Basic manufacturing methods
Blanks for the products in question are obtained by forging or casting, in some cases using cutting technology. The technological process of manufacturing a gear is quite complicated, since it is necessary to obtain a working surface of complex shape with certain geometric parameters. Helical wheels and other products are cut using two main technologies:
- The copying method involves milling, in which a cut between the cavities of the teeth is formed by using disk, modular or end mills. After each cavity is formed, the workpiece is rotated exactly one tooth. Among the features of this technology, it can be noted that the shape of the cutting tool used follows the shape of the cavity.
- The break-in method is much more common today. In this case, machining involves simulating the engagement of a gear pair, one element of which is a hob cutter. In the manufacture of the tool, high-strength metal is used, due to which cutting occurs. Processing by the copying method involves the use of not only a hob cutter, but also a cutter and a comb.
Hob cutters have become quite widespread. A similar tool is represented by a rack; at the time of operation, the workpiece rotates around its axis. The tool is used to produce exclusively gears with external teeth.
Rolling technology is used to produce large gears as well as large quantities. In this case, hot rolling is carried out; due to heating, the degree of workability of the material increases. The crown is obtained by extrusion. To significantly improve accuracy, mechanical processing can be carried out.
The manufacture of shaft gears must also be carried out taking into account operating conditions. There is a high load on this element, so a workpiece made of high-strength hardened steel is used as a base. The toothed gear, the manufacture of which is carried out taking into account the diameter of the shaft, is mounted using the pressing method, fixation is ensured by a key.
Consequences from another bolt pattern
Using inappropriate bolts is a safety hazard. When a bolt pattern occurs, an axial displacement of the entire wheel relative to the hub occurs. At high speeds, the wheel spins unevenly, the car will shake, which is accompanied by a beating in the steering wheel.
When installing wheels, car enthusiasts often encounter such a problem as a discrepancy in the diameter of the fasteners. In this case, eccentric bolts with a movable conical part are suitable, which will eliminate discrepancies in size.
Thread rolling in bolt production
In the production of bolts for critical connections, thread production is most often carried out by rolling. Responsible, for example, are flange connections for the energy, oil and gas and chemical industries.
Rolling - Stages and schemes of rolling
Thread rolling of bolts and studs is a technological process of forming threads on a workpiece by means of its elastic-plastic deformation with a special tool (rollers, dies, etc.). Thread rolling is a type of metal forming.
Thread rolling temperature in bolt production
Depending on the
- mechanical characteristics of workpiece materials,
- tools,
- energy capabilities of thread rolling equipment
Bolt thread rolling can be carried out:
- at normal temperature or
- elevated temperature, under conditions of superplasticity
- and in other modes.
Under the influence of external forces, deformation of the bolt workpiece material occurs; therefore, it is worth taking into account the dependence of the movement of the workpiece material on time.
Main characteristics of thread rolling on fasteners:
- physical parameter for the manufacture of bolt threads - radial elastoplastic or residual movement of the tool turns in the body of the workpiece (or the corresponding radial load on the workpiece during rolling),
- The technological parameter of thread rolling in the production of bolts is the duration of the rolling process.
Rolling process
The process of rolling bolt threads with rollers occurs in two stages:
- extrusion (section AB in Figure 1);
- calibration (section BC in Figure 1).
Figure 1. Making bolts. Curves of changes in the radial displacement of the movable thread rolling roller (1), rolling force 2), torque on the roller 3) and temperature in the contact zone of the tool with the workpiece during rolling 4)
The speed of tool penetration during extrusion can be determined by the radial feed - the amount of radial movement per one revolution of the threaded fastener workpiece:
Sr = dδ/dn.
Figure 2. Thread profiles during rolling with small (a) and large (b) radial feed a) Sr = 0.01 mm/rev; b) Sr = 0.60 mm/rev
Experiments show that with a small radial feed when rolling threads onto bolts or studs, grooves are formed at the tops of the thread turns (Figure 2, a), which gradually disappear or roll up, forming radial folds.
When rolling with rolling with a larger radial feed, the deformation spreads over the entire thickness of the coil, causing a uniform rise in the metal of each compressed section (Figure 2, b). The rise of the metal is proportional to the radial load on the workpiece and, as a consequence, to the depth of penetration of the tool turns into the workpiece. Extrusion ends after implementation:
- predetermined radial penetration (movement) of tool turns into the body of the bolt workpiece or
- achieving the set value of the radial load on the bolt workpiece (rolling force).
With further movement (rolling or rotation) of the bolt workpiece, the resulting thread is calibrated (section BC on curve 1, see Figure 1) with insignificant radial penetration of the tools into the body of the workpiece.
The duration of extrusion during the manufacture of threads for bolts and studs is determined:
- design parameters (for example, thread profile height) and
- physical parameters (elastic-plastic characteristics of the workpiece material, strain rate).
The calibration duration, which directly determines the thread accuracy of bolts and studs, can be freely set by the bolt manufacturer.
To prevent rolling of threads in a filled contour and to prevent crushing of the workpiece under high forces, a stop is used that limits the maximum movement of the movable roller and absorbs excess load.
Equipment used for hot die forging
Special equipment is used to process metal parts using hot die stamping:
- hammer dies;
- hot stamping crank presses;
- horizontal forging machines.
The most common are double-action steam-air hammers and single-action driven friction hammers. The essence of their work lies in the shock nature of the deforming effect on the workpiece.
High-quality redistribution of metal is achieved by simultaneous regulation of the stroke of moving parts and impact force together with tilting of the workpiece. Hammers are relatively inexpensive equipment.
In the GOSH process, crank hot stamping presses are most often used.
Crank Hot Forging Press
The distinctive features of the stamping press design include a rigid drive, which does not allow changing the direction of the slide, and the absence of shock loads.
Forgings produced on presses have higher accuracy due to their rigid motion, especially in height. This reduces the appearance of machining allowances (the main advantage of a press over a hammer).
However, there are also disadvantages. In the absence of preliminary cleaning of the workpiece from scale, it is pressed into the body of the forging. When the heated metal comes into contact with the walls of the press, the workpiece cools due to the large amount of time spent on the deformation process.
Full and abbreviated bolt pattern formula
Manufacturers provide detailed wording that reflects all important meanings. Motorists use abbreviations that do not fully describe the product.
Abbreviated
PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter) is a short formulation that includes two parameters. It is indicated: 4×98 – wheel bolt pattern on a VAZ-2110. The number of four indicates the number of bolt recesses. The number 98 was obtained as a result of the transverse method of measuring their circumference.
Full
Let's look at an example: the full bolt pattern formula is indicated on the rim: 7.5 J×15 H2 5×100 ET 40 D 54.1.
Decoding of alphanumeric groups means:
- 5 JX 15 – rim width 7.5 inches and diameter 15 inches;
- X – indicates that the disc is made by casting or forging;
- J – it is recommended to use the product on single-wheel drive vehicles;
- JJ – marking of all-wheel drive models;
- H2 – the number of protrusions that secure the tires. Models with one protrusion - H1. Absence of protrusions - marking AN;
- Hump - indicates high-quality rubber retention; this feature eliminates depressurization.
Upsetting of metal blanks
Metal upsetting
To manufacture a rod-type part, such as a bolt, a forging that is thickened at one end is required and is produced by upsetting. The upsetting end of the billet of the required length is heated in a forge or slot furnace to forging temperature. The blacksmith places the workpiece on the anvil with the heated end up (Fig. 6.4, a) and uses a handbrake to show the hammer the places of impacts and their force. If it is necessary to plant a small area of the workpiece, but most of it has heated up, then the area not subject to planting is cooled by dipping it in water. Under the blows of a sledgehammer, the heated part of the workpiece is deformed, increasing in diameter and decreasing in length. The cold part of the workpiece, which has tens of times greater resistance to deformation, retains its original shape. Since the flow of the metal of the heated part of the workpiece along the perimeter is not limited by anything, under the influence of impacts the end of the workpiece takes on a barrel-shaped shape, smoothly turning into the lower cylindrical undeformed part.
If the workpiece is placed with the heated end on the anvil and blows are applied to the cold end, then the upset part will be higher and the diameter will be smaller than in the first case. It is obvious that it will not be possible to carry out the upset of the end of a long rod workpiece using the considered method, since the workpiece will lose stability and bend under the influence of impacts. Therefore, end upset on relatively long workpieces is performed using a flat nailer. Nail 2 is installed above the hole in the tail part of the anvil (Fig. 6.4, b), and workpiece 1 is passed through the hole in the nail. Under the influence of the sledgehammer, the protruding part of the workpiece is subject to upset. In the manufacture, for example, of bolts with square heads, a nailer with a corresponding recess is used (Fig. 6.4, c).
Rice. 6.4. Upsetting the end of the workpiece: a - in the usual way, b, c - using a nailer, d - direction of the fibers in the workpiece after upsetting; 1 - blank, 2 - nail, 3 - anvil
As the workpiece settles, the cross-section of its end part increases, and the metal fills the cavity of the nail house. It is obvious that the fibrous structure of the undeformed part of the workpiece remains unchanged after upsetting, while the fibers of the upsetting part will seem to follow the shape of the head (Fig. 6.4, d).
Upsetting the middle of the workpiece is also a type of upsetting. The middle upsetting part of the workpiece is heated to forging temperature in the forge, the workpiece is placed vertically on the anvil and, holding it in this position with pliers, blows are applied to the end with a sledgehammer (Fig. 6.5). These impacts are transmitted through the cold part of the workpiece to its middle part and it, being the hottest part, is deformed, acquiring a barrel-shaped shape. If the ends of the workpiece also become heated during heating, then before upsetting they are cooled with water to the required length.
What are bolts made of or everything about steel!
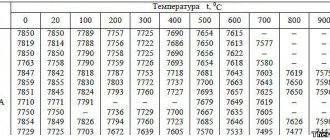
Articles » What are bolts made of or everything about steel! Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon (up to 2% C). According to the chemical composition, steel is divided into carbon and alloy, and according to quality - into ordinary quality steel, high quality steel, high quality steel and high quality steel. Carbon steel of ordinary quality is divided into 3 groups: A - supplied according to mechanical properties and used in most cases when the product made from it is subjected to hot processing (welding, forging, etc.), which can correct the regulated mechanical properties (St0, St1, etc. .); B - supplied by chemical composition and used for parts subjected to such processing in which the mechanical properties change, and their level, in addition to the processing conditions, is determined by the chemical composition (BSt0, BSt1, etc.); B - supplied according to mechanical properties and chemical composition for parts subject to welding (VSt1, VSt2, etc.). Carbon steel of ordinary quality is produced in the following grades: St0, St1kp, St1ps, St1sp, St2kp, St2ps, St2sp, StZkp, StZps, StZsp, StZGps, StZGsp, St4kp, St4ps, St4sp, St5ps, St5sp, St5Gps, Stbps, Stbsp. The letters St stand for “Steel”, the values are the conventional number of the brand as follows from the chemical composition, the letters “kp”, “ps”, “sp” are the degree of deoxidation (“kp” - boiling, “ps” - semi-calm, “sp” - calm). High-quality structural carbon steel, according to the type of processing upon delivery, is divided into hot-rolled and forged, calibrated, round with a distinctive surface finish - silver. According to the requirements for testing mechanical merits, steel is divided into 5 categories.
Category 1 Without tensile and impact strength testing of mechanical properties Hot rolled, forged, calibrated, silver
Category 2 With testing of mechanical properties for tensile and impact strength on samples made from normalized blanks measuring 25 mm (diameter or square side) Hot rolled, forged, calibrated, silver
Category 3 With tensile testing of mechanical merits on samples made from normalized workpieces of the size specified in the order, although a maximum of 100 mm Hot rolled, forged, calibrated
Category 4 With testing of mechanical properties for tensile and impact strength on samples made from thermally treated (hardening + tempering) workpieces of the size specified in the order, although a maximum of 100 mm Hot rolled, forged, calibrated
Category 5 With tensile testing of mechanical properties on samples made of steels in a cold-worked or heat-treated state (annealed or highly tempered) Calibrated
Alloy steel according to the degree of alloying is divided into low-alloy (alloying elements up to 2.5%), medium-alloy (from 2.5 to 10%), high-alloy (from 10 to 50%). As follows from the main alloying elements, steel is divided into 14 groups. High-alloy steels include: corrosion-resistant (stainless) steels and alloys that are resistant to electrochemical and chemical corrosion; intergranular corrosion, stress corrosion, etc.; heat-resistant (scale-resistant) steels and alloys that are resistant to chemical destruction in gas environments at temperatures above 50 ° C, operating in an unloaded and lightly loaded state; heat-resistant steels and alloys that operate under load at high temperatures for a certain time and, at the same time, have the required heat resistance.
Technological production of bolts
There are two fundamentally different methods for manufacturing this type of fastener:
The bolt manufacturing process, regardless of the method, consists of the following steps:
Quality control is carried out at all stages of production. When manufacturing hardware according to an individual drawing, the first manufactured part is checked with the most careful control. If deviations from the technical specifications are detected, the bolt manufacturing process should be reviewed and the cause of the discrepancy should be found.
Manufacturing on a screw-cutting lathe
The stages and methods of processing a workpiece depend on the type of source material (hexagonal or cylindrical rod, characteristics of the metal), as well as on the degree of accuracy of the workpiece. Hot-rolled blanks have less accuracy, which eliminates the possibility of precise centering of the future part on a turret lathe or on a CNC machine.
The technological process of manufacturing a bolt part on a lathe from a cold-drawn hexagonal rod is divided into several stages:
If there are special requirements for the hexagon of the head of the part, the technical process of manufacturing the bolt on a lathe becomes more complicated. To prevent displacement of the head axis relative to the cylinder axis, the workpiece is subjected to additional processing.
Manufacturing of bolts by cold stamping
The first stage of the technical process is preparing the metal for the stamping process:
Scale from the surface of metal workpieces is usually removed by etching. To do this, the rod is immersed in a solution of sulfuric or hydrochloric acid of a certain concentration for a period of 5 minutes to half an hour. To eliminate pickling sludge, the workpieces are washed in hot water. If the etching was carried out using a sulfuric acid solution, the residues are washed off and neutralized by liming the rod.
The production of bolts from a metal rod occurs without heating the metal. The deformation of the workpiece during cold stamping is accompanied by cold hardening—an increase in the mechanical strength of the metal. The finished part is obtained by filling a standard die of a given configuration with the workpiece material. Next, the part is upset—the finished metal hardware is removed from the die.
Advantages of the cold stamping method in the production of bolts:
When choosing a cold stamping method, you should take into account the ratio of the size of the head and the diameter of the rod of the part, as well as the ratio of the diameter of the head to its height and indicators of relative and true deformation. If the ratios for the listed quantities are higher than the critical values, the possibility of manufacturing the part by hot stamping should be considered.
Characteristic differences
Wheel bolts for stamped wheels differ in length and material. Usually good steel is used, which has several types of coating:
It must be said that any type of coating is only a top protective layer. Therefore, it cannot provide reliable protection against corrosion.
To give the stamped disc a more aesthetic appearance, chrome-plated bolts are ideal. If you properly care for your car and operate it normally, the bolts will never rust.
Cold stamping production
The production of bolts using this method requires certain parameters of the raw materials. These include plasticity, uniform composition, mechanical characteristics, absence of external and internal defects (non-metallic inclusions, porosity, scratches and captivity on the surface, gas bubbles).
Surface defects are removed mechanically or by fire. Next, contaminants such as scale and grease deposits are cleaned. The latter is removed by etching, which involves immersing the material in a 10–20% mixture of sulfuric acid or concentrated hydrochloric acid. In the first case, the procedure lasts 15–110 minutes, in the second – 10–30 minutes. Next, they are washed to remove sludge and acid successively with hot and cold water.
Afterwards liming is carried out. In some cases, a lubricating layer is created. Next, for workpieces made of low-alloy steels, phosphating is carried out by using usually a 3% mixture of zinc phosphate salt for 10–15 minutes.
Finally, a lubricant is applied, represented by a mixture of machine oil and molybdenum sulfide or paraffin liquid and ukrinol. Instead, you can use soap emulsion. The final operation is drawing.
Cold stamping involves turning a blank into a product with planned geometric parameters. The name of the technical process reflects that in this case heating of the metal is not used. This reduces elongation and contraction of the material, as well as increases hardness, strength and fluidity. In addition, during the considered stamping of blanks, the material is mechanically strengthened.
This technique has some advantages. Firstly, with its use it is possible to create products of various sizes (up to 5.2 cm in cross-section). Secondly, cold forging provides high productivity. Thirdly, this manufacturing technology uses little material. Fourthly, it ensures final dimensional accuracy, surface finish and part strength.
For cold stamping there are several defining parameters:
- Workpiece deformation. This is the main parameter that determines the technological map.
- The ratio of the height of the head to the cross-section of the final product. Determines the complexity of production.
- The ratio of the cross-section to the length of the upsetting workpiece fragment.
The technological process for manufacturing a bolt according to the above method includes several stages. At the first stage, the initial shape of the head is created. This is done by rolling wire through different molds. The first rolling is aimed at straightening and lengthening it. After rolling, the source material is divided into blanks with a reserve for heads. Next, a core is formed for each fragment by passing it through a press, and the heads are also formed using a number of presses.
The final stage consists of applying the chamfer using roller processing at high speed and under high pressure. Finally, the threaded edge is beveled using a sharpening machine.
The last two operations are carried out by plastic deformation or cutting. Most often, the second technology for producing bolts is used using devices integrated into cold heading mechanisms.
The most commonly used option is single reduction. It is used in the production of alloyed low- and medium-carbon alloys. In addition, this method produces bolts with equal rod diameter and thread section. Reduction is avoided in the manufacture of short products with small heads and threads with a strength of 4.8–6.8. In this case, additional heat treatment is usually not carried out. This manufacturing technology is rarely used, since in this way it is difficult to produce bolts with standard heads, and this often leads to the formation of cracks and other defects on them.
Double reduction technology is relevant for bolts with strength from 4.6 to 10.9 made of alloy steels and medium-carbon alloys. At the initial stage, the rod is compressed by 30%, at the second stage the fragment is processed for threading.
The technology with extrusion before reduction is suitable for the production of high-strength bolts with a resistance of about 100 kg/mm2 without subsequent heat treatment, which reduces the cost of production.
What nuts are needed for stamped wheels?
Today, on some domestic cars, as well as foreign cars made in the USA and Japan, disks are secured with several types of nuts:
- Open,
- Closed,
- With or without collar.
Closed wheel nuts protect the hub from dirt. They are made, similar to bolts, from different materials.
The most commonly used are stainless steel or titanium. When choosing a wheel nut, you need to take into account the most important parameter - thread matching.
Nuts are also made of aluminum. They are designed for mounting wheels on sports cars.
The parts are distinguished by their low weight and increased softness of the metal. Such nuts must be constantly monitored and tightened.
Open type cone nuts are also used to fasten stampings. For wheel tuning, titanium nuts are installed. Their main difference is considered to be high strength and low weight.
However, titanium is a noble and not cheap metal, so not everyone can afford them - their cost is an order of magnitude higher than similar fasteners.
Prices for different types of bolts
The main factor influencing the final cost of the product is the scale of production. With an increase in output, due to cost optimization, the cost of production decreases. The mass production of bolts and nuts is carried out by large domestic and foreign enterprises equipped with automated production lines. They cover the needs of various sectors of the national economy for standard products.
Small manufacturing enterprises equipped with universal turning equipment are focused on the production of hardware in batches of up to 1000 units. The technological process requires significant labor costs compared to mass and serial production, which leads to higher prices for products. The advantages of single production include a wide range of products - if necessary, small companies are able to quickly satisfy any customer need regarding the production of non-standard grade hardware.
Other factors influencing pricing include the type of material used, accuracy class, and type of protective anti-corrosion coating.
What is needed to open a factory
The first thing you need to do is collect information about the state of the market and, taking it into account, draw up a competitive business plan. It will be needed both for internal use and to attract investors, since launching such a facility is quite expensive. It is useful to learn how to find an investor for a business from scratch.
Sample sections of a business plan for the production of hardware:
- description of the enterprise - includes the name of the economic entity, its legal form, a list of its main activities, intentions for the production and sale of products, goals and objectives of the business;
- product description – contains information about the range of goods that are planned to be produced, their technical characteristics, consumer properties, competitive advantages;
- organizational plan – describes the organizational structure of the company, explains the need for selecting certain personnel;
- production plan - describes technological processes, contains data on the features of the equipment used, information on raw materials and materials, includes information on the factors that shape the cost of production;
- financial plan is a key part that covers all issues of financial support for production and the most rational use of available funds, taking into account profit forecasts;
- marketing plan - contains information about the state of the market, an assessment of competition, an action plan to promote the product, etc.
An entrepreneur can independently adjust the structure and content of a business plan or completely entrust its development to a consulting agency. One way or another, you first need to decide on the range of fasteners, familiarize yourself with the technology of their manufacture, and find out what equipment is used for this. As an example, we will consider the production of self-tapping screws, nails, nuts and bolts.
It is useful to read what equipment is needed for the production of composite fiberglass reinforcement. Learn more about which line to choose and how to produce quality products.
A competitive idea for business in regions with active development is the production of scaffolding. Learn more about the types of scaffolding materials, their production technology, cost and price.
Benefits of custom fasteners
If you require high strength fasteners, then you have come to the right place. All our products are manufactured in accordance with GOST, which is a guarantee of quality and allows them to be used for fastening the most critical parts and assemblies.
In addition, TC “Dogma-Krep” can produce fasteners of non-standard shapes and sizes according to customer drawings! We work with each client individually, calculating the cost of manufactured products depending on the complexity of the order and its size. We work quickly, efficiently and in the interests of the client! Contact us, we are always glad to see you!
Bolts and nuts were still used by the Romans during the heyday of their unique civilization. Today it is impossible to imagine how many bolts and nuts in the form of fastening material are used every day in the world. According to experts, 275 of them are required for just one refrigerator. A forklift contains 940, a railroad car contains 1,200, a regular passenger car contains 3,500, and the average jet contains 1.5 million. It is also estimated that 40 percent of all costs fall on the production of hardware.
Making bolts
was put on an industrial basis thanks to the discovery of a thread cutting method. And now in small workshops they use these lathes to turn a bolt and cut threads on it for a car or tractor. But you can't do much with this method. At the end of the 19th century, the American Ward.W made a machine that ensured the production of nuts and bolts in a continuous manner. A metal rod of the required diameter heated to 900 degrees was supplied to special dies. Rolling dies extruded threads in the hot metal. This was the beginning of the continuous production of hardware.
However, this method did not promise high precision thread cutting. To eliminate the shortcoming, the ubiquitous Ward came up with a machine on which threads were cut using the method of cold plastic extrusion of the relief. He significantly strengthened the dies. and made the machine more massive. It should be noted that this method has been preserved to this day with some changes and innovations. That is, cold rolling is the basic principle of bolt production. The production of nuts occurs using approximately the same method. The technology includes a simple but productive scheme. Wire of the required diameter is continuously fed into the bolt cutting machine. The blanks cut to the required length are then passed through a system of stamps, which give them the required shape. And the thread of the required pitch is rolled onto the bolt, ready with a head. There is no provision for preheating the metal, and the fastener is formed by extruding the required parameters.
Modern technologies for the production of hardware ensure a high level of production and profitability. And most importantly, high quality bolts and nuts are produced. Automation of hardware production reduces their cost and marketable price.
How to measure yourself
Measurements must be as accurate as possible, since the indicators differ in close values with a distance of a couple of millimeters, for example, 98 and 100 or 110 and 112, and they are not interchangeable. To eliminate errors, it is recommended to use a caliper or ruler.
Adjacent holes
Here's how to determine the distance between bolt holes. The dimensions of the circle on which the holes are located are taken. The diameter is determined using compatibility tables or by measuring using a ruler. The resulting distance between adjacent fasteners should be multiplied by a factor that depends on the number of holes. The circumference of a VAZ is 9.8 cm, and that of passenger cars is 139.7 millimeters.
Far holes
A simple measurement method is carried out on models with an even number of recesses - for 4, 6, 8 fasteners. Parallel Hole Distance – PCD.
And here’s how the far holes of disks with five bolts are measured: the calculation is made between non-adjacent recesses, the resulting figure should be multiplied by 1.051.
Hub window diameter
Indicative data for the central hub window are indicated in the table and in the complete bolt pattern formula. In the absence of information, readings are measured with a ruler or caliper. The diameter of the hub area on the VAZ 2110 = 58.6 mm.
The bolt pattern is carried out taking into account the relative size of the vertical axis of symmetry of the disk to the area adjacent to the hub.
Making nails
The production of nails is an area of activity where in order to build a successful enterprise, you do not need to invest large sums in purchasing high-tech equipment. Such a business does not require significant labor and material costs.
The nails are made from low carbon steel wire. For each type of product, raw materials of a certain size (diameter) and cross-section are used. The production technology is simple and consists of only three stages:
- preparation of raw materials - at this stage, the wire is unwound and straightened using special rollers and fed into a nailing machine;
- cutting, forming the head and point - the wire enters the impact mechanism, is clamped and cut off;
- finished products are dumped into a storage tank.
The following machines for the production of hardware are involved in the technological process: a hoist (a manual or electric drive device used for unwinding wire) and a nailing machine. The productivity of the latter can range from 100 to 600 units of finished products per minute. It depends on the model.
The total cost of these two machines is about 500 thousand rubles. You can start by purchasing used equipment. Such a purchase will cost 1.5-2 times cheaper.
Hiring staff
The production of hardware is carried out on automated lines, which eliminates the need to hire a large number of workers. To work in production and warehouse areas, the following employees may be required: turners, mechanics, line operators, loaders and technologists.
Room
It is not necessary to build new buildings to accommodate production facilities. You can rent and restore old abandoned objects, of which there are many in our country. This option will be much cheaper.
It is advisable to run the line in an industrial area or in the countryside, since hardening furnaces used in the manufacture of certain types of hardware produce emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere. But if only cold heading and thread rolling machines are used in production, then a workshop can be organized within the city limits. Making nails, for example, can generally be used as a garage production idea.