10.21.2021 Author: VT-METALL
From this material you will learn:
- Determination of the quality of welded joints
- Factors affecting the quality of welded joints
- Methods of non-destructive quality control of welded joints
- Destructive methods for testing welded joints
The quality of welded joints is a key parameter by which the serviceability of the entire product is assessed. It is a mistake to believe that it is influenced only by the skill of the welder; the condition of the equipment and the suitability of the material for the work are no less important.
There are various ways to organize quality control of welded joints, the most popular of which are destructive and non-destructive testing methods. In our article we will tell you what is included in the concept of welding quality, how the inspection is organized and we will analyze the current methods for carrying it out.
Determination of the quality of welded joints
The definition of the quality of welded joints is clearly reflected in GOST 15467-79: this is a set of product properties that will guarantee the satisfaction of certain needs in accordance with its purpose. Therefore, it will be impossible to produce a high-quality welded product without taking into account such parameters as compliance of the material with technical specifications, the technical condition of the tooling and equipment used, compliance with technological regulations and instructions and, of course, the qualifications and experience of the welder.
Ensuring high-quality operational and technical characteristics of the product is possible only with strict adherence to the sequence of operations of the technological process. An important role will be given to various methods of objective control of both individual production operations and the finished product. The correct organization of a technological process implies a control operation as an integral part of it. Detection of deviations is a signal not only for rejecting products, but also for immediate adjustment of the technological process.
Inspection is necessary at every stage of manufacturing welded structures. In addition, the condition of the devices and equipment should be checked periodically. Preliminary control includes checking the quality of basic and auxiliary materials, determining their compliance with the technical specifications and drawings.
After cutting the workpieces, it is necessary to visually check the surface quality and appearance of the part, the presence of nicks, cracks, burrs and similar defects, and also measure using universal and special tools, test fixtures and templates. Particular attention should be paid to quality control of welded joints. To check the geometry of edges intended for fusion welding, special templates are used, and the quality of the prepared surfaces is controlled by special micrometers or optical instruments.
VT-metall offers services:
At the assembly and tack stage, the absence of burns, cracks, the size and location of the tacks, the size of the gaps, the correct position of parts and other defects in the tack areas are checked. Most often, the quality of tack work and assembly is controlled by measurement or visual inspection.
Current monitoring of welding is the most important operation, which includes two tasks: checking the correctness of the welding processes themselves or compliance with the specified parameters of the finished product.
Why should you contact us?
We treat all clients with respect and carry out tasks of any size equally scrupulously.
Our production facilities allow us to process various materials:
- non-ferrous metals;
- cast iron;
- stainless steel.
When completing an order, our specialists use all known methods of metal machining. Modern equipment of the latest generation makes it possible to achieve maximum compliance with the original drawings.
In order to bring the workpiece closer to the sketch submitted by the customer, our specialists use universal equipment designed for jewelry sharpening of tools for particularly complex operations. In our production workshops, metal becomes a plastic material from which any workpiece can be made.
The advantage of contacting our specialists is their compliance with GOST and all technological standards. Strict quality control is carried out at every stage of work, so we guarantee our customers a conscientiously completed product.
Thanks to the experience of our craftsmen, the output is an exemplary product that meets the most demanding requirements. At the same time, we start from a strong material base and focus on innovative technological developments.
We work with customers from all regions of Russia. If you want to place an order for metalworking, our managers are ready to listen to all the conditions. If necessary, the client is provided with free specialized consultation.
Factors affecting the quality of welded joints
In addition to the execution of the seam and adherence to technology, the strength characteristics of the welded joint are also associated with other factors:
- Quality of welded material. Failure of the metal to meet the required characteristics, even if the weld is made correctly, can negatively affect the strength of the connection.
- No less stringent requirements are imposed on the consumables used in welding work. The use of low-quality additives or electrodes will not allow making a correct, strong connection due to the appearance of fragility, fragility, etc. in the structure of the metal itself.
- The equipment used for welding work must have adequate power and be applicable to the required technology (for example, argon arc welding).
- The reliability of the connection of parts (their quality of penetration) can only be achieved with the correct choice of welding modes (polarity and current).
- Preparing the workpieces themselves for welding is an equally important operation. Even a slight deviation in the shape of the edges of the joints can significantly reduce the quality and disrupt the shape of the seam.
Recommended Articles
We recommend articles:
- Gas shielded welding: the essence of technology and a guide for beginners
- How to weld seams: we understand the secrets of welding techniques
- How to weld thin metal: a guide for beginners and professionals
All of the above points should be taken into account when planning work, especially if this concerns important and critical structures.
Methods of non-destructive quality control of welded joints
Visual quality control of welded joints.
Any type of quality control of welded joints should begin with a simple inspection. Most often, this is enough to see external or internal gaps. In addition, this procedure is performed without the use of special equipment. For example, different heights of a butt joint are most likely due to poorly machined surfaces. Therefore, before inspection, it is necessary to thoroughly clean all seams from dust, scale, metal splashes and dirt.
To improve the visibility of minor imperfections, the surface is treated with alcohol or nitric acid. The coating becomes matte, the visibility of pores and cracks increases significantly.
External inspection is the simplest and most effective method of quality control of welded joints, which allows you to detect pores, cracks and sagging. A better check can only be performed using special devices, for example, a magnifying glass in bright light. A magnifying glass increases the efficiency of detecting the smallest cracks and pores.
Radiation method for checking the quality of welded joints.
This method of seam control can be done in two ways:
- using x-rays;
- using gamma radiation.
Checking the quality of welded joints of parts using X-rays is the simplest method. The essence of the technology is that X-ray rays pass through a metal product, and all information about the structure of the metal is reflected on photographic film. The photo can even show hidden defects. With the help of such radiation, slag inclusions, gas pores, edge displacement and similar defects can be detected.
The method of checking the quality of welded joints with gamma radiation has a similar principle of operation, only the following advantages are added:
- the performance of isotopes does not decrease for a long time;
- it is possible to penetrate complex structures;
- has the property of increased radiation permeability;
- The technology is carried out on simpler and more compact equipment.
It must be remembered that radiation of this type poses a great danger to human health. Therefore, such work can only be carried out by experienced specialists wearing protective equipment. And workplace protection can be ensured using lead plates, screens and similar means.
Ultrasonic method for quality control of welded joints.
The flaw detection method using ultrasound makes it possible to detect such hidden defects that can only be determined by reflecting ultrasonic waves from the boundaries of media with different properties. Simply put, a signal is sent by a special device, and after reaching the material, it returns back. But if some defect appears on its trajectory, it will begin to affect the integrity of the wave, which will be recorded by the equipment. Different defects have a specific signal, so it is not difficult to detect the cause and nature of the defect. This technology allows us to identify not only external, but also hidden flaws.
Methodology for magnetic testing of the quality of welded joints.
Destructive testing has the following test methods
Mechanical static tests
A type of destructive research in which the test sample is subjected to a single impact at a certain rate of a constant load. These include the following tests:
- tensile;
- for compression;
- to bend.
Static tests determine mechanical properties - for example, strength and ductility. Without these characteristics, it is impossible to perform a strength calculation of the structure.
Static Tensile Tests (Static Tensile Tests)
The main type of static tests are tensile tests, which are standardized and carried out at elevated, reduced and room temperatures.
The technique for conducting static tensile tests involves applying a load to a standardized sample until it fails. For testing, cylindrical or prismatic samples with certain dimensions are used.
These tests allow us to determine the values of the following parameters:
- yield strength;
- tensile strength;
- elastic limit;
- relative elongation and narrowing.
Static compression tests
Compression tests are used much less frequently than tensile tests, since compression does not allow one to identify all mechanical parameters.
Static compression tests are performed on a universal tensile testing machine. The test results depend significantly on the shape and linear dimensions of the samples. In order to eliminate possible loss of stability during compression tests, short samples are used. The longer the sample, the greater the bending effect.
During compression tests, the following indicators are revealed:
- tensile strength;
- yield strength;
- elastic limit;
- relative shortening.
Static bending tests
Static bending tests are carried out to determine the ultimate ductility of a metal during bending (the ability to withstand plastic deformation). This parameter is determined by the bending angle that causes the first crack to appear in the curved zone of the weld, metal or polymer, which expands during testing.
Mechanical dynamic tests
They allow you to examine metal by exposing it to shock loads, which ensures a high deformation rate. In this context, the most common test is the impact bending test.
Impact strength is a mechanical property that is determined during dynamic tests.
Impact bending tests
The ability of a metal to absorb load energy is called impact strength. This is a significant indicator of the strength of the material. The impact bending test method is carried out by destroying a sample that has a notch - a stress concentrator. The load is produced by the impact of a pendulum pile driver.
Brittle fracture is one of the most critical indicators. Even a small crack grows very quickly. The main danger of brittle fracture is the absence of any precursors. Therefore, an important point in the test is the calculation of the impact strength of the material upon crack formation.
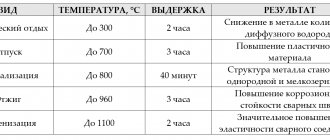
Tests for mechanical aging susceptibility
Mechanical aging is a change in the properties of steel after a conditional period of time. Changes that occur at room temperature are commonly called natural aging. In this case, artificial aging is performed under heating conditions.
3. Static hardness measurement method
It is called one in which the indenter is slowly and continuously pressed into the test metal with a certain force.
Static methods include the following
Measuring the hardness of metals according to Brinell (hardness testers)
One of the oldest methods, hardness is determined by the diameter of the impression left by a metal ball pressed into the surface.
Measuring the hardness of metals according to Rockwell (hardness testers)
This is the most common method of the early 20th century; hardness is determined by the relative depth of indentation of a metal ball or diamond cone into the surface of the material being tested.
Measuring the hardness of metals according to Vickers (hardness testers and microhardness testers)
The widest scale in terms of coverage, hardness is determined by the area of the imprint left by a tetrahedral diamond pyramid pressed into the surface.
Measuring the hardness of metals according to Shore (hardness testers and scleroscopes)
This method is extremely rarely used; hardness is determined by the height of the striker’s rebound from the surface.
Measuring the hardness of metals according to Lieb (hardness testers)
This is the most widely used method in the world today, hardness is defined as the ratio of the velocities before and after the striker rebounds from the surface.
Corrosion resistance tests
Carry out using several methods.
Welded joints made of carbon, alloy and high-alloy steels operating in a chemically active environment are susceptible to corrosion (corrosion). Based on its effect on metal, corrosion is divided into chemical and electrochemical.
Corrosion resistance tests
- Defects in welded joints.
- Formation of crystallization cracks.
- The influence of alloying elements on the tendency of the deposited metal to form cracks.
- Ultrasonic testing of welded joints.
- Austenitic steels.
- Classification of alloy steels.
Chemical corrosion is a process of direct chemical interaction between a metal and its environment, such as the oxidation of iron in air at high temperatures with the formation of scale.
Electrochemical corrosion is the destruction of metal with the participation of electric current, which occurs when the metal operates in water, solutions of acids, salts and alkalis.
There are two types of corrosion: general and intergranular.
With general corrosion, the entire metal surface or part of it chemically interacts with an aggressive environment. Over time, the surface corrodes and the thickness of the metal decreases accordingly.
With intergranular corrosion, metal destruction occurs along grain boundaries. Externally, the metal does not change, but the bond between grains weakens significantly, and during bending tests, cracks form along the grain boundaries in the stretched zone of the sample.
Technological test methods
Technological testing is a type of destructive testing to assess the ability of a material to withstand a certain deformation under conditions as close as possible to production conditions. Technological tests include tests for flattening, bending, spreading, beading and upsetting. Evaluation of the material based on the results of technological tests is qualitative in nature. It is necessary to determine the suitability of a material for the manufacture of products using technology that involves significant and complex plastic deformation.
Methods for studying the structure of materials
Metallographic research is the analysis of the structure of metals and alloys on specially prepared sections using optical microscopy. Metallographic research is important in industries such as metallurgy, nuclear and aerospace, energy and automotive. During metallographic studies, the number of non-metallic inclusions, grain grade, depth of the decarburized layer, content of the ferrite phase and other parameters are determined.
Methods for determining element content
Methods for determining element content include spectral analysis and steeloscopy. Spectral analysis is a study with the help of which, as a result of measuring the spectra of the sample under study, the content of elements of interest in it is determined qualitatively or quantitatively. Steelscoping is a qualitative spectral analysis for the presence of alloying elements, based on the production of hot metal vapors on the surface of the test object using an electric arc, followed by analysis of their spectrum. Methods for determining the content of elements make it possible to classify steels and alloys by grade, as well as check their chemical composition. They are used in industries such as metallurgy, nuclear and aerospace industries, energy and mechanical engineering.
Testing of building structures
Testing of building structures means checking the mechanical characteristics of the materials of foundations, walls, beams, floors and other building elements, determining the presence of damage and defects, identifying cracks, their opening width, depth, as well as determining the reinforcement of structures.
They are divided into the following types:
- Concrete mixtures.
- Construction solutions.
- Cements.
- Sand for construction work.
- Crushed stone and gravel.
- Soils.
- Concrete, structures and products made of concrete and reinforced concrete.
- Ceramic and silicate bricks and stones.
- Porous inorganic fillers for construction work.
- Buildings and constructions.
- Construction materials and products.
9.12 Roads
Applies to newly constructed, reconstructed, overhauled and operated public highways and road structures on them, including design elements (for road and roadside service facilities, only their location is regulated), as well as related processes of design, construction, reconstruction, capital repair and operation of roads and road structures and used road construction materials and products.