The use of inverter welding machines is especially popular among beginners and garage craftsmen, since such machines are easy to use and allow many types of welding work to be performed efficiently. But, despite the ease of operation, the use of an inverter welding machine requires the use of certain types of electrodes for operation. High-quality electrodes help produce reliable and durable welds, and this topic is especially relevant for welders performing custom work, when durability and quality come to the fore.
The modern market offers dozens of types of electrodes for welding machines, and sometimes it is not easy to know which ones are best. What rods can be used for cutting metal with an inverter or for welding with an inverter, how to choose the right electrodes, their diameter and purpose? We will answer these and many other questions in this article. With the help of our article, you will be able to make the right choice of electrodes for welding with an inverter and find out which electrodes a beginner needs first.
What is an electrode and what is the coating for?
An electrode is a piece of metal wire with a special coating - coating. During welding, the core melts due to the temperature of the arc. At the same time, the coating burns and melts, creating a protective gas cloud around the welding area - the weld pool. It blocks access to oxygen contained in the air. As the coating burns, part of it turns into a liquid state and covers the molten metal with a thin layer, also protecting it from interaction with oxygen. So the coating ensures good quality of the seam.
The welding electrode consists of a core and a protective coating
Before starting welding, any electrode is inspected: the coating should not be chipped. Otherwise, you will not achieve uniform heating and a high-quality seam. Also pay attention to the tip of the electrode: the thickness of the coating should be the same on all sides. Then the arc will come out in the center. Otherwise it will be displaced. For experienced welders this is not a big deal, but for beginners it can create significant problems.
It is necessary to monitor the moisture content of the coating. Some of them ignite very poorly in high humidity (for example, SSSI). Due to such “capriciousness” of the coating, they need to be stored in a dry place, ensuring as airtight packaging as possible. You can put the box in a bag, and also put in a few bags of salt that come in shoe boxes.
You should not buy wet electrodes: they can, of course, be dried, but their characteristics will decrease. If it does happen that the electrodes become damp, you can dry them in a regular household oven at low temperatures (they are usually indicated on the packaging). The second way is to put it in a dry, well-ventilated area for a long time.
Coating (protective coating) of electrodes can be: basic, rutile, cellulose and acidic.
Types of coating and their characteristics
There are only four types of coatings:
- Basics.
- Rutile.
- Sour.
- Pulp.
Basic (USSI) and cellulose coatings are only suitable for DC welding. They can be used on critical seams: they create a strong, elastic seam that is resistant to impact loads.
There are more than 200 brands of electrodes for welding, about 100 of them can be used in manual arc welding
The other two (rutile and acidic) can work with both alternating and direct current when welding. But acidic coating is very toxic: you can work indoors only if the workplace is equipped with forced exhaust.
Rutile coating has a greenish or blue tint, the electrodes are easy to ignite. They ignite well even if the inverter has a low open circuit voltage (for reliable ignition of the main coating, a good current-voltage characteristic is required; how to choose an inverter welding machine, read here.). When welding with rutile electrodes (MP-3), the metal hardly splashes, but there is a lot of slag and it is not easy to remove: you have to work with a hammer.
You may be interested in how to weld a gazebo from a metal pipe or how to make a shed on a pipe frame.
This is interesting: Corrugated stainless pipe: production and application features
What can happen if you mix it up during installation?
If the polarity is reversed, the following can happen:
- blown fuses, relays and wires;
- failure of the generator diode bridge;
- burnout of the electronic engine control unit, alarm system.
The simplest and cheapest problem can be a blown fuse. However, this is their main function. You can find a blown fuse with a multimeter by “ringing”.
If you mix up the contacts, then the generator, on the contrary, consumes energy from the battery rather than providing it. The generator winding is not designed for incoming voltage. The battery may also be damaged and fail. The simplest option would be to burn out the desired fuse or relay.
A big problem can be the failure of the electronic engine control unit (ECU). This device requires correct polarity despite its built-in protection. If the fuse or relay does not blow out in time, then the ECU will most likely fail. This means that the car owner is guaranteed to face expensive diagnostics and repairs.
Most devices in a car's electrical system, such as a car radio or amplifier, are protected against polarity reversal. Their microcircuits contain special protective elements.
When “lighting” from another battery, it is also important to observe the polarity and sequence of terminal connections. Incorrect connection will cause a short circuit at 24 volts. If the wires have a sufficient cross-section, they may melt or the driver himself may be burned.
When purchasing a new battery, carefully read the labeling and ask the seller for all the characteristics of the battery. If it so happens that you purchased a battery with the wrong polarity, then it is best to replace it or purchase a new one. Extension of wires and changing the position of the battery should only be done as a last resort. It is better to use a suitable device than to spend money on expensive repairs later.
Main selection criteria
Difficulties that arise when choosing are associated with the emergence of a large number of different electrode options. When searching for the most suitable electrode, you should take into account their division into two main groups:
- Melting.
- Non-melting.
The first type of product is represented by a rod of various diameters with a coating made from a special mixture.
Due to the use of a special coating composition, the created arc behaves better at the time of welding. This is why consumable electrodes are often chosen for devices used in manual arc welding. Non-consumable - today are less common, as they are intended for welding work in a special environment. A beginner will not be able to choose them correctly, as they have a large number of features.
The selection of electrodes for welding with an inverter is carried out taking into account the material from which the workpieces to be joined are made. The properties of the metal largely determine the quality of the resulting weld.
Considering how to choose welding electrodes for an inverter, we note the following points:
- The rod for transmitting electricity and stabilizing the arc is selected for each material, taking into account its chemical composition.
- Carbon electrodes are used to connect products made of low-carbon or low-alloy steel.
- If the products to be joined are made of alloy steels, then electrodes of the MP-3, ANO-21, LB-52U and others are used during welding work.
- The best electrodes for inverter welding of other types of metal are considered to be those in the manufacture of which a core made of alloy steel is used, for example, TsL-11.
- The welding method can be used to join elements made of cast iron. In this case, OZCH-2 electrodes are used.
Experienced welders select the consumable material in question also taking into account the conditions under which the resulting product will be used.
Good, best, best electrodes for inverter welding: rating
Printed and electronic publications periodically conduct surveys among welders, which help determine which brand of electrodes is better.
The rating of welding electrodes includes the following manufacturers: UONI, Resanta, LEZ. The best imported materials, according to the performers: ESAB, Kobe Steel, Lincoln Electric.
The top electrodes were formed thanks to the opinions of both professional and novice welders.
Each of you can also express your opinion by taking part in the survey.
The best (popular) brands of electrodes
Materials for cast iron and stainless steel are not included due to their specificity.
The best (popular) electrode manufacturers
If you see that the ratings are missing a well-deserved brand or manufacturer, write in the comments, they will be added to the survey.
Electrode selection criteria
First of all, it should be borne in mind that electrodes can be of consumable and non-consumable type. The first ones are made of a metal rod, onto the surface of which a special coating is applied, which helps protect the welding zone and increases the stability of the arc. They are used to perform manual arc welding. Products of the second category - non-consumable - are used to perform welding work in a shielding gas (argon), their varieties and features of use will be discussed in a separate article.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
When choosing electrodes for welding using an inverter, you should take into account that the material of the parts being joined will also affect the quality characteristics of the seam being formed. Accordingly, in order to weld different materials, different types of welding electrodes are used. So, for example:
- to connect products made from low-carbon and low-alloy steel grades, carbon electrodes are chosen;
- to connect products made of alloy steel, electrodes of the corresponding brands are used: OZS-4, MR-3 (GOST 9466-75), MR-3, ANO-21, UONI 13/45 (GOST 9467-75);
- if it is necessary to carry out welding work with surfacing or other types of steel, then choose electrodes with a core made of high-alloy metal - TsL-11 (GOST 9466-75);
- in order to cook cast iron, it is also necessary to select electrodes of the appropriate brand - OZCH-2 (GOST 9466-75).
General view of MP-3 electrodes
To date, the following rating of electrodes used for welding using an inverter has been formed.
- ANO. Welding electrodes of this brand are highly flammable and do not require additional calcination. Both novice welders and professionals can work with them equally successfully.
- MP-3 is a universal type; they can even be used to connect uncleaned surfaces.
- MR-3S. Electrodes of this brand should be chosen if increased demands are placed on the characteristics of the seam.
- UONI 13/55 is used for installation of critical structures that require high quality welds. It will be difficult for a novice welder to work with them: their use requires certain experience and high qualifications.
Electrodes UONI 13/55
Types of electrodes for inverter
The central rod is made from various materials. Products are usually divided into categories based on the principle of metal formation to fill the seam. Electrodes are selected depending on the operating conditions and characteristics of the workpieces. For household welding, products with a melting core are more often used.
Tungsten or carbon refractory tools are used in industrial settings.
Melting
The products are equipped with a central core made of carbon or alloy steel (depending on the purpose). When the arc burns, the rod and edges of the parts being connected melt, the metal fills the joint, forming a strong connection. The operator needs to control the remaining length of the product and promptly install a new electrode into the clamp. A protective coating is applied to the surface of the products (using dipping or crimping technology).
Non-melting
For manufacturing, refractory tungsten-based alloys, synthetic graphite or specially treated carbon are used. An arc burns between the tip of the electrode and the elements being connected, which melts the edges of the workpieces. The product provides power supply and gradually wears out, the components do not negatively affect the quality of the metal filling the joint.
Non-consumable electrodes are made from tungsten.
Carbon products can be coated with copper and are used for arc cutting or repairing defects in castings. Tungsten rods are made of pure metal or alloy; the tool is characterized by increased wear resistance. Products made from pure tungsten are designed for alternating voltage, and the introduction of additives allows the use of direct current with direct and reverse polarity.
Classification according to main characteristics
The consumable material in question is primarily classified according to its intended purpose. There are several main groups of electrodes:
- Designed to work with metals that have a low concentration of carbon and alloying elements.
- For joining heat-resistant steels with a high strength index.
- For working with high-alloy steels, for example, stainless steel, in which the concentration of chromium is high.
- Options designed to work with aluminum or copper.
- A separate group includes electrodes intended for connecting cast iron elements.
- For repair work and metal surfacing.
- Universal type products that are used to work with materials of uncertain chemical composition.
A wide variety of chemicals can be applied to the metal rod. According to the type of coating used, 4 groups of products are distinguished; only two are most widespread:
- Main. Products with a basic coating are widely used. An example would be electrodes of the UONI 13/55 brand. They are used to produce seams with high impact strength, mechanical strength and ductility. In addition, the base coating helps protect the seam from the occurrence of crystallization cracks. The choice of this design option is carried out if you need to obtain a responsible design. A significant drawback is that before welding work, the surface must be thoroughly cleaned: oil stains, rust, and scale can cause the formation of microscopic pores.
- Rutile coating. If it is necessary to make a connection on low-carbon steel, then rutile-type electrodes are often chosen. Let's call the most common brand MP-3. The second type is characterized by easy separability of the forming slag and arc stability when supplied with alternating or direct current. During the welding process, less spatter is generated, and the resulting seam has excellent decorative qualities. In addition, the second type of product is suitable for working with workpieces that have a large layer of rust or contaminants on the surface.
The other two types are extremely rare, as they are used in special cases.
additional characteristics
Many other features of the welding carried out determine the requirements for electrodes. An example is the polarity and type of current. The welding inverters used in most cases supply direct current, which can be supplied to the welding zone according to two schemes:
- Reverse polarity involves connecting the plus to ground and the minus to the electrode.
- Straight polarity. In this case, the plus is connected to ground, the minus to the welding electrode.
Reverse polarity is selected in the following cases:
- In order to protect the metal from burn-through, the reverse polarity of the connection is selected. It allows you to work with parts that are small in thickness.
- High-alloy steels are characterized by high susceptibility to heat. That is why, when working with such material, the reverse polarity connection method is chosen.
The most important parameters of the welding process are:
- Diameter of the electrodes used.
- The strength of the welding current used.
- The thickness of the parts to be connected.
It is very important to select the electrode diameter correctly, since if the value is too high, the welding current density is significantly reduced. In this case, the degree of penetration of parts decreases, the width of the weld seam increases and its quality decreases. In addition, manufacturers often indicate what amperage the product is best suited for.
This is interesting: Inch thread: size table, markings, GOST
What criteria should you use to choose polarity?
When choosing the type of connection for a welding machine, you need to pay attention to a number of important criteria. This will prevent defects or excessive consumption of materials and ensure the required strength of the connection.
Sheet metal thickness
Parts whose thickness does not exceed 3 mm are often burned through. To weld such workpieces, a reverse-polar scheme is used, providing an anode thermal spot at the edge of the electrode. This approach is appropriate when processing non-ferrous, alloyed materials.
Types of metals
The positive terminal is responsible for the final heating of the products and the holder. The cathode generates less heat than the anode. When machining refractory steels, it is better to use direct connection when the temperature reaches 4000 °C. For metals that change characteristics when overheated, connect the negative terminal. With direct-polar processing, the seam deepens; with “reverse” processing, it concentrates on the surface.
Types of electrodes
When choosing the brand of electrodes, take into account the type of current. Any variety is suitable for alternating voltage, since polarity does not play any role in this case. For varieties OK, OZS, MR, reverse connection is recommended. UONII and similar modifications are designed for a direct circuit. Manufacturers' recommendations are indicated on the packaging. Many welders prefer universal analogs to other options.
Additives and other consumables
Refractory electrodes used to create an arc are often used with straight polarity. Working with surfacing wire involves the use of only tungsten elements. Coal analogues are unstable to high temperatures, become brittle and crumble.
The best welding electrodes with basic coating
Such rods are characterized by low oxidizing ability, and the resulting welding seam has a low content of hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur and phosphorus impurities. Therefore, it has good crack resistance.
Similar electrodes are used for welding hardening, deoxidized steels and multilayer structures.
ESAB UONII 13/55
92%
buyers recommend this product
See review▶
Electrodes can be used for welding in almost all spatial positions. The deposited metal is resistant to crystallization cracks and is almost completely free of hydrogen.
The rods have a diameter of 2 to 5 millimeters, which allows processing materials up to 8 mm thick.
The permissible calcination temperature before work is 350-400°C. To avoid the formation of pores, welding should be carried out with direct current using a short arc.
Advantages:
- wide range of sizes;
- welding from any position;
- seam strength;
- economical consumption.
Flaws:
- sticking at high current.
ESAB UONII 13/55 are designed for welding low-carbon or low-alloy steel. The ease of operation in any position and the reliability of the resulting seam allow the rods to be used effectively in cramped conditions.
Lincoln Electric SSSI 13/55
90%
buyers recommend this product
The main features of these consumables include low cost and increased service life.
Electrodes can be used when working with materials at sub-zero temperatures and high humidity levels and do not require special storage conditions.
The diameter of the rods is 4 millimeters, the maximum permissible welding current is 160 Amps. Their use is effective in any spatial position, which ensures ease of work with various structural elements.
Advantages:
- high impact strength;
- work at temperatures down to -40 °C;
- minimal splashing;
- stable arc burning.
Flaws:
- require long-term calcination.
Lincoln Electric UONI 13/55 is an excellent choice for arc welding of reinforcing, carbon and alloy steels. Recommended for work in difficult conditions or prolonged use in frosty weather.
PlasmaTec Monolith TsCh-4
88%
buyers recommend this product
A special feature of the electrodes is the ability to work in unfavorable conditions. During welding, a gas bubble appears around the arc, preventing water or dust from entering the joint.
The diameter of the rods is 3 mm. They are characterized by arc stability, low spatter, and ease of both initial and re-ignition. This ensures high weld quality and rapid slag separation.
Advantages:
- protection of the welding zone;
- straight seam;
- economical consumption;
- do not require calcination.
Flaws:
- not intended for vertical welding.
PlasmaTec Monolith TsCh-4 is used for professional welding of thin sheet metal. An excellent choice for tank or pipeline work.
Kobelco LB-52U
86%
buyers recommend this product
They are distinguished by high arc stabilization and large depth of material penetration. Due to the low hydrogen content, the resulting weld is resistant to cracking and has high impact strength.
The diameter of the electrodes is 3 mm, length 40 centimeters. The rods are used for welding metals corresponding to strength classes up to K54, K55-K60. Material processing can be carried out using both direct and alternating current.
Advantages:
- reliable connection;
- fast calcination;
- deep metal penetration;
- ease of slag separation.
Flaws:
- difficulty in re-ignition.
Kobelco LB-52U is suitable for reinforcing the back side of a weld. The rod will be useful for internal processing of pipelines or tanks.
6 Best Welding Generators
How to properly use an inverter welding machine
In experienced hands, an inverter can produce a good seam; you need to follow three rules:
- set the optimal current strength;
- choose the correct electrode diameter;
- take into account the thickness of the parts being welded.
Diameter is the main guarantee of a high-quality seam, and the current density also depends on it. The density cannot be higher, because the arc will be unstable, which means the metal will not be welded as well and the seam will be wider.
Of course, this will not affect the quality, but if aesthetics are important, then it is better to avoid it. If you need to cook thin products, it is better to use a semi-automatic machine.
Inverter welding will produce an unreliable seam, and when choosing thick welding rods, pores will appear in the joint, which will reduce its strength.
To find out the optimal current strength when working with the selected rods, just look at the markings on the packaging. It is not recommended to deviate from this parameter.
How to determine?
It's not that hard to find out. First you need to turn the battery with the front side facing you. It is located on the side where the stickers with characteristics and logo are located. Also, the pole terminals are located closer to the front side.
On many batteries you can immediately see the “+” and “−” signs, which accurately indicate the polarity of the contacts. Other manufacturers indicate information in the markings or highlight the current leads in color. Usually the plus is red and the minus is blue or black.
In the marking, reverse polarity is indicated by the letter “R” or “0”, and direct polarity by the letter “L” or “1”.
Main types of electrodes
According to their intended purpose, consumables used in electric welding are divided into the following groups:
- welding of workpieces made of carbon and low-alloy steels;
- connection of structures made of high-strength and heat-resistant steel grades;
- work on stainless steel;
- electric welding of aluminum and its alloys;
- connection of copper elements;
- welding of cast iron parts;
- performing surfacing and various repair work.
A separate category includes products used for alloys whose composition is unknown and difficult-to-weld grades of steel.
Type of electrode coating
The choice of one type of coating or another depends on the materials being welded, as well as the loads that the structure will experience. There are 4 types of coatings.
Basic (labeling B)
Consumables with a basic coating are used to produce high-quality seams characterized by significant impact strength, strength, and ductility. The seam is resistant to the formation of crystallization cracks and natural aging. These products are used in the manufacture of critical structures that have to be used in harsh climates.
Advantages:
- good mechanical characteristics and high chemical purity of the seam;
- minimum hydrogen in the welded metal.
There are also disadvantages:
- Sometimes pores form in the weld. This can happen when the coating is wet. Pores are also formed if there is scale, rust or oil traces along the edges of the parts being connected;
- storage difficulties;
- slag separation is very labor-intensive;
- short and unstable arc.
Rutile (labeling P)
The area of use of products with rutile coating is electric welding of parts made of low-carbon steels. Technological advantages include:
- stable arc burning when using direct and alternating current;
- minimum spattering of material during inverter welding;
- good slag separation;
- aesthetics of the seam;
- Possibility of use for joining rusty and (or) contaminated workpieces.
The main disadvantage of rutile coating is its limited area of use. In particular, such electrodes cannot be used to connect elements that are planned to be operated at high temperatures. There is another drawback: low chemical purity and high fluidity of the metal.
Sour (labeling A)
The main advantage of coatings marked A is the zero risk of pore formation in the weld area, even if there is a layer of scale and (or) rust on the elements being connected. The features of this option also include ease of ignition and uniform arc burning. This option is used with minimal requirements for the finished structure. Acid coated rods can be used with AC or DC current.
Advantages:
- low cost of work;
- minimal labor intensity for slag removal;
- possibility of use with direct and alternating current;
- ease of storage;
- high level of deoxidation.
The disadvantages include:
- fumes harmful to health;
- high level of metal fluidity;
- welding spatter;
- high probability of hot cracks forming.
Pulp
Products coated with cellulose are marked with the letter C. They are distinguished by stable arc burning at constant current. Such consumables are used when welding main pipes made of low-carbon steel.
Advantages:
- high-quality penetration;
- minimum slag.
This category is not recommended for working with alloys with a high carbon content. Another drawback is hot metal splashes during operation. When used with AC current, additional equipment is required.
- thin (marked M). Ratio from 1.2;
- medium (C) - from 1.45;
- thick (D) - up to 1.8;
- especially thick (G) from 1.8.
The thickness of the coating for quality products ranges from 0.5-2.5 mm. By weight, this is 20-40% of the same parameter of the internal rod.
Advantages of popular brands of electrodes
Many modern types of electrodes for welding using an inverter have the following advantages.
- Easy to weld. Difficulties when welding with such electrodes can arise if you incorrectly select them according to the composition of the core material.
- High quality seam. This parameter is the most important during welding work, and the electrodes of the indicated brands make it possible to ensure it. Using such electrodes for the inverter, you can obtain high-quality internal and external connections, welds of convex and concave shapes.
- Easy slag separation. The slag obtained when welding using such electrodes is easily separated, which makes it possible to immediately see what quality of weld they provide.
- Corroded parts can be welded. Of course, products covered with a layer of rust are cooked very rarely, but these electrodes make it possible to obtain a high-quality and reliable seam even in this case.
- The welding process is safe for the welder in terms of sanitary and hygienic standards.
Electrodes of the ANO brand from the famous manufacturer ESAB
Advantages of modern offers
Modern electrodes, for example, resant and many others, are produced taking into account all established standards . This point determines that the products have the following advantages:
- The welding process is greatly simplified. The use of special materials ensures high stability of the resulting arc. Difficulties can only arise if the electrodes were selected incorrectly based on the composition of the core or coating.
- High quality of the resulting seam. The use of modern consumables allows us to obtain reliable seams even when joining products of complex shapes.
- Separability of slag from metal. When performing welding work, the slag can be separated almost immediately, which allows you to quickly determine the quality of the resulting seam and correct possible defects.
- Electrodes are manufactured in compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards. The welding work carried out is absolutely safe, since no harmful substances are released during combustion.
- Even products that are covered with a fairly large layer of rust can be welded. It is worth considering that to improve the quality of the connection, it is still recommended to clean the surface.
The cost of the product depends on the popularity of the brand and the type of material used to create the coating.
Direct or alternating current
In order to correctly select electrode products, you need to know what type of current the welding process is possible with. In other words, what is better - “constant” or “change”? There are also universal brands that work on both types of current.
Electric welding with inverters using direct current has its own characteristics and advantages:
- There is practically no metal spattering (this saves electrodes);
- ease of use;
- high productivity due to reduced labor intensity;
- persistent and stable arc even in the presence of external negative influences: voltage fluctuations or gusts of wind;
- neat and high quality seam. There are no uncooked areas;
- ability to work with thin metal products.
There are also disadvantages:
- work is possible only with the use of expensive inverter technology;
- unstable arc in difficult places. For example, in the corners.
Two operating modes are possible: with direct or reverse polarity. The first option is used when working with thick metal and when high temperatures are required. Reverse polarity currents are convenient for connecting thin and low-melting metals, as well as dissimilar alloy and stainless steels.
Electric welding with alternating current does not require a rectifier. In addition, such electrodes are universal: they also work with direct current.
Minuses:
- worse connection quality than when using “permanent”;
- low impact strength;
- uneven seam;
- metal splashing.
What does welding polarity affect?
Working with rutile electrodes is possible in both types of polarity. The manufacturer recommends cooking analogues of the UONI type at minus. The heating of the part depends on the welding polarity.
With direct feeding, the workpiece heats up more, allowing the seam section to be made deeper.
With reverse polarity, the element being processed heats up less, and the temperature is concentrated at the end of the electrode. The second mode is focused on processing thin metal and products sensitive to overheating.
Differences in electrodes by brand and diameter
There is an opinion among experienced welders that when using an inverter, you can weld with any electrodes. As a rule, such an opinion is based only on the personal experience of such specialists engaged in performing work of a certain type (welding structures from profile pipes or angles). When performing work using an inverter, no serious requirements are placed on the connection regarding its tightness, so electrodes with a diameter of 0.5–2 mm can be used without problems.
The choice of diameter and brand of electrode should be based on the thickness of the metal that needs to be connected with them. Parts of large thickness require long-term welding; accordingly, the electrode for welding them must be selected with a larger diameter. You still need to learn how to work with small-diameter welding electrodes; they burn out very quickly. Typically, such products are used for tack work.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
Which electrodes are best to choose is also influenced by the type of work for which they are planned to be used. Thus, to perform complex route work, it is necessary to select electrodes of large diameter, and the installation of structures from profile elements can be carried out with products with a diameter of up to 2 mm. These electrodes are used, in particular, in the installation of sectional doors and the manufacture of various enclosing structures from profile pipes and corrugated sheets.
What electrodes are needed for cutting metal
Cutting is a technological process whose purpose is to separate metals into workpieces of the required shape and size.
Types of electrodes intended for cutting:
OZR and ROTEX R electrodes are intended for cutting, gouging and piercing holes, removing defective areas, cutting edges and weld roots. In addition, these brands are used in the manufacture, repair and installation of various structures from different metals and alloys.
Welding purpose
Welding is a common method of creating permanent joints by forming new interatomic bonds. There are several varieties of it, each of which has its own area of use:
- electric arc It is performed using a consumable electrode (N. G. Slavyanov’s method) - a universal, universally used technique used for all types of connections. Its main advantages are high productivity due to maximum mechanization of work processes, as well as good mechanical characteristics of the connection;
- manual arc. It is used when installing steel building systems and connecting pipeline elements. It can be performed even in difficult-to-reach places and in different spatial positions;
- gas. Used when working with steel elements of relatively small thickness, as well as when working with aluminum and copper alloys.
There are other ways to create permanent connections: contact, liquid welding or fastening with a special semi-automatic device.
As for the scope of application, there is probably no industry, be it industrial or agricultural production, where welding is not used. The most common examples are construction work (structures made of reinforcement), connecting pipelines for various purposes. Many owners of used cars know what it means to weld a car body. There is a place for a welding machine in the country (for example, for making a metal fence).
Advantages of welded joints:
- full use of section surfaces to connect elements;
- high level of connection reliability;
- relatively small weight of the structure;
- reduction of allowances for additional processing. This is where welding compares favorably with cast construction;
- reduction of labor and resource intensity of work, which leads to their reduction in cost;
- a good alternative to casting and forging. The use of welding joints allows you to create complex structures from cast or stamped parts;
- the ability to work with innovative alloys, lightweight profiles, rolled sheets, especially pure metals, etc.;
- increasing work safety.
Minuses:
- high risk of various seam defects, which does not have the best effect on the strength of the structure;
- the need for strict adherence to technology;
- the appearance of residual stresses due to thermal deformations;
- change in the mechanical properties of the metal near the seam;
- the need for visual (and in the case of critical structures, selective instrumental) control.
Pros and cons of the two methods
Both methods of welding metal have their pros and cons. Using a direct polarity connection diagram, the following operating features can be identified:
- the result is a deep, strong welding seam that is narrower;
- the stability of the welding arc is noted, which allows complete control of the entire process;
- the ability to weld any metal with a thickness of 3 mm or more;
- when using a welding machine, the workpiece lends itself well to cutting;
- individual selection of electrodes is required. Consumables for AC welding are not suitable for this method. Tungsten rods can be used to join non-ferrous metals.
Welding metal using the reverse polarity method is characterized by:
- obtaining a less deep but wider weld seam;
- a less stable electric arc, especially at low voltage, which can cause an uneven connection;
- possibility of welding medium-thick workpieces and thin metal sheets:
- the need to choose electrodes with a structure that does not collapse when overheated.
When using the reverse polarity method, welding high-alloy steels must be carried out in strict accordance with the technological process.
Selection of products according to other parameters
The type of current, as well as the polarity of its connection, are the most important parameters of welding operations. Welding inverters primarily produce direct current, which can be connected to the workpiece and the electrode in two circuits.
- Straight polarity. With this scheme, the plus is connected to ground, and the minus to the welding electrode.
- Reverse polarity. This scheme involves connecting the minus to ground, and the plus, respectively, to the holder with the electrode.
If you cook with an inverter using straight polarity, the surfaces being connected are subject to significant heating, which does not happen when connecting the polarity in the opposite way. This is why choosing reverse polarity is advisable in the following situations.
- When welding parts of small thickness with an inverter. Reverse polarity in such cases will help protect the material from burn-through.
- Reverse polarity is used to weld parts made of high-alloy steels, which are very sensitive to overheating.
Working with inverter welding
Direct polarity, during which the workpiece is subjected to significant heating, is optimally used for joining materials that are very thick and massive.
When performing any welding work using an inverter, the most significant are three parameters that are interconnected:
- welding current strength;
- electrode diameter;
- thickness of the parts to be connected.
The thickness of the parts being connected has a direct influence on the choice of electrodes. If it is necessary to connect thin parts (up to 1.5 mm), manual welding is not used; semi-automatic machines or devices that allow welding in a protective argon environment are better suited for this purpose.
Options for electrode position when welding
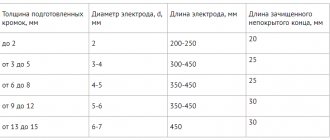
When deciding which electrodes to choose for welding structures of a certain thickness, you can be guided by the following criteria:
- for parts whose thickness is 2 mm, electrodes Ø 2.5 mm are best suited;
- when connecting parts with a thickness of 3 mm, you should choose electrodes Ø 2.5–3 mm;
- if the thickness of the parts to be welded is 4–5 mm, then electrodes Ø 3.2–4 mm are suitable;
- parts with a thickness of 6–12 mm are best welded with electrodes Ø 4–5 mm;
- when the thickness exceeds 13 mm, then the optimal choice is electrodes Ø 5 mm.
It is very important to choose the correct diameter of the electrodes, since if this parameter is exceeded, the welding current density decreases. This will lead to the welding arc becoming unstable, the penetration of parts will deteriorate, and the width of the weld will increase. Many manufacturers indicate on the packaging information about the best current values to use.
Welding electrodes
If such information is not contained on the packaging, then you can follow the following recommendations:
- for welding with electrodes Ø 2 mm, the welding current should be set to 55–65A;
- for products Ø 2.5 mm, a current of 65–80A is used;
- electrodes Ø 3 mm - current 70–130A;
- for electrodes Ø 4 mm, choose a welding current of 130–160 A;
- products Ø 5 mm - current 180–210 A;
- It is better to cook with 6 mm electrodes at a current of 210–240 A.
As it becomes clear from all of the above, for high-quality welding with an inverter, the correct choice of electrodes according to their diameter is important. You should also set the optimal welding current. If, for example, you plan to weld thin metal with an inverter, using large-diameter electrodes, or the welding current exceeds the permissible values, then pores may form in the finished weld, which will significantly reduce its quality characteristics.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
How to use electrodes when welding
General algorithm of actions when working with electric arc welding equipment in domestic conditions:
- Before starting the process, you should prepare your work space and put on protective clothing. There should be no flammable materials or liquids near the welding site; the room should be naturally or forcefully ventilated.
- Inspect the workpieces, clean the joined surfaces from rust or traces of petroleum products. Good electrodes allow you to weld metal products without removing dirt, but impurities can have a negative impact on the strength and appearance of the seam.
- Install the electrode into the handle clamp, set the operating parameters using the regulators on the device body. Since it is difficult for a beginner to choose the right current, you should take into account the recommendations indicated on the original packaging. The power parameters depend on the diameter of the rod, the orientation of the seam or the thickness of the parts being connected.
- Place the workpieces on the table, secure with clamps, and then secure the surfaces with short seams or points (for large or small elements, respectively).
- Check the relative position of the parts and begin welding, ensuring that the electrode is tilted and moving the tip to uniformly fill the joint with metal.
- After the melt has crystallized, remove scale or splashes using a hammer.
Options for the position of the electrode during welding
The quality of the work depends on the qualifications of the welder. For example, with a constant change in the length of the arc, it is possible to burn through sheets of metal or form a seam with a rough scaly structure. When choosing electrodes, the manufacturer's requirements for calcination should be taken into account. The use of products without heat treatment leads to saturation of the melt with gas bubbles. If the welding angle is incorrect, the joint is poorly filled with metal, and if the tip moves unevenly, ruptures or excessive filling of the joint with melt may occur.
Electrodes from foreign manufacturers
Electrodes of the ESAB brand have gained great popularity in the domestic market. A characteristic feature of electrodes from the Swedish manufacturer is that their marking begins with the designation “OK”, followed by 4 digits. Among the wide variety of electrode models of this brand, the following are the most widespread.
- OK 46.00. In terms of characteristics, they are very similar to domestic MP-3 products. Using an inverter, they can cook carbon and low-alloy steels using direct as well as alternating current. When used, the resulting connection is of high quality.
- OK 48.00. They can operate exclusively on direct current; they are used for the installation of particularly critical structures.
- OK 53.70. They are a specialized type; they are used to weld root passages and connect pipe joints.
- OK 61.30 and 63.20. They are used for welding stainless steel parts with an inverter, but before purchasing them, it is important to clarify whether they are suitable for working with the grade of metal you are interested in.
- OK 68.81. Using products of this brand, inverter welding is carried out on parts made of unspecified steel grades, as well as from difficult-to-weld grades.
- OK 96.20. They work on cast iron, and also connect cast iron parts to steel ones.
- OK 92.60. Designed for welding products made of aluminum and its alloys using an inverter.
By the way, the range of electrodes of this brand also includes products that can be used to weld copper and its alloys.
Types of welding arc when welding with electrodes
Device and method of operation of the device
Structurally, the inverter is assembled as a unit of several devices:
- Transformer providing voltage reduction.
- A block of circuits based on metal-oxide-semiconductor type transistors - MOS, in English - MOSFET - metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor, or IGBT - in English, IGBT - Insulated-gate bipolar transistor.
- Choke for stabilizing current ripples.
The device operates as follows:
The mains voltage is supplied to the rectifier, the direct current is converted into alternating current, which has a high frequency. It is transmitted to the welding transformer, from which the voltage goes to the welding arc.
A special feature of the inverter apparatus is its compactness and improved quality of arc operation. Thanks to this, efficiency increases, spatter during operation decreases, and welding parameters can be adjusted. This has led to their popularity and widespread use not only by professionals, but also by amateur craftsmen.
Coatings
Manufacturers often apply special coatings to electrodes to improve their performance. Among the most common coatings are basic and rutile. The base coating is the most popular and is used by a large number of manufacturers. Thanks to him, it is possible to obtain a high quality seam. Well, in combination with the correctly selected electrode diameter and extensive experience, the welder is able to make a weld of the highest quality and weakly subject to mechanical stress.
Rutile coating is popular among craftsmen working with low-carbon steel. Thanks to this coating, the formation of pores in welds is eliminated; such electrodes can be used with alternating and direct current, and can be reused. Also, electrodes with rutile coating are simply more convenient to use when performing work in hard-to-reach places; when melted, such a coating does not emit hazardous substances (unlike other coatings), which allows you to maintain health.