Application and Description of Electromagnetic Rectangular Plate:
use in industrial production for fastening metal workpieces, parts made of ferromagnetic materials Fe, Co and Ni. Plates are often installed on metalworking machines, such as surface grinders, cylindrical grinders, and milling machines. The supply of lubricants during grinding does not affect the quality of fixation of the part to the surface of the plate. Our electromagnetic plates are manufactured in accordance with GOST, divided into standard and small-pole with different pole arrangements. Metal workpieces are fixed by the action of a magnetic field; the moisture resistance of the plate coating allows the use of lubricating fluid, for example, when operating an electromagnetic plate on a surface grinding machine.
Metalwork, page No. 43
Tools for grinding flat surfaces
When grinding, parts can be secured directly to the machine table using clamping bars. However, such fastening is used in cases where the parts cannot be fixed to a magnetic plate or other devices.
Pattern vices (Fig. 10.9a) differ from conventional machine ones in manufacturing precision and the ability to turn. The fixed jaw of the vice is integral with the base 1. The body has grooves for the passage of the movable jaw 2, which is moved by a screw 3. The base of the body has threaded holes for attaching the vice to various devices. All vise planes are machined at an angle of 90°. The pressed-in cylindrical measuring pin 4 is used to measure inclined planes.
Rice. 10.9. Pattern vice (a) and electromagnetic plate (b)
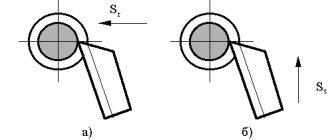
Electromagnetic plates . The design of the electromagnetic plate (Fig. 10.9b) is based on the following principle. If a wire is wound around an iron core (Fig. 10.10a) and a direct current is passed through it, the core will be magnetized. If you now bring a steel object to one of the ends of the core, it will be strongly attracted to the core. After the current in the winding stops, the magnetic action of the core will also stop.
You can bend such a core in the form of a horseshoe (Fig. 10.10b) and also pass current through its winding. In this case, the magnet will be even stronger. By combining horseshoe-shaped magnets into a group, we get an electromagnetic plate.
Rice. 10.10. Diagram of the magnetic action of current (a) and a horseshoe magnet (b)
The magnet poles located on the top of the plate are carefully insulated from its body with non-magnetic alloys (babbitt, zinc), due to which the magnetic forces are not dissipated in the body of the plate, but are directed directly into the body of the part. Only magnetic metals (for example, steel, iron, cast iron) can be attracted to the electromagnetic plate.
Electromagnetic plates are used in various sizes, round and rectangular. Only direct current is suitable for powering them, so machines are installed with devices that convert alternating current into direct current.
Electromagnetic plates provide reliable and quick fastening of the parts to be ground. To maintain the functionality of the plate, it is necessary to protect it from shocks and shocks, and also to ensure that no coolant gets on the windings. Upon completion of work, you should immediately wipe the working surface of the stove dry.
Magnetic plates
In addition to electromagnetic plates, magnetic plates with permanent magnets are used on grinding machines. This type of stove does not require special generators and rectifiers with wiring and distribution devices. However, as a rule, the force of their attraction is weaker than the force of attraction of electromagnetic plates.
The design of a rectangular magnetic plate and its operating principle are shown in Fig. 10.11. Its upper part is made of steel plates 1 with non-magnetic layers 2 between them (Fig. 10.11a). Strong permanent magnets 4 can be moved, closing them either to the iron plates or to the part being fixed. In Fig. 10.11b shows the position of the magnets when fastening parts 5, and in Fig. 10.11c – during their removal or installation. The magnets are switched using handle 3. The lower part of the plate 6 is fixed on the machine table.
Rice. 10.11. Magnetic plate:
a – general view; b – position of the magnets when securing the part; c - the same when installing and removing the part
Segmented grinding wheels for grinding flat surfaces
Surface grinding with solid grinding wheels of large diameter is economically unprofitable due to large waste, increased heat generation and the possibility of breakage during transportation. In addition, if a crack appears or partial destruction of the wheel, it is necessary to replace it entirely and lose a significant amount of usable abrasive material. These inconveniences are eliminated when using wheels made from inserted abrasive segments (Fig. 10.12). If one or more of them breaks, such segments can be easily replaced with new ones.
The insert segments are used until they are almost completely worn out. By releasing 1 clamp, you can remove 2 segments at once. As they wear, the height of the segments decreases, so spacers are placed under them.
Rice. 10.12. Segment grinding
Machining thin parts
Grinding thin parts on the magnetic table of a surface grinding machine requires preliminary preparation of the base planes (Fig. 10.13). The concavity or convexity of the plane of such parts, formed after planing or milling, cannot be eliminated by conventional installation of them on a magnetic plate. Magnets, attracting the part, straighten it, and after removing it from the table, the part again takes its original shape.
Rice. 10.13. Installing thin plates on a magnetic table:
a – convex down; b – convex upward
Sheet parts are especially susceptible to warping. The direction of their bending is always the same, and the concavity is formed from the side of the grinding wheel. The best way to prevent warping is to remove equal layers of metal from both sides of the record. The plate becomes straight or slightly curved. To maintain parallelism of the planes of such parts, grinding must be carried out as follows. The part is laid with the convex upwards and ground until straight, then the processed plane is turned down and the size is maintained from it. Since the first surface will also receive a slight convexity, you have to make several passes and turn the part over several times.
Quality control of treated surfaces
To control the size of parts and the correctness of their shape during surface grinding, various tools are used. Dimensions are measured mainly with micrometers, staples and minimeters.
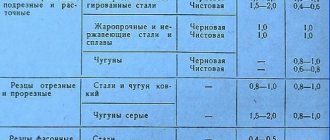
Flatness is checked with a sharp edge of a straight edge applied to the controlled plane, and the size of the gap between them is observed. The amount of clearance is measured with a probe. Parallelism between external planes is checked with a micrometer or other measuring instruments. The parallelism of the internal walls is measured depending on the specified accuracy using a template, gauge blocks and an optimeter.
The perpendicularity of the planes forming internal and external right angles is controlled by squares. The angular profile, depending on the accuracy, is measured with angular measures (accuracy 1′), protractors (accuracy 2′), universal and optical protractors (accuracy 5′) and, finally, templates.
Pages:
master4all.com
Modifications and types of electromagnetic plates for machine tools:
— rectangular electromagnetic plate, powered by a DC source, table mirror dimensions from 100mm*250mm to 630mm*2000mm. Can be used when supplying coolant and emulsion.
— electromagnetic small-pole plate with a transverse arrangement of poles, interpolar distance 15 (3+12), 28 (15+2+11), 4 (1+3), 2 (1.5+0.5).
— electromagnetic small-pole plate with a longitudinal arrangement of poles, high accuracy and tightness.
Electromagnetic rectangular plate PE7208-0057 (200x320mm) price – 47,000 rubles.
Electromagnetic rectangular plate PE7208-0060 (200x630mm) price – 50,000 rubles.
The stove is new, all components are made in Russia, 2-year warranty, quality complies with GOST.
Homemade device options
The Internet contains a sufficient number of different designs created for various purposes. Take a small-sized induction heater made from a 250-500 W computer power supply. The model shown in the photo will be useful to a master in a garage or car service for melting rods made of aluminum, copper and brass.
But the design is not suitable for heating premises due to its low power. There are two real options on the Internet, whose tests and work are filmed:
- water heater made of polypropylene pipe powered by a welding inverter or induction kitchen panel;
- steel boiler heated by the same hob.
Now let's take a closer look at how to make induction heaters with your own hands, and most importantly, how they then function.
We make a heating element from a pipe
If you have been actively searching for information on this topic, you have probably come across this design, since the master posted its assembly on the popular YouTube video resource. After which many sites posted text versions of making this inductor in the form of step-by-step instructions. Briefly, the heater is made like this:
- Inside a polypropylene pipe with a diameter of 40 mm and a length of 50 cm, metal dishwashing brushes are pushed (chopped wire - wire rod can be used). They must be attracted by a magnet.
- Threaded bends are soldered to the pipe for connection to the heating network.
- On the outside, 4-5 PCB rods are glued along the body. A wire with a cross section of 1.7–2 mm² with glass insulation, used in welding transformers, is wound on them.
- The hob is disassembled and the “native” flat-shaped inductor is dismantled. Instead, a homemade pipe heater is connected.
As you might guess, the role of the heating element here is played by metal brushes located in the alternating magnetic field of the coil. If you run the hob at maximum, while simultaneously passing running water through an improvised boiler, you can heat it up by 15-20 °C, as tests of the unit have shown.
Since the power of most induction cookers is in the range of 2-2.5 kW, using a heat generator you can heat rooms with a total area of no more than 25 m². There is a way to increase the heating by connecting an inductor to a welding machine, but this has its own difficulties:
- The inverter produces direct current, but alternating current is needed. To connect an induction heater, you will have to disassemble the device and find the points on the diagram where the voltage has not yet been rectified.
- You need to take a wire of a larger cross-section and select the number of turns by calculation. As an option, copper wire Ø1.5 mm in enamel insulation.
- It will be necessary to organize cooling of the element.
The author demonstrates checking the performance of an inductive water heater in his video presented below. Tests have shown that the unit requires improvement, but the final result, unfortunately, is unknown. It looks like the craftsman left the project unfinished.
How to assemble an induction boiler
In this case, there is no need to disassemble the cheap Chinese stove. The point is to weld a boiler tank according to its dimensions, following step-by-step instructions:
- Take a steel profile pipe 20 x 40 mm with a wall thickness of 2 mm and cut blanks from it to the width of the panel.
- Weld the tubes together lengthwise, joining the smaller sides.
- Weld iron caps hermetically at the top and bottom to the ends. Make holes in them and install threaded pipes.
- Attach 2 corners to one side by welding so that they form a shelf for the induction stove.
- Paint the unit with heat-resistant spray enamel. The assembly process is shown in more detail in the video.
Final assembly and commissioning consists of mounting the boiler on the wall and inserting it into the heating system. The hob is inserted into the socket from the corners on the rear wall of the tank and connected to the mains. All that remains is to fill the system with coolant, bleed the air and turn on the inductor heating.
Here you are faced with the same problem that occurred with the previous model. Undoubtedly, induction heating will work, but its power of 2.5 kW is enough to heat a couple of small rooms when it’s freezing outside. In autumn and spring, when the temperature has not dropped below zero, a homemade boiler can heat an area of 35-40 m². How to properly connect it to the system, see the next video:
Design and operating principle of the electromagnetic plate:
we can make a slab to suit the size of the desktop, the width of the slab varies from 100mm to 630mm, length from 250mm to 2000mm. When connected to a constant power supply, there is an attractive force of at least 60 N per square centimeter. There is a requirement for the minimum dimensions of the installed workpiece; they range from 10-20 mm in the longitudinal and transverse directions. To order, we produce small-pole slabs with a transverse or longitudinal arrangement of poles, the design becomes more complex and more expensive, the client can choose the interpole distance: 4mm, 15mm, 28mm. Due to increased moisture resistance and build quality, the service life of magnetic plates is 10 years. The stove is powered from a constant current source, standard voltage 110V. Basically, rectangular electromagnetic plates are installed on surface grinding machines; when processing a part, the supply of lubricating fluid is turned on; it does not affect the quality of fixation of the workpiece to the plate, nor does it affect the durability of the structure. Connection requires a 110V DC power supply. Plates with transverse poles have increased attractive power compared to conventional ones, and it is also convenient to secure small workpieces.
What is a magnetic plate?
Magnetic plates are a special type of equipment for milling machines, which is needed for processing metal elements, which is necessary for fixing metal elements on the working surface of the machine under the influence of electromagnetic attraction.
Before their appearance, cams were actively used to hold workpieces, which ensured maximum retention during operation. But still, magnetic plates have a number of more outstanding advantages compared to cams:
- there is an alternative to processing several workpieces at once;
- the maximum precision of the impact is ensured, which is associated with the phenomenon of heating the metal part. It expands, but does not deform like a part in clamps;
- provide high reliability of fastening;
- maintain basic performance characteristics at the original level for the entire period of use;
- do not require annual (or more often) technical inspection and repair activities.
But these devices also have disadvantages:
- not used in work that requires high cutting force;
- residual magnetism of workpieces made of steel, but a demagnetizer will help cope with this feature.
Reference! Demagnetizer (demagnetizer) - is necessary to deprive the attractive forces of a tool or workpiece so that metal shavings do not stick to it. Magnetic plates are most often used on grinding, milling and lathes for processing metal-containing products.
Important!
Magnetic plates are very rarely included in the basic equipment of the machine, so they must be purchased and installed separately, taking into account the necessary parameters of the product.
Technical characteristics and accuracy parameters of electromagnetic rectangular plates:
| Length, mm | from 250 to 2000 |
| Width, mm | from 100 to 630 |
| Nutrition | 110V |
| Height, mm | 100 – 120 |
| Attractive force per 1 cm2, N | 60 – 80 |
| Minimum part dimensions, mm | 10x10*2 |
| Execution according to GOST | 30273-98 |
| Flatness of the slab base, microns | 8,0 |
| Flatness of the working surface of the plate, microns | 10,0 |
| Parallelism of the working surface to the base, µm | 10,0 |