Is it profitable?
Environmentally friendly materials are increasingly used in modern construction.
Wood is used in the construction of private farmsteads. Gazebos, bathhouses and even houses are built from logs. This material allows you to build not only housing that is most suitable for living, but also significantly saves the construction budget. Therefore, the production of rounded logs looks like a promising and profitable business. Opening a wood processing workshop is quite simple. The technological process is simple and no special permits or licenses are needed. Workers may have low qualifications. One technologist who knows the process and knows how to control the operation of the equipment is enough. Such an enterprise will be profitable only when the volume of finished products is at least 250 cubic meters. per month. Log rounding is often complemented by other activities. Along with this business, it is best to carry out the construction of houses or small architectural forms made of wood. Large companies involved in the construction of such buildings often open their own production of materials.
A significant disadvantage of the business is its seasonality. Construction work usually stops with the onset of cold weather. That is why in winter it is necessary to find an alternative to income from cylindering logs.
Where to start producing log rounding
A log rounding workshop can be located in a production room, a hangar, or even just under a canopy. The equipment must be protected from the sun and precipitation. Wood blanks and the final products themselves are quite larger in size. The equipment for working with them is also impressive in size. This must be taken into account when choosing premises for production.
The workshop is subject to fire safety requirements. Floors and walls are finished with fireproof materials. The drying chamber is usually installed in a separate room. Blanks and finished products are stored separately. In addition, it is necessary to arrange office space for the administration.
Depending on the volume of production, you need to calculate the required number of workers. In one shift, 3-4 people can handle the rounding of logs at the site. From the administration you will need a director, an accountant and a sales manager.
Functions
The main function that any rounding machine has is the processing of logs as a body of revolution by milling. But to assemble a log house, simply cylindrical blanks are not enough. And in this case, additional equipment capabilities will come to the rescue:
- excavation of grooves to form various locking connections;
- production of parquet dies, timber;
- sawing of linear products;
- sawing timber into carriages and then into edged boards;
- all stages of log rounding, from roughing to final;
- removal of mounting bowls and compensation grooves.
In this case, the log itself is not reinstalled, but cutters and individual components are changed during the work. The result is parts with a wide range of diameters. The limitation concerns the length of the processed logs: the sleds are designed for seven-meter workpieces. A skillful combination of cutters and working techniques allows you to produce complex wooden structures.
How much profit does a company specializing in log rounding make?
Monthly expenses for a woodworking shop include:
- Rent (industrial premises and office).
- Staff salaries.
- Public utilities.
- Raw materials and consumables.
- Transport costs.
- Electricity.
- Advertising.
- Depreciation.
- Taxes.
- Administrative expenses.
An enterprise that processes 250-300 m3 per month spends 25 thousand dollars on all of the above purposes. At the same time, its monthly revenue is 30-34 thousand dollars, which means profit before tax is 5-9 thousand, and after settlements with by the state - 4-7.5 thousand dollars.
Classification
Experts propose to classify rounding machines according to five parameters:
- type of mechanism;
- the method of moving the log;
- level of automation;
- drive power type;
- diameter of the workpiece used (minimum – 80 m, maximum – 500 m).
Two types of mechanisms are used in installations. The first is a pass-through (rotary) one, which allows you to continuously move the wood through the cutter. The second is cyclic (turning), in which processing is performed by repeating a cycle of actions.
If cyclic actions are performed by a cutting tool, the machine is classified as a cyclo-pass type, and if a log moves, it is classified as a cyclo-positional type. In the mechanisms, logs have the ability to both rotate and move rectilinearly along the guides.
What financial investments do you need to make to open your own log rounding shop?
To open an enterprise with a capacity of 250-300 cubic meters. an amount of 80-120 thousand dollars per month is required. It includes: costs for registration and execution of all documents, rental of premises, purchase of equipment, office equipment and furniture, as well as the purchase of additional tools, carrying out repair work and installing a production line. In addition, do not forget that the enterprise will not immediately begin to make a profit. It will take at least 2-3 months until it reaches the level of self-sufficiency, and until that moment you will finance monthly expenses from your own sources.
Features of the design of the design in question
When considering what kind of homemade rounding machine drawings may have, we note that often the design has the following elements in one form or another of their implementation:
- The main and most cumbersome element is the frame. It is on it that stress is concentrated and all other elements are attached. When making the frame, it is recommended to use rectangular pipes. The connection of all elements is often carried out using welding, which allows you to speed up work and create a truly durable structure. However, it is possible to create a frame using a combination of a bolt and a nut. Collapsible frames are more mobile, but have less rigidity.
- Guides along which the power saw and sawing device will move. The length of the logs can reach several meters and weigh tens of kilograms. In order to significantly simplify the processing task, you should create a homemade rounding machine on which the tool moves, and not the workpiece.
- Pasterns: front and back, in some cases, only one. They are necessary to twist the logs during processing. Note that the front one quite often has a dividing head and a workpiece fastening system. Using the dividing head, you can set the rotation angle at each stage of processing, which is necessary to improve the quality of the workpiece.
- As a rule, a milling cutter is used as a cutting tool. There are quite a lot of types of this cutting tool. When considering how to make a cutter with your own hands, we note that the work is complex and involves the use of rolled tool steel, which has increased strength and a low degree of machinability.
- A high-quality cutter has replaceable knives that can be sharpened and replaced if necessary. The cutter itself does not wear out over time.
- To correctly place a log that has a lot of weight, special levers are installed.
- The rollers, acting as a stop, do not allow the log to sag during processing, thereby significantly increasing the quality of the resulting material.
- Almost all models have mechanical brakes that are installed on both sides of the carriage. They are necessary to perform the work of selecting the crown bowl.
- A device that allows you to rotate the steel manually at the time of cutting a longitudinal groove.
Principle of operation
These elements have many drawings that you can use to create a rounding machine with your own hands at home. However, the design can be significantly simplified by taking into account the problems for which it is being created.
What equipment to choose for log rounding
There are three types of log rounding machines:
| Positional, turning type | The name of the machine speaks about the principle of its operation. It is in many ways similar to conventional turning equipment. The rounding of logs occurs while they rotate around their axis, and the cutting tool moves along the workpiece. The price of such an installation is within 200 thousand rubles. |
| Positional, with a stationary workpiece | The log is rounded by rigidly fixing the workpiece. The cutting tool moves along it. The cost of such a machine starts from 250 thousand rubles. |
| Machines with barrel feeding through a processing device | This equipment is highly productive. Its cost starts from 600 thousand rubles, but it pays off faster than others. |
Each of these types of machines has its own advantages and disadvantages. We will also show them in table form:
| Pass-through technology | |
| Advantages | Flaws |
| High processing speed due to continuous supply of workpieces. | The curvature of the source material is not removed during processing. To reduce its size, the workpiece is cut into pieces 1-2 m long. |
| Log rounding can be done in different lengths, without restrictions. | |
| Productivity – 35-40 cubic meters. m. for an 8-hour work shift. | |
| Possibility of additional wood processing: production of block houses, edged and decorative boards. | |
| Positional technology | |
| Advantages | Flaws |
| The ability to eliminate the initial curvature of the workpiece and produce a perfectly flat product. | The length of the workpiece cannot be greater than the dimensions of the machine itself. |
| Poor performance. More time is required to reconfigure the cutting tool. | |
| The need to attract qualified workers who can configure the installation. | |
All equipment can be mechanical, semi-automatic or automatic. Most often in workshops you can find the first type of machines. When choosing from a variety of offers from foreign and domestic manufacturers, you need to take into account two main parameters: productivity and quality of log rounding .
Types of machines
The cost of a rounding machine is based on the power of the device and the availability of additional options to increase the speed and comfort of work. In the simplest equipment modifications, the workpiece is moved manually, but usually a motor drive is installed for this purpose. The carriage speed can reach up to 14 m/sec. Rounding the workpiece in different models takes from 10 to 15 minutes, and when completely processing a log, the time required is about half an hour. Properly organized operation of the machine ensures a finished product output of 100 linear meters per shift.
The equipment has significant power and weight, therefore, before buying a rounding machine, you should make sure that you have a 380-volt power supply and prepare a level area with a concrete base that will compensate for vibration and reduce the noise of the unit during operation. The performance of the device is determined by the modification that allows the number of working operations to be performed and the quality of the wood processed.
Preparation of necessary documents
If you plan to cooperate with government agencies, large woodworking companies or foreign companies, then it is better to issue LLC documents.
In addition, a legal entity is the only option if several founders are involved in the business or you are afraid that the company will go bankrupt (the founders of an LLC do not risk their personal property in such situations). Entrepreneurs who plan to sell products to individuals or small firms can save on registration by completing individual entrepreneur documents. But, regardless of the organizational and legal form of your business, you must choose OKVED codes that correspond to your activity. In this case, the following are suitable:
- OKVED 20.30 (production of wooden carpentry and building structures).
- OKVED 20.10.1 (production of lumber whose thickness is more than 6 mm).
In addition, you need to fill out paperwork with Rospotrebnadzor and the fire inspectorate, and also receive a quality certificate confirming that your product meets established standards. No more permits or licenses are required.
Recommendations before purchasing
For the chosen level of productivity, it is important to consider the degree of automation of the rounding machine.
In mechanized models, the operator loads and unloads logs, configures and adjusts the mechanisms. He also monitors the quality of work performed at all stages of operations.
In automated rounding machines, the specialist servicing it is assigned the role of process controller.
In semi-automated installations, the master joins the process after the machine has completed one cycle of operations.
Note! To create optimal and uninterrupted operating conditions, it is important to select the appropriate type of drive power supply.
Electric can work without interruption, provided that the power lines are reliable or there is an additional power generator. Gasoline requires constant refueling, but does not depend on external factors.
But the main choice is between pass-through and loop types. The pass-through will provide high productivity, sometimes at the expense of the quality of processing. Most models of such machines do not have the ability to make the surface of the log smooth, without burrs and roughness. Cyclic installations work much slower, but at the same time they have a number of advantages:
- provide very high quality processing;
- perform the entire set of operations;
- have compact dimensions;
- The design is stable and easy to maintain.
In addition to all of the above, price, equipment manufacturer and required processing quality play an important role.
Production technology
Now let's move directly to the technology of log rounding. Manual labor is practically not used here. All processing is carried out only on special machines. Wood is prepared for construction only mechanically.
| First stage | It is traditionally preparatory. All raw materials are sorted and knots are removed if necessary. The barrel should be shaped in such a way that it can be conveniently fixed in the machine. First, the top layer is peeled off the trunk. The surface of the wood becomes smooth and it is easier for the equipment to process it. |
| Second phase | Drying is most often carried out naturally under canopies. Humidity should be brought to 15-18%. If such conditions cannot be ensured, then a drying chamber is used. |
| Third stage | The rounding of logs itself is also carried out in several stages. The workpiece is fed by a hoist into the processing zone and securely clamped with special fasteners (headstocks). A head with a milling section and a rounded head begins to move along the beam. The workpiece does not move throughout the entire process. The product is obtained with precisely specified parameters for diameter and surface straightness. Turning and milling machines operate on this principle. There is also rotary type equipment. The disadvantages of its experts include the curvature of the product, which can form. Applying a compensation cut. It is done along the workpiece in order to concentrate the wood cracking areas in one place. Due to its natural origin, this material will sooner or later begin to lose moisture and crack. Thanks to the compensation cut, this process occurs in one designated place. The building, due to such properties of wood in the future, will only improve its thermal insulation properties. At this stage, a laying groove is made. The carriage with the cutting tool runs along the beam and forms the required surface. |
| Fourth stage | A vertical mechanism with a cutter cuts out the crown bowl. This process most often occurs automatically. |
| Fifth stage | It can be considered final, since the blanks are cut according to the design of the future log house. |
After completion of manufacturing, the parts undergo dimensional control; often the log house is assembled without fasteners to check the integrity of the structure.
0
Features of modern industrial models
The main feature of machine models produced by well-known manufacturers today is the use of a laser pointer to control the movement of the carriage. This point determines high processing accuracy and the ability to carry out the entire process without reinstalling the workpiece. Thus, a CNC-controlled carriage with a set of tools moves along guides and performs various types of operations.
Log rounding machine
As practice shows, you can make a model with your own hands that will have manual control and the ability to process workpieces up to 7 meters long.
Milling logs for a log house
Log milling
After forming a flat plane, it is necessary to change the standard configuration of the workpiece. The technology for constructing a log house consists of installing logs on top of each other. As a result, there should be no cracks or sudden changes in wall thickness.
To solve this problem, it is necessary to use a specially shaped cutter, which is installed in the moving part of the machine. Unlike band or disk cutting, it should form not a flat, but an oval notch on the mounting part of the workpiece. Thanks to this, the log house will have optimal wall thickness characteristics, which will affect the degree of thermal insulation.
Stages of milling logs for a log house.
- Rounding. In this case, the cut of the workpiece should have a perfect round shape.
- Calculation of the thickness of the recess to form the mounting groove.
- Choosing a cutter.
- Processing of the log, secondary checking of its geometric dimensions.
But even after this work has been carried out, it is still impossible to erect a log house. A final machining step will be required to create the mounting grooves.
The choice of cutting tool for a log house directly depends on the type of wood. Its hardness, number of knots and geometric dimensions are taken into account.
History of through-type machine technology
The production of rounded log parts is currently one of the most attractive segments of the timber processing market. The main task when organizing such production is the correct choice of equipment, because Currently, many domestic manufacturers offer rounding equipment. We asked the chief designer of Kirovvneshtorg Company LLC, Vladimir Nikolaevich Tyulkin, to express his view on solving this problem.
— Today, there are quite a large number of manufacturers operating on the domestic cylindering equipment market. What do you think is the reason for this?
— The first and most important reason for the presence of a large number of manufacturers is the increased interest of woodworkers in the production of log parts. But if you take a closer look at the range of equipment offered on the market, you can see that all equipment can be divided into three groups: lathe-type positioning machines, rotary-type positioning machines and rotary-type throughput machines. Most domestic manufacturers of cylindering equipment are engaged in the production of positional lathes, because mastering the production of such machines is quite simple. A much smaller number of manufacturers are engaged in the production of rotary machines, because The design of such machines includes a cylindrical spindle (often called a rotary head), the production of which requires significant material and labor costs; in addition, the manufacture of the main parts of the cylindrical spindle, as well as its assembly, requires highly qualified workers.
- This means that the presence of a cylinder spindle significantly increases the cost of the machine, and therefore its market value. As a rule, the presence of such components in equipment complicates its maintenance. What then is the point of using rotary machines?
— The presence of a rounding spindle does make the machine more expensive, but here you need to clearly understand what you are investing in. If an enterprise wants to produce parts for house construction in small quantities (for example, for its own needs, or to fulfill single orders for picky customers), then, of course, it is most reasonable to choose a lathe. But if you plan to organize the production of log house parts on an industrial scale, then you cannot do without a rounding spindle, because At the moment, only the presence of this unit in the machine makes it possible to implement the most productive type of through-processing of saw logs. Based on these considerations, rotary-type positioning machines are the most unprofitable option - with low productivity, they have a fairly high cost. Now about the difficulties in operation and maintenance of cylinder spindles. During operation, the operating and maintenance personnel are only required to correctly adjust the cutting tool mounted on the spindle faceplate and lubricate the spindle in accordance with the manufacturer's requirements. No work on assembling/disassembling the spindle itself is required - if the requirements for the selection of processed raw materials are met and the manufacturers' recommendations for the operation of rotary machines are followed, the service life of the spindle is 5 years or more (depending on operating conditions). After this period, you can overhaul the machine at the manufacturer and continue working. You can be sure that within such a period of time the pass-through machine will be able to recoup all the costs of its acquisition, operation and repair several times over.
— You said that a prerequisite for the correct operation of a through-rotary machine is the selection of raw materials. It is well known that fulfilling this condition is quite complicated, because the presence of longitudinal curvature and strong hardening of sawlogs significantly reduces its cost, which makes this raw material quite attractive from an economic point of view. As is known, positioning machines are not sensitive to these shortcomings of lumber, but a through-type machine will find such raw materials too tough. It turns out that throughput machines do not allow you to take advantage of cheap raw materials?
— This issue has already been discussed on the pages of the magazine “Spindle” No. 5 for 2006. in the article “Secrets of cylinder production.” In order not to repeat myself, I will answer quite briefly. First, I’ll make a clarification: at the moment there is no equipment that is absolutely insensitive to curvature and stiffness. When processing such saw logs on positional lathes, a greater number of passes of the cutter along the log are required, which reduces the already low productivity of these machines; when processing on rotary-type positioning machines, additional passes will also be required, as well as adjustment of the cutting tool before each subsequent pass. And as for the so-called “correction of curvature” with positioning machines - try to draw a curved log, fit a rounded log into its contour, taking into account the tolerances for the positioning of the log, and calculate the percentage yield. Taking into account the obtained percentage yield and processing time, calculate the cost of products made from this “economically attractive” raw material. I don’t think that the resulting cost will be radically different from the cost of products made from high-quality raw materials. And also about correcting the curvature. When processing curved logs on a positioning machine, uneven cutting of layers occurs in relation to the core of the sawlog. As a result, when drying, internal stresses will arise in the resulting log house part, which over time will lead either to reverse curvature of the part or to the formation of large cracks if the part has already been fixed in the log house by that time.
— Returning to the large number of manufacturers of cylindering equipment, are there any patterns in their geographical location?
— It’s probably too early to talk about patterns, but at the moment there are two regions that are leading in the number of manufacturers of cylindering equipment. The Udmurt Republic (mainly Izhevsk) is the leader in the number of manufacturers of positional lathes, and the Kirov region (mainly Kirov), the leader in the number of manufacturers of rotary type lathes.
— How can you explain this localization of manufacturers?
— I can’t say anything about the Udmurt Republic, I think it’s better to ask this question to one of the Izhevsk manufacturers, but as for the Kirov region, the matter is as follows. In Soviet times, in Kirov there was a SPKB “Furniture and Woodworking”, which was engaged in the development and implementation of non-standard equipment in the region. In the late 80s - early 90s, it was transformed into the ARKOS company, whose management decided to start manufacturing equipment for the production of rounded logs.
At that time, the production of such equipment in the USSR was carried out by the Tyumen Design and Research Institute of Forestry and Woodworking Industry. This institute developed positioning machines of the rotary type: the log was clamped in the centers and processed by a rotary head (A.S. No. 683910, 1978; A.S. No. 1052382, 1982). Another machine known at that time for producing rounded logs was the machine pass-through type (Germany). The machine produced a rounded log with a longitudinal groove in one pass.
The management decided to master the production of a more promising and productive through-type machine, although at that time the company only had experience in the production of round rod machines of the KPA-50 type. But despite this, the task was successfully solved: at the end of 1990, machine No. 637 C was manufactured (the number is the project number from the beginning of registration, the letter “C” is the machine). The machine was successfully tested and produced a rounded log with a longitudinal groove with a maximum diameter of a rounded log of 200 mm, just like its analogue.
A total of 37 machines of this type were produced with various upgrades. The design of the machine turned out to be workable, since technical solutions were adopted that were distinguished by their simplicity and originality, namely: the absence of hydraulics and pneumatics; transmission of torque to the feeders through a chain and gears; synchronization of the convergence of the feed levers by gear sectors with the clamping of the latter by springs; fastening the tool holders to the faceplate (T-shaped groove); the use of toothed combs for fixing tool holders; design of tool holders, roughing and finishing knives. These design solutions turned out to be classic and were repeated in the machines, “Kamistankoagregat”, “STIN” (Ramstell).
Some machines, after their modernization (increasing the cylinder diameter to 240 mm), are still in successful operation.
During the operation of the 637C machines, their main drawback was revealed, which is also inherent in their analogue - the machine, namely, the twisting of the longitudinal groove on the log.
In 1991 a line for processing fine gauges was manufactured, consisting of two machines: a rounding machine 624C, which allows producing a smooth cylinder with a maximum diameter of 120 mm, and a milling and sawing machine 630C, which carried out longitudinal milling of the cylinder with subsequent sawing of the shaped profile into boards. About 10 lines of this design were produced. In 1993, the line was modernized and began to consist of a 651C rounding machine with a maximum cylinder diameter of 120 mm and a 652C milling and sawing machine.
The line was produced in this form until 1997. – the time of liquidation and formation, where it underwent another modernization, namely, an increase in the diameter of the rounded log to 140 mm, the use of two roughing and two finishing cutters on the rotor faceplate. A line appeared consisting of machines 663С and 655С.
In June 1999, a 668C machine with a maximum cylinder diameter of 180 mm was manufactured. A distinctive feature of the design was the combination of a rounding spindle, milling spindles and a saw spindle in one machine, which made it possible to obtain edged lumber from a log in one pass. The input part of the machine (feed cage with a log basing mechanism) and the rounding spindle are completely borrowed from the 663C machine. The output part of the machine had an original design, namely: the change in the center-to-center distance between the milling spindles was carried out through the eccentric bodies of the latter; support tables were introduced that were as close as possible to the shaped cutters; Rubber dampers are used to compress the levers of the exhaust ripples. The priority of authorship of the machine is confirmed by the Certificate for utility model No. 13881 of 1999.
After conversion in 2000. the authors of the machine went to work at Kirovvneshtorg Company LLC, where they launched the production of the Termit 200U machine with a maximum diameter of rounded logs of 200 mm. Only by the beginning of 2002 was it able to modernize the 668C machine, increasing the diameter of the rounded log to 200 mm and using a device for regulating the location of milling spindles of its own design, and began its expanded production. Although the design of the machine remained at the prototype level, the technical solutions of the prototype turned out to be so reliable that this machine is operating successfully. Although the design of the saw unit makes it difficult to meet the conditions for stable operation of the saw, described in the article “Why do circular saws burn” in the PROles magazine, March-April 2003 (what the authors of the prototype encountered when testing a prototype).
Along with this, it produced a 682C machine for house construction with a maximum cylinder diameter of 280 mm. The machine was a modernization of the obsolete 637C machine; due to the solid frame, difficulties arise during transportation and installation; the kinematics are completely repeated as on the prototype. Due to the large weight of the log and the weakness of the log clamping mechanism, it is necessary to use additional equipment for loading logs (it is suggested to place a 526T support roller in front of the machine).
Around 2002, it spun off, which began its activities with the production of machines for making crown cups, and began producing rounding equipment, advertising it through. The machines of this company completely repeat the design solutions.
Thus, in the city of Kirov there are now three manufacturers of rotary-type cylinder machines: “Sherwood”, “STIN”, and “Kirovvneshtorg Company” LLC.
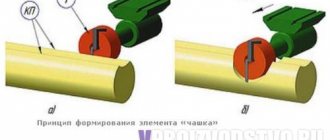
Machine for forming crown bowls
Crown bowl of a log house
The final stage of the work is considered to be milling the crown bowls. They are designed for installing log logs on top of each other. Additionally, they are used to make internal partitions of the house.
The formation of mounting elements occurs only in accordance with technical documentation. It indicates what shape the crown bowl should be in a particular place in the log house, its size and other additional parameters. In some cases, a log house of a non-standard shape may be erected. Based on the initial parameters of the technology for manufacturing mounting elements, there must be a function for changing the angle of inclination of the cutting mill. It can be located at an angle from 45 to 90 degrees.
Additionally, the following parameters are indicated in the machine settings:
- diameter of processed logs;
- forward and reverse feed speed;
- cutter rotation speed;
- power of the power plant.
Entry bushings must be made of special grades of steel and are a mandatory element of the machine equipment. Their shape directly affects the quality and degree of processing of logs for felling.
To increase the speed of work, it is recommended to purchase models of milling machines with a pneumatic clamping function.