In a general sense, iron ores are natural mineral formations that contain iron and its compounds in such quantities that industrial production of iron from the composition is profitable. An ore can be called iron if this metal accounts for a larger amount of the mass of the entire formation. The largest volume of production comes from magnetic iron ore.
- Career way
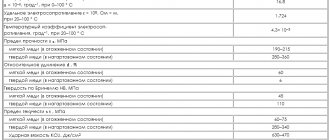
Chemical composition
The properties of iron ore, its value and characteristics directly depend on its chemical composition. Iron ore may contain varying amounts of iron and other impurities. Depending on this, there are several types:
- very rich, when the iron content in the ores exceeds 65%;
- rich, the percentage of iron in which varies from 60% to 65%;
- average, from 45% and above;
- poor, in which the percentage of useful elements does not exceed 45%.
The more by-products there are in iron ore, the more energy is needed to process it, and the less efficient the production of finished products is.
The composition of a rock can be a combination of various minerals, waste rock and other by-products, the ratio of which depends on its deposit.
Chemical composition of iron ores
Composition of iron ores of large deposits
Gap rock may also contain iron, but recycling it is not economically feasible. The most commonly found minerals are iron oxides, carbonates and silicates.
It should be noted that ferruginous rocks may contain a huge amount of harmful substances, among which are sulfur, arsenic, phosphorus and others.
Breed formation
If we consider iron as a chemical element, then it is part of various rocks. However, not all of them are used as raw materials for mining. Iron ore is usually called only those mineral formations that contain a certain amount of the mineral and its extraction is justified from an economic point of view. In nature, iron is distributed in the form of compounds with various substances.
People first began mining iron ore more than two thousand years ago. Thanks to this, it became possible to produce metal products that are more durable than copper ones. Depending on their origin, all minerals containing iron are usually classified into 3 groups:
- Metamorphogenic formations. They appeared on the site of old sedimentary deposits under the influence of high temperature and pressure.
- Exogenous. They formed in river valleys due to the influence of wind and water on rocks.
- Magmatogenous. They were created as a result of high temperature exposure.
It should be noted that these groups are divided into a large number of subspecies.
Types of iron ores
Today, there are many types of iron ores, the characteristics and names of which depend on the composition.
The most common type found in nature is red iron ore, which is based on an oxide called hematite. This oxide contains an amount of iron exceeding 70% and a minimal amount of by-products.
The physical state of this oxide can vary from powdery to dense.
Brown iron ore is an iron oxide containing water. It is often called limonite. It contains significantly less iron, the amount of which usually does not exceed a quarter. In nature, such iron ore is found in the form of loose, porous rock, with a significant content of manganese and phosphorus. Usually richly saturated with moisture, it contains clay as waste rock. Cast iron is very often made from it, despite the insignificant part of iron, since it is very easily processed.
Brown iron ore
Magnetic ores are distinguished by the fact that they are based on an oxide that has magnetic properties, but when heated strongly, they are lost. The amount of this type of rock in nature is limited, but the iron content in it can be as good as red iron ore. Externally, it looks like solid black-blue crystals.
Spar iron ore is an ore rock based on siderite. Very often it contains a significant amount of clay. This type of rock is relatively difficult to find in nature, which, coupled with its low iron content, makes it rarely used. Therefore, it is impossible to classify them as industrial types of ores.
Spar iron ore
In addition to oxides, nature contains other ores based on silicates and carbonates. The amount of iron content in a rock is very important for its industrial use, but also important is the presence of beneficial by-elements such as nickel, magnesium, and molybdenum.
Mining Features
Deposit development can be carried out using open-pit or underground methods. The second method causes less damage to nature, but is more labor-intensive. The extracted rock is delivered to the plant, where the raw materials must first be crushed. The ore is then enriched and the iron is separated from other elements.
This procedure can be carried out in several ways:
- Gravity separation . Pieces of rock have different densities and disintegrate under mechanical stress, for example, as a result of vibration.
- Flotation . Finely ground raw materials are placed in a special chamber, into which air and working fluid are then supplied. Iron particles connect with air bubbles and rise.
- Magnetic separation . The useful mineral is pulled out using magnets.
- Combined . Several methods are used to separate iron from waste rock.
The resulting ore concentrate is then sent to the metallurgical plant.
Applications
The scope of application of iron ore is almost completely limited to metallurgy. It is used mainly for smelting cast iron, which is mined using open-hearth or converter furnaces. Today, cast iron is used in various spheres of human activity, including in most types of industrial production.
Various iron-based alloys are no less used - steel is the most widely used due to its strength and anti-corrosion properties.
Cast iron, steel and various other iron alloys are used in:
- Mechanical engineering, for the production of various machines and devices.
- Automotive industry, for the manufacture of engines, housings, frames, as well as other components and parts.
- Military and missile industry, in the production of special equipment, weapons and missiles.
- Construction, as a reinforcing element or construction of load-bearing structures.
- Light and food industries, as containers, production lines, various units and devices.
- Mining industry, as special machinery and equipment.
Area of use
The scope of ore application is limited to metallurgical production. It is the main raw material for the production of cast iron and various alloys. Thus, various metals are made from ore. However, 2 thousand years ago people realized that in its pure form iron was slightly superior to bronze in hardness. As a result, an alloy of iron and carbon was discovered, called steel or cast iron. The first type of material contains 0.1−2.14% carbon.
It should be noted that for a long time cast iron was not used for the production of objects. Metallurgists of the past considered it a waste due to its low ductility. Only after the invention of cannons did this material begin to be used for the production of cannonballs. Today the situation has changed significantly and cast iron is used in various fields. The leader in ferrous metallurgy is China. This country significantly surpasses other countries in the production of iron and steel. The leading exporters are Australia and Brazil.
The global economy requires more and more raw materials, and iron ore deposits are being actively developed in many countries. However, developed countries often prefer to reduce the volume of their own production, preferring to export relatively inexpensive material. Although the world's iron reserves seem enormous, they are not inexhaustible.
Iron ore deposits
The world's iron ore reserves are limited in quantity and location. Territories of accumulation of ore reserves are called deposits. Today, iron ore deposits are divided into:
- Endogenous. They are characterized by a special location in the earth's crust, usually in the form of titanomagnetite ores. The shapes and locations of such inclusions are varied, they can be in the form of lenses, layers located in the earth's crust in the form of deposits, volcanic deposits, in the form of various veins and other irregular shapes.
- Exogenous. This type includes deposits of brown iron ores and other sedimentary rocks.
- Metamorphogenic. Which include quartzite deposits.
Deposits of such ores can be found throughout our planet. The largest number of deposits is concentrated in the territory of the post-Soviet republics. Especially Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan.
The largest iron ore deposits in Russia
Countries such as Brazil, Canada, Australia, USA, India and South Africa have large iron reserves. At the same time, almost every country on the globe has its own developed deposits, in case of shortage of which, the breed is imported from other countries.
Largest deposits
Russia has more ore reserves than other countries. The deposits are located in different regions. The Kursk magnetic anomaly is a gigantic area of global scale in which ore is mined. There are several large deposits in this area.
Other places rich in these minerals:
- Ural.
- Karelia.
- Kola ore district.
- Western Siberia.
Let us list the large deposits located on the territory of other countries:
- Australia.
- Canada.
- SOUTH AFRICA.
- India.
- Sweden.
- China.
There are also a lot of ore reserves on the territory of Ukraine. Let's list the deposits:
- Krivoy Rog.
- Beloretskoe.
- Kremenchugskoe.
In some deposits, the minerals do not contain much iron; they contain a large amount of harmful impurities. There are deposits with high-quality ore on the territory of Ukraine.
Venezuelan deposits contain 68% iron. More than 10 million tons are in Brazil. In the United States of America, ferruginous quartzites are mined, which require enrichment to improve their quality characteristics.
Different methods for extracting raw materials are used:
- For the open-pit method, all operated equipment must be located near the deposit. A quarry is created up to 500 m deep; this mining method is used when the minerals are not too deep.
- The closed mining method is used most often. The technology involves the creation of mines whose depth reaches 1 km. Ore is mined using special equipment. The closed method is resource intensive and can be risky.
The ore is transported by lifting machines to the processing site. Iron is extracted from these minerals through a heat treatment process, the melting point of which is 1500 degrees. Minerals may contain various impurities. After melting in blast furnaces, the iron is removed and poured into containers. During the heat treatment process, slags are separated.
Let's list the world leaders in iron ore mining:
- BHP Billiton is an Australian-British organization.
- Vale S. A – Brazilian company
- Rio Tinto is a transnational conglomerate.
Ore is mined in many countries. These companies operate power plants, raw material processing and steel production plants. Organizations own their own means of transportation and dictate the cost of minerals throughout the world.
Import and export
Despite the fact that many countries mine ores, this does not mean that they do not purchase it from outside. A huge amount of minerals from Russia and Brazil is supplied to China, since the quality of raw materials there is slightly lower, which affects the metallurgical industry. In addition, the needs for hardware are sometimes not equal, and there is not enough of it to implement all plans.
Most iron-rich minerals are exported from India, Brazil and Australia. This can be explained by the countries' reduced demand for this raw material and its high quality, due to which iron processing requires fewer resources.
Classification
Iron ores are classified according to a number of characteristics.
Read also: How to share Instagram
First of all, the most important factor in economic terms is the percentage of iron. Therefore, ores are divided into a number of types:
- Rich – the content of useful mineral exceeds 50%.
- Conventional ores contain 25 - 50% iron.
- Iron-poor raw materials do not have a significant amount of iron. It contains no more than 25%. That is why such ores are called poor ores.
As for the chemical composition, these are mainly various compounds of iron with oxygen, water and carbon, found in nature in the form of:
- brown iron ores – limonites,
- magnetic iron ores - magnetites,
- red iron ores – hematites,
- spar iron ores – siderites.
Iron-bearing deposits usually contain the following types of ores:
Rock beneficiation methods
In any case, the enrichment procedure is preceded by grinding of the raw materials. At the next stage, enrichment is carried out directly using one of the methods:
- gravity separation,
- magnetic separation,
- flotation,
- complex technique.
The variant of gravitational separation has received the greatest practical application. It has a minimal cost. For implementation, machines such as a centrifugal machine, a vibrating platform, and a spiral are required.
Due to the presence of magnetic properties in substances, the option of magnetic separation works. It is relevant in cases where the others are ineffective.
In practice, a complex effect on ore is often required through several beneficiation methods at once.