TIG welding is a universal technology for joining metals. TIG machines have great potential and allow you to weld different metals, as well as their alloys. This creates a high-quality and aesthetic seam. The features of the equipment are described in detail in the article.
- Marking in Latin letters
- Is argon harmful to a welder?
- The TIG inverter is equipped with a large number of settings
The joining of metals using high temperatures has been invented by mankind for a long time. The methods were constantly improved, and with the advent and development of metallurgy, they reached a qualitatively new level. Welding methods were improved as the requirements for the strength and quality of metal joints increased.
Currently, there is a large variety of equipment for welding metals. One of the most popular is TIG welding. Any welder, even an inexperienced beginner, must have a clear understanding of the operating principles of such equipment and know the methods of working with it.
What is TIG welding?
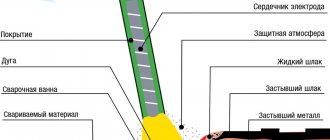
It will be easier to understand the features of the equipment, its advantages and disadvantages if you first familiarize yourself with the operating principles and technological features. TIG welding is a technology for joining metal workpieces using special equipment using a non-consumable electrode in a protective environment. The arc is initiated between the work surface and the tungsten rod. Before starting work, it is sharpened. This is necessary to maintain a stable welding arc and obtain a smooth joint.
A tungsten electrode is fixed in the center of the nozzle. Along the edges of the burner there are technological holes through which inert gas is supplied to the arc combustion zone. The most commonly used is argon. It prevents the formation of an oxide film and promotes high-quality edge joining. Filler wire is used to fill the bath with melt. In composition, it should repeat or be close to the metals being welded.
The history of TIG welding
Joining metals by welding has been used by humanity for many decades. The first developments in joining metal workpieces under the influence of high temperatures appeared at the beginning of the twentieth century. The first steps in this direction were taken by the American engineer Charles L. Coffin. Initially the equipment was simple. It could not be used in industry or for joining alloys.
Non-consumable electrode and protective environment for welding began to be used in the mid-forties of the 20th century. The technology made it possible to combine new materials - aluminum, nickel and magnesium. The method immediately became popular in aircraft production, and later in rocket science. Over time, technology has found its application in almost all sectors of industrial production.
Advantages and disadvantages
Any technological process has both advantages and disadvantages. The most important advantages of TIG technology:
- When welding, shielding gas is used, which makes it possible to form a high-quality and beautiful weld. There are no cracks, pores or voids in the melt. Argon prevents the formation of an oxide film on the surface of the molten metal, which would necessarily form as a result of the interaction of hot metal and oxygen.
- It was not possible to completely eliminate internal stress, but it is so insignificant that it does not provoke deformation of the metal.
- During operation, the metal melt does not splash, the formation of sparks is minimal.
- After completion of welding work, no additional processing of the welded workpieces is required.
- Most metals and alloys can be joined using TIG welding.
- The equipment is characterized by ease of use. A few lessons are enough to learn how to independently form high-quality and aesthetic seams.
Along with the advantages, there are also disadvantages:
- If welding work is carried out in an open area, then it is necessary to protect the workplace from the wind. Otherwise, inert gas will be blown out of the working area, and the quality of the connection will be greatly affected.
- The surfaces to be joined require careful preliminary preparation.
- The burner cannot be held at an acute angle relative to the working surface due to complications in the working process.
- The arc should be moved evenly. If you hold it in any place, a mark will form that will have to be cleaned.
Features of the package
It is quite simple: you need a device to connect the mass and the burner - durable hoses, a reducer that provides regulation of the shielding gas pressure and is installed on a gas cylinder. There are two types of burners used:
- No. 1 - metals with a thickness of no more than 3 mm.
- No. 2 - for thicker structures.
The current value in the first option is not so large, so the body quickly cools down naturally; the second option uses water cooling: a mixture of alcohol-ethanol and distilled water circulates from the device to the burner, cooling the hose and body, and also protecting them from hypothermia in sub-zero weather .
Proper use of the inverter
When doing argon welding from an inverter with your own hands, it is useful for beginners to learn some nuances: first set the machine to the required amperage, connect the hoses . What matters is the type of current being connected, after which you need to adjust the gas supply, checking the table below.
| Gas consumption, l/min | Metals |
| 15—20 | aluminum |
| 10—12 | copper |
| 6—8 | low alloy steel |
| 12—14 | magnesium alloys |
| 10—12 | Nickel alloys |
The arc can now be activated and welding can begin, adding filler wire to improve weld quality.
The welder holds the torch at a certain angle, which allows him to visually correctly perform the metal connection.
We make the device at home
A simple way is to use a regular MMA inverter with parameters suitable for welding, but you need to modify it and reconfigure it . As a result, you get an inverter unit that allows you to weld metal with any type of current connected. You will need a set of hoses to connect a factory-made burner, an oscillator and a current delay unit.
The second option involves making all the components of the circuit yourself - this reduces financial costs, but the performer requires knowledge and high skills in assembly, manufacturing complex circuit boards and parts, as well as a lot of free time.
Application
TIG technology is universal and allows you to connect various metals, as well as their alloys. This determines its widespread use. The main areas of use of the method:
- automotive industry;
- production of parts for various industries;
- astronautics;
- shipbuilding;
- aviation;
- production of medical instruments;
- manufacturing of power tools;
- construction and many others.
TIG devices are in demand both in the private sector and small businesses. They are especially often used in car repairs, in particular, for restoring car bodies or repairing radiators.
Purpose of technology
Since TIG welding allows you to join workpieces not only from steel and copper, but also from other metals, it is used in the following industries:
- automotive industry, production of industrial equipment components;
- shipbuilding and aircraft manufacturing;
- space industry;
- manufacturing of medical equipment;
- production of electrical tools.
Crucible welding is often used in domestic conditions.
Using a device with tungsten electrodes, you can weld car body parts, heating radiators, and metal water pipes.
Operating modes
The installation operates from a unipolar or alternating power source. Changing modes allows you to choose the best option for a specific type of alloy or metal.
D.C
An electrode is connected to the negative terminal, and the plus goes to the working surface. Connecting to a DC power supply provides certain advantages:
- The efficiency of using welding equipment increases.
- The part can be heated to a greater depth. As a result, the connection can be very narrow, but strong due to the large depth of welding of the parts.
- The speed of the welding process increases noticeably.
In direct current mode, it is easiest to weld alloy and stainless steel workpieces.
Alternating current
The minus and plus change in random order during operation. When connected in reverse polarity mode, the surface of the workpiece is effectively cleaned of the oxide film.
Cooking technology and TIG parameters
To connect metal parts using the argon arc method, perform the following steps:
- Clean the edges of the workpieces from dirt and degrease. Even if the parts look clean, you should not skip this step.
- Set the current strength. The quality of the welded joint depends on this parameter. There are special tables that help you choose the right current strength.
- Set the polarity. When working with direct current, choose the direct option. Reverse polarity is used when welding with alternating electricity.
- Sharpen and polish the end of the electrode. When connecting thin metal products, special rods are chosen. They are brought to the point of spiciness. When connecting thick elements, the sharpening angle is changed.
- To initiate an electric arc, a rod is passed along a metal surface. You can activate the TIG Lift option to speed up this process. Sometimes the inverter is switched to non-contact ignition mode. The latter method is available to users of expensive equipment, for whom it is preferable.
Equipment
In order to carry out welding work using a non-consumable electrode in a protective environment, it is enough to have an ordinary inexpensive inverter with a burner designed to supply gas. However, there is special equipment on the market:
- TIG inverter. It differs from the usual one in that it has a built-in unit that generates direct or alternating current depending on the operating mode. Thus, the functionality of the device increases significantly. You can work with ferrous metals, aluminum alloys and other materials.
- Rectifiers. The operating principle is based on the conversion of alternating current to direct current. Belongs to the category of professional equipment.
The choice of installation and consumables directly depends on what materials need to be worked with.
Assembling the welding machine
After purchasing a welding machine, it is necessary to correctly install all components and components. Sequence of work:
- The oscillator is connected to the inverter.
- Attach the ground wire to the positive terminal.
- The negative line is connected to the line with the holder.
- The burner is connected to a hose for supplying inert gas.
- The reducer is screwed onto the argon cylinder.
- The gas supply hose is fixed on the reducer.
At the final stage of preparation, the inverter is connected to a power supply network with a power supply of 220 volts. The oscillator is connected to a 6 volt current source.
Safety regulations
When welding, we must not forget about safety rules. It is necessary to use protective equipment for the welder: a mask or shield, gloves or leggings, special clothing and shoes.
All masks can be divided into active and passive. The sight glass of passive masks is permanently darkened. In active ones, darkening occurs only as a reaction to a light flash from the arc. The advantage of this option is that while the welding process is stopped, the glass becomes transparent and the welder can clearly see the object. There is no need to lift the glass, which is quite convenient.
Main types of welding gaiters:
- Canvas . They are not in demand because they do not perform well the main function of protecting hands from high temperatures and sparks. They easily burn when exposed to sparks.
- Split fibers . Made from specially treated leather from pigs or cows. Resistant to flying sparks. Durable, elastic, hygienic. Does not restrict hand movements. If there is a cotton layer inside, it keeps your hands warm.
- Felt . Convenient for welding work.
There are combined models that use different types of materials. Welding gaiters come in length up to the elbow and cover only the hand. The possibility of tightening the edge of the glove provides additional safety.
A welder's suit must be made of high quality materials. It must be resistant to splashes of molten metal. The requirements for a welder's suit are specified in GOST 12.4.250. The main parts of the suit are the jacket and trousers. The material from which they are made must have great heat resistance. According to the regulatory material, the jacket must cover the trousers by more than 20 cm. The fasteners are closed with flaps. The maximum distance between them on the jacket is 15 cm.
Safety regulations include electrical safety. The argon cylinder must be located at a distance of at least 5 meters from possible sources of fire. The cylinder must be placed vertically and secured to prevent it from falling. Before work, it is necessary to check the condition of the hoses.
Welding technique
Before starting any welding process, it is necessary to prepare the equipment. To set up the device, a specialist needs to perform several manipulations:
- Tungsten electrodes require preliminary preparation. The end of the working rod is sharpened with a needle file.
- After preparation, the non-consumable electrode is installed in the burner. It is held in place by a collet clamp.
- The supply of inert gas is opened - the valve on the reducer of the argon cylinder is unscrewed. It is necessary to immediately establish a sufficient volume of gas supply. The optimal flow rate is 13 liters per minute.
- The mass is connected to the working surface or directly to the table on which the workpieces are welded.
- The oscillator is turned on, and the burner is brought to the surface of the workpiece.
- Next, press the power button, which causes a spark to appear. At the same time, the shielding gas supply opens.
The work surface electrode should be kept approximately 3mm away from the work surface. If the distance is increased, the width of the seam will increase, and the depth of welding, on the contrary, will decrease. The edge of the electrode can be guided in different ways. When working with thin sheets, it is necessary to give preference to oscillatory movements from left to right to avoid burning through the walls. When forming a root weld, the electrode is held evenly. When connecting corner joints, the electrode is held at a position of 45 degrees relative to the main working surface.
Electrodes and their characteristics
When TIG welding, rods are used consisting of up to 99% durable tungsten , various additives help improve the seam joint. For example, WC-20 contain cerium oxides, are operated at low DC values, the arc is easily activated, such electrodes are used for welding small parts.
WL-20, due to lanthanum oxide, does not heat up as much during operation, so its service life is the longest. Electrodes of the WZ-8 brand containing zirconium oxide, work only when connected to alternating current, and are characterized by arc stability. And rods marked WY-20 are resistant to high currents due to the presence of yttrium oxide, and are used for welding particularly important structures.
Types of sharpening
The quality of the seam depends on the form of processing: direct current - the electrodes are sharpened into a cone with a flat area on the contact part, alternating current - the end is rounded. Periodically, the rod is polished to remove minor damage and sagging. If the length of the cone is short, then the width of the seam is similar; for optimal welding of the metal, use a sharpening length equal to two diameters of the electrode.
TIG welding markings
Marking in Latin letters
The name of welding differs in different countries. Therefore, it is important to know the markings, as well as their meanings, so as not to make a mistake with the choice of equipment. For example, in all English-speaking countries, argon arc welding inverters are marked with the abbreviation “TIG”. It stands for “Tungsten Inert Gas”, which translates as “welding with a tungsten electrode in a gas environment”. This marking is most often found in Europe and Asia.
In German, this type of metal welding is called “Wolfram Inert Gas”. Therefore, the equipment is marked with the appropriate designations - “WIG”. In the USA, the abbreviation GTAW is used for this - Gas Tungsten Arc Welding.
Marking on the territory of the Russian Federation
Argon welding using non-consumable electrodes and shielding gases is designated IN and INp. The first abbreviation is used in cases where work is performed with a non-consumable electrode in a protective environment. In cases where filler materials are used, the letter “p” is additionally indicated.
“Argon-arc” or “argon-arc” welding: which is correct?
The spelling without a hyphen is considered correct. According to the provisions of GOST, there is only the concept of argon arc welding. Using a hyphen inside a phrase is considered erroneous.
Argon and welding
Being heavier than air, argon reliably covers the welding zone, preventing active gases from affecting the chemical properties of the weld. This property makes it indispensable for welding active metals, aluminum and copper. As a protective medium, it shows excellent results when welding stainless steel and heat-resistant alloys. For welding ferrous metals, argon is used in mixtures with helium, oxygen or carbon dioxide.
When using argon, you can raise the temperature of the welding arc. This increases the penetration depth of the weld and allows thicker sheets to be welded in one pass. When working with welding machines for argon-arc welding, the protective properties of this gas are manifested not only in protecting the seam, but also protect the material of the non-consumable electrode from oxidation.
Argon does not harm the environment and is not hazardous to human health. The only thing you should be wary of is its ability to accumulate in large quantities. Being heavier than air, argon accumulates in the lower part of the room, displaces air and can cause suffocation to the welder. Good ventilation is the key to preventing such a situation.
GOST 10157 specifies the conditions for the supply of gaseous and liquid argon. Transportation and storage of argon gas is carried out in cylinders under a pressure of 15 MPa in accordance with GOST 949.
Myths about TIG welding
Welding processes in an argon-arc environment have given rise to a number of rumors, some of which are far from reality. It must be borne in mind that any welding process is a harmful activity for people. Especially if you have to work with inert gases. Therefore, safety requirements provide for procedures designed to protect the specialist. If you do not follow them, there is a high probability of causing damage to the welder’s health.
Is argon harmful to a welder?
If you take a chemistry course, it is easy to find out that argon is a common gas in the atmosphere and ranks third in quantity in the atmosphere after nitrogen and oxygen. It is odorless and tasteless, making it difficult to diagnose. The gas is non-toxic and not explosive.
By weight, argon is 1.4 times heavier than atmospheric air, so it easily displaces oxygen from the welding zone. However, this gas cannot be completely called safe. If argon enters the respiratory tract in large quantities, it can cause dizziness and even loss of consciousness.
Safety rules when working with inert gas:
- When working indoors, floor exhaust devices must be installed. At a minimum, it should be located at a distance of at least 20-30 cm from the floor level. in this case, argon will go down and be removed from the room naturally.
- When forming ceiling or vertical seams, personal protective equipment is used. A hose gas mask is sufficient to supply clean atmospheric air.
- When working indoors, oxygen levels must be monitored. If the readings of the measuring instruments drop below the level of 20% oxygen in the atmosphere, then work must be suspended and the room ventilated.
Argon arc welding reduces men's health
This is a myth widely spread among amateur and novice welders. It is generated by ignorance in the field of technology of welding process in a protective environment. The main reason for the appearance of the myth was the use of a weak radioactive metal, such as thorium oxide. It is used in the process of sharpening a tungsten electrode. But its level of radioactivity is significantly below acceptable standards. Therefore, in principle, it cannot have a destructive effect on the human body.
To have no reason to worry and to be sure of safety when performing welding work, you should follow simple safety rules. Namely:
- wear a respirator;
- work with active hood;
- store no more than 3 kg of thorium-tungsten electrodes in one place.
Tungsten dust consists of very small particles, which, when ingested, irritate the walls of the respiratory tract. They do not have a radical effect on health, but it is better to completely protect yourself by wearing a respirator.
TIG welding is capricious in operation
Most devices sold on the domestic market have a wide variety of settings and adjustments. More than manual arc welding (MMA) or semi-automatic (MAG) installations. For this reason, a welder must first undergo special training to work on TIG devices. This must be either an experienced specialist of the highest level or a welder with the appropriate specialization. It is important that the worker is able to correctly configure the installation, use all its capabilities and form a strong, aesthetic and durable connection.
For the welding process, each worker must:
- Select the optimal welding current.
- Set the optimal settings for a specific job.
- Select the correct electrode diameter depending on the current and material.
- Select a filler rod that best matches the metal or its alloy.
- Determine with the choice of inert gas. Pure helium or its mixtures can be used in welding work.
Provided all steps and requirements are met, a specialist will be able to connect metal workpieces of any size or composition. Argon welding is rightfully considered universal. It is used infrequently due to the high material consumption of the process.
Types and features of argon arc welding
Not long ago, three types of argon arc welding were known: manual, mechanized and automatic; more recently, robotic has appeared..
Manual
This type involves manual control of the entire process. The welder manually moves the torch and manually feeds the additive in the form of a rod or wire. This type is applicable both for the simplest household work and for the manufacture of highly complex structures. A significant disadvantage of this method is low labor productivity and the need to have a sufficiently experienced welder.
Mechanized
This type of welding is most often called semi-automatic or semi-automatic welding. The torch control process is carried out manually, and the wire feed is automatic. This type is three times more productive than a manual one. Semi-automatic welding in a carbon dioxide environment is widely used in shipbuilding. There are a lot of long straight seams for joining thick sheets of ferrous metal. Welders with low qualifications can work on these semi-automatic machines.
Automatic
Automatic welding is carried out without the participation of a welder. It can be performed by welding machines of varying complexity. The complexity of the figuration of the seam, which it can handle, depends on how high-quality this machine is. The simplest seam configuration is typical for welding pipes. This is where welding machines mainly “work”. They show the highest labor productivity in the installation of pipelines of various diameters, up to the laying of gas pipelines along the bottom of the sea.
This type of welding does not require welders at all. It would seem that this is wonderful. But despite the fact that the machines work themselves, they are prepared for work, configured and repaired by very highly qualified specialists. The next type of welding requires even greater participation of highly qualified specialists.
Robotic
This type of argon welding appeared relatively recently. Robotic welders have replaced many welders on conveyors, increasing productivity and reducing costs many times over. A person will never be able to keep up with a robot; he will not be able to maintain maximum concentration and work without errors at such a pace.
Of course, there is another side to the coin. Robots are very expensive; in addition to highly qualified adjusters to service them, they need designers to create them and programmers to draw up working programs. Robots have now taken their place on car assembly lines. The more massive the production, the more profitable robotic welding is.
Reliable facts
The TIG inverter is equipped with a large number of settings
The equipment makes it possible to qualitatively join a wide range of steel – low-, medium- and high-alloy. Each material has certain physical and chemical characteristics, which necessitates an individual approach when welding. The choice of parameters is also influenced by the thickness of the material and a number of other factors. It is important to choose the optimal settings, and this is the opportunity that the equipment in question provides.
Gas lines must be intact
To create a high-quality and beautiful weld, constant pressure of inert gas is required. In addition, the entire line eliminates the leakage of expensive consumables. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that a leak of inert gas can provoke an emergency situation in the workplace.
The prototype of the TIG inverter was a tungsten filament
American scientist Irving Langmuir experimentally established in 1916 that a tungsten filament conducts a charge better if its surface is coated with thorium oxide. It was this discovery that became the basis for the creation of tungsten electrodes in the future. They are successfully used in argon arc welding to this day.