541 MPa, tensile strength – 691 MPa, elongation – 16%, contraction – 39%.
Return to content
Heat treatment of steel 14x17n2 modes for hrc 28 32
The invention relates to heat treatment technology and is intended for heat treatment of deformable corrosion-resistant steel 14X17H2, used in marine engineering for the manufacture of complexly loaded parts that perceive significant multidirectional dynamic loads, for example, fasteners, forgings.
There are known methods of heat treatment of 14X17H2 steel, various technological methods and solutions for the heating, holding and cooling procedures, which have found wide industrial application in the mass production of general technical products. However, they do not provide the required level of mechanical performance.
There is a known method of heat treatment of products made from steel 14X17H2 (GOST 5949-75) “High grade and calibrated steel, corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant”, including quenching in oil in the temperature range 1000-1030°C followed by high tempering in the temperature range 620-660 °C and air cooling. However, it does not provide a uniform set of properties in the direction along and across the deformation fibers, regulating only the values of the mechanical properties across the deformation fibers. The known technical solution finds industrial application in the heat treatment of rolled products used in the shipbuilding industry for the manufacture of parts from them in the process of subsequent reforging of rolled products.
The disadvantage of this known method is that it provides lower impact strength, which is determined by the content of δ ferrite in the steel. Steel that contains virtually no δ ferrite has the highest impact toughness; slightly lower for martensitic-ferritic steels containing δ ferrite more than 40%; the lowest impact strength is for steel containing δ ferrite in the range of 10-20%.
As a prototype, a method of heat treatment of stampings of crank shafts made of martensitic-ferritic class steel 14X17H2 was adopted, including quenching in oil from a temperature of 970-1020°C and subsequent double high-temperature tempering, the first and second tempering is carried out at a temperature of 620-670°C with cooling after each vacation in water or oil, with the first vacation being carried out for 4.5-5 hours, and the second vacation for 3.5-4.5 hours. However, the prototype method does not provide high plastic characteristics and impact strength. These shortcomings are eliminated by the proposed technical solution. The objective of the invention is to improve the quality of complexly loaded parts. The technical result is an increase in plastic characteristics and impact strength, which are most important for heavily loaded parts.
This technical result is achieved by the fact that in the method of heat treatment of deformable corrosion-resistant steel 14X17H2, including heating for quenching, cooling in oil, double tempering with cooling after each tempering in water, heating for quenching is carried out at a temperature of 1040-1050°C, heating during the first tempering - at a temperature of 600-610°C. In this case, the holding time during hardening is 3 hours, the holding time during the first tempering is 4.5-5 hours, during the second tempering 3.5-4.5 hours, as in the prototype, the temperature of the second tempering is in the range adopted in the prototype (620- 670°C), in the proposed method 640-660°C. The technical result is achieved by choosing a narrow temperature range during hardening and first tempering. In the structure, after cooling from the quenching temperature to room temperature, martensite is formed and a certain amount of soft structural components of δ ferrite is retained. Carrying out high tempering at the specified temperature leads to the decomposition of martensite into a ferrite-carbide mixture, ensuring a stable state of the tempered martensite component.
The method is carried out as follows.
The blanks are cut from 14X17H2 steel rods, placed in a furnace with a moving hearth and subjected to heat treatment according to the proposed regime. After heat treatment, samples are made from the workpieces for mechanical testing.
An example of the method.
A 1.5 m section was taken from a rod of steel 14X17H2 (the chemical composition is given in Table 1) with a diameter of 80 mm, from which blanks were cut out for heat treatment using a milling cutter. The blanks were cut in accordance with the requirements of GOST 7564-97: longitudinal - bars with a cross-section of 25x25 mm, transverse - washers 20 mm thick. The cut blanks underwent heat treatment in various modes: at average, minimum, maximum and extreme parameter values. The optimal mode was considered to be: hardening at 1040°C for 3 hours, cooling in oil, heating during the first tempering at a temperature of 610°C, holding for 4.5 hours, cooling in water, heating during the second tempering at 650°C for 3.5 hours, cooling in water. The treated samples were subjected to mechanical tests (the results are shown in Table 2). Determination of impact strength was carried out at normal temperature according to GOST 9454-78; tensile testing of samples was carried out in accordance with GOST 1497-84; the susceptibility to intergranular corrosion was determined according to GOST 6032-2003 using the AM method on longitudinal and transverse plates. There was no tendency to intergranular corrosion; the δ ferrite content was determined using the Rozival method on transverse microsections and amounted to 0.1%.
Steel 14x17n2, its characteristics and scope
There are grades of steel with the most favorable ratio of alloying components, and it is difficult to find a complete replacement for them.
Steel 14x17n2 has these properties. We will discuss its characteristics and application below. Due to the possibility of thermomechanical processing of rolled products in a wide temperature range, the final properties are suitable for the manufacture of many parts of various types. But the main properties for which this brand is valued are its possession of the characteristics of stainless steel: high strength, heat resistance, corrosion resistance. These parameters are necessary in the manufacture of parts operating at high temperatures (in this case, up to 400 ºС).
The 14x17n2 grade is used in the production of:
- turbine blades;
- disks;
- shafts;
- bushings;
- flanges;
- parts of compressor machines.