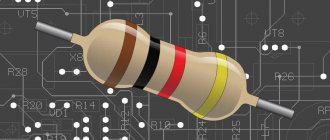
Abrasive tools differ in different parameters, one of which is the grain size of the grinding wheels . This indicator directly affects the quality of the machined surface, the productivity of machining and the amount of material removed by the emery wheel in one pass.
Grit is the size of the abrasive crystal in microns. If the size of ordinary bodies is determined by several parameters (length, width, height), then in the case of abrasive grains we are talking only about width. Such a substance can be electrocorundum, silicon carbide, diamond and other materials with high hardness. The mechanical effect of these particles on the surface being treated makes it possible to change the surface roughness and remove contaminants.
Classification of abrasive wheels
Disks are classified into the following types:
- with undercut (PV – for cylindrical grinding);
- double-sided conical (PVDK);
- straight profile (PP – universal circle);
- with a conical one-sided or two-sided groove;
- ring (K – suitable for flat grinding);
- disc-shaped (T);
- cup conical or cylindrical;
- with a double-sided conical profile (2P: scope of application – thread grinding, slot grinding, gear grinding).
How much does a whetstone cost?
A whetstone can cost 116 rubles or several thousand - it all depends on several parameters:
- material of manufacture;
- manufacturer;
- surface graininess.
The average price of a whetstone, where the price/quality ratio can be called optimal, is 3-6 thousand rubles.
Marking of grinding wheels
Grinding wheels can vary in geometric shape, type of abrasive material, as well as type of bond, wheel grit, hardness, etc. When choosing a grinding wheel, hardness and texture may weigh more heavily than the type of abrasive.
According to various editions of GOSTs, the marking of circles has different designation parameters. Almost every manufacturer labels their wheels differently.
Thus, the complete marking of the varieties of grinding wheels contains:
- circle type;
- grinding material;
- disk dimensions;
- degree of hardness;
- grain size;
- structure;
- binder;
- maximum rotation speed;
- accuracy class;
- imbalance class.
Stones for knife
Ceramic and diamond stones are used for knife blades in the kitchen. They are characterized by fine grain and therefore cannot sharpen the cutting surface efficiently - usually such kitchen devices are used for quickly straightening the blade.
The service life of such blades is short, the abrasive coating on them is thin. Some manufacturers produce a device with three stones - coarse, medium and fine, which makes it possible to increase the level of sharpening of kitchen knives.
Type of abrasive material
The most popular and common materials used in the manufacture of grinding wheels include:
- Electrocorundum. When purchasing such a circle, you can see white, titanium, chrome and zirconium options. The main disc used is white electrocorundum, which is highly self-sharpening. By working with it you can achieve a more even and smooth surface.
- Silicon carbide. There are black and green tones, this circle differs in structure and degree of fragility - it is harder and more durable than the first type described above. Area of application: working with hard alloys, porcelain and marble.
- Elbor. This type of grinding wheel has the hardest abrasive material and high heat resistance. Elbor can be used for sharpening cutting tools and other parts that can be deformed by heat, as well as for working with hard metals.
- Diamond. Another hard type of abrasive wheel. It is used when working with hard materials, glass and ceramic surfaces. It is self-sharpening, but cubonite and CBN have greater heat resistance without compromising strength.
Regardless of the type of abrasive material, all wheels are characterized by the parameters of strength, wear resistance and heat resistance, however, when choosing, you should take into account the main parameter - hardness. The hardness characteristic is prescribed in the standards of GOST 2424 and is calculated using special tables.
For example, the type of grinding material for the 25A F180 K 7 V wheel is white corundum. There are other types of known abrasives:
- normal electrocorundum (13-16A);
- white (23-25A);
- chromium (33 and 34A);
- titanium only one (37A);
- zirconium is also one (38A);
- monocorundum (43-45A);
- black silicon carbide (53 and 54C);
- green silicon carbide (62-64C).
Types of grinding wheels
According to the non-professional classification of grinding wheels, the following types are distinguished:
- Velcro discs
are made of sanding paper on a Velcro base, which is attached to the support using a self-adhesive backing. This material is considered consumable and is used in woodworking, metalworking, repair and construction. The Velcro sanding wheel is installed on a grinder or eccentric sander, as well as on a handmade drill. It is marked with a different color indicating the grain size. For example, brown is suitable for wood and metal, blue is suitable for stainless steel, and black can be used to process minerals. - The flap wheel
is fan-shaped, has good elasticity and easily adapts to any surface. It is mainly used for grinding pipes, fittings, and wood products. - A fiber grinding wheel
is a grinder equipment for processing surfaces made of ferrous and non-ferrous metals and steel. Used for cleaning weld seams and removing spatter. The fiber base for such discs is made by processing cellulose. - The diamond grinding wheel
is used for fine grinding of carbide materials, glass, ceramics, precious and semi-precious stones. The diamond blade has an optimal balance of fragility and strength and has a large working reserve.
Grinding wheel grit markings
When marking grinding wheels, manufacturers indicate only its width (MKM or F with a numerical indicator of grain size). The grain size not only indicates the wear resistance of the abrasive, but also plays an important role when grinding a particular surface.
The grain size of the wheel affects the quality and cleanliness of the surface finish. Consider the material you are working with. To get the cleanest possible surface, you should buy a wheel with the smallest grain size. However, a person working with such a wheel must understand that it quickly becomes greasy and the material being processed often gets burned.
According to GOST from 1980, units equal to 10 microns are used to measure the grain size of wheels. In the modern version of GOST R 52381-2005, circles are marked with the letter F with a certain number (as the number increases, the degree of grain decreases).
For example, the grain number according to the old GOST (M40-M5) and the new one (F280, F320, F360, F400-F600, F800). To decipher: such a disk is used for final finishing and honing of parts with an accuracy of 3-5 microns or less, as well as superfinishing. Or size 40, 32 according to the old GOST and F40, F46 according to the new one: wheels with this grain size are used for preliminary and final grinding of parts with surface roughness of 7-9 cleanliness classes, as well as for sharpening cutting tools.
Which sharpening stone to choose for kitchen knives
For kitchen knives, it is better to choose a water sharpening stone - they “work” faster and allow you to straighten the cutting surface without changing tools until you get the desired result. But you need to remember that some knife materials can rust when in contact with water, which will hopelessly ruin your kitchen tool. In this case, it is better to use oil sharpening stones - sharpening takes a long time, but it is always of high quality, and the blade of the knives does not rust.
As for the grit level of the whetstone, 1500 grit is sufficient for kitchen knives, because 240 grit is too coarse an abrasive surface that greatly thins the knife blade.
Abrasive disc size
The marking of abrasive wheels by size is written as follows: DхТхН (where D is the outer diameter, T is the height, H is the diameter of the hole). The D parameter can reach a maximum size of 1100 mm, the H value can be up to 305 mm, and the T parameter varies from 0.18 mm to 250 mm.
The types of CBN and diamond discs are described in more detail in GOST 24747-90. The marking of the shape of such grinding wheels consists of three or four symbols indicating the cross-sectional shape of the body and layer, its location on the wheel, and also provides information about the design features of the body.
For example, 150x16x32 is the size of a 25A white electrocorundum abrasive wheel.
Reminder when choosing abrasive wheels:
- When choosing the diameter of the circle, you should take into account the number of spindle revolutions and the ability to provide optimal speed.
- The larger the diameter, the less specific wear of the circle. There are fewer grains on the working surface of small circles. So, during operation they wear out unevenly.
- When choosing a diamond wheel, you should take into account the width of the diamond-bearing layer. If used incorrectly, ledges may appear on the surface of the wheel.
Flap discs with a hole (attached) KL and with mandrel KLO
Must comply with the requirements of GOST 22775-77 or internal specifications of manufacturers.
For CL circles the following standard sizes and permissible deviations are established, in mm:
| Outer diameter D | Height, N ± 1 | Bore hole diameter d+ 0.5 | ||
| Nom. | Prev. off | |||
| 100 | ± 2 | 25; 30; 40; 50 | 32; 40; 44,5 | |
| 120 | ||||
| 150 | 25; 30; 40; 50; 75 | |||
| 165 | ||||
| 175 | ||||
| 200 | ||||
| 250 | ± 3 | 50; 75; 100; 125; 140 | 44,5; 50; 75 | |
| 300 | 44,5; 50; 75 | |||
| 350 | 44,5; 50; 75; 127 | |||
| 400 | ± 4 | 50; 75; 100; 125; 140 | 75; 127; 203 | |
| 450 | 75; 127; 203 | |||
| 500 | 75; 127; 203 | |||
By agreement with the consumer, production is allowed
circles with other sizes according to drawings
For KLO circles the following standard sizes and permissible deviations are established, in mm:
| Outer diameter D | Height, N ± 1 | Mandrel length, L ± 3 | Bore hole diameter d ± 0.1 | |
| Nom. | Prev. off | |||
| 30 | ± 1 | 10;15; 20 | 30; 40 | 3; 6 |
| 40 | 15; 20 | 6 | ||
| 50 | 20; 30 | |||
| 60 | 15; 20; 30; 40 | |||
| 80 | 30; 40; 50 | |||
Structure and hardness index
The density of the structure of grinding wheels is indicated by the percentage of the volume of abrasive grains per unit volume of the wheel. The more abrasive, the denser the structure of the grinding wheel will be.
When sharpening a tool, a wheel with a less dense structure is better able to clean the surface of material particles, poses less risk of deformation and cools faster.
Often, specialists use disks of medium hardness, but it all depends on the type of work being performed, the coating being processed and the tool itself.
What are the structure numbers and volumes of abrasive in the grinding wheel:
- dense structures include units of measurement from 1 to 4;
- Average density includes numbers 5-8;
- to open – from 9 to 12;
- a highly porous structure is observed in circles with indicators 13, 14>.
However, do not confuse wheel hardness with abrasive hardness. According to GOST 2424, the hardness of a grinding wheel is distinguished by a capital letter.
According to GOST R 52587-2006, there are the following designations:
- very soft - letters F and G;
- to soft circles – H, I, J;
- medium softness includes markings K, L;
- averages are M, N;
- circles of medium hardness are designated by the letters O, P, Q;
- solids are designated as R and S;
- very hard – T, U;
- Extremely hard ones include V, W, X, Y, Z.
What grinding wheel hardness should I choose? This depends on many parameters - the characteristics of the material or surface being processed, physical properties, and, of course, the power of the grinding machine. If you need to maintain the exact shape of the material being processed, you should purchase a wheel with a high degree of hardness. Soft ones are used to prevent cracks and burns, also when grinding without additional liquid-lubricant cooling of the surface.
For example, let's take the same 25A grinding wheel, which has a hardness class of K and a structure of 7. This means that this disc is medium-soft and has a medium abrasive structure.
Stone for dressing water stones
When using water stones, irregularities form on their surface, which impairs the quality of sharpening knives and other cutting tools; you can correct them:
- sandpaper;
- silicon carbide powder;
- sand;
- diamond block.
But it is easier and faster to sharpen the sharpening tool with special stones - synthetic water stones with diagonal cuts along the surface of the same depth. They can be hand-held or tabletop. In the first case, straightening is carried out with a stone with cuts, in the second, the damaged whetstone is ground/straightened on a fixed one.
The most popular stones for dressing water stones:
| Name | Description | Photo |
| Table stone from the Large series NANIWA Flattening Stone for Sharpening Stones (Truing Stone) | It has the same grain size (24 grit) and is made of silicon carbide. | |
| Table stones from the JUUMA Flattening Stones series | Made from aluminum oxide, they are a series of four stones of different grain sizes. It is noteworthy that they are able to rule even each other. | |
| Suehiro Hand Stones | They have a medium grain size (200 grit), are intended for straightening synthetic water stones, correcting both subtle unevenness and deep “pits” and grooves. |
Bundle type
The bond is an indicator of the bonding of abrasive grains to each other. Modern grinding wheels have three types of bonds:
- V (ceramic, previously marked with the letter K);
- B (bakelite, formerly known as B4 and BU);
- R (volcanic, previously designated by the letter B).
Ceramic marked wheels have materials such as quartz, sand, clay, etc. mixed and ground in various proportions. Such circles are quite high-strength. However, they should not be used for power grinding of metal.
Bakelite or artificial resin wheels are highly elastic and heat resistant. Bakelite is often mixed with reinforcing elements, such as graphite.
The volcanic binder consists mainly of rubber; such wheels are used in certain processing industries.
Using the example of the 25A F180 K 7 V grinding wheel, we will consider the type of bond, where the designation V refers this disc to a ceramic bond.
KLO 80x20x6 14A P60 2 F 40 m/s GOST 22775
For reference. The label must bear the following marking: manufacturer; Manufacturer country; symbol of a circle; date of manufacture (month and year); safety signs ""; blue safety stripe for maximum operating speed of 50 m/s; maximum wheel rotation speed in min-1; “Do not use for wet grinding” sign; designation of the standard establishing safety requirements;
Petal circles with diameters D ⩽ 100 mm may not be marked.