In recent years, plasma welding technology has spread to all industries, including construction and household repairs, and is increasingly replacing traditional types of welding. This is due to the very great advantages of this technology over already known ones.
First of all, the quality of the seam, then, minimal warping of parts, and finally, high purity and waste-free technology. The energy intensity of such welding is approximately the same as other types, and sometimes exceeds them.
Description and scope of plasma welding
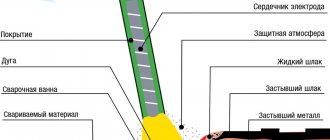
The main difference between this method of joining parts is the high heating temperature (up to 8000 °C). The weld pool is protected by an argon environment. The cooling system prevents a critical temperature increase.
Without this block, the plasma torch melts and the working area heats up to 30,000 °C.
The essence of welding lies in the ability of argon to take on the state of plasma under the influence of an electric arc.
The current, which is a plasma generator, changes the physical properties of the electrically conductive gas.
Plasma welding is used to join workpieces made of materials with a high melting point. Most often, units of this type are used on production sites. Less common are models for work in home workshops.
What is plasma and how does it occur?
Plasma is the state of a gas when it is partially or completely ionized. This means that it can consist not only of neutral molecules and atoms, but also of electrons and ions
having a certain electrical charge or consisting entirely of charged particles. To transform a gas into a plasma state, most of its molecules and atoms must be ionized. To achieve this, it is necessary to apply a force to the electron that is part of the atom that exceeds its binding energy with the nucleus and help break away from it.
For this, certain conditions must be created, which were developed in the field of producing a plasma arc.
The first mention of the development of plasma welding was in 1950. In 1960, some principles for producing plasma flow were introduced and plasma welding technology and equipment were introduced. In our country, research in this area and the development of technology were carried out at the Institute of Metals named after. A. A. Baykova, led the project N.N. Rykalin. After studying the physical properties and energy of a compressed electric arc in an argon environment, converted into a plasma jet, its technical capabilities in the field of welding were determined and special equipment was developed.
Types of technology
The methods differ in equipment operating parameters, scope of application and some other characteristics.
Direct action
The principle of operation of the unit when exciting an electric arc is the same as in electric arc welding: one contact is connected to the electrode, the other to the workpiece. A powerful arc is formed, falling on the metal.
Plasma is produced as follows:
- the terminal is connected to the nozzle, the gas entering the plasmatron is ionized;
- After the contact is transferred to the part being welded, the arc hits the material, the plasma is removed from the nozzle.
To understand what direct plasma welding is and how to work with this method, you need to know that the power of the heated gas jet depends on the current strength. Argon not only maintains a stable arc, but also prevents oxygen from entering the weld pool.
Indirect action
The operating principle of welding machines of this type is based on the following processes:
- Connecting one pole to the infusible electrode, the second to the plasma torch.
- Excitation of an electric arc. The power is determined by the argon pressure in the plasma-forming installation. During ionization, the gas heats up and increases in volume. Argon during indirect welding is consumed more slowly than with direct technology.
- Feeding an arc onto metal with great force. The area being treated melts.
We recommend reading: The principle of acetylene welding with oxygen
With the indirect method, a stable arc is maintained, and the plasma temperature is lower than with direct welding. The installations are used for spraying powders, obtaining thermal effects, and joining materials with low electrical conductivity. Shielding gas is supplied automatically.
Key Features and Benefits
By obtaining a plasma arc, you can significantly expand your welding capabilities. Its main differences from conventional argon welding are:
- high plasma temperature reaching 30000oC;
- small cross-section of the arc;
- the conical shape of the arc, characteristic of argon welding, has been changed to a cylindrical shape;
- the small diameter of the jet allows you to significantly increase the pressure with which it acts on the metal. It is almost 10 times higher than with argon welding.
- The welding process can be supported by a small current ranging from 0.2 to 3.0 amperes.
Such plasma properties provide significant possibilities for this welding before argon arc welding:
- deeper weld penetration is ensured;
- the melting zone is reduced without cutting the welded edges;
- Due to its cylindrical shape and the ability to increase in length, a plasma arc can be used to weld hard-to-reach places.
Working principle of plasma welding
The nature of the functioning of the devices depends on the method of adjusting the parameters.
Manual method
For simple operations on joining non-ferrous and ferrous metals, equipment that does not have automatic control units is used. After the plasma arc appears, the master brings the torch to the part with one hand, and with the other he feeds consumables into the weld pool.
By moving the tool and filler along the joint, the welder forms a strong weld. The manual welding process can be carried out without wire.
Using automation
Such plasma welding machines are used at production sites. The operator controls all parameters remotely.
There are automatic installations of the following types:
- for connecting sheets of metal or pipes;
- single-pass for welding with wire;
- multi-pass;
- for the formation of reinforcing powder coating.
Automatic penetrating arc devices are often used to weld aluminum and aluminum-based alloys.
Requirements and conditions for using the technology
The following requirements apply to plasma arc welding:
- Before starting work, the arc is “twisted”. This is explained by the possibility of decay. “Twist” helps to form a stable thin arc, because the gas quickly ionizes. The part is exposed to a powerful thermal effect, concentrated at one point. This is where melting occurs.
- When welding, you need to maintain a powerful arc. It is capable of melting any metals and alloys, regardless of their thickness and physical properties. The parts are heated to the melting point and even boiling.
- The weld pool is protected with inert gas - argon, acetone vapor, nitrogen. The nozzle simultaneously supplies plasma and protective medium. Therefore, the melt does not interact with air. The material does not oxidize, the seam acquires high strength.
Technological process
It includes several necessary steps: preparing parts, connecting electrodes, starting the burner and warming it up, making a seam while maintaining the desired temperature regime and moving the burner to the site of a new operation and checking the readiness of the burner itself.
Interesting: The principle of operation of plasma welding
Plasma welding technology
The preparation of parts consists of pre-sorting them or delivering them to the workplace already sorted. If the parts are obtained by thermal cutting or rough mechanical cutting, then the edges are processed until the metal is clean and degreased to obtain a high-quality seam.
After this, the parts are brought into contact along the seam line. In production, this is not done “on the knee” as during repairs, but with the help of devices.
Hot seam from plasma welding
If required, fluxes are applied to the weld line. Usually these are strong reducing agents for work at high temperatures (welding fluxes), mixed with low-melting binders, which themselves are reducing agents, or provide a minimum of difficult-to-remove carbon deposits (slag). The molten slag protects the bath from the action of oxygen, and the reducing agent takes it away from the oxides that have already formed. Fluxes are not required for all metals or their pairs.
The burner is started by a high voltage pulse or contact between the nozzle and the cathode for a fraction of a second. The arc lights up, working and protective gases are supplied to the torch, as well as cooling water is supplied to the anode body (for powerful long-lasting torches). The torch warms up until the plasma stabilizes and the welding operation begins.
During welding, the joined edges of the part are melted, and filler material in the form of a tape or rod is introduced into this melt. In automatic welding, the feed is mechanized. Welding is considered as a continuous process of melting and solidification of metal in the weld area and should ensure the solidity of the seam, the same mechanical properties along the entire length, equal thickness of the seam, and the complete absence of cavities, foreign inclusions and impurities.
The molten seam is quite defenseless in relation to many factors, so to obtain quality it is necessary to create special conditions: before the bath, in it itself, and after, in the area of crystallization of the melt. These conditions greatly depend on the metals being welded.
Plasma cutter welding process
After finishing the seam, the readiness of the torch for the next operation is checked, so that the seam does not have to be stopped during the welding process without completing it. Any such interruption, if forced, creates unnecessary mechanical stress, which will then be either difficult or impossible to remove. For this reason, welding of critical seams: vessels (tanks) for rocketry, hulls of sea vessels, especially submarines, vessels for nuclear technology, etc. cooked with a continuous supply of cathodes on burners with powerful cooling of the nozzles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the plasma method include:
- Availability. The plasma torch can be installed on basic welding machines.
- Uniformity of the welded joint. Due to the high temperature, a uniform, thin seam is formed in the treated area.
- Ability to control metal penetration.
- High performance. The high speed of seam formation reduces the labor intensity of the work.
- Wide scope of application. The universal method is used to join workpieces made of other materials.
The negative qualities of this welding method include:
- high cost of the plasma torch and work;
- difficulty in execution (the welder is required to have special skills);
- the need for additional care of the devices (you need to regularly clean the plasmatron, replace the electrode and burner);
- the need for a continuous supply of argon to the apparatus;
- the need to cool the main equipment components;
- high energy consumption.
We recommend reading: How to cook semi-automatically without a gas environment
Disadvantages when used at work
In addition to its advantages, plasma welding has several negative aspects, because of which it turns out to be less optimal than similar ones. Below we will look at what shortcomings it contains:
- increased cost;
- due to the dissipation of energy in space, the atmosphere and the metal of the electrode, it has a reduced efficiency factor (efficiency);
- ensuring the supply of water and plasma-forming gas;
- Difficulty in use makes it unsuitable for normal or everyday work.
How to use plasma welding
To work using this method, the welder must have a permit and comply with safety requirements.
General provisions and rules
When working with plasma equipment, consider the following recommendations:
- before starting welding, prepare the place and special clothes for the master;
- check the serviceability of the main elements of the device, the pressure in the cylinders;
- weld aluminum and its alloys at low current;
- the plasma torch is purged before starting welding work;
- novice craftsmen use microplasma welding (this method is considered safer);
- An experienced welder independently chooses the most convenient technology for himself.
Safety precautions
The following labor protection requirements apply to the work process:
- When welding using the plasma method, the likelihood of electrical injury increases. Do not use cables with damaged insulation and refuse to use a dielectric mat.
- As the current increases, the noise level increases. In this case, use hearing protection - headphones, earplugs, and a noise mask.
- To protect the respiratory system, craftsmen install a local exhaust hood from melt vapors and gases.
- To prevent damage to the visual organs, glasses with light filters are used.
Working with non-ferrous metal
When welding such materials, a lower exposure temperature is required. However, due to the high thermal conductivity, the power of the electric arc must be quite high.
The difficulty of welding may lie in the oxidation of non-ferrous metals under the influence of oxygen, but most oxides are easily reduced.
The presence of organic oxidizing radicals in the plasma - aqueous-alcoholic or acetone solutions - is sufficient.
Thin-walled metals
When welding and cutting such workpieces, the torch should not be brought too close to the work area. In this case, the likelihood of through defects in the seam increases. The plasma arc pressure on the material is higher than a simple one. The welding current is maintained at 12-14 A. Sometimes lower values are sufficient.
Are there any disadvantages?
Many unanimously answer this question like this: “High price!” Of course, compared to argon-arc devices, the purchase of plasma devices requires large financial investments, but whether this fact should be considered a minus against the background of a number of increased capabilities is a moot point.
In fact, the disadvantages are rather high-frequency noise with ultrasound, the release of “metallic” vapors, optical radiation - infrared, ultraviolet - and harmful ionization of air. However, if personnel are properly equipped with work safety accessories and if the requirements for operating the equipment are observed, all these negative impacts can be avoided.
What are plasma devices?
The units differ in technical characteristics and scope of application. The main classification feature is the current strength of the plasma arc. This value, depending on the type of apparatus, lies in a wide range.
For microplasma welding
The current strength of such units does not exceed 25 A. Despite this, they are quite functional. Microplasma devices are used for joining thin-walled elements, precision and complex work, and cutting metal.
They are easy to use and maintain. The diameter of the burner nozzle is less than 3 mm. The devices operate on direct current. To produce plasma, acetylene mixtures and copper-plated electrodes are used.
Average by current strength
The device, in some respects, resembles a household inverter that produces a current of 50-150 A. However, the scope of application of a medium-current plasma device is not so wide; it is mainly used for cutting sheet metal.
We recommend reading: The nuances of using gas welding
The working gas is often air, but argon or helium can be used. The plasma torch and burner have a complex structure. Some devices are equipped with an additional liquid cooling system.
High current equipment
The device is capable of delivering more than 150 A. Devices of this type are practically not used in domestic conditions and on small construction sites. They are used in large manufacturing enterprises.
The installations have a complex design. The burners are equipped with modern cooling systems. When welding, infusible electrodes alloyed with thorium or beryllium are used.
welding equipment
It is important not to confuse plasma welding machines with metal cutting equipment.
The former are also known as plasma-arc devices, the latter - air-plasma. The latter are not intended for welding metal workpieces! Among the well-known manufacturers are:
- ;
- "Multiplaz";
- "Plasarium".
Read more about the products of these companies and the products of a number of foreign companies in the following sections.
Gorynych
Devices under the Gorynych brand use water or its mixture with alcohol to form plasma, while water vapor performs a protective function. When processing products, a thin anti-corrosion film of oxides is formed over the seam.
To weld metal using Gorynych, gas cylinder equipment or transformers are not required, so a tangible advantage of the devices is their mobility. To activate the equipment, a household network with a voltage of 220 V or an independent current generator is required.
The Gorynych mobile plasma welding machine is designed for metal with a thickness of 0.5 to 8 mm. The temperature of the arc formed by water and plasma reaches 6000 degrees. The process safety requirements are very strict. For example, a well-thought-out ventilation system is not necessary, since the air is not only not poisoned by harmful gases, but is also partially saturated with oxygen.
The cost of installations depends on the power and current. Thus, the multifunctional plasma device “Gorynych” can have three modifications:
- 8 A (suitable for small household work, soldering; costs 29,000 rubles);
- 10 A (wide range of possibilities, including metal cutting; 30,000 rubles);
- 12 A (powerful unit for processing sheets more than 1 cm thick; 33,000 rubles).
Consumables for operating the equipment are inexpensive. For example, a welder will need a welding nozzle (about 200 rubles) and a cathode (200 rubles). The cutting nozzle costs the same.
Multiplaz
The operating principle of the installation is similar to the Gorynych MPK - plasma is formed using an aqueous-alcohol solution.
Another similarity is compactness (the power supply together with the plasma torch weighs just over 6 kg);
here - the absence of strict requirements for room ventilation. The difference from the previously named brand is in power and, therefore, cost. You can learn about the first from the labeling. The popular model “Multiplaz 3500” (3.5 kW) will cost 90 thousand rubles.
Plazarium
The equipment uses an inverter circuit that guarantees arc stability independently from voltage surges. There are sensors that monitor the process temperature and prevent equipment failure. User advantages - compactness, lightness of equipment, availability of consumables.
The modification "Plasarium SP 3", whose power is 2.6 kW, costs about 40 thousand rubles.
Models from foreign manufacturers
Among the popular plasma cutting machines are:
- Fubag (a German concern representing the PLASMA 25, 30, 40, 65 T, 100 models; they are practical, high-performance, but most models are suitable for cutting metal);
- BlueWeld and Telwin (Italy; the line includes devices with contactless start; there are single-phase and three-phase devices, including for manual operation);
- Aurora (China; inexpensive devices with a long cable; there is a non-contact start; some of the devices, in addition to plasma, perform semi-automatic and manual welding, which indicates versatility).
An example of a microplasma welding machine is the SBI PMI 50 TL (including the Basic model). The water-alcohol solution is replaced with an argon-helium or argon-hydrogen mixture. The device can be programmed for a specific operating mode and can be combined with robotic manipulators. Basic is a high-power device that has the functions of the basic model.
When choosing high-quality equipment for plasma welding, pay attention to the models of the above-mentioned companies. They are distinguished by ease of operation, environmental friendliness, and economical energy consumption. A wide range of capabilities makes plasma welding machines a leading position among analogues, and the moderate cost of the models makes the buyer’s choice easier.
Which plasma welding device do you think is the best? Share your opinion in the comments.
Design and structure of the plasma apparatus
The process of plasma formation takes place in a plasmatron. The unit is a cone open on both sides, in the central part of which a refractory tungsten electrode with alloying additives is installed.
In the lower section of the main block there is a nozzle from which plasma is supplied under pressure. The substance that forms it is a mixture of argon and hydrogen. Gas is forced into the cone through the top hole. When heated, it expands and comes out of the plasmatron as a powerful jet. A nozzle is used to regulate the flow.
Scheme for obtaining a plasma jet
Plasma conversion is achieved by applying a strong electric field, created by the arc as it passes through the gas, to the forced gas entering through the torch nozzle.
Thus, to transform an electric arc into an electrified plasma jet, two conditions must be met:
- compress it;
- run a special gas through it to create plasma.
Compression is provided by a special plasma torch device. As a result, the thickness of the jet decreases and the pressure increases. At the same time, gas is supplied to the arc, which, under its influence, heats up and turns into plasma. Due to heating, the gas expands and increases in volume. As a result, it rushes out of the nozzle at high speed. Moreover, if a conventional electric discharge has a temperature of about 5000-7000°C, then the plasma can reach 30,000°C.
To form plasma, argon is used mainly with the addition of a small amount of helium. The electrode must also be protected with neutral argon. Tungsten products with the addition of thorium or yttrium are chosen as the electrode.
Plasma welding technology is characterized by high temperature and small arc diameter, which provides significant power.
Description of the most popular device for plasma welding “Gorynych”
This device consists of 2 separate modules - a plasma generator and a control unit. Water is used as a plasma generator.
The unit is compact in size and has low energy consumption. It is often used in domestic conditions.
The operating principle of the device is as follows:
- Low-temperature plasma is formed due to the arc that occurs between the contacts.
- The water is heated to extreme temperatures. Under pressure it turns into a directed plasma jet.
Any home master can learn to work with the Gorynych device. The device is easy to use; it comes with instructions with a detailed description of connection methods. The unit can be used for welding, cutting, soldering, and extinguishing fire.
Briefly about homemade devices
You can create a simple device for plasma welding with your own hands.
The design includes the following elements:
- Tungsten electrode cathode. It is secured with a screw or welded to a steel holder.
- Handle made of dielectric material – phenol plastic, fluoroplastic.
- Steel or brass cover.
- Gas supply fitting.
- Copper nozzle. The part must be replaceable, because it wears out quickly. The thread between the anode and the nozzle is treated with graphite.
- A distillation cube for supplying vapors of a water-alcohol mixture.
- Welding transformer. It must generate powerful electrical impulses. The secondary winding is made up of a small number of turns of thick copper cable.
An arc is formed after pressing the “Start” key. Initially, the spark ignites in a dry burner. Then the arc switches to current-driven combustion mode. After heating the anode, instead of air, the heated alcohol mixture becomes the working gas.