In plastic injection molding, two main methods are used - injection and intrusion. All the rest are essentially their developments and variations in order to obtain better quality parts of complex configurations, multi-layer and multi-color products.
Types of injection molding
About this method of polymer processing
Plastic injection molding (PIM), along with extrusion, is the most common and studied method for processing plastics into finished or semi-finished products. Unlike extrusion, this method allows you to immediately obtain a part of specified dimensions and almost any geometry (with some limitations - see below). Casting is used mainly in the production of thermoplastic products, however, this processing method is also encountered from time to time for thermoset plastics. If the equipment for processing thermoplastics is called an injection molding machine (TPA), then thermosets are processed on thermoset machines, which are structurally different from TPA. In general terms, the equipment for this production method is often simply called an “injection molding machine.”
The casting pressure developed by injection molding machines is in the range of 80-140 MPa (800-1400 bar), however, leading companies and specialists in the manufacture of tooling (molds) do not recommend loading molds with pressure significantly higher than 100 MPa.
Plastic processing by injection molding is carried out on injection molding machines of the piston or screw (screw) type, and the first type of injection molding machine was until recently considered obsolete and out of use. However, after 2010, injection molding machine manufacturers returned to interest in piston plastic injection as the most accurate process. However, as a rule, modern equipment is screw-based, and the injection machine injection unit consists of a pair of screw-material cylinder.
Video 1. Operation of a modern injection molding machine
Basic casting technologies
There are three main plastic injection technologies:
- Extrusion or injection molding. One of the most common technologies. Among its disadvantages, it is worth noting the high cost of injection molding machines; also, competent organization of the technological process requires special education.
- Blown. Used for making hollow products. For example, plastic bottles and other containers. The essence of this technology is that the polymer is first heated to a certain temperature and then blown onto a cooled mold.
- Thermoforming. This technology involves the use of compressed air or pressing. Most often, disposable tableware and food packaging are made using this method.
Applications of injection molding
Plastic molding has been used for more than half a century and allows for mass production of plastic parts weighing from hundredths of a gram to tens of kilograms. The smallest products can be, for example, microscopic lenses, components of small mechanisms, etc. The largest are various containers, including tanks and boxes with a volume of several cubic meters, plastic pallets, structural elements, etc.
Products obtained by the described processing method, in addition to their obvious advantages, have several limitations. In addition to the obvious limit on overall geometric dimensions due to the limited dimensions of the mold, there are several less noticeable ones. For example, the wall thickness of any product usually does not exceed a few millimeters. This is important for the economics of the process, because an increase in wall thickness leads to a sharp lengthening of the production cycle and a corresponding increase in cost and decrease in productivity. This limitation is removed when using a special method - gas casting (see below). On the other hand, the pressure of the injection molding equipment may not be enough to produce parts that are too thin-walled or very long. In addition, the product must be technologically advanced, that is, comply with the described method. Its design should assume a more or less equal-thickness structure, uniform filling with the polymer melt and simple, in most cases automatic, removal from the mold cavity.
Injection method
The name comes from the Latin word inject, which means to inject. During molding, plastic mass is injected into a casting mold and hardens there. During solidification, in order to obtain the required strength of cast products, it is necessary to maintain a certain compression. To meet this requirement, the process must proceed quickly so that all corners of the cavity can be filled before the mixture begins to solidify. This is a prerequisite for achieving high-quality molding. In this way, parts with different wall thicknesses and fine surface relief are obtained.
When producing large castings with thin walls, the viscosity of the melt may prevent it from flowing normally at the pressure required to ensure quality. In this case, it is recommended to apply the mixture into the cavity simultaneously from several points - through different gates. Sometimes several injection units may be used for this purpose.
This increases the cost of equipment and is justified in large-scale and mass production. For example, the production of plastic interior panels in the automotive industry.
The components are injected into the mold from the so-called material cylinder (LM), the force is created by the piston. The volume is initially calculated so that the melt completely fills the cavity and gating system.
Operating principle of injection molding machine
The injection molding machine loads granular (much less often powdered) polymer from the raw material loading hopper into the loading zone of the material cylinder. Then, by heating and plasticizing (mixing) the molten mass with a screw, it transforms into a viscous-flowing (close to liquid) state. After collecting the required dose of polymer, the injection molding machine, using the force created by a hydraulic cylinder, injects molten plastic into the mold. Then, in its cavity, the casting is kept under pressure and the cooling stage (for thermosets - hardening).
During the last stage of the production cycle, the machine opens the mold and pushes out the finished product; less often, the products are removed by the operator (semi-automatic mode). Modern production units include, in addition to injection molding machines, various automation equipment, usually called “robots”. Modern robots are involved in removing the casting from the mold area; they can also insert labels and embedded parts into the tooling cavity, and, in addition, participate in the “further fate” of the molded part, for example, in its post-processing, laying and packaging.
Manufacturers of liquid plastic
Manufacturers of two-component plastics, mainly foreign:
- Cosmofen - German.
- CRYSTAL CLEAR – Smooth-On, USA.
- Liquid plastic of the PolyCast brand is produced in Italy.
- NATICAST-manufacturer Italy.
- EasyFlo –Polytek, USA.
- Axson F160 – Axson, France.
- PU plastic JETICAST 70 – China.
Russian manufacturers:
- Yaroslavl paint and varnish.
- Novosibirsk LLC "TECHNOCENTER" - Sofradecor.
- Silagerm 4010 – PRODUCTION ASSOCIATION “TECHNOLOGY-PLAST”.
- Liquid PVC TN – “TechnoNikol”.
The use of one-component liquid plastic allows you to reliably protect structures from negative influences, and the use of two-component liquid plastic allows you to create unique products with your own hands.
Features of working with injection molding equipment
When processing thermoplastics, the temperature of the mold should not be higher than the glass transition temperature of the polymer or its crystallization temperature, therefore, mold cooling or thermostatting must be used. In thermoset processing, on the other hand, the mold is heated using various methods to a temperature above the curing point of the thermoset plastic.
Figure 2. Form installed on the injection molding machine
When making molds, it is important to remember the need to organize ventilation channels (evaporations), through which the molten mass, with its pressure, must displace air from the cavity of the technical equipment. The lack of fumes leads to numerous difficult-to-remove defects in finished plastic products.
Molds for plastic injection can be hot runner or cold runner. Hot runner molds are more modern, characterized by the absence or minimal amount of waste (gates), faster production cycle times, stable technological processes and less waste. The hot runner system transfers injection pressure to the mold area with minimal loss. However, hot runner molds are not recommended for processing some non-heat-resistant plastics, such as rigid PVC compositions.
Figure 3. Hot Channel Control Device
Features of the use of various polymers
For plastic injection molding, different components are used that differ in physical parameters.
Low density polyethylene
LDPE is characterized by rapid melting. After cooling, it crystallizes and changes hardness. It is necessary to maintain a certain pressure and ensure the most uniform heating of the mold. Therefore, for cooling, water inlet is provided near the gating nozzles, and outlet is provided at a distant point. Filling with coolant is quick and the mold is well ventilated.
High Density Polyethylene
Compared to polyethylene NP, HDPE is characterized by better crystallization and a lower degree of fluidity in the molten form. Plastic molding of this type is widely practiced to produce products with thin walls, but at the same time sufficient structural rigidity is ensured.
Polypropylene
PP is characterized by crystallinity not exceeding 60%. The process is performed under reduced pressure and a fairly high plasticization temperature, which, depending on the type of material, can reach 280 ºC. The melt pressure is formed at a level of 140.0 MPa. The viscosity of the resulting mass is regulated by the shear rate and slightly depends on the temperature regime.
Polystyrene
PS is a material that, as a result of injection molding technology, is characterized by easy fluidity when molten. Allows the production of products that are characterized by structural rigidity and thin walls. The polymer is sensitive to overheating.
Impact-resistant polystyrene
UPS is a polymer that has a slightly higher viscosity than regular polystyrene and shrinks more when cooled. Used for thin-walled parts with increased resistance to mechanical stress.
Acrylonitrile butadione styrene plastic
ABS plastic is characterized by high viscosity in the molten state, is difficult to process and requires high pressure. It is used for the manufacture of parts with thin walls, but unlike, for example, polystyrene, ABS plastic has high rigidity and shock resistance.
Polymethyl methacrylate
PMMA makes it possible to obtain products of various shapes and configurations. It is characterized by low thermal stability and sensitivity to overheating with loss of physical parameters. Requires additional drying. The processing process requires precise temperature control. The peculiarity of the material is the formation of bubbles when injected into a cold mold, therefore the number of smooth transitions in it is minimized.
Polyvinyl chloride
PVC is widely used for injection molding because it is easy to process. The material is sensitive to temperature conditions and loses its properties when overheated. When in a molten state, it is characterized by instability and autocatalytic destruction, manifested in a different color shade. The color range can vary from ivory to cherry. To obtain all the properties of the polymer, it is necessary to carry out the plasticization process in a minimum time.
Polyamide
PA is a crystalline thermoplastic, characterized by hygroscopicity and good mass flow. When in a molten state, the volume increases by 15%. Due to the low thermal stability, the molding process for this type of plastic is completed in a minimum amount of time. Bubbles may form in the melt. The material requires additional time to dry thoroughly. The plasticization process is carried out at a pressure of 100 MPa. When filling injection molds, particle orientation is allowed.
Polycarbonate
PC is a heat-resistant polymer. It is characterized by high thermal stability and increased viscosity in the molten state, depending on the temperature. The mold is heated to a temperature of 100 ºС. Due to the increased hygroscopicity of the material, normal injection molding requires preheating in the cylinder of the injection molding machine and thorough drying.
Polyethylene terephthalate, polybutylene terephthalate and polyoxymethylene
PET, PBTF and POM are classified as polymers characterized by high thermal stability. The molding process for this type of plastic involves additional drying until the moisture content is reduced to 0.01%. In the molten state they have a medium viscosity, which decreases with decreasing temperature. To obtain thin-walled products, blowing with air is used.
Parameters of injection of polymer material for LPD
The pressure developed during injection of injection molding machines depends on several parameters:
- viscosity of the molten polymer,
- features of the gating system, in particular the presence of a cold or hot channel,
- mold designs,
- design of the plastic product and the melt inlet location.
The pressure in the mold during injection of the molten polymer mass increases as the mold cavity is filled and the casting is further exposed. In this case, as a rule, the value of the specified holding pressure reaches 30-50 percent of the specified parameter value. These parameters on modern injection molding machines are set in the control system and implemented using the hydraulic (less often the most modern - electric) system of the injection molding machine.
Liquid plastic how to use
When using Cosmofen, the composition is applied to a cleaned and degreased surface. From the tube you need to squeeze the required amount of glue onto the junction of the plastic parts in a thin, even layer. You can smooth out the glue with a finger soaked in acetone, but first you must wear rubber gloves. But there is no need to try to rub it into the joint. The composition is applied in small sections 30-40 cm long to prevent rapid hardening of part of the seam.
Water-based material for wood processing is applied with a brush, roller, or spray gun; polyurethane enamel is also used for painting all other surfaces. In any case, the manufacturer indicates the methods of application on the packaging of the material.
It is difficult to say which liquid plastic is the best; it all depends on the area of application and the task being performed.
How to remove liquid plastic
If glue accidentally gets on the plastic parts of a double-glazed window, you can remove it with a thin blade and then clean the area with a special solvent.
Drops of aqueous liquid plastic can be easily cleaned with water before they dry. Dry paint particles can also be removed with the tip of a knife or similar tools.
On a metal surface, liquid plastic, if we are talking about Cosmofen, is removed using solvents, and its dried substance is easily removed in the form of a film, because the adhesion of this material to metal is zero.
Features of choosing an injection molding machine
Read more in the article Selecting an injection molding machine
When choosing a injection molding machine for plastic injection molding, first of all, the volume of the dose is taken into account, that is, the amount of polymer melt required to produce each specific product. Also important is the clamping force of the injection molding machine, the compression force necessary to fix the mold during the injection and holding stages. If the closing force is selected incorrectly, the mold will open slightly. The third most important parameter is the geometry of the area where the equipment is attached to the injection molding machine, namely the size of the machine plates and the distance between the columns, as well as the “mold height”. These values determine the maximum and minimum size of the injection mold for installation on a particular injection molding machine.
In addition to the indicated most important basic parameters for selecting injection molding machines, several more special ones are used, which are described in detail in specialized industry literature. For example, the value of the maximum injection speed, the load capacity of the injection molding machine plates (primarily the movable plate), the ratio of the screw length to its diameter L/D, the presence of an intrusion mode, etc. It is also important to equip the injection molding machine with various components and options. For high-speed machines, hydraulic accumulators for injection and other movements are used. To connect robots and other auxiliary devices, the injection molding machine controller should be equipped with Euromap 12 or Euromap 67 connectors. Actual melt pressure sensors, molded part drop sensors, and others are used.
Injection-press
Another variation that differs in the molding procedure. Initially, a heated plastic component is injected into the composite mold. The parts of the stamp are then compressed, compressing the mass and distributing it throughout the space.
This option is used for cases where high-quality filling of the extreme sections of the cavity is prevented by a drop in injection pressure. For example, a part has thin walls of large width; the viscosity of the melt prevents normal spreading.
This method requires the development of a press design that allows additional compression of the introduced composition after the parts of the stamp are closed.
Working on a vertical injection molding machine
This technology differs from the commonly used one in that a vertical type injection molding machine is used, and the mold also opens in the vertical direction. The method is good for small-scale production, because It is possible to use molds that are simpler and less expensive to manufacture. Vertical LPD is also widely used when using embedded elements (usually metal). The main disadvantage inherent in such casting is the complex automation of the process - products cannot fall out of vertical molds and they have to be removed manually or by robot.
Cascade casting (with shut-off valves)
This type of processing is gaining increasing popularity due to the fact that with relatively low investments it is possible to radically improve the quality of manufactured products. Cascade injection is possible only with the use of a special type of hot runner mold and differs from the standard one by the presence of a hot runner system with shut-off valves. The valves can be controlled pneumatically, hydraulically or, more recently, electrically and are carried out using special devices. The cascade allows you to control the injection of polymer into the mold at the request of the injection molding machine operator. In this way, it is possible to avoid adhesions, traces of flow of polymer material, burns and many other types of defects in LPD.
Application of liquid polymer
Molded plastic is often used as flooring. On its basis, the production of self-leveling floors has become widespread. This plastic has a number of distinctive qualities:
- versatility of use for any type of coating;
- ease of cleaning;
- strength;
- high waterproofing;
- resistance to aggressive liquids and environments;
- resistance to sunlight;
- aesthetics;
- Possibility of use in rooms with any temperature and humidity.
The use of liquid polymers in various activities
Flowable polyvinyl chloride compounds are used to seal polymer windows. Polyvinyl chloride, when introduced into window cracks, promotes rapid chemical welding with the plastic structure, resulting in a transparent, homogeneous structure.
Injection pressing
This technological process differs from the standard one in that the polymer material is injected into a slightly open mold (in this case it is appropriate to use this name for the equipment) a short time before its final closure. The final compaction of the polymer and the formation of the finished product are carried out when the mold is completely closed. Various products are made from both thermoplastics and thermosets using injection molding. The method is applicable in the case of insufficient characteristics of the injection molding machine for a given casting, in particular the clamping force. Also, the quality of such pressing on an injection molding machine is less dependent on the orientation of macromolecules during injection (anisotropy), which can improve the quality of the product in terms of less shrinkage (if necessary), better mechanical properties and less warping.
Intrusion
Intrusion is the process of partial filling of the forming cavity in extrusion mode due to the rotational movement of the screw. It is usually used for the production of heavy, material-intensive plastic products. Thus, it is possible to use injection molding machines with an injection volume that is insufficient for a given product, because the mold is filled not only due to the translational, but also due to the rotational movement of the screw in the initial position. For intrusion, it is important that the polymer material is sufficiently fluid and that the gating channels have a sufficiently large cross-section. It is also important to note that not all injection machines are equipped with an intrusion mode; it is necessary to check its availability in the machine specification.
Bicomponent and multicomponent injection
The essence of bicomponent and multicomponent injection molding is the use of two or more types of polymer, or the same plastic, but different colors, to produce one product on one injection molding machine. As a rule, in the case of this type of casting, injection molding machines with two or more plasticizing units are used (pairs of screw - material cylinder). First, the first component is injected into the mold, then additional cavities are opened in one way or another and the second component is injected, etc. In rare cases, components are supplied at the same time. When using bi- and multi-component (multi-color) plastic injection molding, technological equipment becomes much more complex. As a rule, molds with two or more separate hot runner systems are used. As for the possibilities of switching from one component to another, either rotary mechanisms are used directly in the mold, or the so-called “rotary table” as part of a bicomponent injection molding machine.
Advantages of the method
Polyurethane injection molding has a number of advantages:
- in the process of such manufacturing, a small percentage of defects is obtained;
- serial production possible;
- cheap material;
- it is possible to reuse the material, which reduces costs;
- no need for a foundry worker.
However, there are also disadvantages to plastic injection molding. One of them is the need to use only proven and high-quality equipment so that the method is economically feasible and cost-effective.
This disadvantage can be easily overcome if you find the right supplier. If you are looking for where to buy equipment for plastic injection molding, then contact us! is a supplier of reliable equipment for any production.
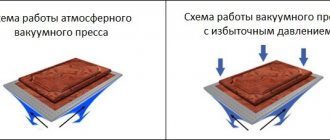
Gas casting
For the injection molding production of very thick-walled polymer products, almost the only suitable technology is gas injection. Plastic processing in this way is carried out on standard machines, but using adapted molds and a special module for generating gas injection connected to an injection molding machine. The essence of the process in the general case comes down to the delivery of an incomplete dose of polymer material into the forming cavity, followed by the injection of gas compressed under a pressure of 5-20 MPa into the melt mass through special injectors. The gas compacts the plastic “from the inside” and presses it against the walls of the mold. This produces a fully molded part with voids inside. Gas injection can be used, in particular, to compensate for sink marks when there is a large variation in product thickness. In addition, it is important that LDP with gas is produced at a reduced pressure of the melt in the mold, which allows the use of injection molding machines with lower clamping forces than with the standard process.
Molding of plastics into silicone - affordable small-scale production at home
Many of those who print on a 3D printer are faced with either the need to receive a batch of models in a short time, or to copy a successful part, or to obtain products with strength characteristics that exceed those of plastics for home 3D printing. A 3D printer is not always capable of performing such tasks, but it is perfect for creating a single sample, or master model. And then materials produced by Smooth-On, probably the most popular manufacturer of cold-curing materials, come to our aid.
In this review, we will compare the most basic and popular silicones, polyurethanes and additives to them, take a brief look at the main methods of creating molds and products, think about where this can be used and, finally, create your own silicone mold and model. Before writing this post, we completed a three-day training at the official Smooth-On dealer in Russia to understand all the intricacies of silicone casting.
Process overview
The process of creating products using the casting method is almost always the same: we create a model, use it to create a silicone mold, fill it with material, and get a product. But depending on the model, the required properties, and the number of castings, each stage can change dramatically. There are several ways to both create the mold and the finished product.
A few words about preparing 3D printed models. The company Smooth-On turned its attention to this technology and released a special varnish called XTC-3D. It perfectly smooths out the blemishes characteristic of printed models, visible layers that will definitely transfer to the silicone mold, and gives the surface a smooth and glossy appearance. You can read a detailed review of XTC 3D here.
Methods for creating forms
• Solid fill
The easiest way: the model is placed in formwork (a special sealed container made of ordinary plexiglass, plastic or other material), fixed in it and filled with silicone. Well suited for simple two-dimensional models, reliefs, souvenirs and branding products.
• Split shape
Similar to the previous one, only the model is placed taking into account that the form will be cut completely or partially to facilitate removal. The model can be suspended with wire or placed on a thin support. The method is intended for more complex geometry, technical products, and complex shapes.
• Two-piece form
This is one of the most difficult methods. It involves placing the model on a clay or plasticine base, which divides the silicone mold in half.
Special locks are placed on the base, which will ensure precise alignment of the two shapes and no displacement. The formwork is assembled around the base, sealed with hot glue or plasticine, and the first half of the mold is poured into it. Then, after the silicone has cured, the mold is turned over, the clay or plasticine is scraped off, the silicone is coated with a release agent, and the other half of the mold is poured.
• Spread method
This method creates so-called “stocking” molds, when silicone exactly follows the shape of the object and has a thickness from 3 mm to several centimeters. To create a “spreadable” mold, you need sufficiently viscous silicone that does not flow off the model. You can use either silicones specially designed for this purpose, called thixotropic, or regular ones, but modified with thickeners.
The silicone is applied with a brush or spatula in several layers, alternating viscosity and curing speed to ensure the shape is as detailed and durable as possible. Once all the layers are ready, a special compound is used to create a hard outer shell that will hold its shape.
Plastic pouring methods
The simplest method is simply pouring plastic into a mold; it is suitable for home use and allows you to achieve acceptable quality. But, if necessary, for a better result, it is possible to use high-pressure units, which will almost completely remove air bubbles.
To do this, the mold, together with the filled plastic, is placed in a chamber in which a pressure increased to 4 atmospheres is created. The mold must remain in the chamber while the polyurethane is curing. With this pressure, the bubbles are reduced to sizes almost invisible to the eye, which significantly improves the quality of the product.
Another method, the so-called run-in casting, is used to create hollow products. A small amount of plastic is poured into the mold, about 10% of the total volume, the filling hole is closed, and the mold begins to rotate along all planes, manually or on a special rotary machine. In this case, the plastic hardens on the walls of the mold, creating a hollow model, which can significantly reduce the weight of the product and save material.
Overview of silicones
• Mold Star Series 15, 16, 30 Silicones for creating molds based on platinum. They cure at room temperature and form a strong, flexible and highly detailed shape. Designed for casting silicone, polyurethane, resins, polyester, wax and other materials. Chemically sensitive and unable to work with latex, sulfur and some other compounds. The most basic and basic silicones, capable of solving most problems. The number in the name reflects the hardness on the Shore A scale. It has low viscosity, which allows in most cases to work without degassing equipment. The material is two-component, the parts are mixed in a convenient ratio of 1:1 by volume. Mainly intended for creating forms using continuous filling.
• Rebound 25, 40 series A series of silicones for creating molds using the “spread on” method, which consists of applying silicone with a brush or spatula to the surface of the model. It has high viscosity and the ability to modify properties using thickeners and accelerators to create a high-quality multilayer form. Two-component, mixed in a 1:1 ratio by volume.
• Equinox 35, 38, 40 series Silicone pastes with a lifetime of 1, 4 and 30 minutes. Designed for manual mixing, the consistency resembles thick dough. The numbers correspond to Shore A hardness. It has extremely high tensile strength and durability. When cured, it is safe for pouring chocolate, caramel and other ingredients.
• SortaClear Series 18, 37, 40 Series of translucent silicones. A feature such as optical transparency is used to create complex cut shapes - the product is perfectly visible, which allows you to make an accurate cut. Like the Equinox series, it is safe in contact with food. There are also a large number of additives for silicones that have a variety of effects. Accel-T and Plat-Cat are curing accelerators, Slo-jo - increases the life of silicone, Thi-Vex increases the viscosity of silicone and allows you to spread it with a brush or spatula on the model, Silc-Pig - these are concentrated pigments for painting.
Review of polyurethanes
• Smooth-Cast Series The most basic and popular series of polyurethanes for creating final products. The line includes more than 10 types of different plastics with a variety of properties, allowing you to choose the material specifically for your project. For example, Smooth-Cast 300 has a short pot life of 3 minutes and a cure time of 10 minutes, allowing you to quickly reproduce large batches of parts. Smooth-Cast 305 is similar to the previous one, but it “lives” for 7 minutes, which allows you to degas mixed components and get an even better product. ONYX has a deep black color that cannot be achieved with dyes, 65D ROTO is designed for creating hollow models using the “break-in” method, 325 is indispensable for accurate color reproduction, 385 cures with virtually no shrinkage and copies the product as accurately as possible.
• TASK Series A series of special-purpose polyurethanes. Designed for industrial use and has specific properties for specific tasks. For your convenience, we have created special filters by area of application:
• Food grade: Smooth-Sil 940, Sorta Clear series, Equinox series, TASK 11.
• Architectural, pouring concrete and other abrasive materials: VytaFlex Series, Brush-On Series, Ez-Spray Series, PMC Series.
• Medical: simulation of tissues and organs Dragon Skin Series, Slacker additives, Ecoflex 0030, Ecoflex Gel, Body Double.
• Prototyping: Almost any polyurethanes and silicones, depending on the tasks and requirements. Series Mold Max, Mold Star, Smooth-Cast, TASK.
• Special effects and makeup: Skin Tite, Body Double, Dragon Skin, Alja-Safe, Ecoflex, Soma Foama, Rubber Glass, Encapso K. It is worth noting that this division is still conditional, and is given to roughly imagine the capabilities of the wide range of the Smooth company -On.
Process overview
We will only use materials and equipment that can be used at home. We will try to create the most difficult two-part mold to manufacture.
We will need: • Platinum silicone Mold Star 30 • Polyurethane casting Smooth-Cast 300 • Varnish for 3D models XTC-3D • Pack of vinyl gloves • Several disposable plastic cups • Mixing containers • Hot glue gun • Formwork material (plastic panels) • Sculpting clay • Several paint brushes
The master model will be a model of a test bolt that is quite popular among printers. We printed it with black PLA plastic on Picaso 3D Designer with a layer thickness of 100 microns. We did this specifically to demonstrate the effect of XTC 3D, since not every 3D printer can print with a quality of 50 microns.
Next is processing so that the cast model does not take on the layering of the printed object. We treat the bolt with XTC-3D varnish (you can read more about this process here), and then sand it to get a smooth matte surface.
Now the model is ready to be filled with silicone. We place it on a clay base, with which we will create a silicone mold of two parts.
The model should be exactly half immersed in the clay, so we begin the process of leveling the clay. The edges should be as smooth as possible and completely adjacent to the model; the quality of separation of the silicone halves depends on this. We remove excess clay and enclose the model in plastic formwork.
We process all plastic joints with a hot glue gun and close the formwork, finally process the clay base, and make recesses in it for locks.
Everything is ready to pour silicone. Since two-component silicones and polyurethanes tend to separate into fractions, they must be thoroughly mixed in a container before each use. After mixing, measure out equal amounts of the two components by volume and begin mixing.
For this brand of silicone, degassing in a vacuum chamber is not necessary, which is very convenient: the appearance of bubbles that can ruin our shape is eliminated. Slowly pour silicone into the formwork, to its lowest point.
And leave it to harden. The curing time for this brand of silicone is 6 hours. After this time, we free the model from the formwork.
Then we remove the clay, thoroughly clean the model from its remains, and lubricate the silicone with a release agent. If it is unavailable, you can use regular Vaseline, but the quality will be slightly worse.
And then we repeat the process completely, filling the second half of the silicone mold.
After another 6 hours, the silicone mold is ready. Using a blade, we carefully separate the halves, take out the part and evaluate what we have done.
The locks that were laid in the clay base are clearly visible, there is good detail, despite the fact that the dividing line ran through rather difficult places, such as depressed letters.
In fact, for this model this is not the most optimal way to create the form. But we were interested in testing this particular method, despite the difficulties.
So, everything is ready to pour polyurethane. We connect the two halves of the form using formwork elements for rigidity, fasten them with rubber bands, tape or another method, and proceed to prepare the polyurethane.
Mix both components well, shaking them for 5-10 minutes. After this, let it sit for a while so that the bubbles that have formed come out. Everything else is exactly the same as with silicone: measure out equal amounts by volume and mix them. And then you need to act quickly: the lifetime of this polyurethane is only 3 minutes, and time begins to tick as soon as you mix the two components together. So we stir quickly, but carefully, so as not to create unnecessary bubbles, and immediately pour it into the mold.
After about 3 minutes, depending on the volume of material, the plastic will quickly set, and after 10 minutes the part is ready for removal.
The model is ready. Absolutely all details of the original are transferred.
Conclusion
I would like to note that the use of Smooth-On materials in combination with 3D printing opens up truly enormous possibilities. Now you can produce products from a huge number of materials with a wide variety of properties, and not be limited to just classic PLA and ABS. In addition, small-scale production will become available: by printing just one copy and properly processing it, you will be able to create the number of copies you need at home in a fairly short time. To achieve an acceptable result, it is not at all necessary to use expensive equipment.
If you need small-scale production services, Top 3D Shop is at your service.