What is an electrode: device
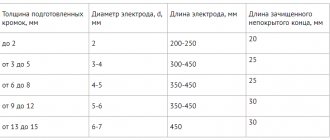
This is a rod made of metal or other electrically conductive composition. It ensures the supply of current from the device to the object that requires welding. The elements come in different lengths: from 25 to 45 cm. Each of them has a protective coating. It prevents the oxidation process. Only a small part of the consumable remains “bare” - the part that is inserted into the holder. Therefore, when searching for components, it is important to consider their thickness. Three-millimeter ones are considered the most popular. Options of 1 and 2 mm are less popular among specialists. Thin ones are used with steel sheets and other parts that require a jewelry approach. You can easily find five-millimeter elements in stores, but beginners rarely need them. Rods with an end larger than 3 mm are needed for alloys that form thick sheets. To work with them, you need a high-power device, which not every beginner has. The variety of choices makes you wonder how to choose the right welding electrodes for an inverter and select their diameter according to the thickness of the metal for high-quality welding. We recommend that you be guided by the following principle: compare the values on the components and the material you plan to deal with. For example, for 2mm metal sheets, use 2mm rods.
What current is used to perform welding?
Both direct and alternating current are suitable for welding, but they have certain features:
- permanent increases the speed of work and makes it possible to obtain good quality seams.
- variable allows better protection of the weld pool, but increases the spattering of the metal and worsens the impact strength of the weld metal.
When operating on direct current, direct and reverse polarity are used. When direct, the part is connected to the positive pole, and the electrode holder is connected to the negative pole. In this case, the part heats up more, so it is optimal to use it for welding thick cast iron, low-alloy, low- and medium-carbon steels.
With reverse polarity, the part is connected to the negative pole, and the electrode to the positive, and it is this that heats up more. This connection method is indicated in the electrode marking with the number 0. It is convenient for welding thin-sheet parts made of low-, medium-, high-alloy and low-carbon steels.
High-quality welding is ensured not only by the experience of the welder, but also by the correct selection of electrodes
Classification of consumables
| by appointment | designation | |
| for carbon and alloy structural steels with a tensile strength of up to 600 MPa | e38, e42, e42a, e46, e46a, e50, e50a, e55, e60 | at |
| for alloyed structural metals with a tensile strength of more than 600 MPa | e70, e85, e100, e125, e150 | l |
| for heat-resistant materials that have undergone alloying | e09m, e09mkh, etc. | T |
| welding of high-alloy parts with special properties | e12x13, e06x13m, e10x17t, etc. | V |
| surfacing of surface coatings with special characteristics | e10g2, e11gz, e16g2khm, etc. | n |
Identifying common groups among a great variety of options is a difficult task, which not all experienced craftsmen undertake. They are schematically divided according to their purpose, the chemical composition of the fused alloy, types, thickness, material from which they are made, and mechanical properties. Experienced specialists use those consumables that they are used to, or those that satisfy them in terms of price and quality ratio. When choosing, they usually take into account two criteria:
- The type of metal you will need to work with. If welding work is carried out at home, then most often we are talking about iron and alloys based on it - the so-called ferrous ones. In this case, the only thing a beginner should consider is the carbon content. Find out what kind of steel you will be dealing with: high, medium, low carbon or cast iron. Acquaintance also often has to start with “stainless steel”.
- Design requirements. Before deciding which electrodes to choose for inverter welding and how, it is necessary to understand whether the seams will be subject to vibration loads or temperature changes. In this case, you should pay attention to rods with enhanced properties.
Features of the welding electrode
During welding, the molten metal is exposed to air, absorbing its constituent gases, as a result of which it becomes brittle. In order to protect the melt zone from the harmful influence of the atmosphere, a slag coating is constantly located on the surface of the electrode. The composition of such a coating determines the optimal area for using the electrode and the composition of the metal entering the seam.
The best welding electrodes have a surface coating, the sequence of formation of which is based on established principles of metallurgy, physical and chemical laws. High-quality coatings protect the metal from deformation, ensure stability of the arc and better give the process the proper quality due to:
- A good coefficient of continuity of the coating, the surface of which has smooth edges/edges;
- Minimize splashes of molten metal;
- Stability of the welding arc;
- Controlled penetration of metal into the seam;
- Necessary physical and mechanical characteristics;
- Easy removal of slag from the surface;
- Consistently good metal deposition rate (during surfacing).
A review of the various types of metal electrodes intended for arc welding shows that they can be divided into non-insulated, thin-coated, or completely shielded.
Surface coated electrodes are the most popular source of filler metal. The best coating composition ensures ease of use, the chemical composition of the seam, and the durability of the product.
Classification by type of coating
There are 4 options:
Basic or calcium fluoride
Identified by the letter "B". It consists of calcium and magnesium carbonates. It may contain marble, magnesite, dolomite. These elements have a low oxidizing ability, due to which the process of removing oxygen from the molten metal is faster. The second name appeared due to the fact that the slag diluent is natural calcium fluoride - fluorite. The advantage of calcium fluoride electrodes is their low hydrogen content. This factor allows you to obtain a strong seam, without gases and impurities, and also minimize the risk of hot cracks. Consumables with a main protective layer are ideal for pipelines carrying hydrogen sulfide compounds, as they resist cracking well. But there is also a nuance. Everything must take place with a direct current of reverse polarity, since calcium fluoride inhibits the operation of components with alternating voltage and the welding arc may burn unstably. Choose electrodes with this type of coating if you plan to work with steel with a high sulfur content or a material that must withstand heavy loads or will be regularly exposed to high temperatures. They are also suitable for welding rigid structures.
Rutile
Despite the fact that a different type is called “main”, this is the option used in 95% of works. The gas released during combustion is non-toxic, so this is the safest solution for the health of the master. The metal seam made with the concentrate is resistant to cracks, does not bend or break, since the consumable material increases viscosity. This coating is ideal if the welder works with a short seam, because the arc burns well even if the voltage in the network fluctuates. For people who have not yet developed their hand and cannot hold it throughout the entire work process, this is the best option. In addition, you can operate with it in any spatial plane.
Sour
Suitable if welding work needs to be accelerated by forcing or lengthening the arc discharge. This is the most toxic type. Due to the increased level of splashing, it can only be interacted with in the lower position. It should not be used for high-temperature calcination. Not recommended for beginners.
With cellulose coating
Half consists of organic compounds - flour, starch, cellulose, half of natural and synthetic silicates. These are very thin consumables, so they can be used in any plane. With their help, a seam is created very easily, which increases the speed of completing the task several times, but the surface of the seam is uneven and requires grinding. Choose cellulose coating if you have to work with carbon and low-alloy steels. It is also suitable for hard-to-reach structures, since the diameter of such elements is minimal.
| type (designation in marking) | stamps |
| main (b) | uoni-13/45, uoni-13/45a, uoni-13/45, uoni-13/45a, uoni-13/45r, tmu-46, uoni-13/55, uoni-13/55k, uoni-13/ 55s, uoni-13/55u, uoni-13/55r, uoni-13/65, ozs-22r, 55-u, fno-t, fno-tm, fno-tm/n, its-4, its-4s, OZS-18, etc. |
| sour(s) | omm-5, cm-5, mez-4, etc. |
| rutile (r) | ano-21, ano-21m, ano-36, ozs-4, ozs-12, ozs-30, ozs-32, etc. |
| cellulose (c) | vsts-4, vsts-4m, oma-2, vsts-4a, etc. |
| mixed: carbonate-rutile (rb) | ozs-28, ano-3, ano-4, etc. |
| rutile-carbonate-fluoride | ozl-9a, etc. |
| ilmenite | ozs-41, mr-3u, mr-3r, etc. |
| rutile-cellulose (rc) | ano-13, fno-29m, etc. |
| acid-rutile (ar) | ano-6, ano-6m, ano-17, ozs-23, ano-24, etc. |
| rutile-ilmenite | mr-3m, etc. |
| with iron powder (g): rutile with powder filler (rzh) | ozs-6, ano-1, ano-27, uoni-13/55tzh, etc. |
| other (n) | for cast iron, non-ferrous alloys, salt. |
In what spatial positions can welding with electrodes be performed?
Welding can be carried out in different spatial positions, but most types of electrodes have certain limitations. These features are included in their labeling:
- electrodes that can be welded in any spatial position are marked with the number “1”;
- electrodes that are not suitable for making vertical seams from top to bottom are marked with the number “2”;
- electrodes that are not suitable for making vertical seams from top to bottom and ceiling ones are marked with the number “3”;
- electrodes that can only be welded in the lower position are marked with the number “4”.
How to choose electrodes for welding with an inverter
Metal diameter and thickness
Compare these two criteria. They should be approximately the same. For inverter equipment, rods up to 2 mm are usually taken, because they are not suitable for larger orders.
Purpose
There are many subtleties. The choice depends on the work technology you will use, welding equipment, and source material. Universal advice - don’t chase cheap offers. Of course, a master can perform a task efficiently using any means at hand, but you should pay attention to mid-price options that minimize mistakes and won’t break your pocket.
Performance indicators
The types of electrodes depend on the specific qualities required in the deposit or weld. The main properties include:
- Corrosion resistance;
- High tensile strength;
- Suitable for welding specific materials (versatility);
- Plastic;
- Relative location of the weld;
- Can be used on any type of current and polarity.
In the weld zone, a temperature regime is provided at which oxidative processes are sharply activated. To ensure that the composition of the metal produced by welding is of high quality, the best welding electrodes have a surface coating.
Which electrodes are best for cooking: choose by type of metal products
Fence
Consumables with rutile coating are a win-win for a beginner. This is AHO with numbers 4,6, 21, 36., MP-3, OK-4600. You can also take rods of mixed recipes “Monolith”, “Granite”, “Arsenal”. The advantage is easy initiation of the electric arc. You will be able to weld with a tear, and pores will not form in the seam. Effective when you need to quickly erect a multi-meter structure.
Thin metal
To avoid burning holes, look for elements with a minimum diameter: we have already discussed how to choose the right electrode for welding above - correlate it with the thickness of the sheet.
Pipes
Gas is treated with grades OK-46 and LB-52. For the heating system, purchase E42A, UONI-13/45, for water supply - MN-5 and MNZh5.
Channel
It all depends on the size of the part. If they are small, then he chooses five or six millimeter ANO-21. You can even cook rusty surfaces with them. If the dimensions of the channel are impressive, only UONI-13/55U. They do not limit the master: alternating and direct current, reverse and direct polarity.
Rails
Experts recommend brands UONI-13/45 and UONI-13/55.
The essence of manual arc welding
Before we talk about electrodes, let's understand what manual arc welding is. An arc is a flow of particles formed during the ionization of the anode and cathode. The ionization process itself is formed by the interaction of current and short circuit. At the same time, the welding process is also influenced by the composition of the electrode coating and oxygen obtained from the atmosphere. Together, these processes lead to heating of the arc and the release of a large amount of heat, sufficient to melt the edges of the parts being welded. The edges then cool, forming a strong and reliable seam.
The key element in this process is the electrode. Without it, it is impossible to ignite the arc and keep it burning. Welding can be done using one or more arc welding electrodes. There is no single classification of rods, since the types of electrodes for manual welding can be divided into many small categories: from purpose to materials of manufacture. By the way, the electrodes themselves for electric arc welding can be made not only from metal, and we will talk about this later.
Choosing electrodes for welding with an inverter for beginners: how and which ones to choose by type of metal
Very often, at home, the main criterion that guides a novice welder is the material.
Stainless steel
This is one of the most frequently used components, so consumables for it are even included in a separate group. For manual use, take the TsL-11 - it is a reliable and easy-to-use option.
Cast iron
It also has its own group of consumables. They are nickel, copper and iron-copper-nickel. Give preference to the OZCH brand. For a malleable alloy, product numbers 2 and 6 are suitable, for a cast alloy – 1 and 3.
Armature
Products with rutile or basic coating ANO-21 are suitable for this.
Galvanization
Popular products made from this material are UONI 13/55, TsU-5, TsL-20, TMU-21.
Copper
Special consumables for ductile metal – OZB-2M and ANTs/OZM-2.
General principles by which electrodes can be classified
The electrode is a coated metal wire. It is made from materials that are similar in composition to the metal of the main product. Based on the adopted welding technology, the electrodes can be selected as consumable (then goes into the weld) and non-consumable - non-consumable (in the latter case, a filler rod is required). The electrode can also have a piece or continuous design (wire).
How to choose the best electrodes for inverter welding
Experienced professionals recommend the following brands:
Calcium fluoride coating
- ESAB;
- SSSI 13/55.
Rutile layer
- AHO-4;
- MP-3;
- OK 46.00.
Stainless steel
- NZh-13;
- OZL-8;
- TsL-11.
We told you how a novice master can choose suitable consumables, gave instructions on which options to choose if you cannot yet assess the situation from the height of your own experience, and told you how to choose a certain electrode diameter. We hope our recommendations will allow you to do the job efficiently and help you further improve your skills. is engaged in the sale of bandsaw machines; for individual consultation, please contact our managers at the contact numbers listed on the page.
Selection of electrodes depending on the type of seam
It is also advisable to select electrodes for manual arc welding according to the type of seam with which you are going to weld metal. In addition to the standard horizontal, vertical, inclined and angled seams, there are also oblique, butt, beveled and many others. This is more useful for experienced welders, but novice welders should also know this information. Now let's talk about what types of electrodes there are for manual arc welding.
Types of welding machines
Welding machines are divided into 2 groups: household and professional. Household appliances are designed to operate from a standard 220 V network with a frequency of 50 Hz. The current strength usually does not exceed 200 A, and the continuous operation time is short. Such welders allow you to perform the necessary welding work in the home. Professional equipment is distinguished by higher current strength (they can produce a current of more than 200 A) and operating time. They can be powered from a 380 V network. Such devices are used in welding oil pipelines, on construction sites and in other industries. The main function of all welding machines is to provide alternating or direct current.
There are several types of welding machines: transformers, rectifiers and inverters.
Transformers convert high voltage alternating current into lower voltage alternating current. The disadvantage of transformers is the inability to obtain a stable arc, as well as their large dimensions and weight. They are sensitive to power surges, and experience is required for successful operation. As a rule, they are used for rough welding of cheap steels.
Rectifiers convert alternating current to direct current. They allow you to get a stable arc and ensure a high-quality seam. They can cook stainless steel and aluminum, as well as low-alloy steels.
Inverters are the most popular welding machine nowadays. It has fairly high power with small dimensions and weight. They are functional and easy to use. They ensure stable arc burning and do not sag during power surges in the network. They can weld thin-walled metals. All types of electrodes are suitable for the inverter. Which electrodes for welding with an inverter are best to choose, read the article at the link.