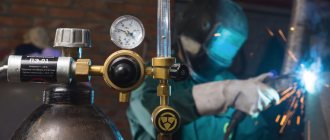
The efficiency of high-temperature processing of metals is increased by welding mixtures of shielding gases used to create a protective cloud over the molten metal. It is much more profitable to use special gas mixtures for welding than pure gases. Several standardized compositions have been developed for use in carbon, low- and high-alloy steels and non-ferrous metals.
It has been experimentally proven that mixtures improve the quality of the melt, reduce the amount of metal spatter, and increase the productivity of the welder. Welding seams become plastic, and arc combustion is noticeably stabilized. The influence of harmful factors is reduced by reducing smoke, and working conditions are improved.
Properties and purpose
The welding mixture, which creates a protective cloud over the melt pool, can have both positive and negative effects on the welding process. Noble gases behave differently:
- Argon, due to air ionization, supports the arc and ensures high-quality metal transfer. When working with thick-walled workpieces and rolled metals with high thermal conductivity, argon, which is characterized by low energy output, is ineffective.
- Helium is preferable from this point of view, but has less effect on the stability of the arc and does not improve the transfer of metal additive to the surface of the workpiece.
- Carbon dioxide provides good protection due to its high density and reduces splashing of liquid metal.
Each individual gas has unique properties; when combined, they neutralize the negative effects of individual components and enhance the positive effects. The compositions were selected by trial and error in order to improve the quality of seams and welding speed.
In the mixture, shielding gases protect the melt pool much more effectively and reduce the likelihood of defects forming.
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide or carbon dioxide in its pure form is used for welding. It is used for parts made of carbon and low-alloy steels, as well as nickel and iron-nickel alloys, including products of large thickness.
Pure carbon dioxide has a higher density than air, so when introduced into the welding zone, it displaces air, providing a protective environment. Carbon dioxide is colorless and odorless, stored in steel cylinders in the form of a liquid substance under pressure, and supplied to the work area using a special reducer. Can be used for any type of welding - manual, semi-automatic or automatic. Carbon dioxide is most widely used in semi-automatic welding.
Iron and carbon, which are part of the parts being welded, are oxidized when welding in a carbon dioxide environment and under its influence. Therefore, to form a weld, a special filler wire is used, which contains silicon and manganese, which prevents oxidation of the metal. The consumption of carbon dioxide depends on several factors: the thickness of the metal of the workpieces being joined, the diameter of the filler wire and the parameters of the current supplied to the electrode.
Gas mixtures
For welding, 4 gaseous colorless substances are used, displacing them from the working area:
- hydrogen, which promotes embrittlement of metals;
- nitrogen, which forms solid slag compounds;
- oxygen, which actively oxidizes metals.
The displacement of gas-air components occurs due to the high density of protective gases; they form a sedentary cloud. All welding gas mixtures have a specific gravity greater than that of air. The concentration of components was selected experimentally, and the influence of gases on the welding mode was taken into account. Argon-based mixtures significantly expand welding capabilities and increase the efficiency of welders. Minimize the risk of defects in welding seams.
Argon and carbon dioxide
For welding non-ferrous metals, profiles and rolled high-alloy steels, a welding mixture of argon and carbon dioxide is used. Argon reduces the activity of carbon dioxide, and CO2 increases the heat transfer of argon. Welding carbon and low-alloy steels in a protective Ar+CO2 cloud is much more efficient than in each individual gas. With a carbon dioxide concentration of within 20%, thick-walled metal structures are boiled even when the surface is heavily contaminated.
Argon and oxygen
The composition is used for welding low-alloy and nickel-alloyed steels. With a low concentration of oxygen, it is possible to avoid porosity of the seams; argon prevents the formation of oxides. The Ar+O2 combination is used with various types of welding wire, expanding the capabilities of the welding process by increasing arc energy and stable combustion. The metal cooks faster. Smooth seam beads are formed with uniform heating of the filler rod. The strength of the connection increases due to the expansion of the diffusion layer.
Argon and helium
Inert gases are combined in different proportions. The most common compositions are 7:3 and 1:1. The Ar+He composition is used when working with various metals:
- cast iron of various densities;
- with low-alloy and alloy steels with high nickel and chromium content;
- non-ferrous alloys based on copper, aluminum;
- refractory workpieces.
Main differences
The main differences between carbon dioxide and welding mixtures are as follows:
- carbon dioxide can only be used for welding certain types of metals - carbon and low-alloy, but welding mixtures have a wider range of applications - they can be used to weld parts made of non-ferrous metals and various alloys;
- carbon dioxide is homogeneous, and welding mixtures consist of different gases that must be mixed using special equipment in strictly established proportions;
- The welding productivity in a welding mixture environment is almost twice as high as the welding productivity in a carbon dioxide environment.
Which is better: welding mixture or carbon dioxide?
Experts decide on their own what is best to cook, taking into account the strength of the joints and the cost of consumables. To isolate the melt formed during the welding process, you can use inert gases argon and helium, carbon dioxide or a welding mixture. With the introduction of inert gases that do not interact with the melt into active ones, the ability of carbon to dissolve in the liquid metal decreases. CO2 is an active gas; when used in its pure form, it saturates steel and non-ferrous metals.
Advantages of using a gas mixture:
- stream transfer of electrode surfacing is facilitated;
- the seams are more flexible;
- the risk of porosity formation is reduced;
- the process of metal melting is accelerated;
- the strength of connections increases;
- less smoke, released substances are retained in the melt zone;
- when the filler wire is fed unevenly, the rhythm of the work is maintained;
- Due to the minimization of spatter, the consumption of electrodes and wire is reduced.
Advantages of welding in a carbon dioxide atmosphere:
- low cost;
- the ability to cook in any spatial position;
- good welding of joints.
Welding productivity when using special mixtures that protect the melt pool from oxidation increases by 50%, while energy consumption does not increase.
What gas is needed for gas welding
Often, gas welding and the gases that are used in it are confused with semi-automatic welding and the gases that are used for it. Let's briefly tell the difference. Gas welding is performed due to the combustion of flammable gas, while in semi-automatic welding the gas is used for protection; it does not burn.
Acetylene
Most often, acetylene is used as a welding gas for gas welding. This gas is lighter than air, colorless and has a faint odor. When burning, the temperature of the acetylene flame is in the region of 2950-3120 degrees Celsius. Acetylene is very flammable even from a static discharge, because cylinders with this gas are filled with a porous substance that is impregnated with acetone.
It is also used for gas cutting, but less frequently. More often, pyrolysis or natural gases are used for this purpose; we’ll talk about them later.
Natural
Natural gases are used much less frequently for welding than acetylene due to their low combustion temperature, but they are used very often for cutting because they are inexpensive compared to acetylene. The use of natural gases is safer than acetylene because they are less flammable. Their combustion temperature is much lower, somewhere in the region of 2100-2300 degrees Celsius.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is an alternative to acetylene in gas welding. This gas has no color, no taste, and is also odorless; it is lighter than air. Hydrogen is also highly fluid and explosive when mixed with air. For welding, hydrogen is not used in cylinders, but is produced in special devices for hydrogen welding from water under the influence of electric current.
The use of hydrogen instead of acetylene provides better, smoother welds. But despite this advantage, this method is rarely used in practice. Since there are a number of difficulties that arise during the welding process. One of them is the appearance of a large amount of slag during the welding process, which requires the introduction of additional components into the metal melt.
Also, a hydrogen welding machine requires electricity to operate, depriving this method of the autonomy inherent in gas welding. Roughly speaking - If you have electricity, why get gas, you can just brew it by hand welding.
Useful article - 9 main types of welding machines used everywhere
Pyrolysis
This gas is obtained at large oil refineries as a by-product of the oil refining process. Once produced, the gas requires certain purification and treatment to reduce its chemical reactivity. Its properties are very similar to those of natural gases.
It is used for cutting metals, but quite rarely for welding due, again, to the low combustion temperature.
Selection of welding mixture for semi-automatic machine
Filler wire is produced without a protective coating; semi-automatic devices provide a supply of protective gases. They are mixed according to calculations to create the required combustion temperature, at which the metal blanks and wire do not melt too quickly. With a rational selection of the gas mixture for semi-automatic welding, the process of forming seams is simplified.
Gas mixture selection table for various alloys:
| Carbon structural steels (sheets, narrow sections) | ||||||||
| Wire size(mm) | Joint size (mm) | Current (A) affects welding speed | Name of the mixture according to GOST and international standard | Component composition of the mixture | ||||
| Ar | CO2 | O2 | He | |||||
| 0,8 | 1 | from 45 to 65 | K-3.1 (Argoshield 5 marking possible) | 92% | 6% | 2% | – | |
| 1,6 | from 70 to 80 | |||||||
| 1 | 3 | from 120 to 160 | K-3.2 (Argoshield TC marking possible) | 86% | 12% | 2% | – | |
| 6 | from 140 to 160 | |||||||
| 1,2 | 6 10 | from 250 to 270 from 140 to 160 | ||||||
| 1,2 | 10 | from 270 to 310 from 140 to 160 | K-2 (possibly labeled Pureshield P31) Universal mixture | 82% | 18% | – | – | |
| 1,2 | 10 | from 290 to 330 | K-3.3 marking possible (Argoshield 20) | 78% | 20% | 2% | – | |
| Alloy steels (heat-resistant, heat-resistant, stainless, acid-resistant) | ||||||||
| 0,8 | 1.6 | from 70 to 855 | NP-1 (possible Helishield HI marking) | 13,5% | 1,5% | – | 85% | |
| 1,0 | 3 6 | from 100 to 125 from 120 to 150 | NP-2 (possible Helishield H7 marking) | 43% | 2% | – | 55% | |
| 1,2 | 6 10 | from 220 to 250 from 120 to 150 | ||||||
| 1,2 | 10 | from 120 to 150 from 260 to 280 from 270 to 310 | NP-3 (possibly marked Helishield H101) | 60% | 2% | – | 38,0% | |
| Aluminum alloys | ||||||||
| 1 | 1,6 | from 70 to 100 | NP-1 (also designated H1 and the inscription Helishield-Н1) | 13,5% | 1.5% | – | 85% | |
| 1.2 | 3 6 | from 105 to 120 from 120 to 140 | – | |||||
| 1,2 | 6 | from 160 to 200 | NP-2 (also designated H7 and the inscription Helishield-H7) | 43% | 2% | – | 55% | |
| 10 | from 120 to 140 | |||||||
| 1,6 | ||||||||
| 1,2-1,6 | from 130 to 200 | |||||||
| 1,5-2,4 | from 300 to 500 | NP-3 (possible markings H101 and Helishield-H101) | 60% | 2% | – | 38% | ||
When using a tungsten electrode and a wire additive, compositions of two inert gases are used:
- НН-1 (full name Helishield-Н3), in this mixture the concentration of helium is within 30%, argon no more than 70%. the gas mixture provides more efficient heating, the metal melting rate increases, and a smooth surface of the seam is formed.
- NN-2 (international marking Helishield-H5) is two inert gases mixed in equal proportions: argon and helium. The universal mixture is used to join black and non-ferrous workpieces of almost any thickness.
The component and quantitative composition affects almost all parameters and modes of metal welding.
How are the materials similar?
Welding mixtures and carbon dioxide have one thing in common - they are used to create an environment that improves the quality and productivity of welding work.
Conclusions: To summarize, we can conclude that welding mixtures have an advantage over carbon dioxide due to wider capabilities for working with different materials, higher productivity and obtaining higher quality and stronger joints. It should be noted that working with carbon dioxide may be preferable in the narrowly focused area of working with certain materials and in semi-automatic welding.
Application of mixtures
Oxygen-free mixtures are chosen for high-speed penetration and welding of non-ferrous metals. They produce excellent clean welds with a smooth profile, little surface oxidation, provide low levels of reinforcement and provide high penetration rates. They provide stability to the electric arc when joining materials thicker than 9 mm, and reduce the likelihood of seam defects.
When feeding the gas mixture semi-automatically, the wire feed speed is reduced and the torch heats up faster. We have to adjust the operating mode and select massive heads. To work with mixtures efficiently, professional skills are required.
When choosing ready-made welding gas mixtures with oxygen, the characteristics of the compositions are taken into account. K-2 is considered ideal for ferrous and low-alloy steels. Others were developed for metal of various thicknesses, deep penetration and welding of thin-walled sheets and profiles without deformation. Oxygen-containing compounds are used for short and long seams, restoration surfacing of worn parts. Can be used everywhere: for automatic robots, manual, semi-automatic welding in all spatial positions. Special compositions are selected for profiled rolled steel and for surfacing.
Working with welding mixtures requires professional skills
When manual welding, it is important to maintain the distance from the workpiece to the nozzle. It is necessary to constantly maintain a distance within 15–20 mm from the joint to prevent lack of penetration. The burner is placed at a right angle. It should be taken into account that oxygen mixtures increase the fluidity of the molten metal; problems are possible when working in a ceiling and vertical position.
What is TIG welding
This is welding work with a non-consumable electrode in a gas cloud. To create a general or local heating zone, a graphite or tungsten electrode is used. The melting point of the rods is much higher than that of the processed material. Protection from atmospheric oxygen is provided by inert or active gases.
Advantages
The spread of the method was facilitated by a number of undeniable opportunities:
- connecting dissimilar metals together;
- reliable protection of the weld pool from the external environment;
- stability of electric arc performance;
- high quality seam;
- the ability to reliably weld metal sheets up to 0.8 mm thick (automotive);
- reduction of local heating and destruction of the crystal lattice of the metal being joined.
Self-mixing of gases
Theoretically, the mixture can be prepared directly at the workplace; at the welding areas there are special posts with the installation of rotameters - devices that control the consumption of components per unit of time from each cylinder. Based on the indicators of the rotameters, the composition of the gas mixture supplied to the welders’ workstations is adjusted using gearboxes.
When working with several cylinders at the same time, the composition of the welding mixture will not be ideal. When making gas mixtures yourself, it is impossible to achieve the exact percentage of components down to tenths. The consumption of gases and, accordingly, additives will certainly increase.
Shielding welding gas is the optimal mixture used in the heat treatment of metals. Ready-made formulations are ordered from specialized suppliers or directly from manufacturing plants.
Table of advantages and disadvantages
Name
Advantages
+ increase in productivity due to increasing the mass of deposited metal per unit time;
+ reduction of excess consumption of filler material by reducing the amount of splashes;
+ increased joint plasticity and density due to less pore formation and, accordingly, a significant increase in joint strength;
+ reducing the amount of harmful aerosols and fumes in the workplace, which improves hygienic working conditions;
+ process stability even with uneven supply of filler wire.
— for a mixture of argon with oxygen, increased oxidation of metals, which reduces the strength of seams, as well as the formation of carbon monoxide, which is harmful to health;
— a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide is explosive, which requires special precautions when carrying out work;
— when working with a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide is also formed due to the interaction of carbon dioxide with atmospheric oxygen, so the operator must work in a special mask.
+ the ability to weld thin metal sheets that do not deform, as well as relatively thick workpieces in any spatial position, that is, to make horizontal, vertical and ceiling seams;
+ formation of a good arc, which is convenient for welders with little experience;
+ low cost of the welding method and carbon dioxide itself;
+ safety at work;
+ the ability to weld metals with different characteristics;
+ simplicity and availability of equipment for welding;
+ high quality of the resulting seams;
+ when connecting parts with a large thickness of metal, carbon dioxide releases a lot of heat, which increases productivity.
— increased spatter formation, which makes it necessary to clean welds after welding;
- the strength characteristics of the seams are lower than with submerged arc welding methods or coated electrodes, so it is not recommended to use this method for parts that will operate under low temperatures or shock loads.
What is the point of replacing argon with a gas mixture?
- Log in to reply to this topic
#1 Sergey new
I am a novice welder - a retiree, so I apologize in advance, maybe my question is stupid.
What is the point of replacing argon with a gas mixture? Just to make it cheaper? Or does it affect the quality of welding?
In our city, a 40-liter cylinder is filled with argon for 800 rubles, and with a mixture of 82% argon and 18% carbon dioxide for 750 rubles. 50 rubles do not make weather for household purposes, so it probably makes sense to cook in pure argon. I'm right?
- Top
- Insert nickname
#2 Simfer
- Participant
- Messages: 762
- City: Simferopol
the meaning of replacing argon with a gas mixture
- Top
- Insert nickname
#3 supoplex
Why, I didn’t care, I was just passing by.
- City: Parnu, Estonia.
Simfer, Aluminum is cooked with pure argon on P/A. But they don’t cook stainless steel anymore.
Sergey new, Maybe you meant replacing carbon dioxide with the above mixture?
- Top
- Insert nickname
#4 Sergey new
Simfer , Aluminum is cooked with pure argon on P/A. But they don’t cook stainless steel anymore.
Sergey new , Maybe you meant replacing carbon dioxide with the above mixture?
For now, I need to make a choice about what gas to buy so that I can eventually learn how to cook my car. As I understand it: simple steel (even an American Ford) can be welded in carbon dioxide, but I would like to learn immediately (even in a couple of months or six months) high-quality welding, both in a mixture of gases and in argon. The point of my question is precisely that the difference in the price of argon and the mixture is insignificant, so is it worth saving these 50 rubles? Will the quality of welding in argon be better than welding in a mixture of gases? Well, in principle, I don’t consider carbon dioxide.
- Top
- Insert nickname