Fasteners are used wherever two or more structural elements need to be connected. Due to their universal properties, as well as a wide variety of types, fasteners are used in literally all areas of life and production - in construction, mechanical engineering, furniture production, electronics, etc.
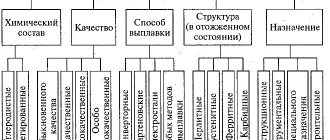
Most fasteners are made from ordinary carbon steel, which has properties such as strength and reliability. Depending on the method of application, the metal can be coated with either a layer of zinc or a special polymer composition, which makes the fastener resistant to moisture.
Despite the universal qualities of steel fasteners, there are cases when its use is impossible. For example, steel may be too heavy or insufficiently conductive - situations may vary depending on production conditions.
If steel fasteners cannot be used, other metals and alloys are used - aluminum, copper, titanium, nickel, brass, etc. The required qualities of the metal are determined by the specific conditions of use - these can be:
- Increased strength.
- Low specific gravity.
- Ability to withstand high temperatures.
- Protection from acids.
- Suitable magnetic properties.
- Required conductivity, etc.
The reliability of the entire structure as a whole largely depends on the correct choice of metal from which the fasteners are made. This is of greatest importance in industries with increased danger - for example, in the nuclear industry, energy, etc. That is why specialists take great responsibility for what this or that fastening element is made of.
Types of hardware made of non-ferrous metals
In most cases, fasteners made of non-ferrous metals are structurally no different from conventional steel hardware. Of course, for non-standard designs, unique fasteners can be made from non-ferrous alloys, however, as a rule, the range of hardware is limited to such products as:
- Bolts. They are threaded rods with an octagonal head. As a rule, they are used in conjunction with a nut.
- Nuts. They look like a flat die with a threaded hole. They are manufactured with both octagonal and round outer parts.
- Hairpins. Rods of different lengths with external thread. They are used together with nuts, or screwed directly into structural elements.
- Washers. Fasteners in the form of disks with an internal hole. They are used in conjunction with bolts to strengthen the places where the fasteners come into contact with structural elements.
- Inserts . They are bushings with internal threads. Used to create blind threaded connections.
As you can see, fasteners made of non-ferrous materials are structurally no different from ordinary hardware. The main difference lies in the characteristics of strength, thermal conductivity and electrical transmission ability, determined by the characteristics of the metal. Next, let's look at the features of metals in more detail.
Equipment for the production of nuts
The main equipment for production are machines for upsetting and threading.
Most enterprises purchase equipment from Taiwan. Presses must have a closed design for safe cutting of products. It is advisable to choose forming matrices in a round shape, as it provides excellent balancing characteristics. The connecting rod mechanism must be made of alloy steel. An important feature is the oil filtration system (usually magnetic), which reduces costs.
Nut setting machine from Taiwan
For thread cutting, it is recommended to use pneumatic machines with multiple spindles for high speed operation. Such spindles can be programmed for different types of work, for example, for long and short threads or left and right. It is also worth taking care of overload and jam fuses.
Aluminum fasteners
One of the main advantages of aluminum fasteners is their low weight, which allows them to be used to reduce the specific weight of structures for various purposes. Thanks to this feature, aluminum hardware is used to create aircraft, space satellites, and lightweight automobile engines.
Another important factor determining the use of aluminum fasteners is its high conductivity. Therefore, aluminum hardware is, among other things, used in the wiring of power lines, as well as in the production of electrical equipment components.
Aluminum is divided into forged and cast. For the manufacture of hardware, forged aluminum is used, which, in turn, is marked in a certain way. The digital designation indicates the properties of the alloy - the more aluminum in the alloy, the lower the digital value (1 - pure aluminum without impurities).
The letter values indicate the following:
- N – increased strength under deformation load.
- O – the material was fired.
- T – heat treatment.
- F – aluminum has not undergone factory processing.
- W – hardened metal.
The degree of heat treatment is indicated by markers T4 or T6. For example, T6 means that the metal, after heating, was placed in a special furnace, where it cooled slowly at a controlled temperature. When choosing aluminum fasteners, you need to take into account all the parameters of the metal, otherwise the products will not meet the tasks assigned to them.
Production process
You can learn how nuts are made in Russia from the patents of various factories. There is a well-proven method according to RF patent No. 2361695. It uses the cold stamping method.
Stamping process according to GOST
The first step is to obtain a workpiece using drawing or calibration. Next, the product is formed on presses in five stages (the method is similar to the production of bolts):
- At the first or third stage, upsetting is carried out, formed into a cylinder and a preliminary hole is marked.
- On the fourth, a jumper is formed for the final hole and gives an almost finished look.
- Fifth, punch a hole in the middle.
After going through the stamping stage, the nut is threaded or rolled. The product is ready, all that remains is to test it. The main parameter is the load that the product can withstand before the thread breaks. Various tests are also carried out for horizontal rupture, artificial aging and deformation under various loads.
The hot forging method is very common. The cut pieces are heated to 1200 degrees. Next, a hydraulic hammer stamps hexagons with holes inside. The next step is cooling and threading using oil. Sometimes hardening is used. To do this, the product is placed in an oven at a temperature of 800 degrees, quickly cooled and immersed in oil for 5 minutes. The second heating is carried out for an hour to minimize brittleness and maintain strength.
The detailed production process is shown in the video.
Copper fasteners
Copper has even greater conductivity than aluminum, and therefore copper fasteners are also used in connecting power lines and in the production of equipment powered by electricity. The disadvantage of copper is its high cost, which is why it is used less often than cheaper aluminum.
Another disadvantage of copper is that when exposed to moisture, it quickly oxidizes, becoming covered with a dense coating. To prevent copper from oxidizing, other metals are added to its composition - nickel, zinc, etc. The alloys obtained by adding other metals do not oxidize, due to which they can be used in the production of structures whose operation involves constant contact with water.
APPENDIX 1 (for reference). Weight of steel bolts (version 1) with coarse thread pitch
APPENDIX 1 Reference
| Bolt length, mm | Theoretical weight 1000 pcs. bolts, kg, with nominal thread diameter , mm | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 36 | 42 | 48 | |
| 8 | 4,306 | 8,668 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 10 | 4,712 | 9,394 | 16,68 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12 | 5,118 | 10,120 | 17,82 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 14 | 5,524 | 10,850 | 18,96 | 27,89 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 16 | 5,930 | 11,570 | 20,10 | 29,48 | 43,98 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 18 | 6,336 | 12,300 | 21,23 | 31,12 | 46,21 | 65,54 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 20 | 6,742 | 13,020 | 22,37 | 32,76 | 48,45 | 68,49 | 95,81 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 22 | 7,204 | 13,520 | 23,51 | 34,40 | 50,69 | 71,44 | 99,52 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 25 | 7,871 | 14,840 | 25,22 | 36,86 | 54,05 | 75,87 | 105,10 | 133,3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 28 | 8,537 | 16,330 | 26,92 | 39,32 | 57,40 | 80,29 | 110,60 | 140,2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 30 | 8,981 | 17,120 | 28,52 | 40,96 | 59,64 | 83,24 | 114,30 | 144,8 | 193,0 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 32 | 9,426 | 17,910 | 29,43 | 42,59 | 61,87 | 86,19 | 118,00 | 149,4 | 198,6 | 237,0 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 35 | 10,090 | 19,090 | 31,28 | 45,34 | 65,24 | 90,62 | 123,60 | 156,3 | 207,0 | 246,9 | 340,6 | — | — | — | — |
| 38 | 10,760 | 20,280 | 33,18 | 48,00 | 68,59 | 95,04 | 129,20 | 163,2 | 215,4 | 256,9 | 353,3 | — | — | — | — |
| 40 | 11,200 | 21,070 | 34,36 | 49,78 | 71,25 | 97,99 | 132,90 | 167,8 | 221,0 | 263,5 | 361,8 | 474,8 | — | — | — |
| 45 | 12,310 | 23,040 | 37,45 | 54,22 | 77,30 | 105,70 | 142,10 | 179,4 | 235,0 | 280,1 | 373,0 | 500,9 | — | — | — |
| 50 | 13,420 | 25,020 | 40,53 | 58,67 | 83,35 | 113,60 | 152,40 | 190,9 | 249,0 | 296,7 | 404,1 | 526,9 | 834,5 | — | — |
| 55 | 14,530 | 26,990 | 43,62 | 63,11 | 89,39 | 121,50 | 162,40 | 203,7 | 263,1 | 313,3 | 425,3 | 553,0 | 872,1 | 1304 | — |
| 60 | 15,640 | 28,970 | 46,70 | 67,55 | 95,44 | 129,40 | 172,40 | 216,0 | 278,9 | 329,9 | 446,5 | 579,0 | 909,8 | 1356 | — |
| 65 | 16,760 | 30,940 | 49,79 | 71,99 | 101,50 | 137,30 | 182,40 | 228,4 | 293,8 | 348,8 | 467,7 | 605,1 | 947,4 | 1407 | 2009 |
| 70 | 17,870 | 32,910 | 52,87 | 76,44 | 107,50 | 145,20 | 192,40 | 240,7 | 308,8 | 366,5 | 491,1 | 631,1 | 985,0 | 1458 | 2076 |
| 75 | 18,980 | 34,890 | 55,96 | 80,88 | 113,60 | 153,10 | 202,40 | 253,0 | 323,7 | 384,3 | 513,6 | 659,7 | 1023,0 | 1509 | 2143 |
| 80 | 20,090 | 36,860 | 59,04 | 85,33 | 119,60 | 161,00 | 212,40 | 265,0 | 338,6 | 402,1 | 536,1 | 687,5 | 1061,0 | 1561 | 2211 |
| 85 | 21,200 | 38,840 | 62,13 | 89,77 | 125,70 | 168,90 | 222,40 | 277,7 | 353,6 | 419,8 | 558,6 | 715,2 | 1098,0 | 1612 | 2278 |
| 90 | 22,310 | 40,810 | 65,21 | 94,20 | 131,70 | 176,80 | 232,40 | 290,1 | 368,5 | 437,6 | 581,0 | 743,0 | 1141,0 | 1663 | 2345 |
| 95 | — | 42,790 | 68,30 | 98,64 | 137,80 | 184,70 | 242,40 | 302,4 | 383,4 | 455,4 | 603,5 | 770,8 | 1181,0 | 1715 | 2412 |
| 100 | — | 44,760 | 71,38 | 103,10 | 143,80 | 192,60 | 252,40 | 314,7 | 398,3 | 473,2 | 626,0 | 798,5 | 1221,0 | 1766 | 2479 |
| 105 | — | — | 74,47 | 107,50 | 149,90 | 200,50 | 262,40 | 327,1 | 413,3 | 490,9 | 648,5 | 826,3 | 1261,0 | 1826 | 2546 |
| 110 | — | — | 77,55 | 112,00 | 155,90 | 208,40 | 272,30 | 339,4 | 428,2 | 508,7 | 671,0 | 854,1 | 1301,0 | 1880 | 2614 |
| 115 | — | — | 80,63 | 116,40 | 162,00 | 216,30 | 282,30 | 351,8 | 443,1 | 526,5 | 693,5 | 881,8 | 1341,0 | 1934 | 2690 |
| 120 | — | — | 83,72 | 120,90 | 168,00 | 224,20 | 292,30 | 364,1 | 458,1 | 544,2 | 716,0 | 909,6 | 1381,0 | 1989 | 2760 |
| 125 | — | — | 86,80 | 125,30 | 174,00 | 232,10 | 302,30 | 376,4 | 473,0 | 562,0 | 738,5 | 937,4 | 1421,0 | 2043 | 2831 |
| 130 | — | — | 89,89 | 129,70 | 180,10 | 240,00 | 312,30 | 388,8 | 487,9 | 579,8 | 761,0 | 965,2 | 1461,0 | 2098 | 2903 |
| 140 | — | — | 96,06 | 138,60 | 192,20 | 255,80 | 332,30 | 413,5 | 517,8 | 615,3 | 806,0 | 1021,0 | 1541,0 | 2207 | 3045 |
| 150 | — | — | 102,18 | 147,50 | 204,30 | 271,60 | 352,30 | 438,1 | 547,6 | 650,8 | 850,1 | 1076,0 | 1621,0 | 2315 | 3187 |
| 160 | — | — | 108,38 | 156,40 | 216,40 | 287,40 | 372,30 | 462,8 | 577,5 | 686,4 | 895,9 | 1132,0 | 1701,0 | 2424 | 3329 |
| 170 | — | — | 114,58 | 165,30 | 228,50 | 303,20 | 392,30 | 487,5 | 607,4 | 721,9 | 940,9 | 1188,0 | 1780,0 | 2533 | 3471 |
| 180 | — | — | 120,68 | 174,20 | 240,60 | 319,00 | 412,30 | 512,2 | 637,2 | 757,5 | 985,9 | 1243,0 | 1860,0 | 2642 | 3614 |
| 190 | — | — | 126,88 | 183,10 | 252,70 | 333,80 | 432,30 | 536,9 | 667,1 | 793,0 | 1031,0 | 1299,0 | 1940,0 | 2751 | 3756 |
| 200 | — | — | 133,08 | 191,90 | 264,70 | 350,60 | 452,20 | 561,5 | 697,0 | 828,6 | 1076,0 | 1354,0 | 2020,0 | 2860 | 3898 |
| 220 | — | — | — | 209,70 | 228,90 | 382,20 | 492,20 | 610,9 | 756,7 | 899,6 | 1166,0 | 1465,0 | 2180,0 | 3077 | 4182 |
| 240 | — | — | — | 227,50 | 313,10 | 413,80 | 532,20 | 660,3 | 816,4 | 970,8 | 1256,0 | 1576,0 | 2340,0 | 3295 | 4466 |
| 260 | — | — | — | 245,20 | 337,60 | 445,40 | 572,20 | 709,6 | 876,1 | 1042,0 | 1346,0 | 1687,0 | 2500,0 | 3513 | 4751 |
| 280 | — | — | — | — | 361,50 | 476,90 | 612,20 | 759,0 | 935,9 | 1113,0 | 1436,0 | 1798,0 | 2660,0 | 3730 | 5035 |
| 300 | — | — | — | — | 385,70 | 508,50 | 652,20 | 808,3 | 995,6 | 1184,0 | 1526,0 | 1910,0 | 2820,0 | 3948 | 5319 |
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
Full symbol
The full designation of bolts, screws, studs and nuts is standardized by GOST 1759.0-87 “Bolts, screws, studs and nuts. Technical specifications"
In the post-Soviet space, in accordance with GOST 1759.0-87 and GOST 18126-94, the following symbol scheme has been adopted for bolts, screws and studs and nuts made of carbon steels and non-ferrous alloys:
For washers, a slightly different symbol scheme is used according to GOST 18123-82 “Washers. General technical conditions":
The above diagrams have a general appearance, with all possible elements. Depending on the type of fastener, the designation may contain more or fewer elements. It should also be noted that some types of bolts, studs, nuts and washers have their own specific symbols, standardized by a specific standard (for example: foundation bolts GOST 24379.1-80, studs for flange connections GOST 9066-75, etc.)
Titanium fastener
Titanium is a durable and lightweight metal used for the manufacture of high-reliability fasteners. Plus, titanium is not afraid of moisture, and also does not oxidize when in contact with aggressive chemicals. These features make it possible to use titanium fasteners in the manufacture of structures operated in extremely difficult conditions - aircraft, satellites, military equipment, etc.
However, titanium is one of the most expensive metals, which significantly limits the possibilities of its use. Therefore, titanium fasteners are used only in cases where there are no other alternatives.
Marking of bolts according to their strength class
The bolt marking system, the meaning of which can be viewed in special tables to determine which type of fastener is right for you, was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). All standards developed in Soviet times, as well as modern Russian regulatory documents, are based on the principles of this system.
Bolts and screws with a diameter of more than 6 mm are subject to mandatory marking. For fasteners of smaller diameter, markings are applied at the request of the manufacturer.
Markings are not applied to screws that have a Phillips or straight slot, and products that have a hex slot and any head shape are required to be marked.
Unstamped bolts and screws that are made by turning or cutting are also not subject to mandatory marking. Marking is applied to such products only when required by the customer of such products.
Standard location of markings on bolts
The place where the bolt or screw is marked is the end or side of its head. If the side part of the fastener is selected for this purpose, the markings should be applied with recessed marks. Convex markings in height should not exceed:
- 0.1 mm – for bolts and screws whose thread diameter does not exceed 8 mm;
- 0.2 mm – for fasteners whose thread diameter is in the range of 8–12 mm;
- 0.3 mm – for bolts and screws with a thread diameter greater than 12 mm.
The geometry of various types of threaded fasteners is regulated by individual GOST standards. As an example, we can consider products manufactured in accordance with GOST 7798-70. Such hexagonal head bolts, belonging to the category of normal precision products, are actively used in various fields of activity.
GOST 7798-70 specifies both the technical characteristics of such bolts and their geometric parameters. The materials of GOST 7798-70 can be found below.
About the strength of washers
The properties of these elements are not determined by tensile strength and fluidity, since their main task is to uniformly distribute the load on the supporting surface. An analogue of strength is their hardness - the value can range from 35 to 45 HRC. The purpose of the elements is determined by the material of manufacture and the protective coating. Uncoated elements are used in places where there is no exposure to moisture; zinc or oxidized coating makes it possible to use fasteners outdoors without the threat of corrosion.
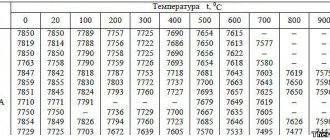
Calculation of loads for stainless steel bolts
Knowing the strength characteristics of austenitic alloys, it is not difficult to calculate the maximum load on bolts using the formula. For example, an M12, A2-70 bolt is taken.
Np0.2 = As x Rp0.2 = 84.3 x 450 = 37935 N
, Where:
As
– design cross-sectional area M12 (see GOST R ISO 3506 Table A.1.)
Rp0.2
– yield strength
To determine the calculated working load, the resulting value must be divided by at least 20: 37935 / 20 = 1896 kg, and for greater confidence in the safety of the bolt kit, it is better to divide by 30.
Strength class is the most important characteristic of stainless steel, prescribed in the national standard GOST R ISO 3506-1-2009, which should be taken into account when calculating the load on a bolted or stud joint.
Source: krepcom.ru