Gas bonding or metal cutting was not possible until the Frenchman Devy realized in 1836 that acetylene (ethylene) based on calcium carbide could burn. Then they began to use it in street lamps and headlights of cars and steam locomotives. Much later, his fellow countrymen Fouche and Picard described a “welding pool” during gas-melting welding based on the same acetylene.
But it was in the Soviet Union that the industrial production of acetylene and its “packaging” in durable white steel cylinders was first started. This made it possible to increase the productivity of welders by 20 percent, without losing acetylene by the same amount. So gas welding of metals - steel, cast iron and non-ferrous - became available in any, even remote, area.
Weaknesses and nuances of technology
If we started with the pros, it would be fair to dwell on the cons. The disadvantage of the heating rate of the metal is that it is low.
In addition, the working area with this method is “spread out” - a very large heating zone for the metal, due to which a lot of thermal energy is lost. There is also such an unpleasant phenomenon as warping.
Thus, the productivity of the working process is not very high, and with increasing thickness of the edges of the workpieces being welded, it decreases even more.
Therefore, if your metal sheet is more than six millimeters thick, start thinking about using gas welding somewhere else. It is better to cook a thick edge, for example, using the arc method.
Injector and non-injector burner.
Gas welding is not the most expensive welding method, this is well known. But welding gas - acetylene and oxygen, which they like to use as a welding gas mixture, are still more expensive than electricity.
And if you add the rather high risks of explosions and serious fire danger that instantly arise if flammable liquids, gases, oxygen cylinders and elemental calcium carbide are handled incorrectly, the enthusiasm decreases a little.
Gas welding technology is excellent for a wide range of welding jobs: from joining aluminum and steel parts to working on bronze and cast iron.
Let us immediately note that gas welding is capable of almost all metals, including such capricious metals as copper, lead or cast iron: they are welded more easily by gas technology than by any other.
How to "gas"?
Acetylene is still widely used today where small amounts of welding are needed, especially in emergency situations. Other flammable gases are also widely used: hydrogen and natural gas, propane (separately and mixed with butane) and petroleum, as well as gasoline and kerosene vapors.
But ethin is the king among them in terms of calorific value and thermal properties of the torch (this can be seen in the photo of gas welding) in its mixture with O2. And it is used more than other gases for these purposes.
Pros and cons of technology:
- no power supply required;
- inexpensive equipment and accessories;
- is carried out only manually;
- Not high quality of products in terms of mechanics and durability.
Technical aspects of the gas welding process
The peculiarity of gas welding is the democratic nature of its seams, which can be made in all positions in space - from the bottom to the ceiling.
The most difficult situation is with ceiling seams, since in this case the molten metal must be maintained and quickly distributed along the entire length of the seam using the increased pressure of the gas mixture from the flame.
The most popular seams with this method are butt seams. Gas welding is not friendly with overlapping and T-joints. The fact is that both types of seams require extremely high heating of the metal. In addition, this method has a high risk of severe warping.
If the edges of the workpieces are thin and beaded, they are welded without the use of filler wire to form continuous or intermittent seams, which can also be single- or multi-layer.
It is clear that before welding it is necessary to clean the edges and surfaces of metal workpieces in the most thorough manner.
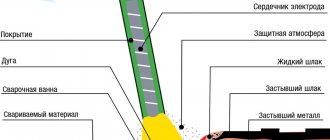
One of the most important technical components of the gas burner is manipulation of the gas burner. The gas welding technique involves keeping the flame about 5 mm from the end of the core, without touching the metal surface.
The weld pool is formed under the pressure of gases on the liquid metal, they seem to inflate it around the edges.
The filler wire is immersed in the weld pool. The heating intensity of the working area can be changed. This is done by changing the angle of inclination of the copper mouthpiece of the burner to the surface of the workpiece. The dependence here is direct and understandable: the greater the angle of inclination, the higher the heating of the metal from the flame.
The torch mouthpiece should be moved along the seam. At the same time, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the weld pool: the metal in it must be protected by gas pressure from the unwanted effects of ambient air. This must be done to protect the metal from the oxide film.
Separately about pipe welding
When welding pipes at the joint, no sagging should form on the inside of the seams. They will impede the movement of liquid through the pipe. In addition, you cannot melt through the walls.
Pipe welding is carried out using one layer and in just one pass. In this case, the convexity of the seam should not exceed 1-3 mm. The joint should be as smooth as possible.
The most popular methods
Welding in the lower position.
Gas welding methods can be described and listed in several thick volumes.
Let's take the most common of them:
Left welding
The left-hand method of gas welding is the most common among craftsmen of any qualification. Used to join metals with thin edges and low melting points. Left and right welding are two sides of the same coin, it’s easy to remember.
Right welding
The right welding method is suitable for working with metals with a thickness of more than 3 mm and high thermal conductivity. It should be noted that the weld seam during right-hand welding is of higher quality due to better protection of the metal by the flame.
The use of flame heat with the right method is more economical, and the process speed is almost 20% higher. To the same piggy bank of advantages you can add savings in gas costs of about 10%.
The filler wire must be taken with a diameter that is exactly half the thickness of the metal workpiece. The wire cannot be thicker than 8 mm.
Welding using through bead
This gas welding technology involves the gradual, step by step, movement of the flame to melt the upper edge of the hole in the workpiece and apply a layer of molten metal to the lower edge of the same hole.
First, the metal sheets are fixed vertically, leaving a gap between them half the thickness of the workpiece itself. The seam is formed in the form of a roller, which connects the parts. It is dense, without any pores or slag residues.
Welding using baths
Here the name speaks for itself. The principle of the method is the formation of more and more new pools along the seam. As soon as one of them is formed, the end of the filler wire is inserted into it, melts there, and then moves to the reduction section of the burner fire.
Meanwhile, the nozzle mouthpiece moves further along the seam - to the next section. Each new bath overlaps the previous one by approximately one third of the wire diameter.
This method is used to connect thin sheets when it is necessary to make butt or corner types of seams. This is a favorite type of welding for pipes made of low-alloy steel or low-carbon alloys.
Multilayer gas welding
It is used for very critical types of work, as it is characterized by rather low productivity, and welding gases are required here in large volumes - the method is not cheap. In it, the lower layers are annealed during surfacing of the upper and subsequent layers.
The result is excellent forging of each layer before the formation of the next seam. This method significantly improves the quality of the weld metal.
The process occurs in short sections. Pay special attention to cleaning the surface of the underlying layer before applying the next one.
Oxidizing flame and deoxidation welding
Cylinders for gas welding.
This technology was created for joining parts made of low-carbon steel alloys. The flame here has a sharply oxidizing character, as a result of which iron oxides are formed in the weld pool. If there is oxidation, so-called deoxidation is also necessary.
This is achieved using a special filler wire with high proportions of manganese and silicon. An excellent method with productivity 10% higher than other methods.
General safety rules
When performing welding work, safety rules must be observed. Only serviceable equipment may be used. The work place must be at least 10 m from the source of open fire.
We recommend reading: What is automatic welding
The post must be equipped with individual means for extinguishing fires. If only acetylene is used, then a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher or sand is required.
Water should not be used to extinguish fires caused by this substance. If there is a fire, you need to bend the hose in the area of the gearbox, and then close all the valves.
Nuances with different seams and different metals
Horizontal seams are formed using the right-hand gas welding method. There are situations when the process is carried out from right to left with the mouthpiece at the bottom of the bath and the wire at the top. This way the seam is formed faster and easier, and the molten metal in the bath does not flow down.
Vertical seams, on the contrary, are made in the left way with a bottom-up direction. If the metal is thick, use a double bead seam.
Ceiling seams are one of the most difficult to perform. Here you first need to heat the edges of the workpiece, then until they melt, a wire is placed in the bath, which quickly melts.
The liquid metal in the bath is kept from flowing down by the pressure of the gases from the burner. Welding is done in the right way. It is best to use multi-layer seam technology with multiple passes.
Low carbon steel can be welded with almost any gas. It is important to select the correct filler wire: it must also be made from low carbon steel.
Alloy steels come in very different compositions. Therefore, there is not and cannot be a single method of gas welding for them. If the alloy is heat-resistant and stainless, parts made from it are welded using wire containing nickel and chromium.
There are certain brands that can only be welded using molybdenum as a filler wire.
Copper and its alloys always require a high flame. During melting, it is extremely fluid, so the gap must be kept minimal. In addition to copper wire, flux mixtures are used to deoxidize the weld metal.
Brass is a very difficult metal to work with due to its composition. There is a high risk of pore formation in the weld due to the volatility of zinc. This risk can be significantly reduced by supplying more oxygen to the burner mixer and using brass wire as an additive.
Bronze is another capricious alloy. During welding, it is important not to burn out its important elements from the composition: tin, silicon and aluminum. Therefore, the flame should be reducing, and the additive should be bronze with the addition of silicon, which will help further deoxidize the seam.
Advantages and disadvantages of welding with a gas torch
Gas welding of metals has a solid list of advantages:
- The method does not involve the purchase and use of complex and expensive equipment. It does not require, for example, an inverter or semi-automatic device.
- Consumables used in gas welding are widely available on the market; you can find any composition or model without difficulty.
- No special protective equipment is required, even when gas pipe welding.
- The main welding parameters are well regulated: the flame of any required power, the level of metal heating temperature.
Gas torch welding method.
There are some disadvantages too:
- Heating of the metal is too slow, especially in comparison with an electric arc.
- The heating zone around the gas burner is too large, resulting in a lot of energy being lost to no avail.
- The heat from the burner is diffuse and difficult to concentrate.
- The method is still more expensive than the electric arc method: the price of gases is higher than the cost of electricity.
- As the thickness of the workpiece edges increases, the speed of the work process decreases due to high heat dissipation.
- It is almost impossible to automate the process.
https://youtu.be/21M1DpwTEB4
What do you need to buy to start welding?
This question is answered in the article - Tools and accessories for manual arc welding: a basic set. In short, to start welding with an inverter at home, you will need:
- Electrodes.
- Welder mask.
- Gaiters or protective gloves.
- Protective trigger, trousers and closed shoes.
- Welder's hammer and brush for removing slag.
A specialist talks about choosing a mask for metal welding in this video.
The optimal choice for a novice welder is a mask with a “chameleon” type filter.
Its invaluable advantage, compared to a conventional protective shield with tinted glass, is that the welder can see the parts being welded. He does not need to raise and lower the mask, because... “Chameleon” automatically darkens when a welding arc appears and reliably protects the eyes.
When the welding process stops, the glass is automatically cleared. This makes the job easier. A beginner in welding will not pick up the so-called. “bunnies” from a bright arc flash if the mask with ordinary glass is not lowered in time.
A few words about consumables
What gas is used for welding is not an unimportant question that you need to understand in order to make the right choice. The types of gases used vary and the choice depends on several factors.
Oxygen
Oxygen, for example, is completely colorless and odorless. It has a special role; it acts as a catalyst for metal melting processes during welding. Oxygen is stored and transported in cylinders with constant pressure. This is not an easy task, but it is quite doable.
The main thing is to know and follow the safety rules when handling oxygen cylinders and the gas itself. For example, the presence of technical oil can lead to fire: therefore, it is necessary to strictly exclude the slightest contact with such oil.
Gas burner flame.
In no case should there be a source of heat or direct sunlight in the rooms where cylinders are stored.
How to obtain welding oxygen: this is done quite simply - from atmospheric air using specialized equipment.
Oxygen is divided into three types based on purity:
- premium grade with a gas concentration of 99.5%;
- first grade with 99.2%;
- the second – with 98.5%.
Acetylene
This is the second most popular gas used in gas welding for both welding and cutting. It is also colorless and odorless. Acetylene may explode if pressurized or heated. It is made from calcium carbide and water.
Acetylene is not the cheapest gas, but its advantages make it very popular among welders. It's all about the combustion temperature - it is remarkably high for acetylene, especially in comparison with cheaper gases such as methane, propane or kerosene vapor.
Flux and filler wire
These are the main participants in the process of weld formation. The filler wire must be absolutely free from the slightest signs of dirt or corrosion. Sometimes, instead of wire, you can use a strip of the same metal as the workpiece for welding.
Fluxes are necessary to protect the weld pool from the harmful effects of external factors. Most often, borax and boric acid are taken as components of flux mixtures, which can be applied directly to the workpieces being welded or to the filler wire.
The only metal that can do without a flux mixture is carbon steel. Well, a special need for the presence of flux arises when welding copper, aluminum and their alloys.
What is needed for gas welding/cutting
Gas welding equipment is simple and convenient to carry and transport. For any type of fuel, gas welding devices have an oxygen prefix. Because without it the process is practically impossible.
Main equipment for gas welding: cylinder or generator (gas holder), cutter. In the generator, calcium carbide produces acetylene (its formula is C2H2) mixed with water. They are mostly used by professional gas welders in their work, since this method is explosive. Therefore, in everyday life, at car service stations, in various workshops, and on sea vessels, only bottled acetylene is used.
Gas and oxygen cylinders. Oxygen does not burn, but it enhances combustion. When combined with various mineral or synthetic oils, including food grade ones, an explosion may occur.
Therefore, to service blue cylinders, almost medical sterility is required: clean gloves, well-washed or grease-free keys, gearboxes.
Each type of gas has its own valve and reducer so that there is no additional reaction with the metal. The valves for acetylene are steel, oxygen and propane/butane are brass. Reducers designed for a certain pressure are connected to them: acetylene - 2.5 MPa (5320 liters of gas in a cylinder), oxygen - 15 MPa (6000).
Porous material (charcoal) is poured into white cylinders and acetone is poured in, and only after that acetylene is pumped in. Another chemical reaction occurs inside and additional acetylene is produced.
How to cook with gas welding? Mixing oxygen with gases is the same. In the cutter, the flame amplifier is combined with ethyne and the vapor comes out of the burner nozzle after ignition with a blue fire.
Necessary equipment for gas welding
Water seal
This is a simple and effective protection of the pipe, acetylene generator and other elements from fire in the form of reverse draft from a gas burner. The water in this seal must be at a level that needs to be monitored. It is usually located between the burner and the acetylene pipe.
Gas cylinders
These cylinders are of different colors depending on the type of gas. A strict rule applies to all cylinders: never paint the top to avoid contact between paint and gas. Another technical nuance: copper valves cannot be installed on acetylene cylinders due to the high risk of explosion from the interaction of acetylene and copper.
Hoses for various purposes
Burner device.
Hoses are needed for many things: supplying gases and hot liquids. In addition, they must work under pressure, so these are not garden hoses for watering a vegetable garden, but serious devices with special technical characteristics.
Hoses come in three categories:
- with a red stripe for pressure up to 6 atmospheres;
- with a yellow stripe for flammable substances;
- with a blue stripe for pressure up to 20 atmospheres.
Gas-burners
Gases and vapors from flammable liquids are mixed in the burner mixer. They are produced in a huge variety, divided into injection and burners without it, of different powers and so on.
Gearbox
A necessary item where there is high gas pressure.
Reducers reduce the pressure of the gas leaving the cylinder. They come in two types: direct and reverse acting. Advanced models with silver plating are available for working with liquefied gas: they do not allow such gas to freeze at the outlet of the cylinder.
Gas post
This is a special work table for welding. The best option for a post is a tabletop with the ability to rotate and fix it. A good post is equipped with exhaust ventilation and a good storage system for welding tools.
https://youtu.be/7_k6hZ0SyPo
Requirements according to GOST
The gas welding process is manual; the quality of the weld is assessed subjectively and depends on the skill of the welder. There are no GOST standards for the results of work. However, there are a number of requirements for compliance with the technology.
The quality of calcium carbide used in welding is regulated by GOST 1460-2013. In addition, regulations establish the pressure parameters in the reducer and cylinder, the characteristics of the filler wire, and the requirements for the generator. There are GOST standards for burners and hoses.
Gas welding: hybrid version with semi-automatic
This technique adds the use of an electric arc and a shielding gas - most often argon. In this situation, the technology can well be called hybrid.
Gas welding seams.
Here are the steps involved:
- connecting the device to the network;
- fixing the filler wire through the hole in the torch;
- adjusting gas pressure using a reducer;
- determination and setting of filler wire feed speed;
- regulation of other parameters - welding current and voltage;
- fixing the burner at an angle to the surface of the workpiece before igniting the burner;
- start of welding.
It should be noted that the technical characteristics of all consumables, as well as equipment elements, are clearly and clearly stated in GOSTs. In other words, the gas welding process is well regulated.
For example, the following parameters fall under GOST standards:
- characteristics of the acetylene generator;
- hose types;
- gas pressure regulated by a reducer;
- type of gas burners;
- types of filler wire;
- standards for gas cylinders, etc.
Recommendations
When studying the essence of the gas welding process, it is necessary to understand that working with flammable gases requires increased caution and attention. It is recommended for a beginner to take into account the advice of experienced welders and apply them in practice:
- for study and training it is better to use oxygen and acetylene;
- for welding with propane it is better to use a GZU 3-02 torch and Sv08g2s wire;
- before cooking the product, it must be thoroughly cleaned;
- for gas pressure welding, it is better to use hydraulic equipment (press) for reliable bonding;
- The left and right methods have their advantages and disadvantages, so the choice is made by the master, depending on the situation.
We reviewed the basic concepts and materials for flame and gas press welding. For them, a standard mixture of oxygen and acetylene is predominantly used. In some cases, propane welding is used for replacement. This process is not easy and has many nuances that will be difficult for a beginner to take into account. In this regard, novice welders are not recommended to weld with propane. The quality of the seam and the ease of work are affected by preliminary preparation.