Advantages of jet type EDM machines:
- Precision machining of any conductive materials
- Low processing cost
- Fast payback of equipment
- No need for additional equipment
- Processing of large workpieces
What is it used to make:
- Matrices
- Punches
- Stamps
- Injection molds
- Gears
- Impeller
- Keyway
- Tooth cutting
- Trims along the contour of the product
What should you pay attention to when choosing?
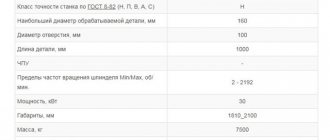
It’s no secret that accuracy indicators directly depend on the quality of the frame and ball screw; when choosing EDM equipment, special attention must be paid to the maximum load on the work table, the maximum height of the workpiece, the diameter of the ball screw and rail guides. The differences in the maximum load on the work table are explained by the use of a bed from a younger model of an electroerosive machine - this certainly reduces the cost of the machine, but entails the use of a smaller diameter ball screw and rail guides, which undoubtedly affects the durability of the equipment. For example: the maximum load on the working table of the Tosun DK7732 machine is 500 kg, and the load of the DK7725 machine is 300 kg, which corresponds to the standard indicators of Chinese manufacturers.
All of our equipment is used in our own production, so we are always ready to demonstrate the distinctive features, perform electrical discharge machining and measure the processing results.
Structure and types of equipment for EEE
A typical EDM machine includes:
- several electric motors operating autonomously from each other;
- electrode-tool supply unit;
- bath with working environment;
- table for placing the workpiece being processed;
- control scheme.
The equipment in question is classified according to the following criteria:
- According to technological purpose. It is possible to distinguish universal, specialized and special machines for EEE;
- Based on the principle of arrangement of the main components. It can be made horizontal and inclined, but a vertical layout is more often used;
- By type of table: fixed or coordinate;
- By type of bath – removable or rising;
- According to the degree of accuracy - equipment for work of ordinary precision and precision;
- Based on the principle of excitation and subsequent regulation of electrical discharge parameters.
The size range of types of electrical erosion equipment of domestic production is determined by the requirements of GOST 15954.
DIY electric spark machine
One of the main parts of an electric spark installation, which you can implement with your own hands, of course, subject to all safety rules, is given below. It should be noted that this is only one of many designs that can be used in machine design.
Approximate diagram of a spark discharge generator
The work table of the machine must be equipped with an oxide removal system (continuous supply of oil or kerosene). They reduce the likelihood of depositing an oxide film on the surface of the part and, as a result, stopping sparking. For breakdown, reliable electrical contact is required. As a basic option, you can use a bath filled with liquid.
The electrode is a brass or copper wire of the required diameter, which is fixed in a clamp. The clamp, in turn, is a part of the vertical rod of the crank mechanism, which is driven by an electric motor. The frequency of reciprocating movement of the electrode is selected depending on the characteristics of the material being processed.
All conductive parts and cables must be properly and reliably insulated, and the installation itself must be grounded. You can see how homemade homemade installations work in the video:
It should be noted that homemade machines will never equal the capabilities of industrial ones, for example the ARTA series. They may be suitable for the production of handicrafts or use as one of the types of hobbies, but they are not “up to par” for working in a workshop or metalwork shop. Not to mention that the complexity of the electrical circuit and the need for precise coordination of kinematics and capacitor discharge make them very difficult to adjust.
Methods for producing an electrical discharge in the working circuits of machine tools
Dimensional processing can be carried out by spark, pulse and arc discharges. In the first case, a spark discharge of low duty cycle is formed between the cathode and anode, but with precisely specified characteristics of the interelectrode gap. Such machines are compact, distinguished by high accuracy of operation and surface quality after electroerosion, ease of regulation by technological parameters, but at the same time they have low power, and, therefore, productivity. Areas of expedient use of such machines are precise cutting of difficult-to-cut materials (in particular, hard alloys), and production of parts with complex contours. They can also be used to remove broken tools, etc.
Diagram of a wire-cut electrical discharge machine
An increase in the energy of the electric discharge is achieved by introducing a pulse generator into the circuit, which increases the interval between adjacent discharges and at the same time increases the thermal power during a single electrical erosion event. As a result, work productivity increases, but accuracy decreases, and the surface of the machined part may have a fairly extended heat-affected zone, which is not always acceptable. Electric pulse machines are used where more significant metal removal per unit of time is required.
If it is necessary to ensure even higher metal removal (and not only to change the shape of the original workpiece, but also to strengthen it), electric arc machines are used. The productivity of such equipment increases several tens of times, since the arc, unlike other types of electrical discharge, burns continuously. To control the technological parameters of the arc discharge, it is compressed by the transverse flow of the dielectric medium, which is constantly and under high pressure pumped through the arc combustion zone by a pumping unit provided in the machine circuit. Electric arc machines can be used to produce large blanks for rolls, hot hammer dies, etc.
Electric spark machine diagram
Metal processing by the electric spark method is very common, so it is very difficult to consider all types of equipment and models of specific installations. They are all united by common structural elements:
- DC source;
- capacitor;
- vibrator;
- mode switch.
A design operating in an electric spark mode may differ in a number of characteristics that allow it to work with a particular material, but the general principles of constructing a working circuit are the same.
The battery of capacitors is coordinated with the mechanical movement of the electrode, the discharge occurs at the moment of maximum approach of the working surfaces. Relaxation pulse generators determine the maximum charge of the capacitor at the maximum amplitude of deviation from the approach point. After the spark discharge, the capacitor has time to charge fully.
Application of different types of electrical discharge machines
Among the electric spark type equipment, the MA4720 copying and piercing machine is considered one of the most accurate. It is designed to work with difficult-to-process workpieces of complex configuration, for example, for carbide die equipment, molds, and molds. The productivity of the machine does not exceed 70 mm3/min, but it is possible to achieve an accuracy of 0.03...0.04 mm, with a fairly low roughness of the final surface (not higher than Rz 0.32...0.4 μm in finishing processing modes). The work table is moved by a CNC system. The dimensions of the work table and the permissible range of values of the interelectrode gap between the anode and the cathode do not allow the production of products with overall dimensions of more than 120×180×75 mm on this machine.
An example of an electric pulse machine is the widespread model 4E723, also equipped with a CNC. Higher specific power values make it possible to achieve EDM productivity of up to 1200 m3/min, with a processing error in finishing modes within 0.25...0.1 mm. Higher accuracy is achieved with EDM of shaped surfaces. The machine is also used primarily in tool production, but the surface roughness increases noticeably - up to Ra 2.5 μm, so grinding will be required after processing in most cases. The machine can perform EDM of parts with overall dimensions of 620×380×380 mm, as well as cutting shaped grooves.
These types belong to universal electroerosive machines. An example of specialized equipment is the model 4531 electrical discharge machine, which produces profile cutting of complex contours using a non-profiled electrode. The 4531 machine uses a brass wire that is continuously rewound across the electrode gap, generating a discharge between the cathode and anode. With a relatively low productivity (no more than 16...18 mm3/min for steel; for hard alloy the productivity is even lower), the 4531 machine, in principle, allows for an error of ±0.01 mm, therefore the equipment in question is effective in the production of die cutting dies matrices of particularly complex configurations and templates The maximum dimensions of the cut contour are 100×60 mm.
Scope of application
Electroerosive machines are indispensable when working with materials that are difficult to machine - hard and heat-resistant alloys, stainless steel, titanium, tungsten. Due to the current strength, they can penetrate deeply and cut out highly complex contours.
At the same time, CNC electroerosive machines provide processing accuracy down to small fractions of microns, which becomes especially important when working with expensive alloys, where cutting losses are unacceptable. The machines are in demand in the aerospace, medical, aircraft, and jewelry industries.
Principles of optimal choice of technology and machine size for EDM
The initial data are the accuracy of the contour, the dimensions (depth) of the thermally modified zone, as well as the desired removal rate per unit time. For machines working with non-profiled electrodes, it is important to have devices for automatic threading of wire, and for pulse machines - generators that allow the use of bimetallic wire, which increases the productivity of EDM.
To improve the quality of the process and reduce erosive wear of the electrode-tool, it is better to use oil as a working medium (the most common is a mixture of industrial-20 oil with kerosene). In principle, for products with increased tolerances, it is possible to use water.
The technological capabilities of electroerosive machines are significantly expanded by the presence of additional devices (for example, for producing conical surfaces).
To remove metal from 20,000 mm3/min and above, only electric arc machines should be used. The smallest operating error of such equipment is achieved with reverse polarity when using graphite electrodes. At the same time, the relatively high surface roughness - not lower than Rz 0.8...1.6 μm - forces, after EDM with an arc discharge, to provide for finishing grinding of the resulting contour. The pumping pressure of the working medium must be at least 50...60 kPa.
Operating principle of an electric spark machine
The processing of metals by the electric spark method is based on the property of electric current to transfer a substance during breakdown. At high voltage and direct current (1-60 A), the anode (positively charged electrode) heats up to a high temperature in the range of 10-15 thousand degrees Celsius, melts, ionizes and rushes to the cathode. There, due to electrical interactions, it settles.
To prevent a full-fledged electric arc from occurring during operation, the electrodes are brought closer together only for short moments, lasting a fraction of a second. During this time, a spark occurs, destroying the anode and growing the cathode. The treated area is heated and exposed to electric current for milliseconds, while the neighboring areas and the underlying layer do not have time to warm up and their structure is not disturbed. The problem of borderline states does not arise in principle.
If cutting or drilling is required, the working tool serves as the cathode, and the workpiece serves as the anode. When building up, strengthening the surface or restoring the shape of a part, they change places. For these types of processing, special machines have been created, each of which performs its own operations.
The tools used in EDM installations are brass or copper-graphite electrodes, which conduct current well and are inexpensive to manufacture. With their help you can cut and drill the hardest alloys. To prevent the cathode metal from settling on the electrode and increasing its size, the process occurs in a liquid medium - the liquid cools the melt droplets, and it cannot settle on the electrode, even if it reaches it. The viscosity of the liquid determines the speed of movement of material particles, and they cannot keep up with the current. The metal settles in the bath as a sediment and does not interfere with the further passage of current.
When increasing the surface of parts or strengthening, metal is transferred from the anode to the cathode. In this case, a positive electrode is fixed to the vibration installation, serving as a metal donor, and the part is connected to the negative pole. No water or oil is used in this process, everything happens in the air.
Machine feed drives
Only recently has the production of electric spark machines begun, namely with completely new linear motors. In this release, work was done and corrected on speed control and acceleration, uniform movement, reverse, ease of maintenance, etc.
The linear motor in this release of machine tools has a motor containing only a few elements: an electromagnetic stator and a flat rotor, which contain only a gap of air between them. There is also another important element and this is an optical measuring ruler with high resolution (0.1 microns). Without this measuring device, the control system will not be able to recognize the coordinates.
Machine spindle units
The spindle is made in the form of a massive rotor, with a mounting collet located inside it, and at the upper point of the cavity formed by two counter-facing conical surfaces, a working fluid intake (catcher) is installed. This spindle design improves working conditions on the machine.
Fig. 1 – Spindle of an electric spark machine
In the sliding bearing 1 there is a spindle 3 rotating through a V-belt drive 2, made in the form of a rotor, in the concentric bore of which a collet 4 is located on a tense or tight fit, for fastening along the outer surface of the workpiece 5. The internal cavity of the rotor is formed by two counter-facing conical surfaces 6 and 7, The working fluid supplied from the hydraulic pump through tube 8 into the hole of the workpiece, under the influence of the centrifugal forces of the rotating spindle, is collected at the periphery of the internal cavity (pocket) of the rotor, from where through the intake 9 through tube 10 it enters the filter element of the hydraulic pump.