Welding metal parts has been known to mankind for a long time. However, with the development of metallurgy, the emergence of new alloys and compounds, technology began to improve in order to meet all the requirements of emerging realities. Any novice welder needs to learn more information about TIG welding: what it is, how to use the equipment, what strengths and weaknesses it has.
TIG welding
History of appearance
At the end of the 19th century, the American scientist Charles Coffin was the first to use inert gases for welding metal products. His research was based on the experiments of Russian physicists Vasily Petrov and Nikolai Slavyanov, who discovered the arc method of welding parts. The new technology did not allow welding workpieces made of aluminum and magnesium, which was due to a change in the degree of oxidation of the materials when interacting with air.
In the 30s XX century TIG welding technology was improved by American scientists Russell Meredith and Northrop Aycraft. In 1941, inert gases began to be actively used for welding magnesium on direct current. A few years later, specialists at Northrop Corporation began using TIG technology to join aluminum, magnesium and nickel parts. This contributed to the development of the aviation industry and rocket science.
The essence of the TIG welding process
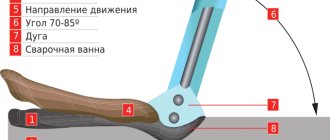
Translated from English, the abbreviation TIG means “tungsten + inert gas” (Tungsten + Inert Gas). The operating principle of TIG welding is the burning of an electric arc in argon. This inert gas is heavier than air. It protects the materials being welded from exposure to oxygen. Argon prevents the oxidation of metals. The result is a neat and durable weld.
Electrodes for argon arc welding are made of tungsten. The melting point of this chemical element is 4000 °C. It can work with all types of steel. To weld a strong seam, you need to periodically sharpen the tungsten electrode. This procedure will increase the service life of the electrical conductor and reduce the risk of reducing its service life. The following values of electrode sharpening angles are distinguished:
- 10–20 °C: at low electric current.
- 20-30 °C: at average current values.
- 60-120 °C: with increased electric current.
If the sharpening angle is less than 20 °C, then the physical properties of the tungsten electrode will change. At high temperatures (above 90 °C), the stability of the electric arc during combustion decreases. Sharpening must be done along the surface of the electrical conductor so as not to deform it. Turning is carried out using grinders, wheels made of fine-grained abrasive materials and sandpaper. To ensure high sharpening accuracy, it is recommended to attach the electrode to the rod of a screwdriver or drill.
The sharpened electrical conductor is fixed to a conical tube located on the burner nozzle. Part of the electrode is covered with a case that prevents short circuits. For TIG welding it is necessary to use RGA-150 or RGA-440 torches. Their main parameters are specified in GOST 5.917-71.
GOST 5.917-71 Manual torches for argon-arc welding type RGA-150 and RGA-400
1 file 287.76 KB
A torch with an electrical conductor is placed in a weld pool with an inert gas. As a result, the electrode is isolated from oxygen. The launch of argon is controlled using function buttons on the torch. When setting up the torch, it is recommended to increase the electrode extension. In this case, the electric arc will be able to weld hard-to-reach elements of metal workpieces.
In the process of argon arc welding with a consumable electrode, an electric arc is ignited. During its combustion, the edges of the welded parts melt. In weld pools without gas, the electronic arc will not burn stably. As a result, the porosity of the seam will increase, reducing its strength.
When TIG welding, it is not recommended to use non-consumable electrodes. In this case, the electric arc will not ignite when the tungsten conductor interacts with the metal surface. When igniting an arc with non-consumable electrodes, a weak spark is formed, which is due to the high degree of ionization of the inert gas.
If during TIG welding a gap is formed between the metals being welded, then filler wire must be used. This device will create a strong seam that is not subject to tears or breaks. The diameter of the wire depends on the width of the workpieces being welded and the shape of the seam.
To create strong metal joints using TIG technology, the following devices are used:
- The source of electric current is the power supply.
- Oscillator - a device for generating high-frequency current that ignites an electric arc.
- An inverter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current.
- Cylinders with inert gas.
- A gearbox is a device for converting transmitted power into useful work.
- Gas-burner.
- Connectors and fastening mechanisms.
Using this equipment you can weld products made of stainless steel, brass, copper and bronze.
To choose the right tools for TIG welding, you need to consider the following factors:
- power supply voltage;
- the presence of an option to change polarity;
- the ability to weld thick parts over a long period of time;
- the presence of a liquid cooling system designed to lower the burner temperature;
- the ability to adjust the operation of the inverter using the display;
- Ability to work on production lines.
The main apparatus for argon arc welding is a welding inverter. It is capable of converting direct current into alternating current by changing its frequency. The welding inverter has the following advantages:
- High efficiency and structural strength, which allows you to create high-quality seams in a short period of time.
- Autonomy of work. During operation, the welder can change the location of the inverter.
- Compactness. The device is small in size and weighs no more than 3 kg.
- High efficiency, which allows you to create a large number of seams with minimal resource costs.
- Low energy consumption, which allows you to save a lot of money.
- Low control complexity. The welder can regulate the smooth supply of current manually.
A welding inverter can be constructed at home using graphic diagrams. To do this, you need to purchase a set of hoses, an oscillator and a device for delaying the flow of electric current. Self-assembly of a welding inverter will save a large amount of money. To carry out installation work, a person must know the basics of mechanics and have experience working with circuit boards and small parts.
Sharpening electrodes
The main element in welding is the tungsten electrode. TIG welding electrodes require constant care. It consists of regularly sharpening its tip. This ensures a good weld.
There is a rule - when welding with direct current, the tip of the electrode is sharpened cone-shaped, and with alternating current - spherically. The length of the cone can be calculated by doubling the diameter of the electrode. For stability, the end of the cone should be slightly blunted.
Electrode sharpening angle values for TIG welding:
- at a small current value - 10-20°;
- average - 20-30°;
- for high current - 60-120°.
If the sharpening angle is less than 20°, then the capabilities of the electrode are reduced, and at an angle of more than 90°, arc burning may lose stability. It is also negatively affected by the risks that arise on the surface during sharpening.
To make them minimal, TIG electrodes must be sharpened lengthwise. Turning occurs with the help of a grinder, a fine-grained abrasive wheel, emery, rotating the electrode in the hand. To make sharpening uniform, the rod is secured in a screwdriver or electric drill. In this case, it is necessary to set small rotation speed values. To protect against dust, you should wear a mask.
Application
TIG welding is actively used in industry due to the high combustion temperature of the electric arc. This technology allows you to weld parts made of carbon and stainless steel, cast iron, aluminum and other refractory metals. TIG technology has found application in the following areas:
- mechanical engineering;
- food industry;
- construction of buildings and infrastructure;
- construction of oil rigs and drilling structures;
- laying of pipelines;
- astronautics and rocket science;
- construction of airplanes, trains and ships.
TIG welding is used in domestic conditions. Using this technology, you can repair cracks in a car radiator, make kitchenware or metal towel rails.
Advantages and disadvantages
The following advantages of argon arc welding are highlighted:
- When welding metal, its surface does not deform, which is due to the narrow heating zone.
- The weld seam does not require cleaning.
- Environmental friendliness: TIG welding does not have a negative impact on the environment.
- Versatility: this method of welding metals can be used when processing parts of different thicknesses and shapes.
- Low complexity of the technological process. Welding products using TIG technology can be performed by welders who are not highly qualified.
- Argon does not allow the parts being welded to interact with oxygen, which increases the strength of the weld.
TIG welding has the following disadvantages:
- High cost of the equipment used.
- Low efficiency when welding products outdoors. To protect metals from oxygen, it is necessary to increase the supply of inert gas, which leads to excessive consumption of resources.
- To process hard-to-reach areas, it is necessary to further trim the electrode or increase its extension.
- When using the TIG Lift function during operation of welding inverters, marks may appear on the surface of the workpieces.
The main disadvantages of TIG welding depend on the welder’s professional skills and work experience.
What it is?
People started welding metals quite a long time ago. However, old and modern welding are very different. TIG welding is one of the most modern methods of joining metal workpieces. Its main principle is the use of a tungsten electrode introduced into the atmosphere of a chemically inactive gas. A rod of this kind itself is usually classified as a “non-melting” category.
The welder has to sharpen the electrode tool, otherwise it is impossible to achieve a constant stable existence of the electric arc. The official definition of the term TIG is argon arc welding using an infusible electrode tool. Of course, even tungsten can melt - but only at a temperature not lower than 3500 degrees. Sometimes the scheme involves supplying not argon, but another neutral gas. It is worth noting that in technical documentation this method may have other names. For example, in German-language literature the term WIG is used. There is also the name GTA, which does not indicate the chemical properties of the gas used.
Tungsten gas welding came into commercial use in the 1940s. It became a real salvation for the aviation industry, and later for rocketry, where other connection methods were no longer satisfactory. Quite soon, engineers from other industries also appreciated the advantages of TIG. The main characteristics of this method:
- maximum uniformity of the seam (the appearance of pores and abnormal cavities is excluded);
- reduction of internal mechanical stresses;
- no melting spatter;
- Suitable for virtually any pure metal or alloy;
- no need to further process the workpieces after joining;
- the opportunity to generally master the equipment and working methods in 2-3 sessions;
- low efficiency of work in the open air (without insulation from the wind);
- the need for careful surface preparation;
- complication of work due to the unacceptability of an acute angle of burner placement;
- the need to clean out marks left by the electric arc.
Crucible welding is suitable for working with almost all types of steel. When the electrode tool is located in the collet, it is rigidly fixed in the torch. Excess length is hidden by an additional cap, which eliminates the risk of short circuit. The final part of the burner is a special ceramic nozzle. In its middle there is an electrode surrounded by an insulating gas.
When the plates are separated by a gap, or the goal is to obtain a weld with high resistance to tearing and fracture, filler wire must be used. The cross-section of this wire is determined by the required thickness of the product and specifically the seam. In some cases, a pulsed version of TIG welding is used. This option implies that the current parameters change from maximum to minimum in a relatively short time. Both direct and alternating current can be used for operation. Both the type and thickness of metal blanks are taken into account. It is imperative to understand the differences between TIG and MMA.
The second option - MMA involves the use of a coated electrode. This approach eliminates the use of insulating gas. Melting electrodes leave a reinforced seam. You can work with steel confidently using MMA equipment. The TIG technique allows you to effectively manipulate aluminum and other non-ferrous metals.
Welding power source
To supply electricity during the TIG welding process, the following types of power sources are used:
- Power supply for MMA welding. It has an external current-voltage characteristic that allows ignition of an electric arc.
- AC/DC power supply. It is equipped with functional buttons that allow you to adjust the shape of the seam. With this device you can weld with both alternating and direct current.
- PROTIG and MECHTIG installations. They are based on a DC inverter power supply. The welding process is controlled using a computer device.
It is necessary to select a power supply in accordance with the circuits of the welding inverter. Otherwise, the devices will not be able to connect to a single electrical network. It is important that inverters for TIG welding are equipped with moisture separators. They do not allow moisture to penetrate the argon environment. If liquid gets on the surface to be welded, many cracks will appear on the seam.
Rating of inverter devices
Modern welding inverters have made the work of welders much easier and have made a leap in electric welding. The three best models, according to user reviews, include:
- Svarog TECH ARC 205 B (Z 203);
- Resanta SAIPA-190MF;
- FUBAG IN 176.
The Svarog TECH ARC 205 B (Z 203) model is one of the most durable and reliable argon arc welding machines produced by a Russian manufacturing company. Its main characteristics:
- input voltage - 187−253 V;
- welding current TIG - 10−200 A;
- type of output current - constant;
- power - 9 kV * A.
The efficiency of this device is 85%, it has arc forced with touch ignition type. The model is small in size and weighs 8 kg, so it is indispensable for frequent movements. The manufacturer provides a warranty period of 5 years. The device does not overheat, electrical energy consumption is insignificant.
The Resanta SAIPA-190MF device is intended for professional welders. These devices are produced in China and sold in Latvia. This device allows you to weld with almost all types of welding. Welding current in TIG mode is from 10 A to 190 A, and the on-time is 70% at maximum current. It has high-quality penetration and takes metal up to 10 mm.
The main disadvantage of this model is its dimensions and weight - more than 18 kg.
The FUBAG IN 176 device is manufactured by a German company for professional electrical equipment. The model is distinguished by its functionality, microprocessor control, small dimensions and weight - 4.5 kg. This device can be used to weld in any position, adjusting the welding current during operation.
The model has a patented design. It makes it easy to move from object to object and effortlessly work in hard-to-reach places.
Welding materials used
TIG welding requires the following materials:
- protective gases;
- electrical conductors (electrodes);
- filler rods and wires.
Welding materials ensure stable combustion of the electric arc and obtain pore-free welds with high resistance to mechanical stress.
Shielding gases
Shielding gases for TIG welding affect metal transfer, shape and physical characteristics of the weld. They allow you to increase the speed and efficiency of welding. Argon is most often used as a shielding gas. It has low thermal conductivity and low ionization potential. When welding parts in an argon environment, the seam is deep and narrow.
Helium can also be used as a shielding gas for TIG welding. It conducts heat easily and has a high ionization potential. When welding products in a helium environment, the width of the seam increases. This inert gas ensures stable wetting of the workpieces being welded along the edges.
Electrodes
Electrodes for argon arc welding consist of durable tungsten, which is one of the most refractory chemical elements.
They improve the quality of the seam and heat up slightly when an electric arc burns. The following table shows the consumption of tungsten electrodes for argon arc welding of parts made of various materials: Electrode consumption
| Material to be welded | Surface thickness, mm | Diameter of electrical conductors, mm | Consumption per 100 m of seam, g | |
| For manual welding | During automatic welding | |||
| Stainless steels with high heat resistance | 1 | 1,5 | 8,3 | 3,9 |
| 2 | 2 | 23,4 | 10,9 | |
| 3 | 3 | 83,3 | 39 | |
| 4 | 4 | 132,2 | 125 | |
| 5 | 5 | 165 | 156 | |
| Magnesium and aluminum alloys | 2 | 2 | 23,4 | 10,9 |
| 4 | 3 | 83,3 | 39 | |
| 5 | 4 | 132,2 | 156 | |
| 7 | 5 | 165 | 156 | |
Tungsten electrodes for argon welding do not require the use of additives and various wires. To improve the technical characteristics of electrical conductors, it is necessary to pre-sharpen them. This procedure will ensure a stable arc while welding workpieces.
Reliable facts
The TIG inverter is equipped with a large number of settings
The equipment makes it possible to qualitatively join a wide range of steel – low-, medium- and high-alloy. Each material has certain physical and chemical characteristics, which necessitates an individual approach when welding. The choice of parameters is also influenced by the thickness of the material and a number of other factors. It is important to choose the optimal settings, and this is the opportunity that the equipment in question provides.
Gas lines must be intact
To create a high-quality and beautiful weld, constant pressure of inert gas is required. In addition, the entire line eliminates the leakage of expensive consumables. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that a leak of inert gas can provoke an emergency situation in the workplace.
The prototype of the TIG inverter was a tungsten filament
American scientist Irving Langmuir experimentally established in 1916 that a tungsten filament conducts a charge better if its surface is coated with thorium oxide. It was this discovery that became the basis for the creation of tungsten electrodes in the future. They are successfully used in argon arc welding to this day.
Effect of current polarity on the TIG welding process
Welding metals using TIG technology can be carried out in various ways. Tig welding modes depend on polarity. This parameter determines the nature of the interaction between the inert gas and the electrode. There are 2 types of polarity:
- Direct: increased input of thermal energy into the product being welded. Features a narrow melting zone.
- Reverse: increased heat input into the electrode. The melting zone is shallow.
Reverse and direct polarities are distinguished by the asymmetry of heat release. This parameter is characterized by the voltage in individual areas of the arc and the type of current.
D.C
When welding parts with direct current, straight polarity is used. Welding in this mode has the following advantages:
- Low electrical energy consumption.
- Allows you to process narrow areas of parts.
- Increased welding speed and efficiency.
DC welding is characterized by a highly complex technological process, so it is rarely used.
Alternating current
When welding workpieces with alternating current, reverse polarity is used. In this mode, the pole change is carried out automatically. Alternating current ensures the stability of the electric arc. It allows you to clean the surface of metals from the oxide film, which improves the quality of the weld. Welding with alternating current is characterized by a low complexity of the technological process and is often used in large industries.
Gas used
The main gas for TIG mode is argon. It is heavier than oxygen, so it displaces it from the torch zone, providing protection. Another gas is helium. The second largest substance by mass, after hydrogen. Despite the high cost, helium provides an increase in arc power by 1.5-2 times. The result is deeper metal penetration and increased productivity.
Due to its technical properties, helium is used for working with refractory materials. Responsible operations are carried out on a mixture of gases: Ar about 35-40%, He about 60-65%. This gives the following combination of advantages: light gas provides deeper penetration, and heavy gas stabilizes arc performance.
Welding technique
TIG welding is performed according to the following algorithm:
- Assembling the welding machine: connecting the inverter to the oscillator, winding up the gearbox, preparing an argon cylinder, connecting the torch.
- Cleaning the surface to be welded.
- Supply of inert gas.
- Turning on the burner and igniting the electric arc.
- Adjustment of arc movement, wire feeding.
- Seam formation.
During welding, the torch must be held in the left hand. The angle between the electrode and the wire should be 90°. The electrical conductor must be placed at a distance of 0.2 cm from the surface to be welded. It is important to set the argon supply correctly; the gas must be supplied before turning on the power source.
Basic parameters of manual TIG welding mode
The manual argon arc welding mode has the following parameters:
- welding current: characterized by polarity and strength;
- electrode diameter;
- welding speed;
- current strength;
- shielding gas consumption.
There are also additional options for manual TIG welding. These include the position of the weld, the coating of the electrode and the thickness of the parts being welded.
Features of welding aluminum and aluminum alloys
Aluminum welding must be done with alternating current, which will allow the metal surface to be cleaned of the oxide film. Before welding, it is necessary to degrease the workpieces using a solvent. When machining aluminum, the filler wire must move along the weld. It must be placed in front of the electrical conductor. The highest weld quality when welding aluminum is ensured when welding parts in a horizontal position.
Equipment
In order to carry out welding work using a non-consumable electrode in a protective environment, it is enough to have an ordinary inexpensive inverter with a burner designed to supply gas. However, there is special equipment on the market:
- TIG inverter. It differs from the usual one in that it has a built-in unit that generates direct or alternating current depending on the operating mode. Thus, the functionality of the device increases significantly. You can work with ferrous metals, aluminum alloys and other materials.
- Rectifiers. The operating principle is based on the conversion of alternating current to direct current. Belongs to the category of professional equipment.
The choice of installation and consumables directly depends on what materials need to be worked with.
Safety regulations
When welding parts using TIG technology, you must follow safety precautions:
- The head must be protected by a mask with a viewing glass.
- Felt or split leather gloves are put on your hands.
- The body must be protected by a suit with high heat resistance.
- The argon cylinder must be placed at a distance of 5 m from the power source to prevent fire.
- Check the operation of the main devices before using them.