Liquefied propane is used both in everyday life and in production. Bottled gas is indispensable for autonomous gasification, which is why containers are often installed at dachas and other remote places. If the valve breaks off the cylinder or other malfunctions of the regulating device occur, it is recommended to contact specialists. It is not always possible to replace it yourself.
Balloon valves: types and replacement
The valve for a gas cylinder is a very special representative of shut-off and control valves.
After all, this unit must ensure not only accurate dosing of gas flow, but also absolute tightness of both the housing and the mounting unit for the fittings and cylinder. The classification of shut-off valves for cylinders is based on the contents of high-pressure containers.
And based on this principle, valves are divided into:
- Fittings for liquefied gas cylinders
- Fittings for oxygen cylinders
- Fittings for propane-butane cylinders
However, there are no special design differences between the valves. However, the markings for these devices are completely different. Thus, the oxygen cylinder valve is marked in blue, the propane valve in red, the acetylene valve in white, the hydrogen valve in green, and so on, in accordance with GOST standards.
Indications for replacement
In order to send the cylinder in time for repair work and performance testing, perform an external inspection and pay attention to the following:
- Is the shut-off valve flywheel spinning?
- on the body and valve of the cylinder, whether mechanical deformation is visible in the form of abrasions, cracks and traces of corrosion damage;
- validity of technical inspection data;
- feeling the smell of the gas-air environment next to the cylinder;
- skewed or damaged shoe at the base;
- absence of a plug on the fitting.
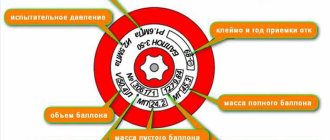
Before replacing the valve of a gas cylinder with your own hands, the user needs to be able to not only externally determine the malfunction of the cylinders, but also identify counterfeit products. All cylinders that are permitted for use in Russia must be produced in a certified production facility and comply with GOST requirements. This can be easily determined by examining a metal plate on which the main text is located on 2/3 of its area, and all letters must be the same height, equal to 6 mm.
Data on the cylinder:
- Permissible pressure in MPa;
- test pressure in MPa; volume in liters;
- factory number;
- date of issue “MM.YY.AA”, where M is the month, G is the year of manufacture, A is the year of the next inspection;
- empty tank weight in kg;
- mass of container with gas in kg;
- the next check is in the “R-AA” format, where “R” is the stamp of the state verifier, A is the year of validity of the certification.
To replace the valve you need a gas wrench
VALVE DESIGN
In the standard version, propane gas cylinders with a volume of up to 27 liters are equipped with KB-2 valves or VB-2 valves. The second option is considered more reliable. The gearbox is connected to the valve using a fitting thread and a union nut. The degree of tightness of the connection is adjusted with an open-end wrench. A disposable gasket is installed for sealing.
The connections to the valve are not always tight and often lead to gas leaks.
Structurally, the valve consists of the following elements:
- steel body in the form of a tee with thread;
- locking part;
- flywheel;
- seals.
The type of valve must match the characteristics of the contents of the container and the cylinder itself.
The color of the cylinder indicates what kind of gas is there:
- red color – propane-butane;
- black – nitrogen;
- blue color – oxygen;
- green – hydrogen;
- white color – acetylene.
Checking tightness and completing work
When checking the tightness of the valve connection, you will need to pump gas under pressure into the gas cylinder. This can be done in two ways:
- Pump gas using compressor equipment or a car pump.
- Connect two cylinders with a hose, the first of which is empty (tested), and the second is filled with gas.
First, under the control of a pressure gauge, you need to fill the test cylinder with gas with a pressure of 1.5-2 atmospheres. After this, soap foam is applied to the connection and the tap is opened slightly. If soap bubbles are not inflated anywhere, then the connection is sealed. But if even slight swelling of foam appears, you will have to re-tighten the valve.
When immersing the valve in water, it is advisable to close the side fitting with a plug so that water and suspended particles contained in it do not get into the locking mechanism
If the cylinder is small, then you can immerse its valve in a small bowl of water and see for bubbles.
After replacing the shut-off valves, the corresponding mark must be placed in the gas cylinder passport.
Types and design of valves
The threads of valves for gas cylinders are standardized, but they themselves can have a variety of designs. The choice of valve model is influenced by the type of chemical substance being stored, production features of operation and the amount of money.
Before purchasing new equipment, you should familiarize yourself with the design options and the internal structure of the valves.
Classification of shut-off valves for cylinders
The design features of gas cylinder valves are determined not by the whims of engineers, but by safety considerations.
Depending on the material used, shut-off valves are divided into brass and steel . The choice of metal for the manufacture of the valve body is determined by the type of gases contained in the cylinder.
There are the following types of shut-off valves, depending on the type of chemicals stored:
- Acetylene. The body of such cylinders is painted white. Special valves are used in cylinders containing acetylene, chlorine, ammonia and other aggressive substances.
- Oxygen . The cylinders are painted blue and are intended for storing oxygen, argon, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and other inert gases.
- Propane-butane . They are painted red and are intended for storing substances corresponding to the name and other gaseous hydrocarbons. The most common valve type model for such a cylinder is VB-2.
Valves for acetylene cylinders are not made of brass because the substances they contain may react chemically with copper. Typically, carbon or alloy steel is used to manufacture shut-off valves of this type.
Gas valve device
A standard gas valve has the form of a tee, each fitting of which has an external thread. More advanced models may have an additional protrusion - a safety valve. Its purpose is to relieve excess pressure in the event of a full cylinder heating up or in case of incorrect filling.
The lower fitting of the valve is used to connect to the gas cylinder, the upper one is used to attach the flywheel, and the side one is used to connect communications for gas outlet and injection. The arrangement of the gas cylinder tap is quite simple.
Shut-off valves usually consist of the following general elements:
- Brass or steel body.
- A stuffing box valve or flywheel connected to the body with a union nut.
- Internal locking mechanism with valve and stem.
- Sealing gaskets.
- Plug for the outlet.
You can examine in detail the design of valves on gas cylinders of each type in the presented images.
The cylinder itself is solid, and it’s unlikely that anything will break there. Therefore, the majority of malfunctions concern gas valves.
- Repairs are carried out in a well-ventilated area;
- We open the shut-off assembly to allow the remaining gas to escape;
- To turn the valve manually or with a gas wrench, you need to warm up this element. In this case, there is no danger, since the cylinder contains only gas vapors, and not their mixture with air, which is explosive in the first place. The only thing that needs to be monitored is moderate heating of the structure, since overheating can increase the pressure in the cylinder. The point of warming up is that the metal expands and it becomes possible to unscrew the valve even manually, or with a slight lever force in the form of the same gas wrench;
- After removing the element, the conical fitting is sealed - a sealant or fluoroplastic tape is applied to it;
- A new valve is installed, after which the fact and time of repair are entered into the cylinder passport. Installation is carried out with a special torque wrench, which makes it possible to correctly dose the forces and not break the thread. The maximum pressure allowed in this case is 480 Nm for steel and 250 for brass valves;
- Having removed the valve from the cylinder, it is necessary to drain the condensate from it, if we are talking about propane-butane, which we widely use. This procedure is practically never performed by anyone, despite the fact that it is extremely desirable. However, it is necessary to drain it away from residential buildings, since this condensate has an extremely unpleasant odor.
Important! Working with gas cylinders is potentially dangerous. Moreover, there is a strict ban on removing taps in artisanal conditions. Remember that it is best to entrust this matter to professionals, and you should proceed with independent actions only if you are confident in your abilities, ready to strictly follow the rules, and, of course, the urgency of repairs. If there is even the slightest opportunity to transfer this task into the hands of a specialist, it is strongly recommended to take advantage of it.
In general, the gearbox, which is non-separable, must be replaced every six years. As for the hoses, they must be reinforced and subject to inspection no earlier than once every six months when replacing the cylinder.
Mandatory Precautions
Before replacing the gas cylinder valve, precautions must be taken. Work must be carried out in such a way as to protect people from potential hazards and keep the equipment in working condition.
The following precautions are used when preparing to replace a gas valve:
- The remaining contents of the cylinder can only be vented in an open space. An exception can be made only for nitrogen, air and argon.
- The work area should be well ventilated, although it is advisable to carry out work outside.
- There should only be one closed gas cylinder within the workplace.
- The flywheel must be unscrewed slowly to prevent electrification.
- You can begin replacing the valve only after the pressure in the cylinder and outside has been completely equalized.
When screwing the valve into the cylinder, fum tape or special lubricants are used, which provide increased tightness and strength of the connection. When replacing a faucet, such seals greatly complicate the process of dismantling it. To solve this problem, you can heat the valve with a hairdryer.
There is no need to save on gas fum tape, because high-quality material will eliminate the need to twist the valve due to gas leaks
You can heat the shut-off valves only after bleeding the gas from the cylinder and closing the tap. In this case, the procedure is safe and will not lead to unpredictable situations.
An alternative to a hairdryer is to wrap a cloth around the valve and then pour boiling water over it. With this heating method, any suitable plug should be screwed onto the outlet fitting to prevent water from entering there.
After taking all precautions and warming up the shut-off valves, you can begin to unscrew the valve, which can be a difficult task at home.
Gas cylinder valve: device and features.
All locking devices are designed almost identically and consist of the following parts:
- A steel body in the form of a tee, each side of which has a thread: the bottom - for screwing onto the cylinder, the top cylindrical - for the valve nut, the side - for the plug;
- The locking part, which includes a bypass valve and a rod that transmits the torque element from the flywheel to the valve;
- A flywheel, which is connected to the valve stem using a nut.
- Sealing gaskets, which are located between all parts and provide additional reliability of this design.
A distinctive feature of this locking device is its ability to withstand constant pressure from 15 to 190 atmospheres.
Features of the device and marking of the gas valve
The manufacture and use of gas cylinder installations is carried out according to the still valid Soviet GOST NoNo 15860, 949-73, 9731-79 and 12247-80. The vessels are made from steel grades: 45, 30KhMA, 30KhGSA and 34CrMo4. The maximum permitted pressure varies from 1.6 MPa to 19.6 MPa, and the wall thickness ranges from 1.5 to 8.9 mm. The cylinder is equipped with a cap that screws onto a special thread and completely protects the valve. In some designs it is welded and thus protects the valve from damage.
- metal or composite body of the gas cylinder installation;
- shut-off and control valves;
- protective cap;
- transport fixing rings;
- shoe for structural stability;
- metal plate with technical data.
The standard GB valve is made in the form of a tee with three outlet threaded fittings. The latest models are available with safety devices in the form of an additional protrusion to relieve excess pressure generated by heating or incorrect filling. The fitting at the bottom is connected to the GB, the flywheel is attached to the top, and the one installed on the side is for technological filling and discharge of the medium.
Valve for propane gas cylinder
Types of valves are classified according to the type of reagents being filled:
- Acetylene - white with a special valve for contact with chemical active substances.
- Oxygen - blue, intended for filling: O2, Ar, H2, N2 and CO.
- Liquefied gas – red for flammable hydrocarbons. They are equipped with a crane brand – VB-2.
Types of cylinders
Products are distinguished by type of filler:
- for compressed and liquefied gases;
- oxygen;
- acetylene;
- containing propane-butane.
There are different types of cylinders depending on the type of gas in it.
To transport compressed and liquefied gases, steel cylindrical vessels are used, with a volume from 0.4 to 55 dm 3, with a conical hole in the neck with a thread. It is into this hole that the balloon shut-off valve is screwed into. The valve design is different for each gas, so that oxygen valves do not screw into cylinders with another gas.
To install the valve, you need to fit a male threaded ring onto the safety cap neck. The safety cap protects the cylinder valve from impacts during transportation.
The outer color of the cylinder and the color of the gas name differ depending on the type of gas in it:
- blue with black lettering – contains oxygen;
- white with red lettering – contains acetylene;
- dark green with red inscription – contains hydrogen;
- red with white lettering – contains propane.
There is no paint on the upper spherical part; the passport data of the cylinder is stamped here. The passport data includes: type, serial number, trademark of the manufacturer (plant), empty weight of the product, capacity, test and working pressure, date of manufacture, Gosgortekhnadzor stamp, quality control department stamp and the date of the next test.
An oxygen cylinder is a cylindrical steel vessel with a spherical bottom and a neck for a shut-off valve. A “shoe” is welded at the bottom for installation in a vertical position. The oxygen cylinder also has a threaded ring for a protective cap.
The passport data of the cylinder is indicated on the top part.
Acetylene is stored in white cylinders, their design is similar to that for oxygen. The acetylene valve does not have a connecting thread; the gearboxes are secured with a special clamp, which is located directly on the gearbox itself.
Cylinders for propane-butane are welded in design, made of sheet steel with a longitudinal seam and circumferential seams along the bottom. Steel thickness – 3 mm. The upper bottom has a “neck”, and the bottom has a “shoe”. A special feature of the valve design for propane-butane is that the side fitting has a left-hand pipe thread for 14 threads.
The rim on the cylinder in most cases has 4 holes. You can attach a metal corner about a meter and a half long to them with bolts.
PHOTO: YouTube.com If there are no holes, the corner can be safely welded to the shoe, this is safe because the rim does not have direct contact with the container
And then, as in the second option, lower the cylinder with the valve down, secure the valve in a vice and, resting against the corner, rotate the cylinder.
Reducers are designed to reduce the pressure of compressed gas in a cylinder or pipeline to the operating pressure at which the gas must enter the torch or cutter, and to automatically maintain this pressure at a given level. In addition, with the help of a reducer, the pressure and flow of compressed gas are regulated, as well as the supply is shut off when work stops.
The quality and efficiency of the process of gas welding, cutting and other types of gas-flame processing of metals largely depend on the operation of the gearbox. To correctly select gearboxes, you need to know its characteristics and be able to determine them. The main characteristics of gearboxes include operating pressure, throughput, adjustment sensitivity, pressure drop and reduction limit.
Throughput is characterized by the amount of gas that can be passed per unit of time, usually in dm 3 / s (m 3 / h). Ramp gearboxes have a throughput capacity of up to 6945010 -3 dm 3 /s (250 m 3 /h), and station gearboxes - no more than 1666810 -3 dm 3 /s (60 m 3 /h).
The sensitivity of the adjustment P (kgf/cm 2 ) is characterized by a change in the operating gas pressure when the adjusting screw is turned by 90, or ¼ turn, and is determined by the formula
where P – pressure gauge readings at the set operating pressure in kgf/cm2;
P2 – the same after turning the adjusting screw ¼ turn in kgf/cm 2.
For on-site oxygen reducers, P is usually 0.51.5 kgf/cm 2 (0.050.15 MPa).
The pressure drop is the amount of change in operating pressure in the low pressure chamber of the reducer when gas extraction is stopped. The pressure drop P is determined by the formula
,
where P1 is the pressure in the working chamber after stopping gas extraction in kgf/cm2;
P2 – the same for gas extraction in kgf/cm2.
For stationary gearboxes P is 1530%.
The reduction limit is the lowest gas pressure in a cylinder or network at which the operating pressure in the reducer begins to drop quickly. Typically, the reduction limit is approximately twice the operating gas pressure after the reducer: P1min 2P2, where P1min is the pressure in the cylinder,
P2 – working pressure.
One of the problems when operating gearboxes is gravity flow, i.e. leakage of gas from a high-pressure chamber into a low-pressure chamber when the valve is completely closed. This occurs due to wear of the valve or its loose fit to the seat. To eliminate gravity, the valve seal is ground and polished with sandpaper stretched over the glass, and the valve seat is ground in.