A foundation bolt, or more precisely, an anchor, is an important element of any building structure, be it a multi-story building or a private building. They are used both on small objects and on large ones, such as bridges and foundations of factory workshops. Their main task is to ensure reliable adhesion of the walls to the foundation. This increases the stability of the building and also protects it from various seismic activities and natural loads.
In this article we will talk about what foundation bolts are. What types of them are found and how to choose the right fasteners depending on the purpose of the building and other characteristic features of the building.
What are foundation bolts-anchors
Structures of this kind are primarily intended for industrial purposes and are intended for fixing metal structures - machine tools, machines and other industrial equipment - to concrete. In essence, they act as mortgages. And this article will tell you in detail about the dimensions, length, weight of foundation bolts (anchors).
This video will tell you what a foundation anchor is:
Product structure
Fundamentally, the design of a foundation bolt is no different from a conventional anchor:
- a notched pin – inserted into the wall of a structure or used as a fastening element for a mechanism;
- anchor part - extension, embedded in a concrete base;
- the upper part of the anchor can vary greatly in shape and is determined by its purpose.
The principle of fastening, which ensures the retention of the structure, also fully corresponds to the concept of an anchor - an anchor. Three forces can act:
- friction - the fastener absorbs the load from the structure and transfers it to the monolithic base due to the friction forces that arise during expansion. Which, in fact, determines the obligatory presence of an expanding part;
- stop - the load perceived by the fastener and compensated by the resistance of the material itself;
- gluing is a load compensated by stress at the point of contact between the base material and the anchor. This factor operates in chemical foundation anchors and in cases where the structural form does not provide for support.
The design and dimensional parameters of foundation bolts-anchors are regulated by GOST 24379.1-80 and GOST 24379.0-80.
Since the fastener is designed to secure heavy structures in very dense materials, its strength must be outstanding. Typically, high-quality or high-quality carbon steel, as well as low-alloy steel, are used for this. It is possible to make anchors from stainless steel, but, as a rule, such products are made to order. Only galvanized fasteners may be used.
Advantages and disadvantages
Products of this kind are highly specialized.
In their field, foundation bolts have no competition, but they are not used in other fields. The advantages of anchors include:
- very high load-bearing capacity;
- wide variety of designs. The methods of fastening equipment are different, so products are produced with a wide range of design differences;
- There are 2 installation methods available. This allows the use of bolts both during construction and at later stages;
- large size range - depending on the purpose, products with lengths from 15 cm to 5 m are produced;
- Despite the fact that high-quality steel is used for manufacturing, the cost of the products is relatively affordable.
Disadvantages of the product:
- the foundation anchor is not universal. Its scope is limited to the installation of structures on a concrete base;
- its use requires certain knowledge, since accurate calculations are important here, taking into account the foundation material, design features, installation method and much more.
The following describes the types of foundation bolts.
This is interesting: Production and operation of tubing pipes
Technical characteristics of connecting fasteners
Before installation, you will need to take into account all possible anchor parameters in order to select bolts.
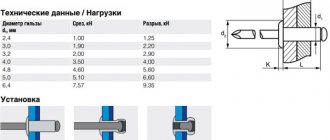
Fastening blanks are produced with a stud diameter of 1-14 cm, with a maximum connecting bolt length of up to 5 m. Production can only use raw materials with the highest strength indicators.
Finished products exist in different classes, separated by strength, where the smallest permissible parameter is 4, and the highest is 13.
During practical application, additional processing is allowed.
What are foundation bolts?
Foundation bolts belong to the category of anchor-type fasteners, the principle of operation of which is determined by their very name. The word "anker", if translated from German, means "anchor". It is no coincidence that such a definition is used in relation to fasteners of a certain design.
Literally cutting into the structure of the material of the structure, such a fastening element forms a reliable connection with it, capable of withstanding significant static and dynamic loads. Naturally, in order for the load-bearing capacity and reliability of such bolts to be at the proper level, only high-quality and durable materials are used for their manufacture, and their surface is covered with a layer of zinc, which protects them from the effects of negative environmental factors.
Foundation bolts with collet end (type 6.1)
Considering that such bolts can be used for installation in foundation structures of various sizes, the length of these products can vary significantly. Thus, on the modern market you can purchase anchor-type foundation bolts with an embedment depth from 15 centimeters to 5 meters. The diameter of such bolts, which increases with their length, can also correspond to different values.
Areas of application
The main task of foundation bolts is to ensure reliable adhesion of the walls to the base. Anchors are installed in several ways: by driving into a pre-drilled hole, and by laying at the stage of pouring the foundation. The second method is considered more reliable, but requires a careful approach to installation, since it is necessary to take into account not only the distance between the anchors and the depth, but also the accuracy of installation relative to the vertical axis.
In addition, anchors are used to attach machines to foundations. The main task here is to remove the load from the concrete that is created by the vibration of the machine. Such fasteners have a slightly different design, and can also be mounted at the pouring stage in the form of an embed or in drilled holes.
Anchors can also be used in the construction of extensions, when it is necessary to connect a new wall to an old one. In this case, the task of the hardware is not only to reliably connect the structures, but also to evenly distribute the load between them.
Basics of the principle of connecting anchors
Anchor connectors are held inside the foundations due to the influence of various forces - emphasis, gluing, friction, but they arise when the monolith interacts with the connection.
During the spacer of the expanding collet, similar forces arise; the stop is distributed over the bolt, where it is compensated by internal resistance, which contradicts the breaking force.
Bonding eliminates the pressure arising from shear stress at the point of contact between the anchor and the concrete.
The choice of fasteners is carried out based on the expected load on one point. The features of the base are taken into account to find the desired type of fastening. An important factor is the main characteristics of the foundation: type, degree of strength, structure.
The size of the anchor system used is selected based on the physical parameters of the structure being installed. The larger and heavier the structure, the longer and thicker the bolts should be.
Then, the optimal distance between the bolts is calculated, according to the weight, dimensions of the attached structure or technical support.
Recommendations for the correct installation of anchors can be viewed in the following video:
The use of such hardware
The area of use of the foundation anchor is determined by its qualities: high load-bearing capacity and durability. Application is limited to the base material.
Fasteners can only be installed in heavy, dense materials:
- concrete – heavy and especially heavy;
- natural stone;
- solid brick; fastening into hollow brick is prohibited.
Despite the specificity, many works are carried out using anchors, both large industrial and household ones:
- first of all, this is the installation of industrial equipment: machine tools, machines, pressing and electrical equipment, and so on;
- when repairing foundations, new fragments are bolted to old ones;
- when installing a beam grillage - in this case, the anchor is fixed in the pile, and the tie-rods are attached to it. This method, in addition to reliability, also ensures the absence of cold bridges;
- anchors mount the base during installation in order to use them as fasteners for the facing material. This option is more reliable than laying hooks under the cladding;
- In everyday life, a foundation bolt is most often used when attaching large-scale attachments. The anchor is stronger and more durable than self-tapping screws and dowels.
Operating conditions for bolts during concreting
According to the specifics of operation, a distinction is made between design and structural foundation bolts. In the first case, the anchor distributes the load and transfers it to the foundation. In structural fasteners, the main task is the stability of the mechanisms. That is, the bolt prevents the structure from shifting, displacement and deformation.
According to the installation method, foundation bolts are classified into:
- installed before the concrete solution hardens. This is the most common installation method;
- by drilling a hole into the finished foundation. The method is relevant for expansion bolts and straight bolts. A hole is drilled to calculate the diameter of the fastener, where the anchor bolt is then mounted. This method is not suitable for connecting fasteners during the construction of high-rise buildings. They will not be able to withstand wind loads.
Foundation anchor bolts can be used for installation to solid foundations. Therefore, a preliminary assessment of the quality of the foundation is important. For example, it is prohibited to install anchor bolts into hollow bricks.
Scope of application of bolts:
- for fastening industrial equipment. These can be machines, technical units, pressing machines and others;
- reconstruction of the foundation. To strengthen it, you will need to install new ones in parallel with the old bolts;
- installation of reliable bolts to strengthen the base;
- fastening of attachments (domestic use).
Popular product brands
Many companies are engaged in the production of foundation bolts. These products are quite simple to manufacture and are quite in demand. The most famous foreign companies include Simpson Strong-Tie, Hillman Group, USP. In Russia, Neva Resources is also the largest.
- The cost of products depends on the size, the quality of the steel, and the design.
- A straight carbon steel foundation bolt will cost 70 rubles. per kg. The same stainless steel fasteners cost from 613 rubles. per kg.
- A bolt with a conical end costs from 320 rubles. per kg. But just a flat anchor plate for a bolt will cost 3,202 rubles. per piece
- A composite foundation bolt costs from 355 to 5750 rubles. per piece
A foundation anchor is a special type of fastener designed to fix heavy structures to dense material. It is indispensable when fastening equipment, for example, or building structures, but is practically not used in other areas.
Main types
Anchor bolts, which are used for embedding in foundation blocks, are produced by modern industry in various sizes and designs. If we talk about the classification of such fasteners, then all of them can be divided into several main types.
Curved
Such products, manufactured in accordance with the requirements of GOST 24379.1-80, are made in the form of a metal pin, the end of which has a curved shape and resembles a hook. In accordance with the above GOST, the maximum length of such fasteners is 180 cm. They are used in foundation structures made of reinforced concrete.
A bent foundation bolt consists of a stud, two nuts and a washer. The latter can be enlarged for mounting equipment with a large diameter of mounting holes
With anchor plate
Such bolts, the length of which according to GOST can reach up to 5 meters, are also used for installation in reinforced concrete foundation structures. Structurally, foundation bolts of this type are a metal pin, on the lower threaded end of which an anchor plate is fixed using additional nuts, ensuring their reliable fixation in the concrete base.
The design of the anchor plate depends on the design of the foundation bolt
Composite
The depth of embedding of such bolts can also reach several meters. The design of such fasteners, which are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of regulatory document 24379.1-80, includes a metal pin, a threaded rod, a coupling and an anchor plate. Composite foundation bolts are used in cases where it becomes necessary to tie one structural element to another.
Composite foundation bolts are equipped with various types of studs
Removable
The regulatory document for the manufacture of bolts of this type is also GOST number 24379.1-80. A removable bolt, which is a metal pin equipped with a special anchor system, is used for embedding into brick, stone and reinforced concrete foundation structures. With the help of such fasteners, engineering and technical structures for various purposes are installed.
The anchor reinforcement of removable foundation bolts is made of composite, cast or welded
Direct
These are foundation bolts, which are ordinary metal pins. Their length can reach 140 cm. Straight bolts must also meet the requirements of GOST 24379.1 from 1980. Bolts of this type can be installed in a ready-made foundation. In such cases, special glue or cement mortar is used to fix them in pre-drilled holes.
Straight bolts provide reliable fastening only on a solid base, eliminating deformation loads
Installing anchor bolts in the foundation: step-by-step instructions
Three conditions are determined due to which strong foundation bolts provide reliable fastening in the foundation:
- Bolt friction force. This is explained by the fact that the immobility of the element depends on the distribution of the load on the fastening element and the foundation itself.
- Emphasis. A strong anchor bolt independently compensates for loads.
- Gluing. Upon contact with the foundation, shear stress is formed, which also takes on part of the load.
Also, when working with foundation surfaces, glue-based bolts are used to enhance strength. Sloxane and epoxy adhesives are used in cases where it is necessary to secure a structure with asymmetry.
If the foundation is subject to constant loads in the form of vibrations, it is better to use spacer fasteners. Tapered bolt anchor bolts are excellent at withstanding static loads, but are not intended for installations where there is a potential risk of impact.
The foundation bolt installation process includes several steps:
- First you need to study the features of the foundation bolts that you plan to use for work. There are markings on the products. In accordance with it, you can determine the type of bolt and maximum permissible loads.
- If the high-quality anchor bolt is suitable for its intended purpose, you can begin work. At the preparatory stage, the locations for fixing the bolts are determined.
- There are rules for installing anchor bolts. For example, when calculating the distance between them, they are guided by the depth of the hole. The distance between the bolts is twice as large as the insertion itself.
- When installing anchor bolts in wet concrete, all work must be completed before it hardens. The anchors must fit smoothly, since even minor tilts can lead to further deformation.
- The final stage of installing durable anchor bolts. The bolts need to be fastened. A metal plate or wooden base is suitable for this. Some types (as described above) are installed in already hardened concrete. In this case, it will be enough to drill the surface and insert the fasteners.
Varieties
No matter how simply a monolithic foundation is constructed, in reality it turns out that there are many factors at work here that significantly affect the reliability of the fastening. Accordingly, foundation bolts have many varieties.
By design features
Based on their design features, foundation anchor bolts are divided into the following types.
- Curved - consists of a stud, washer and two nuts. One end of the pin has a curved shape - a hook. According to GOST, the maximum length of the product reaches 180 cm. An anchor is used for fastening metal and reinforced concrete structures. The washer can be of different sizes to suit equipment with different mounting holes. Fasteners are used if the height of the foundation does not depend on the depth of the anchor.
- With anchor plate - at the lower threaded end of the pin there is an anchor plate secured with threaded nuts. The slab determines the reliability of fastening in concrete. The structure can be different, which is determined by the structure of the foundation. The maximum length of the product is 5 m. An anchor is used for fastening metal and reinforced concrete structures. This option is installed for concreting. It has a smaller embedment depth, and therefore is used when the height of the base depends on the embedment depth.
- Composite with anchor plate - in addition to the threaded rod and anchor plate, a coupling appears, which allows you to connect the two parts of the anchor bolt. In this way, two structural elements mounted by turning or sliding are connected. The general installation scheme is as follows: a part of the stud with a coupling is concreted into the foundation, then the mechanism is installed and the upper part is screwed into the coupling. The screw-in length is at least 1.6 times the thread diameter.
- Removable - mounted in a poured foundation. The anchor plate can have different designs: welded, cast, flat anchor plate. This option is designed for fixation into a concrete, brick or stone foundation. Most often they are used to secure rolling equipment, since it is subject to high dynamic loads. Also, removable fasteners are required in cases where, as practice shows, the bolts will have to be replaced over time. The removable bolt is mounted slightly differently: only the anchor part is concreted into the foundation, and the stud is installed after the foundation is laid out.
- Straight is the simplest modification, consisting of a metal pin and nut. The length can reach 140 cm. This option is designed for installation in a ready-made solid foundation, when deformation loads are excluded. A straight anchor is attached to an adhesive or cement mortar and is held in place by adhesive forces. Their usual application is construction work.
- Spacer with a conical end - installed in a finished foundation, a hole is pre-drilled for it. The fasteners are fixed using expanding collets or cement mortar. Fasteners are also used in construction work, but when constructing structures subject to vibration loads.
Foundation anchor bolt (varieties)
According to operating conditions
Fasteners vary depending on operating conditions:
- calculated - the anchor absorbs the load that occurs during operation of the equipment and transfers it to the foundation;
- constructive - their main task is to ensure stable operation of mechanisms and prevent accidental shifts. In this case, resistance to overturning or displacement is provided mainly by the weight of the structure or machine itself.
By installation method
Based on the installation method, the following types of foundation bolts are distinguished:
- installed before concreting - most types are fixed in this way: curved, with an anchor plate, and so on;
- those installed in a finished foundation are straight and spacer. To install them, you need to drill a hole in the concrete. An anchor that is fixed into a finished base is prohibited from being used in the construction of high-rise buildings, since the wind load is the main one for them.
The production of foundation anchor bolts is captured in this video:
Installation conditions and recommendations
The foundation hardware is supported by:
Friction creates a load that acts on the fastener. The foundation is glued to the bolt with glue or mortar; this compensates for the force of impact and ensures its uniform distribution. The acquisition of the necessary elements is carried out after determining by calculation the diameters, lengths and the required quantity for reliable fastening. Parts of small length will be needed in areas not subject to shock and vibration. Bolts with a diameter of 6 cm require an increase in the mass impact on the connection point, and with dynamic forces acting, the parameters are increased.
The type of elements depends on the climate of the region. In the Northern regions with low temperatures, low-alloy steel is used for production.
Builders perform accurate and correct installation according to a previously drawn up detailed diagram. They provide for the distribution of fasteners with a distance between adjacent elements and their immersion in depth. To prevent the foundation from being deformed, the installation is carried out moving away from its edge. According to the standards, the location of the bolts should not be less than the immersion value.
A reliable installation is considered to be the installation procedure at the time the foundation is laid out; the concrete firmly holds the hardware that connects the structure. Place the bolts vertically in the uncured solution at the same depth. After the concrete has hardened, they are tied together using metal strips. The immersion must correspond to the foundation thickness; the product is lowered without exceeding half the value of this parameter.
Production is also carried out in a finished foundation block. For installation, holes with diameters exceeding the size of the bolt are drilled. The master knows the distribution of reinforcement in the base and, when performing the procedure, bypasses these areas so as not to destroy the structure. After the process is completed, the recesses are filled with concrete mixture or adhesive.
Builders consider glue to be a more reliable method for adhesion. Then install the fastener vertically.
Such installation work is used when its production is necessary, but not planned. For this purpose, you will need hardware with conical ends with a thickening on the rod. As the part is tightened, the collet expands with a reliable grip. The fastening is applicable for light objects that do not create vibration processes during operation.
Correctly selected foundation bolts allow entire enterprises to operate without accidents. Competent settlement operations in this area will help to eliminate emergency situations. Directories and regulatory documentation will always point in the right direction; they combine the work of research groups based on examples from emergency situations.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Calculation of foundation bolts, characteristic features of use
Calculation of foundation bolts, instructions on the necessary parameters, design data are presented in building codes and regulations. The manual for them contains
Foundation bolts.
Installation of anchor bolts.
Foundation bolts for construction work.
During construction work, a huge number of different types of fastening elements are used that perform certain functions. A special place is occupied by threaded rods of various shapes, commonly known as foundation bolts. We will talk about the design of these fasteners, their types and use in this article.
Purpose of fasteners.
Bolts, sometimes called foundation anchors, are intended for fastening the lower crown of log structures to the building support, as well as connecting with other materials of external walls or installing various machines and mechanisms in industrial enterprises. In addition, to strengthen the base of the house, U-shaped or H-shaped steel profile parts, called channels and I-beams, are often attached to it.
Installation of anchor bolts in the foundation.
Purpose of foundation fasteners.
It is impossible to attach building blocks or beams to a smooth strip reinforced concrete or slab foundation without fear of all sorts of deformations and displacement of the structure. To solve this problem, long rods of one shape or another, called anchor bolts, are used.
8.2. Increasing the mass and rigidity of foundations when strengthening them (Part 9)
During the operation of centrifugal smoke exhausters in the recirculation of gases of the GD-26×2 brand to turbine units with a capacity of 800 thousand kW, increased vibrations of the bearings of the smoke exhausters and the bearings of their engines arose.
As a result, bearing failures occurred. In addition, vertical cracks with an opening width of 0.3-2 mm appeared in the body of the foundations of the smoke exhausters, which ran from the upper edge of the foundation to the ground surface and were located in the places where the machine was attached to the foundation (Fig. 8.12, a). The reinforced concrete massive foundations of smoke exhausters are made in the form of a single monolithic block with the necessary ledges and recesses. The upper part of the foundations was significantly weakened by the wells of anchor bolts, while the distance from the edge of the wells to the edge of the foundations in the places where bearings and smoke exhausters were attached was less than required. The measurement results and the obtained vibration modes (Fig. 8.12, b) of the examined smoke exhauster foundations showed that the upper part of the foundations is not a single massif, but is divided into separate conglomerates by through cracks.
The amplitude of horizontal vibrations of the upper edge of the foundation reached 0.07 mm, and the amplitude of the frame and bearing of the smoke exhauster - 0.25 mm, which indicated the absence of a rigid connection between the machine and the foundation. The reasons for this were a decrease in the rigidity of fastening anchor bolts in the foundation body due to the presence of cracks and damage to the integrity of its upper structure, as well as weakening of the tightening of anchor bolts due to the accumulation of plastic deformations in the bolts under the combined action of dynamic loads and high temperatures that arose due to insufficient thermal insulation cars. The latter also contributed to the occurrence of additional temperature deformations in the upper part of the foundation.
The condition of the foundations required immediate strengthening, which was carried out as follows. The upper structure, weakened by recesses and cracks, was reinforced to its entire height with a reinforced concrete belt-cage 0.5 m thick (Fig. 8.12, c, d), which ensured the foundation rigidity required by calculation, as well as a reliable connection between the machine and the foundation due to an increase in the rigidity of the upper part of the foundation in the places where the anchor bolts are attached. Existing cracks were cemented with an expanding cement mortar and filled with epoxy resin where the anchor bolt was installed. To ensure reliable tightening of the fastening nuts, an elastic element was introduced into the anchor bolt tightening unit. At the same time, it was recommended to strengthen the thermal insulation and ensure a gap between its surface and the foundation elements of at least 100 mm. The frame of the cage (class A-II steel, with a diameter of 12 and 8 mm, with a pitch of 200 mm, was connected to the foundation reinforcement by welding using separate rods at the level of the foundation grids. The cage was concreted with concrete grade M 300.
The work examines cases of strengthening individual structural elements of frame prefabricated monolithic foundations of turbine units by increasing the rigidity of these elements operating in the frequency range close to the resonant one. The increase was achieved by increasing the thickness of the concrete sections of the elements (with the addition of reinforcement according to calculation), as well as by introducing additional metal connections.
Strengthening the foundations of impact machines is mostly carried out during reconstruction in connection with the installation of more powerful equipment on the foundations or in case of significant vibrations of buildings. Cases of strengthening such foundations caused by errors in their design or construction are described in the works.
Strengthening the foundations of impact machines (such as forging and stamping hammers, impact piledrivers) is mainly limited to the reconstruction of the hammer part. As an example (data from M.I. Zabylin), let us consider strengthening the foundation of a headframe, the underframe part of which (Fig. 8.13) in the upper part was destroyed during operation into separate conglomerators, and the reinforcing mesh was torn. Before strengthening, the conglomerators were partially removed. In drilled vertical holes with a diameter of 40 mm, reinforcing bars with a diameter of 36 mm of class A-II were installed using epoxy glue to a depth of about 1 m. A reinforcement mesh of concrete made of concrete grade M 300 was attached to these bars to the height of the remote part of the destroyed concrete.
Alphabetical index of terms in Russian
| anchor | 4 |
| driven anchor | 29 |
| screw-in anchor | 30 |
| injection anchor | 23 |
| capsule anchor | 24 |
| adhesive anchor | 21 |
| metal anchor | 12 |
| mechanical anchor | 10 |
| plastic anchor | 13 |
| drop-down anchor | 19 |
| expansion-adhesive anchor | 22 |
| countersunk anchor | 27 |
| anchor with press washer | 26 |
| anchor with wedge clip | 16 |
| anchor with extension | 15 |
| rigging anchor | 28 |
| disc anchor | 25 |
| persistent anchor | 14 |
| friction anchor | 18 |
| chemical anchor | 11 |
| self-tapping anchor screw | 17 |
| sleeve anchor | 20 |
| anchorage depth | 35 |
| anchor embedment depth | 34 |
| depth of installation hole for anchor | 33 |
| anchor group | 5 |
| diameter of mounting hole for anchor | 32 |
| temperature range for anchor installation | 39 |
| temperature range of anchorage operation | 40 |
| anchor dowel | 8 |
| anchor expansion zone | 31 |
| anchor fastening | 1 |
| pre-installation anchor fastening | 2 |
| Anchor fastening for through installation | 3 |
| construction base | 6 |
| Ultimate condition of anchorage | 37 |
| anchorage load-bearing capacity | 36 |
| anchor life | 38 |
| anchor rod | 7 |
| disc element | 9 |
Appendix A (for reference). Classification scheme for anchors and anchors
Appendix A (reference)
Figure A.1
| UDC 692.97:006.354 | OKS 91.120.01 |
| Key words: anchor, anchorage, classification, terms and definitions, anchor group, load-bearing capacity of anchorage, limit state of anchorage, service life of anchorage | |
The electronic text of the document was prepared by Codex JSC and verified according to: official publication M.: Standartinform, 2019
GOST standards
Anchor bolts are considered the most common method of securing buildings to the foundation. In parallel with assessing the quality of the parts themselves, there must be a thorough check of the foundation. Otherwise, there is a risk of breaking the bolted connections. The concrete must be strong enough to hold the anchor bolts. If the concrete is weak or porous, drilling bolt holes may cause cracking or crumbling. Therefore, no guarantee of strength exists in such cases.
Although supporting walls can provide structural stability, additional measures must be taken to reduce the likelihood of damage. Projects are developed taking into account not only permanent impact factors, but also potential seismic hazards. According to the Uniform Building Code, developed based on GOST, it is established that foundation slabs must be bolted to the foundation with bolts with a diameter of 1/2 inch at a distance of no more than 1.8 meters from each other. One bolt should be placed within 30.5 cm of each end of the plate section.
GOST standards regulate not only the structural features of bolts, but also prescribe the material from which parts should be made. The basic rule for all types of durable anchor bolts is production technology from alloy and carbon steel. If this is due to marking according to GOST, zinc is additionally applied to improve the properties of the bolts. It improves quality by protecting fastening systems from corrosion.
Zinc can be applied in two ways:
- Galvanic. The bottom line is that a hydrolysis bath is used for processing. Zinc atoms coat the surface of the anchor bolt.
- Diffusion. Galvanization occurs under the influence of high temperatures. Using the heating method, atoms penetrate the surface of the fastener.
Both methods have worked well, so you can use any of them to achieve results. It is important to adhere to the rules and regulations set forth in the building code.
What is material fluidity
For a clear example of the concept of metal fluidity, you can take two pieces of kitchen equipment - a fork and a knife. By bending the fork in any direction, we deform the product. The material of the spoon only changed its shape, the product did not break - this indicates the high elasticity of the material from which the fork is made. In this example, the strength of the fork material is significantly higher than its fluidity.
A steel knife will break under such impact. The material from which this product is made has approximately the same fluidity as strength. Despite the fact that the knife is made of durable steel, in this example it can be considered fragile.
Another practical example is the process of screwing a nut into a bolt, which can increase its length only under a certain influence on it. If excessive force is applied when tightening the nut, it will not increase the length of the bolt, but break the threads on the fastener.
The next indicator used when calculating the strength of bolts is the percentage of elongation. It shows the length of the deformed part before it fails. Each bolt, to a certain extent, can be considered flexible and capable of being extended to a certain extent without compromising its properties. This indicator is measured as a percentage, by how much the part can be extended, compared to the original parameters.
Equipment according to GOST
GOST was developed on the basis of regulatory construction documents. It regulates the size of products, their quality, storage and transportation features.
As for the packaging requirements, the fasteners must consist of the following parts:
- main rod;
- anchor fittings;
- tile and sleeve;
- coupling and washer;
- clamping scurvy;
- screw;
- pipe.
Some components may be missing depending on the modification. To understand, in straight bolts the thread is screwed on only one side. Also there is only the center rod and nut. If we consider other more complex fasteners, their structure is improved and designed depending on the functions performed, the specifics of the fastening and the application. There can be several fasteners in the form of nuts and washers.