Welding electrodes are special metal rods used for welding. They come in several types, depending on the type of welding and metals. Electrodes must be used strictly for their intended purpose. They are divided into metal (consumable and non-consumable - tungsten, thoriated, etc.) and non-metallic (non-consumable - coal or graphite). Consumable electrodes can be coated (cast iron, steel, aluminum, bronze, copper) or uncoated. The holder for this equipment is usually selected separately; it is desirable to have the ability to fix electrodes of different diameters.
Main types of electrodes
This welding equipment is divided into main classes, depending on the type of metal used:
- For welding heat-resistant alloy steel;
- For high alloy steel;
- For structural steel (for arc welding);
- For metal surfacing;
- For non-ferrous metals;
- For cast iron;
- For thin metal (the thinnest are less than 2 mm in diameter).
Types of electrodes by type of coating
The letter designations indicate the type of electrode coating:
- A – acid coating, containing silicon, manganese, iron;
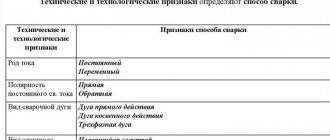
- B – main coating, which includes calcium fluoride and calcium carbonate. Suitable for welding with direct current of alternating polarity;
- C – cellulose coating with an organic base;
- R – rutile coating. Additionally contains organic substances and minerals.
Types of electrodes by welding position
Choosing the position of the current conductor is a serious aspect of the welding process. There are several valid position options:
- Any provisions;
- Any position other than vertical from top to bottom;
- Bottom (vertical from top to bottom and horizontal);
- Bottom position.
Types of electrodes for operation with direct current
This type of welding is the easiest, safest and most reliable, ensuring an even seam. In this case, special electrodes are used that are suitable specifically for conducting direct current:
- MR-3S. Has blue markings. It is used for welding carbon and low-alloy steel, provides a high-quality and even seam, and facilitates the process.
- OZS-4. Electrodes with red markings. Suitable for welding carbon and low-alloy steels, as well as oxidized surfaces.
- OZS-12. These are red electrodes intended for critical structures (made of low-carbon steel). Welding in all positions except vertical is acceptable.
- SSSI 13/45. Products with a basic coating for welding vessels under pressure, metals of great thickness, as well as for the process of welding possible defects. Suitable for low alloy and carbon steel.
- SSSI 13/55. For working with pressure vessels, building metal structures (from low-alloy and carbon steels).
Types of electrodes for welding on cast iron
Since cast iron is one of the most common materials, it is worth considering separately the types of electrodes used for welding products made from this material. It should be noted that direct current electrodes are used to melt cast iron.
- MNC-2. Allows welding in the lower, vertical and semi-ceiling positions with direct current of reverse polarity.
- OZCH-2. For malleable and gray cast iron in the lower and vertical position, with direct current of reverse polarity.
- MNC-4. For cast iron of any type in vertical and downward positions (direct current of reverse polarity).
- TsCh-4. Used only in the lower position for cold and hot welding. Allows the fusion of cast iron with another type of steel. At high voltage the current becomes alternating.
- OZCH-4. For working with any type of cast iron, in the upper and lower positions, exclusively with direct current of reverse polarity.
- OZZHN-1. Electrode for cold welding of ductile and gray cast iron in the lower and vertical position.
- OK 92.18. For welding when heated (with direct and alternating current).
Welding technique
Attention is also paid to the welding technique used. Modern welding equipment allows you to set the required parameters for working with thin metal of various types. Among the features of the work carried out, we note the following points:
- It is necessary to correctly draw the edges of the elements being connected.
- Often the joint is made by burning. This technology is suitable for experienced users.
- If possible, the plates are placed overlapping. In this case, the possibility of burnout is eliminated. It is recommended that the electrode be in contact with the lower product, thereby improving the quality of the connection.
There are several common welding methods. An example would be:
- At low current, the rod is moved strictly along the seam.
- When the indicator increases, processing is carried out with an intermittent arc.
- To reduce the likelihood of seam deformation, welding is carried out in a checkerboard pattern.
In some cases, a backing can be used, which also reduces the likelihood of burning through thin metal. Reducing the arc length reduces the likelihood of overheating of the treated area. The electrode should be held at an angle of 45 degrees.
Characteristics and selection criteria
One of the main parameters of welding electrodes is its coating, or rather its composition:
- Rutile coated conductors. This also includes conductors with mixed rutile-based coating. These are the most popular electrodes, characterized by ease of ignition. Used with alternating and direct current in any position.
- With basic coating. Typically used for DC welding. They provide a plastic seam, but are characterized by difficult ignition and increased sensitivity to humidity.
- With a sour coating. Like products with rutile coating, they are used for inverters, however, work in this case must be done in a well-ventilated area.
- For beginners, electrodes of the OZS-12 type are suitable, while UOSI are more related to professional work.
- Manual arc welding involves the use of a welding inverter. The components for this device must be dry and undamaged. They are selected according to the type of inverter, regarding the technical characteristics of this device.
- The weight of one electrode for each individual brand is different, depending on the materials used. The weight of electrodes in a pack according to the standard should be 3 kg, 5 kg and 8 kg for electrodes with a diameter of 2.5 mm, 3-4 mm, 4 mm, respectively.
Features of welding thin galvanized sheets
To weld galvanized steel, you will have to completely remove zinc from the edges being joined. To do this, you can use a sander or hand abrasives.
You can get rid of the galvanized layer by burning it out using a welding machine. But the welder needs to be especially careful. Zinc vapor is toxic to humans and can cause severe poisoning if ingested. You can only work in an open area or indoors, provided there is a powerful exhaust hood at the workplace.
Which brand of welding electrode should I choose?
Products from both foreign and Russian companies show high performance. The most common brands of welding electrodes have a large number of positive reviews among professional and novice welders. The most popular companies producing electrodes with basic and rutile coating:
- SSSI. The product UONI 13/55 has a basic coating, has an affordable price, and provides a reliable seam. Moreover, it is affordable and popular, so it can be easily purchased from any relevant store.
- Kobelco. Products from this company also have a base coating and require pre-calcination to remove excess moisture. Suitable for welding pipes and serious structures.
- ESAB-SVEL. The equipment of this company does not require serious calcination, since it is not highly sensitive to moisture. Work can be carried out at a minimum current, which allows you to work with thin-walled steel.
- Lincoln Electric. The electrodes from this company are inexpensive, have fast ignition, and form a high-strength seam.
- OZL-8. Electrodes for welding stainless steel, as well as metals containing chromium and nickel. They are distinguished by their high cost.
- Resanta MP-3. If this product becomes damp, prolonged calcination at medium temperature will be required, otherwise the quality of the seam will noticeably drop.
In addition to popular brands of electrodes, there is a variety of welding elements that have a narrow scope and are not used in everyday life.
In general, it is worth noting that the quality of the seam formed, the speed of the process, safety and comfort of work depend on the parameters and characteristics of the selected welding electrodes. Reliable equipment guarantees reliable work results, which is why it is necessary to select it carefully and responsibly.
Problems of welding thin-walled products
It is not recommended to carry out such work if you do not have the required skills. The most common problems are:
- Formation of a strong influx. The weld pool may blur and even collapse. Therefore, a lot of attention is paid to this point.
- Burning of thin material occurs with strong spot heating. As a rule, a similar problem arises when choosing a high current rating.
- The appearance of a low-quality roller. Controlling a short arc is quite difficult, as is the spread of molten material.
If the distance between the product and the rod is large, this can lead to the formation of a long arc. It is characterized by a higher exposure temperature in the melting zone.
In conclusion, we note that the main problems can be avoided by gaining experience, using a modern apparatus and a more suitable electrode. this is due to the fact that new inverters allow you to set optimal current values. In addition, high-quality electrodes form a stable arc even at low current. Therefore, you should not skimp on purchasing consumables, as otherwise it will be quite difficult to obtain a high-quality seam.
Flaws
The disadvantages include the following properties:
- The need to use additional fasteners so that the parts remain in place during the process and do not move;
- The equipment must have fine adjustment when working with low current parameters so that the mode can be accurately selected;
- Extremely precise adherence to the given modes is necessary so as not to spoil the parts;
- The number of defective seams here is statistically higher than when working with thick metal;
- It is necessary to take a responsible approach to choosing a protective coating for the electrode in order to increase safety during welding, which already depends on what grades of metal are used in this case;
- To work, you must have sufficient experience in this field.
What does the coating affect?
To obtain a high-quality seam, it is very important to choose the right electrode. The main role is played by the coating material, the types of which were discussed above. In order for a novice welder to understand the importance of choosing a coating, let’s consider its main functions and tasks:
- Arc stabilization. To increase the stability of the arc, substances with a low level of ionization are applied to the outer part of the products. This is necessary to saturate the arc with ions that stabilize the combustion process.
- Protection from atmospheric gases - when a welding arc is formed, the components of the surface coating during combustion create a protective cloud and form a slag layer, protecting the bath from exposure to oxygen. Slag reduces the cooling rate of the metal, which is necessary for the effective removal of gases and unnecessary impurities.
- Metal alloying - helps to improve the weld.
- Deoxidation - to remove oxygen from the seam, special compounds are used. These compounds are called deoxidizers, which react with oxygen to bind the metal.
- Bonding - to secure the surface layer to the metal rod, silicate glue is used, which helps stabilize the arc.
As you can see, a seemingly simple consumable for welding equipment called an electrode has a complex chemical composition, the quality of which determines the efficiency of welding work. In order for the metal connection to be of the highest quality and reliability, you need not only to learn how to operate welding machines, but also to choose electrodes for the work from proven and reliable suppliers.
Are there special rods for cutting metal?
Beginners are interested in how to cut metal with an inverter. Previously, this issue was relevant, but now in industry they use electrodes for cutting metal.
Masters of the old school still use ordinary elements for cutting, but rather out of habit. Special welding elements produce a reliable arc, quickly oxidize the metal and remove it from the cut.
Welding with an inverter goes quickly. They reach 3−6 mm in diameter.
Technological process
It is quite difficult to weld thin metal using ordinary manual electric arc welding. To eliminate continuous burns along the entire length of the welded ends, a certain technology is used:
- electrodes of small diameter are selected;
- the smallest welding current is set;
- In order for the welding arc to have a stable combustion, high-frequency currents are used. An oscillator is connected for this purpose.
A connection is selected in advance that completely eliminates burn-through. If the thickness of the metal sheet is thinner than 2 mm, the best electrode will be the diameter of which does not exceed 1.6 mm. It must have appropriate coverage. The value of the welding current is adjusted so that it is enough to melt the electrode. It usually ranges from 50-70 amperes. Using an oscillator, a normal arc burns. The device helps to quickly obtain an arc, it eliminates the occurrence of burns.
Return to contents
How foreign rods have proven themselves
Foreign manufacturers supply a large number of welding elements for inverter welding. European companies have proven themselves well.
Their products are suitable for any welding: for refractory, carbon metals, for welding pipelines, for working with non-ferrous metals.
Craftsmen who work to order or weld difficult elements choose foreign modifications. They are of higher quality than domestic ones because they undergo strict control.