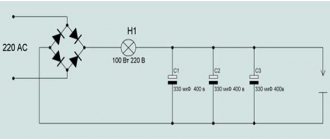
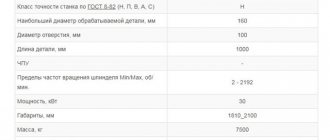
Many beginning furniture makers are faced with the need to create facades based on MDF boards. Moreover, the requirements for products in a highly competitive environment are quite high. Products must be of high quality, meet modern standards and trends, and in addition, in order to have a stable flow of customers, the entrepreneur must fulfill their orders as quickly as possible. It is possible to get the job done efficiently and quickly only if you use technologically advanced tools for the job. In this case, these are CNC machines. We will explain below what they are and how they work.
Numerical control - what we're talking about
In a highly competitive environment, manufacturers are required to supply high-quality products to the market in large volumes. It is difficult to do them manually, when the human factor affects the speed and productivity of labor, the possibility of errors and irregularities, and in some cases does not allow the plan to be realized. But with the use of computer technology, the process is much more productive. In particular, the rate of production increases, as well as increased accuracy. Classic equipment in workshops is controlled by a person. He is responsible for directing the movements of the main parts of the machine. But CNC machines are equipped with a computerized system that itself regulates all movements and also allows for the smallest adjustments. The control command gives numeric command codes to all elements. Programming takes place using software; engineers, furniture designers, and planners work with it. One programming language ensures precise communication of requirements. Since the task remains in the system’s memory, you can select one of the command sets at any time to switch from producing one part to another. Let's explain the term: CNC machines are “smart” factory equipment with numerical control. They are gradually replacing classical units in large production workshops, but due to their high cost and difficulties in handling (knowledge and basics of programming and design in software such as AutoCAD are required), they are not common in private use.
What types of program control systems are there for CNC machines?
CNC devices differ from each other by a program control system. Devices are produced with two types of control - positional and contour.
Positional control differs from the second one in that the movement of the working elements is carried out at a given point, while the direction of movement is not specified. As a result, the CNC device system will automatically search for a short path between points.
For devices with CNC contour control, working elements move along a certain path and at a certain speed. Thus, the desired characteristics of the processed contour are achieved.
It is impossible to say which of these systems is better. After all, to process a complex shaped surface, you need to use a CNC contour system, and to drill or ream it, a product with position control is ideal.
There is also adaptive software control. It allows you to automatically adapt the product to the changing conditions of the technological processing system.
Operating principle and brief description of the system
This is a linear sequence of actions that consists of the following intermediate actions:
- the person sets the basic parameters, designs the manufactured model in a graphic editor, and is responsible for the correctness of the drawing and characteristics of the product;
- a computer program processes graphics and text data, calculations, systematizes them, and translates them into a machine-readable format;
- the control system stores mathematical formulas and numerical values, develops a sequence of actions and issues commands to all elements of equipment;
- working tools perform mechanical actions according to a given algorithm, guaranteeing accuracy and speed of movements.
The result is a completed goal, towards which the artificial intelligence worked together with a person. An operator constantly monitors the equipment; he can make adjustments to the operation of the machine, pause it, see and correct problems, and also re-equip it for new tasks. Basically, the program sets the following parameters:
- engine power;
- speed of production of a function;
- moments of acceleration and deceleration to obtain the desired qualities of the workpiece (very typical for manipulations with metal);
- rotation of cylindrical and round elements;
- the direction of movement is especially important in cases of artistic cutting - each bend is determined by an exact mathematical formula.
Design and device of a CNC machine
Classic elements of the unit (they may vary slightly depending on the specifics of the production process):
- bed, that is, a strong base in the form of a table or vertical installation for sawing;
- feed box - it is responsible for all rotations, straight-line movement and bends, how many possibilities the whole device has, generates speed and direction;
- headstock and tailstock, one of which is controlled by a spindle, that is, changes its location (can be installed both mechanically and mechanically);
- calipers - are responsible for fastening and changing tools, they receive movement commands from the feed box, and are responsible for the strength of the element being processed;
- rod mechanisms - tools that perform the actions themselves, that is, various drills, knives, reamers.
In one of the headstocks there is a system with speed switching, this will allow you to rotate the workpiece with the required acceleration. The second is necessary only for strong fixation and is associated with instrumentation. The operating principle of CNC machines is automated control of this entire structure. The commands are sent directly to the feed box, from where mechanical forces already originate, affecting all other parts.
Characteristic
The peculiarity of working on such equipment is that all actions are carried out with precision and minimal human influence. This is due to factors:
- Basically, CNC equipment is placed vertically, because this way it takes up less space, chips (metal, wood, plastic) are easier to remove from the working surface, there is less risk of clogging, and it is also easier to manipulate large items at an angle that are difficult to immerse on a horizontal surface. table top.
- Load-bearing structural parts are made of very strong substances, metal alloys, which are additionally reinforced with stiffeners. This need arises due to the possibility of long-term continuous operation with heavy workpieces.
- The lathe type of CNC machine is usually equipped with an automatic interchangeable magazine with cutters and tips, which themselves change as they wear out or when the desired tool is changed.
Classification of modern CNC control systems for machine tools
The international classification provides for the following classification of CNC machines:
- NC (Numerical Control). The peculiarities of this system are the use of punched paper or magnetic tape as a software carrier, which makes it impossible to make changes to the program, since all operating algorithms are implemented in hardware.
- SNC (Stored Numerical Control). This system retains the functions of the NC class, but has a larger memory size, which allows the program to be stored in an electronic device.
- CNC (Computer Numeral Control). The basis of this class is a Microcomputer, which is programmed to perform CNC work. Its peculiarity is the ability to change and adjust at the time of operation both the CP for processing the part and the operating programs of the system itself in order to take into account the features of a particular machine as much as possible.
- DNC (Direct Numeral Control). Controls devices within the GPS and automated parts. Systems of this class are controlled from a top-level computer.
- HNC (Handled Numerical Control). An operating system that allows you to enter UE at the workplace from the remote control.
- PCNC (Personal Computer Numerical Control). This is a symbiosis of a PC and CNC, which has great capabilities and has an open architecture.
Numerical Control Basics
The entire system is divided into three subsystems:
- Control is the center, it is from here that commands are given, the programming language is deciphered, and contact between the operator and the installation occurs here. The processor is located inside the rack, and outside are the screen and buttons. Adjustment is possible using the user interface. There are closed and open systems, the former have a narrow set of functions, adjustments cannot be made to them, often only special programs can provide a new type of work. The latter are easier to control and are tested for compatibility with commands and computer software.
- Drives - mechanics and electronics are concentrated here, which drives all other parts. The engine provides energy to the lead screws, which trigger the processes of rotation of the workpiece, movement of the cutters, etc. To be precise, the device contains several electric motors at once, each of the ready-made ones is responsible for one unit.
- Feedback. This is a series of sensors that collect information about the position and speed of movement of the component parts and transmit this information in the form of mathematical formulas to the control unit for processing the entire cycle and adjustments.
Degree of automation
The following key parameters are distinguished in the control systems of CNC machines:
- Type of drive. The motor can be stepper, stepped or adjustable.
- Control method: continuous, positional, rectangular, mixed.
- How the software is loaded: via flash media, on disk, using magnetic or punched tape.
- How many coordinates can be controlled simultaneously and what is the range of permissible error when entering them.
The number that appears in the machine article after the letter F characterizes the degree of automation of the device:
- 1 — data is typed on the keyboard, a digital display is provided.
- 2 - for a milling or lathe this means a rectangular control method, for a drilling and boring machine - a positional one.
- 3—contour or continuous control. This method is convenient for processing complex parts.
- 4—multioperative surgery. It combines the above functions.
If instead of a number there is a letter “C”, this means “cyclic type”. The algorithm of such machines is cheap and simple, but this is enough to produce series of workpieces of the same type.
Features of numerically controlled machines
The first unique characteristic is the high importance of computer-aided design. At this level, the main activity of the engineer takes place, then he can only check the correct execution of commands and transfer all subsequent activities to adjusters and operation specialists. Digitization of the graphic model into a programming language supported by the CNC system occurs automatically. The two main actions of specialists are adjustment (readjustment) of equipment and supervision of the operation of the machine.
Advantages of CNC systems
CNC systems are full cycle technology. It is extremely reliable, has extensive functionality, can be configured flexibly, and is designed for long-term intensive use. Production costs and defect rates are minimized.
With the help of such devices, it is possible to perform extremely precise and complex processing, which was previously beyond the capabilities of either previous generations of machines or manual workers. The productivity of a CNC machine is 5 times higher than that of a non-CNC machine. Even an operator without specialized training as a turner or miller can set up and launch the required circuit.
- August 24, 2020
- 2225
Areas of application
In fact, you can do most of the operations that can be done with classic manually operated units. You can process:
- wood, solid wood or blocks, plywood, chipboard and other types of compressed shavings;
- metal structures - from the smallest bearings to large sheets and massive automotive parts;
- stones (granite, marble) and other naturally formed rocks;
- plastic and other synthetic materials of varying hardness.
For each type of product presented, it is necessary to re-equip. The main differences are how the workpiece will be secured and what cutters and tools the mechanism will be equipped with. The program gives many commands, including:
- cutting, sawing, cutting off the top layer or end side;
- milling (a cylindrical rotating element undergoes completely symmetrical processing);
- making holes and cavities;
- engraving;
- carving and much more.
Since a CNC machine works on various materials, it is used in various industrial areas - from sawmills to jewelry and mechanical engineering.
Purpose
The technological capabilities of the devices make it possible to determine which model is best to use to perform a particular task. This factor allows us to divide the machines into six groups:
- turning;
- drilling and boring;
- milling;
- grinding;
- electrophysical;
- multi-purpose.
Lathes are designed for processing external and internal surfaces. With their help, you can also cut threads, both from the outside of the workpiece and in its inside.
Milling machines process flat and spatial body parts. In addition to standard milling, they can be used to: drill, bore, and cut threads. Drilling and boring units have similar capabilities, but their main task is focused on processing holes. Multipurpose devices allow you to perform almost the entire range of processing operations, but are expensive.
The electrophysical group includes three types of machines:
- electroerosive;
- electrochemical;
- laser
These types of machines allow complex processing. They are used when it is almost impossible to process the workpiece in any other way. The main working tool of the devices is a wire electrode. For its manufacture the following materials are used: brass, copper, molybdenum, tungsten. The presence of anti-corrosion additives ensures higher quality production of products.
Tools on machines require periodic change and adjustment. In this regard, another type of classification is distinguished - according to the method of changing the processing mechanism. According to this type of classification, there are three ways of changing:
- manual change and manual fastening;
- manual change and mechanical fastening;
- automatic change.
Devices with automatic tool changing do not require operator intervention during operation. They belong to the class of modern expensive devices and are compatible with various CNC systems.
Advantages
There are many advantages, among them:
- high speed;
- increased productivity;
- long wear of parts;
- no risk of exposure to human factors;
- reduced vibration and noise during production;
- the ability to cut products of non-linear configuration;
- ability to retool and work with various materials;
- simplified task for employees.
With a large number of orders, the need for constant, long hours of equipment operation, as well as when implementing design solutions, purchasing a CNC machine is economically profitable. But for small-scale production, costs often exceed profits.
Some restrictions
If operations take place on old equipment, then many possibilities are not included in their code, for example, movement can only occur translational or rotational, but not figured. This is due to the limited coordinate axes. The older and more budget-friendly the model, the slower its speed of processing information, issuing commands, and at the same time the slower the completion of the cycle. It is better to purchase modern units if you do not want poor functionality. Also, not all engineers will be able to handle them, but only specially trained people.
Common terms used to describe CNC machines
In machine tool equipment there are words that denote narrow concepts. Let's look at them:
- two-axis project - movement can occur only in two planes, without affecting the vertical;
- 2.5-axis - the Z axis (up - down) is present, movement along it is possible, but not simultaneously with the other two;
- 3-axis – all measurements at one time;
- 4-axis - the ability to rotate is added to the above.
In the article we explained what CNC machines are and what the abbreviation stands for. Be careful when working with this equipment. We invite you to familiarize yourself with our range of band saw products. for 15 years on the Russian market. During this time, we covered almost all cities of the country.