Her Majesty the trumpet! Of course, it makes our lives better. Like that:
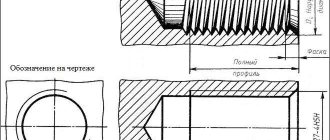
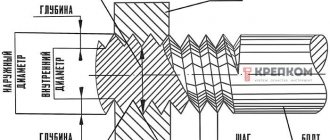
The key characteristic of any cylindrical pipe is its diameter. It can be internal ( Dу ) and external ( Dn ). Pipe diameter is measured in millimeters, but the unit of pipe thread is inch.
At the junction of the metric and foreign measurement systems, the most questions usually arise.
In addition, the actual size of the internal diameter often does not coincide with Dy .
Let's take a closer look at how we can continue to live with this. A separate article is devoted to pipe threads; click here to read more.
Calculator
conversion from millimeters (mm) to inches (in):
conversion from inches (in) to millimeters (mm):
Table of hose diameter sizes in inches and millimeters
| metric system, in mm | British, in inches | |
| 4 | — | — |
| 5 | 3/16″ | three sixteenths of an inch |
| 6 | — | — |
| 6,3 | 1/4″ | one fourth of an inch |
| 6,4 | 1/4″ | 1 4 |
| 8 | 5/16″ | five sixteenths of an inch |
| 9 | — | 5 16 |
| 9,5 | 3/8″ | three eighths of an inch |
| 10 | 3/8″ | 3 8 |
| 12 | 1/2″ | one second inch |
| 12,5 | 1/2″ | 1 2 |
| 12,7 | 1/2″ | 1 2 |
| 13 | 1/2″ | — |
| 14 | — | — |
| 15 | 5/8″ | five eighths of an inch |
| 16 | 5/8″ | 5 8 |
| 18 | 3/4″ | three quarters inches |
| 19 | 3/4″ | 3 4 |
| 20 | 3/4″ | — |
| 22 | 7/8″ | seven eighths of an inch |
| 25 | 1″ | one inch |
| 27 | — | — |
| 28 | — | — |
| 30 | — | — |
| 32 | 1 1/4″ | inch and a quarter |
| 33 | — | — |
| 35 | — | — |
| 38 | 1 1/2″ | one and a half inches |
| 40 | 1 1/2″ | — |
| 42 | — | — |
| 43 | — | — |
| 45 | 1 3/4 | one three quarters inches |
| 48 | — | — |
| 50 | 2″ | two inches |
| 51 | 2″ | — |
| 52 | — | — |
| 53 | — | — |
| 55 | — | — |
| 60 | — | — |
| 63 | 2 1/2″ | two and a half inches |
| 65 | — | — |
| 67 | — | — |
| 70 | — | — |
| 75 | 3″ | three inches |
| 76 | 3″ | — |
| 78 | — | — |
| 80 | — | — |
| 81 | — | — |
| 84 | — | — |
| 87 | — | — |
| 89 | 3 1/2″ | three and a half inches |
| 90 | — | — |
| 100 | 4″ | four inches |
| 102 | 4″ | — |
| 104 | — | — |
| 105 | — | — |
| 107 | — | — |
| 110 | — | — |
| 120 | — | — |
| 125 | — | — |
| 127 | 5″ | five inches |
| 130 | — | — |
| 132 | — | — |
| 133 | — | — |
| 140 | — | — |
| 150 | — | — |
| 152 | 6″ | six inches |
| 153 | — | — |
| 156 | — | — |
| 160 | 6 1/2″ | six and a half inches |
| 175 | — | — |
| 178 | 7″ | — |
| 180 | — | — |
| 190 | — | — |
| 200 | — | — |
| 203 | 8″ | eight inches |
| 229 | 9″ | — |
| 250 | — | — |
| 254 | 10″ | ten inches |
| 270 | — | — |
| 280 | 11″ | eleven inches |
| 300 | — | — |
| 304 | 12″ | twelve inches |
| 312 | — | — |
| 313 | — | — |
| 350 | — | — |
| 410 | — | — |
| 460 | — | |
| 610 | — | — |
Inch volume value
The cross section of the pipe, expressed in inches, is easy to decipher. Diameter is most often measured in inches. 3.35 centimeters corresponds to one unit. The decoding of the indicator is different because the product is measured by the diameter inside the pipe, and not outside.
For example, for a one-inch workpiece, the internal diameter varies from 2.55 to 2.71 centimeters. The thickness of the walls affects its size.
A one-inch pipe has an outside diameter of 25.4 millimeters, and a two-inch pipe has a diameter of 50 millimeters. What then do the numbers 33.249 or 66498 mean?
Threads on inch pipes are made on the outer volume. Thus, the internal volume and thread diameter are related conventionally. Therefore, the size of pipe products is calculated by adding the numbers 25.4 or 50 and two wall thicknesses of the product.
Reference! To correctly convert one value to another, measurements are taken from the inside. Because, based on external measurement data, the result will be incorrect and the installation will be performed incorrectly, since the pipes have different wall thicknesses.
It should be borne in mind that each manufacturer focuses on its own pipe manufacturing standards.
If difficulties arise in decoding, you should seek the help of professionals who will help you choose the necessary products.
Cast iron
Such products are used for installing water supply systems outside the building. In residential premises, cast iron water supply is installed extremely rarely. This material has high strength, but increased fragility. Its main disadvantage is its heavy weight and high cost. The operation of such cast iron products is designed for many years.
To compare the sizes of cast iron plumbing products, below is a table showing the dimensions of Class A cast iron pipe.
Types of steel pipes according to their production method
- Electric welded (straight seam)
For their manufacture, strips or sheet steel are used, which are bent to the required diameter using special equipment, and then the ends are connected by welding.
The effect of electric welding guarantees a minimum seam width, which makes it possible to use them for the construction of gas or water pipelines. The metal is in most cases carbon or low alloy.
The indicators of finished products are regulated by the following documents: GOST 10704-91, GOST 10705-80 GOST 10706-76 .
Please note that a pipe manufactured in accordance with standard 10706-26 is distinguished by the maximum strength among its peers - after creating the first connecting seam, it is reinforced with four additional ones (2 inside and 2 outside).
The regulatory documentation indicates the diameters of products produced by electric welding. Their size ranges from 10 to 1420 mm.
- Spiral seam
The material for production is steel in rolls. The product is also characterized by the presence of a seam, but unlike the previous production method, it is wider, which means the ability to withstand high internal pressure is lower. Therefore, they are not used for the construction of gas pipeline systems.
A specific type of pipe is regulated by GOST number 8696-74.
- Seamless
The production of a specific type involves the deformation of specially prepared steel blanks. The deformation process can be carried out both under the influence of high temperatures and in a cold way (GOST 8732-78, 8731-74 and GOST 8734-75, respectively).
The absence of a seam has a positive effect on the strength characteristics - the internal pressure is evenly distributed over the walls (there are no “weak” places).
As for diameters, standards control their production with a value of up to 250 mm. When purchasing products with sizes exceeding those indicated, you have to rely only on the integrity of the manufacturer.
It is important to know!
If you want to buy the most durable material, buy seamless cold-formed pipes. The absence of temperature influences has a positive effect on preserving the original characteristics of the metal.
Also, if the ability to withstand internal pressure is an important indicator, then choose round products. Profile pipes cope better with mechanical loads (metal frames, etc., are well made from them).
Here are a couple more excellent slides of creative advertising for a pipe manufacturer:
Metal products and their outer diameters
All types of metal pipes are manufactured at the factory, based on their outer diameter “Dн”. Standard diameters are shown in the table below.
In industry and construction, they mainly use products whose diameters are in the range of 426–1420 mm. Intermediate standard sizes of water pipes are taken from the table.
Small D metal products are mainly used for laying water pipes in residential buildings.
Medium D metal pipelines are used for laying city water supply. Such water pipes are used by industrial systems involved in the extraction of crude oil.
Large sizes of steel pipelines have found application in the creation and laying of main oil pipelines. They are also used in the gas industry. Through such pipelines gas is supplied to every corner of the planet.
How to deal with import designations
There are not only products from domestic manufacturers on the market. There are pipes marked according to the American system. Let's start with the fact that they distinguish between two types of pipes: pipes and tubes. Both words translate as pipe, but they are intended for different systems and the requirements for them are different.
Pipes type
Type of Pipes - electric welded and seamless. They are designed for transporting liquids and gases. So this is exactly the type that can be used in our heating and water supply systems. The main characteristic of pipes type pipes is the internal diameter. There are two strength standards in this group, which determines wall thickness and operating pressure.
- Schedule 40 or standard. The designation may include st (as in the figure below). These are products with standard wall thickness.
- Schedule 80 or extra heavy. The designation is EX. This is a material for use in high pressure pipelines.
Difference in internal diameters of Pipes of different strength categories: standard and heavy.
As you understand, with the same external size, the clearance will be different. Let's take a two-inch pipe as an example. It is designated as NPS=2″ internal diameter in different designs differs:
- standard (standard) schedule 40 - 2.067 inches (which is approximately equal to 5.25 cm);
- extra heavy schedule 80 - 1.939 inches (approximately 4.925 cm).
These categories standardize wall thickness and maximum operating pressure. The outer diameter remains constant, but the actual inner diameter changes with the wall thickness. That is, NPS=2″ describes the inside diameter, which will be about two inches, but will vary depending on the wall thickness. Here the situation is similar to our standards: there is a certain list of values to which actual parameters are rounded when labeling. Once again: if we are talking about a two-inch Pipe type pipe (the marking says NPS), you need to understand that we are talking about the internal diameter, but it will not be exactly two inches. It will be either a little more or a little less. Same with other sizes in inches.
Type Tubes
The word Tubes refers to pipes that are marked by outer diameter. The internal one will depend on the wall thickness. Therefore, this standard also contains the concept gauge, which can be translated as gauge. It just indicates the wall thickness.
The same diameters of steel pipes do not mean the same weight
The marking is marked with ASTM. The numbers following the abbreviation describe the outer diameter. In this group, we may be interested in copper pipes.
Which pipe is considered small - medium - large?
Even in serious sources I have seen phrases like: “We take any pipe of average diameter and...”, but no one indicates what this average diameter is.
To figure it out, you should first understand what diameter you need to focus on: it can be internal or external. The first is important when calculating the transport capacity of water or gas, and the second is important for determining the ability to withstand mechanical loads.
External diameters:
- From 426 mm is considered large;
- 102-246 is called average;
- 5-102 is classified as small.
As for the internal diameter, it is better to look at the special table (see above).
Plastic
Nowadays, their plastic counterparts have become an alternative to metal pipes. Moreover, their sizes vary widely. The material for such a product is:
- Polypropylene;
- Polyethylene;
- Metal-plastic.
Each manufacturer of such pipes sets its own size chart. Therefore, if one system is being manufactured, it is advisable to use parts from the same manufacturer.
Of course, there will definitely be discrepancies, but they will be minimal and will not cause any particular difficulties for a good master. If a person has little experience, he will have to make some efforts to fit all the sizes.
The table of sizes of plastic pipes for water supply using polypropylene of various densities shows the most popular models.
When all kinds of communications are laid, builders also use other diameters of plastic water pipes.
The diameters of water pipes in the table help you select the appropriate product for repairs or other work.
How to check quality
Since the internal clearance can be different, you have to control the external dimensions and wall thickness. Thickness is more important. It must be measured at different points, at both ends of the pipe. Approximately this parameter can be tracked by the mass of a linear meter.
By the way, there can be considerable deviations in wall thickness. The standard allows deviations both upward and downward. If the diameter of steel pipes is no more than 40 mm, permitted deviations are up to 0.4 mm in the direction of increase and up to 0.5 mm in the direction of decrease. There are two categories of pipe production: regular and high precision. For products of increased precision, the deviation towards decreasing wall thickness is slightly less.
Permissible deviations for VGP
Examples of designations for pipes that are manufactured in accordance with this standard: pipe 20*2.8 GOST 3262-75. It should be read as a pipe with a standard diameter of 20 and a wall thickness of 2.8 mm. From the table you can determine that this is a pipe of normal strength with an outer diameter of 26.8 mm. There you can also find the approximate mass of a meter depending on the thickness of the walls.
History of inch
- The origin of the word "inch" is derived from the Dutch duim, which literally means "thumb". However, another word is used as an international designation for this measure of length - inch;
- Like all old measures of length, the inch originates in human anthropometry and is equal to the length of the outer phalanx of the thumb. In addition, it is equal to 1/12 of a foot (from the English foot - foot) and 1/36 of a yard (according to legends, a yard was equal to the distance from the nose to the end of the thumb of the outstretched hand of King Henry the First of Britain);
There is an opinion that Henry's sword was one yard long.
All traditional measures of length are of anthropometric origin.
- In different countries and at different times, the inch took on different meanings. The Viennese inch (Austria-Hungary) is 2.63 cm, the French one is 2.707, the Old Polish one is 2.48, the New Poland one is 2.4, the Prussian model of 1816 is 3.766 cm;
- In Russia, this measure of length was introduced by Peter the Great. Before this, in trade and in calculations, domestic units of measurement were used, also based on anthropometry - vershok (the length of the first phalanx of the index finger), span (it is measured between the thumb and index fingers separated to the maximum distance), arshin (the length of the step of an adult);
- Currently, the most common is the English inch. Since 1958, it has been agreed to be considered equal to 2.54 cm.