This is an amplifier that not only has two low-power channels, but also has a high efficiency rate with a low current-consumption ratio.
This device provides exceptional value for sensitive “systems” with characteristics such as low offset (300 µV typical), common mode range to ground, and high differential input pressure capability.
The op-amp simplifies circuit design with the following advanced features: unity gain stability, lower offset voltage of 3 mV (maximum at room temperature), and a “much lower” quiescent current of 300 µA. Serious electrostatic discharge (2 kV, HBM) and built-in EMI and RF filters allow the device to be used in the harshest and most environmentally demanding “grids”.
It is worth saying that this device is capable of functioning even in unipolar power supply structures (4-30 Volt range), this is due to the presence of a dual internal unit that protects the entire system from short-term short circuits.
LM358 circuit
The design of the device includes several housings on which operational amplifiers are mounted. This means that there are not two “inputs” and “outputs,” but much more.
It contains a unique output stage that was revolutionary upon release. Unlike other electrical equipment of the time, it kept the received optical load close to ground, which is useful for single-supply circuits. The ~50uA current regulator can pull the signal to the "foot" because the various transistor emitters do not have a strong counter flow of charged atoms, unlike other power generators of this period and the current era.
In addition, the device contains additional source lines. These connections provide a constant "desired" (I) bias that is independent of the differential starting voltage. This constant current provides a high effective input impedance. Without the necessary sources, the "receive" bias current will vary from zero to twice the normal motion value (as the differential input voltage changes).
This is a common occurrence with other bipolar transistor op amps. Only the TS321 is an exception to this rule, since it does not have auxiliary keys.
↑ 5. Some features
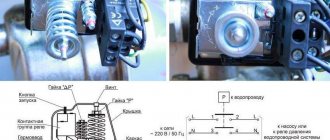
During operation, the heater-regulator works “like an iron.” If the LED is on, heating is in progress; if the LED is off, the desired temperature has been reached. But there are some peculiarities here. Since there is no forced mixing of water, the temperature in the tank is distributed unevenly. Let's take the first cycle. Heating is in progress. When the water near the thermistor and it itself warm up to the desired temperature, the water near the heating element will already heat up much more. The average temperature will be increased and heating will be uneven. But after several heating-cooling cycles, the average temperature will be close to the set one. To minimize the deviation of the average temperature in the tank from the set one, one should search for the optimal relative position of the heater and sensor in the tank.
I consider the best solution for a country shower to be a system of two tanks with hot and cold water and a standard mixer. Hot water heats up to 60...70 degrees. The mixer will allow you to get any temperature, but I was given a different task.
Characteristics of LM358
A unique invention of its kind, with a huge number of interesting features.
Our device consists of two independent amplifiers, which are designed to operate the network from the initial generator in a wide voltage range. “Action” from separate power batteries is also possible if the difference between the two of them is within the pressure range.
It should also be said that the low current consumption does not depend on the value of the supply voltage, because electric current amplification units and all circuits of conventional operational amplifiers, which are easily implemented in systems with one U power supply, can operate directly from a standard source with a value of five Volts.
Speaking about technical properties, it is necessary to highlight the following:
- Wide power supply range from 3V to 36V;
- Has a quiescent current of 300 μA;
- The instrument bandwidth is 1.2 MHz;
- The input common mode voltage extension is capable of detecting conditions near ground, which allows it to play the role of a “protector” in an electrical circuit;
- A low starting voltage of 3 mV at 25° degrees is capable of maximizing efficiency;
- The presence of internal “RF2 and “EMI” filters guarantees the safety of the device when operating in structures with single-polar power supply.
To achieve the best performance from your device, use the following methods:
● Use bypass capacitors to reduce associated noise (by providing low impedance power supplies);
● Connect low value ceramic emergency capacitors (up to 0.1 µF) between each pin and ground, located as close to the device as possible;
● Make sure you “physically” separate the digital and analog grounds, paying attention to the current flow;
● Reduce “spurious communication”.
It’s worth mentioning the charging device on the LM358. When operating op-amps, they often produce an installation that serves as charging and has a solid level of stabilization and control of pressure at the terminals.
A notable property is the presence of a silicon diode in its composition, which ensures accuracy when the resistor is turned on.
Simple DIY thermostat
We made such a simple thermostat with our own hands.
Photo of the back side of the board.
This DIY device can be safely used as a thermostat for an incubator or dryer. When using a sealed thermistor (temperature sensor), its scope of application is already expanding; it will play a good role as an aquarium thermostat.
A simple DIY thermostat in action
Main Parameters of LM358
The sensor has several key parameters at once. These are the ones that will be discussed in this section.
Let's start, perhaps, with “limited gain,” which is denoted as follows: [gopen.]. This is a certain indicator that demonstrates how many times the “op-amp” has increased the operating frequency of the initial signal.
Now let's look at the second most important element - [vout.] - the voltage at the output. [vout.] cannot be infinite, because it is precisely this that ensures equality in transition phases.
And finally, [rres.] is the resulting resistance, which shows the maximum “value” of the resistors used in the circuit.
Types of LM358
There are several types of op amps that we are talking about. Firstly, it should be noted that there is not one classification feature, but three at once.
The “systematization” should begin with such a feature as the area of use.
So, there are programmable and alternative types. If we talk about the first, then it must be said that they are very cheap and easily accessible, because, as a rule, they are in “circulation” only in measuring modes. But the latter, in turn, are distinguished by a high price, since their structures contain powerful units that can minimize the consumption of external load, which ensures absolute safety from short circuits of the entire electrical system.
Now let's move on to the division by “bases”: there are electronic (1) and polar (2). 1 - work due to their intensive control of the flow of particles that move between the cathode and anode, that is, minus and plus. 2 - operate by regulating and monitoring the resistance value at the terminals, which determines the direction of the initial signal.
And, of course, the third sorting. It is determined by the speed of operation of the electrical appliance. Of course, we will consider high-speed and medium-acting ones.
“CUs” are characterized by the maximum possible displacement speed, because they contain several differential outputs. But “SU” is completely the opposite - they do not possess the required amount of the above-mentioned elements, and also have a low emission frequency during a unipolar process.
Principle of operation
To demonstrate how a high-speed comparator with hysteresis works, you need to take a circuit with two outputs.
Photo – diagram of the comparator operation
The connection diagram, from which you can understand the principle of operation of the comparator, is shown above. Using an analog signal at the + input, called "non-inverting", and the output, called "inverting", the device uses two similar signals of opposite polarity. However, if the analog input is greater than the analog output, then the output will be “1” and this will turn on the open collector of transistor Q8 on the LM339 equivalent circuit to be turned on. But, if the input is at a negative level, then the signal will be equal to “0”, which is why the collector will be closed.
Read also: How to quickly remove a bruise from your eye
Almost always, a two-threshold or phase comparator (for example, on transistors, without an amplifier) acts on the inputs in logic circuits, and accordingly, operates at the level of a certain power network. This is a kind of transition element between analog and digital signals. This principle of operation makes it possible not to specify the certainty or uncertainty of signal outputs, since the comparator always has some capture of the hysteresis loop (regardless of its level) or a final gain.
LM358 connection
Our technical tool is perhaps the most popular technical device in satellite electronics, because it can be used in various structures that increase the level of block signals in various generator installations, in analog-to-digital converters and in other devices.
Since it is considered one of the elements that can achieve a wide range of applications in the design of those systems that control the level of temperatures and other characteristics, its connection diagram is based on conventional circuits.
So, the sensor leads are connected to power networks (unipolar or bipolar), where the “main signal” is formed.
Only then, current lines are formed in the amplifier structures, capable of regulating and controlling our “impulse”, converting it so that the value is suitable for the proper functioning of the electrical network (that is, with minimal losses).
Once connected, it will be possible to determine the temperature, which varies in the range from one degree Celsius to a thousand. It is the value of T that will determine how the following elements of the system will organize their activities:
- subordinate amplifier;
- current deformation formalizer;
- “refrigerator” voltage conversion;
- double block with reverse regulation value;
- integral differential control housing;
- software designer;
- output frequency controller.
Purpose
Why do you need a comparator and how to use it without an amplifier? In most cases, this device is used in simple computer circuits where it is necessary to compare incoming voltage signals. This can be a charger for a laptop or phone, a scale (mass meter), an AVR mains voltage sensor, a timer (composer type lm 358, microcontroller, etc. It is also used by various integrated circuits to control input pulses, providing communication between the signal source and its destination center.
Photo comparators for computer
The most popular example is the Shimmer trigger comparator. It operates in multi-channel mode, which means it can compare a large number of signals. In particular, this trigger is used to restore a digital signal that distorts communication depending on the voltage level and distance of the power source.
This is an analogue of a standard comparator, just with more advanced functionality, which provides measurement of several incoming signals.
Photo – op-amp comparator
There is also a roughness comparator. This is a device that helps to visually determine the condition of a surface that has already been treated. The use of this device is justified by the need to determine the tolerances of previously processed surfaces.
Analogs LM358
Our tool has a sufficient number of prototypes, which, of course, we will tell you about. Perhaps we should start with the most popular “LM”: “258”, “158”, “209”, “4092”, “307”, “2902”. They have similar characteristics and have an almost identical internal structure. This is explained by the fact that they are produced, most often, from one production facility.
If we talk about those devices that still have slight differences regarding thermal or electrical properties, then, first of all, it is necessary to note: “na-157”, “op-122”, “sa 358”, “ta-6165” ", "ora-257". The structural composition of the above sensors is of less quality, so they cost less, but they last a long time.
Description of more famous
Remembering those meters that are most similar to ours, one cannot fail to mention a number of their features that play a key role in operation.
So, let's highlight the following:
- Frequency compensation implemented internally;
- Large constant voltage gain: 100 D;
- Wide Bandwidth: (1.1 MHz) (with temperature compensation)
- Very small power supply current on the channels (virtually independent of holding power and power supply);
- Small initial bias current and U-th: 20 nA and 2 mV;
- The scale and volume of incoming “gravity” voltage includes negative rails;
- Large change in output pressure: from zero Volts to plus or minus one and a half.
Description of lesser known
The so-called “cheap analogues” have the following characteristics:
- High signal transmission coefficient to the primary phase;
- Lightweight integrated circuit view;
- The presence of “non-inverting” and “inverting” points;
- Simplification of complex mathematical modules;
- The resistance at the terminals is zero (there are rare exceptions to the rules).
Advantages and applications of LM358
The operational amplifier has a number of advantages that need to be mentioned. So, this device has high sensitivity, excellent compactness and excellent reliability. In addition, it is universal in use, because it does not include complex nodes in its system that act as interference.
As we said earlier, our device operates in both bipolar and unipolar processes, this is explained by the high speed and maximum possible frequency of signal emission.
Due to the presence of such high-quality and effective properties, LM358 finds wide application in people's lives. It is used in:
- Set-top boxes, turntables and DVD players;
- Homemade film panoramas;
- Gas meters and meters;
- Simple players;
- Digital nodes and installations;
- Multimedia systems;
- Field transmitters;
- Electric motor installations;
- Engines and generators;
- Thermometer sensors;
- Libra.