Application
So, let's start with the most obvious, in our opinion, but no less important question, namely, what 20khn3a steel is used for. Most often, parts are made from this type of steel, which are subsequently subjected to a carburizing process. This means that such parts will need to combine surface hardness and internal plasticity in the future.
Such requirements are usually imposed on products that, during their operation, will in one way or another be subject to loads, including shock. In this case, the hard surface layer will prevent deformation of the part, and the inner soft layer will take on all the physical consequences of the impact and absorb them without harm to the part. This category includes shafts, studs, bolts, gears and bushings, and much more.
Steel grade 20ХН
General information| Type of delivery |
| Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 4543-71, GOST 259071, GOST 2591-71, GOST 2879-69. Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 1051-73. Polished rod and silver 14955-77. Strip GOST 103-76. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71. Pipes OST 14-21-77. |
| Purpose |
| Gears, bushings, fingers, fasteners, and other parts that require increased viscosity and moderate hardenability. |
Chemical composition
| Chemical element | % |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.17-0.37 |
| Copper (Cu), no more | 0.30 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.40-0.70 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 1.00-1.40 |
| Phosphorus (P), no more | 0.035 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0.45-0.75 |
| Sulfur (S), no more | 0.035 |
Mechanical properties
| holiday t, °С | s 0.2, MPa | s B, MPa | d5,% | y, % | KCU, J/m 2 | HRC uh | ||||||||
| Sample with a cross section of 10 mm. Hardening 850 °C, oil. | ||||||||||||||
| 200 | 1050 | 1290 | 11 | 48 | 90 | 62 | ||||||||
| 300 | 1000 | 1220 | 50 | 80 | 60 | |||||||||
| 400 | 910 | 1100 | 11 | 51 | 75 | |||||||||
| 500 | 770 | 950 | 14 | 54 | 110 | |||||||||
| 600 | 650 | 770 | 20 | 60 | 180 | |||||||||
Mechanical properties depending on the section
| Section, mm | s 0.2, MPa | s B, MPa | d5,% | KCU, J/m 2 | ||||||||||
| Hardening 860 °C, oil. Vacation 180 °C. | ||||||||||||||
| 20 | 750 | 1130 | 10 | 85 | ||||||||||
| 40 | 600 | 990 | 10 | 90 | ||||||||||
| 80 | 520 | 870 | 10 | 90 | ||||||||||
| 100 | 510 | 860 | 10 | 90 | ||||||||||
Mechanical properties of the rod
| Section, mm | s 0.2, MPa | s B, MPa | d5,% | y, % | KCU, J/m 2 | |||||||||
| Quenching 860 °C, water or oil. Quenching 760-810 °C, water or oil. Holiday 180 °C, water or oil. | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | 590 | 780 | 14 | 50 | 78 | |||||||||
Technological properties
| Forging temperature |
| Started 1250, ended 830. [108]. Sections up to 50 mm are cooled in air, 50-100 mm in a mold, 101-200 mm in a closed mold. |
| Weldability |
| limited weldability. [2]. |
| Tendency to release ability |
| inclined [81] |
| Flock sensitivity |
| sensitive [81] |
Critical point temperature
| Critical point | °C |
| Ac1 | 735 |
| Ac3 | 805 |
| Ar3 | 790 |
| Ar1 | 660 |
| Mn | 410 |
Impact strength
| Delivery condition, heat treatment | +400 | +300 | +200 | +20 | -20 | -50 |
| Hardening, high tempering. | 68-72 | 91-94 | 44-46 | 81-89 | 62 | 43 |
Hardness
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | HRC e surfaces | NV |
| Normalization 860 C. Cementation 910 C, 16 hours to a depth of 1.6-1.8 mm. | 262-290 | |
| Cool in air to 860 C, then oil. Hardening 770-780 C. Tempering 190 C. | 59-62 |
Endurance limit
| s -1, MPa | n | s B, MPa | s 0.2, MPa | Heat treatment, steel condition |
| 320 | 20E+6 | Sample 6 mm in diameter, smooth. Normalization 880C. Holiday 650-670 C. | ||
| 210 | 20E+6 | 550 | 340 | Specimens with a diameter of 6 mm with a notch R=1mm. HB 170 |
Hardenability
| Distance from the end, mm / HRC e | |||||||||||
| 3 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | ||||
| 36.5-47.5 | 34-44.5 | 28-41 | 23-35.5 | 20.3-32 | 19-32 | 17.5-30 | 17.5-28 | ||||
| Quantity of martensite, % | Crit.dia. in water, mm | Crit.dia. in oil, mm | Crete. hardness, HRCе |
| 50 | 33-52 | 12-28 | 31-37 |
| 90 | 23-34 | 6-14 | 38-43 |
Steel Cementation
And since we mentioned the carburization of steel 20khn3a, it’s worth telling you, albeit briefly, about what this process is. The very essence of the process is to saturate obviously low-carbon (usually up to 0.2% C) steel with this same carbon, thereby giving it hardness. However, one must understand that such a process will carbonize only the surface layer of the metal product in the range from 0.5 to 2 millimeters, leaving the middle soft and pliable.
The carburization process itself, which gives 20khn3a steel the characteristics of increased strength, occurs at elevated temperatures (850-950 °C) in a carbon-containing environment. Enterprises usually use gas carburization using methane or carbon monoxide, but a similar procedure can be carried out using charcoal or sodium carbonate solution.
When heated to the above-mentioned temperature, steel enters the active phase and absorbs carbon from the external environment. However, this process is quite slow. To carburize a layer of one millimeter, it takes from 4 to 10 hours, depending on the carburization method.
Legend
Mechanical properties
| HB | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| MPa | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa |
| Brinell hardness | Impact strength | Relative narrowing | Elongation at break | Yield strength | Short-term strength limit |
Chemical composition
As is known, the characteristics of absolutely all grades of steel depend primarily on the alloying elements in its final composition. It is the addition of chemical elements that ultimately gives steel the necessary properties, be it hardness or, conversely, ductility, resistance to corrosion or shock loads. This is why it is sometimes so important to study the composition of steel. The easiest way to do this is to look at the corresponding GOST. Steel 20khn3a is mentioned in many GOST standards, therefore, in order to make your search easier, we will provide a list of all elements and the values of their mass fraction in the composition of the steel right in this article.
It looks like this:
- Carbon – 0.2%.
- Chromium – 0.75%.
- Nickel – 2.95%.
- Manganese – 0.45%.
- Silicon – 0.27%.
- Copper – 0.3%.
- Sulfur and phosphorus – 0.025%.
Structural alloy steel 20ХН
Brand 20ХН – purpose
Structural alloy chromium-nickel steel 20ХН is used for the manufacture of parts with moderate hardenability and high toughness - hexagons, circles, squares, strips, bushings, gears, fasteners, pins, and other products.
Steel 20ХН - domestic analogues
| Rolled metal grade | Substitute |
| 20ХН | 15ХР |
| 18ХГТ | |
| 20ХНР |
Characteristics
| Brand | GOST | Foreign analogues | Classification |
| 20ХН | 4543–71 | There is | Alloy structural steel |
Material 20ХН – technological properties
| Flock sensitivity | Weldability | Tendency to temper brittleness |
| sensitive | restricted welding | inclined |
Brand 20ХН – chemical composition
Mass fraction of elements no more than, %:
| Silicon | Manganese | Copper | Nickel | Sulfur | Carbon | Phosphorus | Chromium |
| 0,17–0,37 | 0,4–0,7 | 0,3 | 1–1.4 | 0,035 | 0,17–0,23 | 0,035 | 0,45–0,75 |
Steel 20ХН – mechanical properties
| Assortment | GOST | Dimensions – thickness, diameter | Heat treatment | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| mm | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa | |||
| Bar | 4543–71 | 15 | Hardening. Vacation | 780 | 50 | 14 | 590 | 780 |
Material 20ХН – hardness, MPa
| Assortment | GOST | HB 10-1 |
| Rolled after annealing | 4543–71 | 197 |
Brand 20ХН – temperature of critical points, 0С
| Critical points | Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar1 | Ar3 | Mn |
| Temperature | 735 | 805 | 660 | 790 | 410 |
Steel 20ХН – impact strength, J/cm2
| Heat treatment | KCU at temperatures | |||||
| -500WITH | -200WITH | +200WITH | +2000WITH | +3000WITH | +4000WITH | |
| Hardening. High holiday | 43 | 62 | 81–89 | 44–46 | 91–94 | 68–72 |
Material 20ХН – exact and closest foreign analogues
| Italy | USA | Sweden |
| UNI | — | SS |
| 18NiCrMo5 |
Characteristics
All the basic properties of any steel grade are inevitably studied, further checked and ultimately entered into a regulatory and technical document, that is, GOST. For example, in order to better understand the topic of the article and the topic of metallurgy in general, we advise you to pay attention to GOST 8479-70, as well as GOST 4543-71, 7417-75 and 103-2006. While studying these documents, you will most likely come across incomprehensible terms and designations, which you would also do well to familiarize yourself with so that studying such documents is not so difficult.
However, we are a little distracted from the topic. Since we have already become familiar with the chemical composition of 20khn3a steel, we can quite accurately determine its main properties. This steel, thanks to the admixtures of nickel, chromium and copper, is endowed with good corrosion resistance, which is very important for many parts made from this type of steel. In addition, the increased nickel content increases hardenability, which will undoubtedly facilitate the carburization process.
Carbon is primarily responsible for hardness here, which, undoubtedly, is extremely small to ensure the initial hardness of 20khn3a steel. Silicon and chromium improve the situation slightly, but their effect on the strength and hardness of steel is extremely insignificant.
Properties of steel grade 20ХН3А
The specific gravity of the material is 7850 kg/m3. The final product made of steel of this grade undergoes heat treatment in the form of quenching and tempering.
The primary forging temperature reaches 1220°C, the final temperature is 800°C. Workpieces with a cross-section of up to 100 mm are cooled in the open air. With a cross section of more than 101 mm, the part is cooled in special pits.
The Brinell hardness of the material reaches 10 -1 = 255 MPa. Critical points are reached at temperatures:
- Ac1 = 730°
- Ac3(Acm) = 810°
- Ar3(Arcm) = 700°
- Ar1 = 615°
- Mn = 340°
Machinability is available in the hot-rolled state, with a Brinell hardness of 177 units and a tensile strength of 610 MPa.
The material is classified as having limited weldability. The following welding methods are available for it:
- manual arc (RDS);
- argon-arc submerged arc (ASA).
The alloy is flake-sensitive and has a tendency to temper brittleness.
Characteristics of material steel 20ХН3А
| Brand: | 20ХН3А |
| Substitute: | 20KhGNR, 20KhNG, 38ХА, 15Kh2GN2TA, 20KhGR |
| Classification: | Alloy structural steel |
| Application: | Gears, shafts, bushings, power pins, bolts, couplings, worms and other cemented parts, which are subject to the requirements of high strength, ductility and toughness of the core and high surface hardness, operating under shock loads and at low temperatures |
Chemical composition in % of material 20ХН3А
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 0.17 — 0.24 | 0.17 — 0.37 | 0.3 — 0.6 | 2.75 — 3.15 | up to 0.025 | up to 0.025 | 0.6 — 0.9 | up to 0.3 |
Temperature of critical points of material 20ХН3А
| Ac1 = 730, Ac3(Acm) = 810, Ar3(Arcm) = 700, Ar1 = 615, Mn = 340 |
Mechanical properties at T=200C of material 20ХН3А
| Assortment | Size, mm | Eg. | sв, MPa | sT, MPa | d5, % | y, % | KCU, kJ/m2 | Thermal change |
| Bar | F 15 | 930 | 735 | 12 | 55 | 1080 | Quenching and tempering |
| Hardness of material 20ХН3А after annealing | HB 10-1 = 255 MPa |
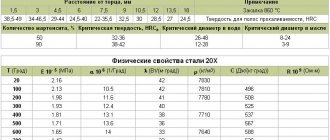
Physical properties of material 20ХН3А
| T, Grad | E 10-5, MPa | a 106, 1/Grad | l, W/(m deg) | r, kg/m3 | C, J/(kg deg) | R 109, Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.12 | 36 | 7850 | 270 | ||
| 100 | 2.04 | 11.5 | 35 | 7830 | 494 | 300 |
| 200 | 1.94 | 11.7 | 34 | 507 | 350 | |
| 300 | 1.88 | 12 | 33 | 7760 | 523 | 450 |
| 400 | 1.69 | 12.6 | 33 | 536 | 550 | |
| 500 | 1.69 | 12.8 | 31 | 565 | 650 | |
| 600 | 1.53 | 13.2 | 31 | 7660 | 586 | |
| 700 | 1.38 | 13.6 | 30 | 624 | ||
| 800 | 1.32 | 11.2 | 28 | 703 |
Technological properties of material 20ХН3А
| Weldability: | limited weldability |
| Flock Sensitivity: | sensitive |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | inclined |
Designations
Mechanical properties:
| sв | Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
Physical properties:
| T | Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [degrees] |
| E | Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 200 - T), [1/degree] |
| l | Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | Specific heat capacity of the material (range 200 - T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
Weldability:
| No limits | Welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment |
| Limited weldability | Welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment |
| Difficult to weld | To obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing |
Manufacturing and properties of the most common products made of steel 20ХН3А
Rods GOST 4543-71
These parts are hardened in oil at a temperature of 820°C, then they are tempered in water or oil at a thermometer reading of +500°C. The cross-section of such products is 15 mm. The conditional yield strength reaches 735 MPa.
The parts are quite durable. Their temporary tensile strength can withstand up to 930 MPa. Relative elongation after rupture can reach 12%, narrowing – 55%.
Forgings GOST 8479-70
These products are hardened and tempered. Their cross-sectional diameter reaches 100 mm. The proof strength varies from 590 to 685 MPa. The ultimate tensile strength of products occurs at 735-835 MPa. The relative elongation of the walls of the product after rupture is 13-14%, narrowing 42-45%.