Welding work on a car body may be required in two cases - severe wear due to corrosion and damage after road traffic accidents (RTA).
Exposure to high temperatures destroys factory protection, deteriorates the properties of metals and causes accelerated corrosion in the welding zone. But the skillful use of modern technologies minimizes the severity of the consequences.
The inevitability of body rusting processes
Automakers are constantly improving the quality of their products. Cars are equipped with power plants and transmissions that can operate for a significant period without major repairs.
But there are also components that, even with the most modern technologies, can get damaged very quickly. These parts include the body.
The load-bearing part of the car is constantly exposed to negative environmental influences. Moisture, chemicals, and sudden temperature changes cause corrosion processes that, if no measures are taken, can cause significant damage to the body and make it practically unusable.
Why is corrosion dangerous?
At the initial stage, corrosion can easily be eliminated using special means, followed by painting the element.
But there is one rather serious problem - rust usually appears in hidden places (bottom, sills, wheel arches) and it is difficult to detect it in a timely manner.
On visible parts of the body, traces of corrosion appear when the processes of metal destruction have developed and it is no longer possible to eliminate them by chemical treatment.
In general, corrosion primarily damages the load-bearing elements that provide rigidity to the body.
If no measures are taken at all, then in a relatively short period of time the load-bearing part of the car will lose the ability to withstand loads, which will lead to distortions and “sinking” of the body.
In addition, the car will lose its presentability - a brown coating on visible elements and holes clearly do not make the car visually beautiful.
Why is a semi-automatic machine better?
The use of semi-automatic welding machines is the optimal solution for body repair. This device makes it possible to obtain a neat and durable weld. It is suitable for welding metal of different thicknesses. Also, using a semi-automatic machine, gas welding of non-ferrous metals is performed. A special feature of the device is the presence of a special coil. To use it, select the desired location and press the button: during the welding process, the feed wire and coil will unwind and direct the required amount of electrode into the working area.
In addition, the tool is easy to learn and quite effective. The choice of a semi-automatic machine for body work has its own characteristics and nuances.
Methods for solving the problem
There are three options for solving the problem. The first of them is to carry out anti-corrosion treatment of the body in a timely manner.
Another method to get rid of rust on a body is to replace the entire load-bearing part. But all this will cost a lot of money. After all, you will have to not only purchase a body, but then also solve problems with government agencies, since, after replacing the load-bearing part, we get, in fact, a new car. In general, this option is not suitable for everyone.
The third way to solve problems with emerging rust is to cut out the areas damaged by corrosion and then seal everything using a welding machine.
This option is considered quite common due to its comparative cheapness, and with the right approach, traces of body restoration are not noticeable. In this case, no problems with the organs will arise, since the car will have a “native” body.
A positive aspect of carrying out body restoration work using welding is the ability to perform it in a garage, since this does not require much equipment, and you can learn how to operate a welding machine in a couple of hours using scrap materials.
The main problem in welding a body with your own hands is that the thickness of the metal of different components of the load-bearing part is different and varies from 0.7 to 3 mm.
In addition, sometimes it is necessary to weld metal elements of different thicknesses together. If the welding machine is set up incorrectly, the metal can easily be burned through, that is, all work, in fact, will be in vain.
Read on topic : How to remove rust from a car body.
Welding wire
To weld semi-automatically, you need to choose a wire that will have a similar diameter. Semi-automatic welding is carried out together with copper wire. For the work, a special wire is used, sold in auto parts stores, and not a standard analogue.
If the wire used is not made of copper, it must have a copper coating. This element provides:
- uninterrupted electrical contact;
- replaces welding flux.
A material with a thickness of 0.3 to 3 millimeters is required. If the device is used without carbon dioxide, we prepare a wire that contains flux. This element provides protection and improves welding quality. But such material is more expensive than ordinary wire. When using standard wire, you will need to adjust the polarity.
When choosing a wire, you need to make sure that its diameter is suitable for the welding tip.
Which welding method is better to weld a car body?
To weld the body you can use:
- Carbon dioxide semi-automatic;
- Inverter.
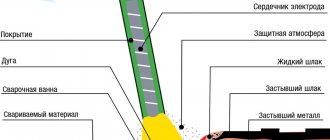
A carbon dioxide semi-automatic machine is considered the most suitable equipment for carrying out body repair work. This machine allows you to weld products up to 6 mm thick. It is used for welding ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
The electrode in a carbon dioxide semi-automatic machine is a wire fed to the burner from a reel.
The peculiarity of this equipment is that welding occurs in a protective gas environment, which ensures the displacement of air from the combustion zone, protecting the seam from oxidative processes.
Carbon dioxide is used to weld ferrous metals, and argon is used for non-ferrous metals.
When the device is configured correctly, the metal in the combustion zone melts, providing a reliable connection. And the compact burner allows you to get to almost any place.
The disadvantage, but it is rather conditional, is the stationary nature of the semi-automatic device. Moreover, the device itself is relatively small, but the gas cylinder is very massive. But usually all welding work is carried out in the garage, so this drawback is not significant.
The inverter is less suitable for body welding. This is a conventional electrode apparatus that performs welding using high-frequency currents.
Such equipment is compact and relatively easy to use. In addition, a gas protective atmosphere is not used here, which somewhat simplifies the work - we just take the device, connect it to the network and you can start welding.
But the inverter has much more disadvantages than the semi-automatic one.
- Firstly , each metal requires very precise adjustment of the supplied voltage.
- Secondly , welding thin products with an inverter is very difficult, since the slightest mistake leads to burning.
- Thirdly , after changing the electrode (due to its length), it is very difficult to control the welding process, and with a new electrode it is not always convenient to get to the required place.
In general, if an inverter is used, it is better to use it on the load-bearing elements of the body - side members and bottom, where the thickness of the metal is relatively large. And it is better that all work is performed by an experienced welder.
The best option for welding body parts is a carbon dioxide semiautomatic machine. They can weld any elements of the load-bearing part. But if there is no such device, then an inverter will do, but they need to do everything very carefully and carefully.
Weld seam
If there is a large amount of damage, body welding is usually performed in four ways:
- one-sided - used when the part needs to be melted along its entire length;
- double-sided - continuation of the previous action, which involves removing the root of the seam and welding on the other side;
- single-layer – used for connecting small elements in a single-pass manner;
- multilayer - used if parts of greater thickness are connected.
Body preparation
A very important stage in restoring the body is the preparatory work. First of all, it is necessary to correctly assess the condition of the body parts.
And to do this you will have to disassemble the car:
- Dismantle the interior, completely (remove the seats, upholstery, dashboard, you may have to dismantle the doors);
- Remove the wings;
- Remove everything from the trunk;
- Remove old traces of bodywork.
As already noted, the first spots of corrosion appear on the bottom, sills and wheel arches. These are the ones you need to pay attention to first.
As for the thresholds, very often the rust is located inside them, so to assess their condition you will have to cut off the boxes (if there is corrosion on them, then this will have to be done in any case).
The second important point in the preparatory work is determining the boundaries of areas that require replacement.
If, for example, there are holes in the bottom, then you need to cut out an area with fairly good indentations, since the metal near the hole is already “infected” with corrosion.
However, you should not cut out anything that has traces of rust on the surface. In many areas, corrosion is only superficial and to eliminate it, it is enough to treat it with chemicals followed by anti-corrosion treatment.
In general, only those elements that have already rotted or that corrosion has greatly changed the structure of the metal should be replaced (they will soon rot).
It is not difficult to identify such areas; just use a screwdriver to pick at the surface and assess their condition.
After cutting out all problem areas, we prepare replacement material.
If these are external elements, then you will have to purchase the required body elements (fenders, sill boxes, and the sills themselves) from the car market.
For the bottom, if the cut out parts are small, almost any metal of the required thickness will do, but it is still better to use body metal. In the case of overall parts, it is better to purchase a new bottom.
Nuances of the work
The next step is to adjust the body elements to size. To do this, you will have to take measurements, cut off excess, in some cases bend the edges, etc.
In general, you need to make sure that the new element fits as tightly as possible to the body.
You need to try to ensure that the maximum number of welding points overlap. Butt welding should only be used for external elements.
- Firstly, when overlap welding, very precise fitting of the elements is not required.
- Secondly, for a number of body elements the use of a continuous seam is not allowed. These, for example, are thresholds.
In the factory, their components are connected to each other by spot welding. In garage conditions, you can use stitch welding (a seam 1-2 cm long is made, then we retreat 4-5 cm and make the next one).
Also a good option for lap welding is some kind of spot welding. This method consists of making holes along the perimeter of the new part (in places where it is adjacent to the body part) (at a distance of 4-5 cm from each other). Welding is then carried out along these holes.
As for the bottom, a continuous seam can be used here, and double-sided welding is allowed.
That is, they attached a piece of metal, welded it around the perimeter from the interior side, and then walked along it from the outside.
In general, when carrying out welding work, you should be guided by the location and thickness of the metal.
Security features
Body welding is carried out in special non-flammable clothing. Additional protective equipment reduces the risk of harm to your hands and face. This is done using gloves and a protective mask. It is advisable that clothing cover the entire body. It is necessary to minimize the number of depressions, pockets, folds, and other areas where a drop of welding may fall.
If the procedure is performed on a metal floor, to increase safety during work, it is recommended to place a rubber mat or wear galoshes.
The welding device must be grounded. The ability to work is allowed only with devices with an automatic shutdown mode in case of an emergency.
The room must have good ventilation. When performing welding work, gases are released that can harm human health. You can use a special exhaust system. This condition will reduce the risk of poisoning to a minimum.
How to properly restore a body?
An important condition for successful welding of the body is the correct setup of the device.
Therefore, before starting work, you should check on available materials.
We simply take two pieces of metal of the appropriate thickness and try to weld them, and be sure to use the same method that will be used on the body (overlapping or end-to-end, with stitches or through holes). During the testing process, we adjust the device.
It is important to ensure that there is no burning, and that the metal melts well and is connected to each other.
When using an inverter, it is important to select the electrode thickness and welding current. As a rule, 30-40 Amperes of current are required per 1 mm of electrode. Therefore, a 2.5 mm electrode requires 75-100 Amperes. You also need to take into account the thickness of the metal, so the correct data is indicated in the table.
But this is provided that the network produces 220V. If the voltage in the network drops, selecting the current may become more difficult, so it is important to do test welding before the main work.
Also, you should not weld the part sequentially (attach it and start welding from edge to edge), since this may cause the element to “lead.”
You should do this: attach the part, grab it in several places, and only after that we go around the entire perimeter.
After welding the element, the welding points must be cleaned of flux. If it is an external element, you will have to grind them down to ensure a smooth surface.
If the welded element will cover something (for example, a threshold box), then the internal surfaces must be treated with corrosion inhibitors and then covered with anti-corrosion materials. The resulting seams should also be properly processed.
As for the external parts, the entire surface is puttied and primed to completely hide welding marks, after which the body parts are painted.
Setting up regulators
An example is the semi-automatic device Helvi Panther 132 . It has three regulators that affect the current parameter. The two toggle switches have only two positions: “1” and “2” on the first, “min” and “max” on the second. The third one smoothly regulates the wire feed. And the speed at which the wire is fed depends on the magnitude of the current. This means that the device independently regulates the current depending on the wire feed.
Semi-automatic welding
As an example, we can give the settings of this semi-automatic machine for different thicknesses of the metal being welded. The thin sheet was “cooked” well at the settings: “1”, “max”, and the smooth adjustment was at “7”. It is better to try thick sheets on the setting: “2”, “max”, “8”.
When working with a semi-automatic machine, there may be different welding results. Depending on the current strength, you can get the following results:
The result of welding with different currents
First case
The current is too low, so the metal does not spread over the surface, and the part does not warm up, which worsens the mating. It turns out that there is no “penetration”. You will need to increase the current.
Second case
The current is correctly adjusted, the metal spreads sufficiently and heating of the part being welded is noticeable. A small metal drop is visible on the back of the sheet.
Third case
The current is greater than the permissible value. The molten drop from the wire has sank too much. On the other side there is an obvious large drop of molten metal.
Fourth case
A significant excess of the permissible current to such an extent that through burns are formed. A significant reduction in current is required until a small drop appears without burning.