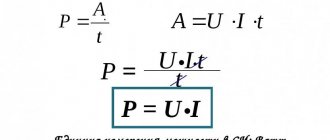In vehicle maintenance instructions, you can often find tables indicating the torque for tightening fasteners.
It is especially important to observe the value on parts such as the intake manifold, cylinder heads, and suspension joints. Service station technicians use special devices: torque wrenches.
This is an expensive item: if it is used occasionally, it is not worth purchasing. Therefore, many car enthusiasts who service cars themselves make a torque wrench with their own hands.
It’s not possible to make a tool completely free of charge: at a minimum, you need a factory key, as well as a device that fixes torque.
What is a torque wrench used for?
A certain tightening torque on the mating parts is necessary for uniform contact of the planes. In addition, if a gasket is installed along the contour, the uneven force of the bolted connections can destroy it.
A torque wrench allows you to tighten bolts with an accuracy of hundredths of a millimeter. In addition, it is often necessary to perform torque tightening of the bearing seat with high precision.
The manufacturer calculates torque values based on the type of material and design features of the unit. When building a car at a factory, all fasteners are tightened according to specifications: as a rule, this work is performed by assembly robots.
And when servicing, repairing, replacing parts, the required force is provided by a hand tool: a torque wrench.
Its main advantage is the ability to work in a wide range of settings. You simply set the operating limit with your own hands, or visually control the dynamometer needle.
That is, a universal torque wrench does not allow you to equally accurately tighten the nuts with a force of 2 N.m. and 100 N.m.
Tool manufacturers produce torque wrenches in several ranges:
- the most popular “size”: 40 – 210 N.m. It allows you to perform most repair work on the vehicle chassis;
- A precise torque wrench (from 2 N.m. to 50 N.m.) is intended for engine repair and maintenance. Setting up the carburetor, tightening the spark plugs, assembling the crankshaft and connecting rods. Work on replacing the intake or exhaust systems is also carried out with a small range torque wrench;
- tightening limit from 200 N.m. and higher is intended for power elements of powerful structures. In relation to cars - perhaps only wheel nuts.
Other factors
Exhaling through the nose also engages your sense of smell, and thus you can feel more taste, in addition, nicotine is well absorbed through the nasal mucosa, which can be another factor in getting more nicotine from the liquid.
Air flow Reducing the air flow makes the puff tighter and cigarette-like, while opening the air ducts allows you to move on to the hookah bar. By adjusting the air supply, you can determine your ideal device setting.
Mouthpieces The choice of mouthpiece is another parameter that is worth considering: the wider it is, the more suitable it is for puffing directly into the lungs; narrow and long elements make it more difficult to puff, bringing the sensation closer to puffing on a cigarette.
Some liquid refills for electronic cigarettes, such as those with cinnamon flavoring, give a fairly strong hit to the throat, regardless of the nicotine concentration and the level of propylene glycol, which also needs to be taken into account.
How does a torque wrench work for a car?
There are two design solutions: torque limitation and visual process control. Let's look at each of them in detail.
The so-called ratchet
Externally, it is not much different from a conventional lever with a ratchet for socket heads. Actually, this is what she is. A simple ratcheting mechanism with adjustable operating force turns an ordinary handle into a torque wrench. The secret is in the design of the ratchet. It allows the gear to rotate in any direction.
In the return direction, when you retract the handle for the next rotation of the head, the force is minimal. But in the working direction, where force is applied, the ratchet tooth jumps off the gear when the specified value is reached.
In the handle of the shank there is a rotating nozzle. It adjusts the tension of the ratchet spring.
How does the system work?
When the set torque value is reached, the ratchet gear begins to slip. The handle turns with a characteristic sound, but the nut does not tighten.
The ratcheting torque wrench is semi-automatic. It makes it possible to tighten the nuts without fear of overtightening them.
Measuring scale
The torque wrench does not have a torque limiting mechanism, but a dial or digital dynamometer is connected to the rotary mechanism. When force is applied to the handle, the needle deflects and the value of the applied force can be recorded.
The principle of operation is quite simple: the arrow maintains a constant position relative to the head of the key, and the handle bends like a spring torsion bar. As a result, the scale shifts relative to the tip of the arrow in proportion to the applied force.
The disadvantage of this model is that there is no automatic limiter. You simply control the force applied to the handle. This allows for a more accurate measurement (unlike a ratchet, which operates discretely), but there is a possibility of mechanical error when dosing force.
It is difficult to make a homemade torque wrench based on a ratchet; the technology requires metal-working machines and precision calibration. But a tool with a dynamometer is quite within the capabilities of a home craftsman.
How the tool works
Semi-automatic torque wrenches resemble in shape and design a regular ratchet wrench, which is used for socket heads. The only significant difference from its “brothers” is the presence of a special ratcheting mechanism, which allows the built-in gear to rotate in two directions.
For example, to return the handle of a tool back after a full rotation, you need to apply relatively little force. But to tighten the nut you need to apply a little more force.
When the required value is reached, the ratchet gear simply begins to slip (a characteristic sound is heard), as a result of which the nut or bolt is no longer tightened. This eliminates the possibility that the thread will break.
Torque wrenches with a force measurement scale by default do not have the ability to limit torque when a specified value is reached. In this case, this moment must be controlled independently using a mechanical or electronic digital measuring scale.
A homemade almost torque wrench, depending on the design, can work according to the example of the first and second options described above.
Why do we count Newtons and meters?
Before you start making a simple homemade torque wrench for tightening bolts and nuts, you will need to do some calculations. For example, to achieve a tightening torque of 10 N*m, you need to apply a force equal to one kilogram of force to a lever or arm 1 meter long.
But in a home workshop or garage, a meter lever is not the most practical and convenient option. Ideally, it is better to use a lever within 20–50 cm. And in order to correctly calculate how much force needs to be applied to the lever to achieve the required tightening torque, you need to count Newtons and meters.
However, it is not at all necessary to go into the jungle of mathematical equations. The required values can be easily calculated in proportion. That is, if we take as a basis that to obtain a torque of 10 N*m, you need to apply a force of 1 kg on a meter-long lever, then it is similarly easy to calculate how much force will need to be applied to a lever of shorter length.
The shorter the lever used, the greater the force required to tighten the bolt or nut - this is, so to speak, an axiom. For example, if instead of a meter lever you use a lever 50 cm long, then to obtain a torque of 10 N*m you need to apply a force equal to 2 kg.
If you use a lever with a length of, for example, 22 cm, then the force will be already 4.5 kg. In other words, you need to divide the torque (10 N*m) by the length of the lever (in this case - 0.22 m) and multiply by 0.1. Using this simple formula, you can easily calculate how much specific force is required to tighten the nut.
Buy or make?
In the process of performing auto repair work, almost every vehicle owner is faced with the fact that it is necessary to tighten a bolt or nut by applying a certain force, but there is no torque wrench at hand. Don’t run to the store to buy an expensive instrument, use it for 20–30 minutes and forget it for a year.
Therefore, the best option is to make a homemade torque wrench for tightening nuts and bolts. Moreover, you can make a tool like a ratchet with a ratchet mechanism, as well as one made by analogy with a simpler design - using ordinary hand scales.
Options for homemade torque wrenches
First, let's remember the school physics course. Torque is measured in newtons per meter. Without going into formulas, practically this means: 10 N.m. – equal to a force of 1 kg applied to a lever 1 meter long.
That is, if you measure 1 meter from the center of the spanner head and attach a dynamometer to this point, you can measure the tightening torque of the nut with a high degree of accuracy.
This method is far from new: owners of VAZ and UAZ cars, when repairing the rear axle gearbox, used a manual developed back in the USSR.
The shank nut, which compressed the tapered bearing races, was tightened with strictly measured force. The torque was controlled using a home dynamometer, and in its absence, an “accurate” measuring device was made from a steelyard.
In fact, this is the prototype of a homemade torque wrench. Only the axle shaft flange is used as a lever.
How to measure tightness
To correctly measure the tightening using a homemade device, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- Assemble the device and bring it into working condition - attach the steelyard to the handle, set it to zero, if possible, set the weighing limit with an alarm, and at the end - put the necessary attachment on the working part of the device or initially select an open-end wrench of a suitable size.
- Place the wrench on the nut or bolt. The device will show an accurate value only if the connection with the fastener occurs directly through the lever, and with the participation of one or more adapters and extensions, an error of up to 5-8% is possible when giving the result.
- Carefully pull the steelyard so that its position is strictly perpendicular to the axis of the lever, and the load indicator is not distorted, decomposed into vectors.
- If a normal force has been achieved, the device will confirm this with the measurement result, and the nut will not budge. If the tightening was not sufficient, the fastener will rotate around its axis until the required torque is achieved.
Important!
To prevent the bolt connection from breaking, you should not put an excessive load on the homemade dynamometer, and tighten only at the nominal values prescribed in the technical manual for servicing a particular part in the car. Otherwise, there is a risk of deformation of factory products.
Retightening a bolt on a car wheel
How to make a torque wrench with your own hands so that it is convenient to use?
A meter key handle is not the most practical option. Let's use the rule for calculating force depending on the length of the lever. There is no point in studying formulas; quantities are calculated in proportions.
The shorter the lever, the more force must be applied (while maintaining the amount of torque):
- lever 1 m, torque 10 N.m., force 1 kg;
- lever 0.5 m, torque 10 N.m., force 2 kg;
- lever 33 cm (already convenient to work), torque 10 N.m., force 3 kg.
For production you will need:
- handle for working with square socket heads (for greater versatility - with an extension).
- clamp for fixing the force measurement point.
- measuring device: you can use ordinary scales such as a steelyard or a cantor. The optimal measurement range is from 100 grams to 50 kg.
Having measured the required length from the center of rotation, we fix the clamp on the lever.
The device is ready in 15 minutes. You can mark several points for installing the clamp, depending on the moment being measured.
If you don’t want to make a separate tool with your own hands, use a standard set of wrenches (open-end on one side, socket on the other). The principle of operation is exactly the same.
For each key (since they are of different lengths), we compile a calculation table in advance. You can use a ready-made smartphone application:
We enter the received data (lever length, cantor readings), and we see the finished result in newtons per meter.
Tighten the bolt with a homemade torque wrench - video
Conclusion: Having a steelyard worth 300 - 500 rubles. (it is found in almost every home), you can save on buying a factory torque wrench: the price is about 2000 - 3000 rubles.
Source: obinstrumente.ru
Tips from professionals when making a key
The tool may not work the first time, and the measurement will be incorrect. However, any experienced master can give several detailed tips, following which every beginner will achieve the desired result.
If you do not have a lever or materials for it, you can use a regular wrench with an open-end grip on one side and a box grip on the opposite side. However, the ratio of length and torque should be calculated more carefully here, since the size of the arm will most likely be a fractional number.
For better fixation of the steelyard to the lever, you should be especially careful about the place where it is installed. The best option is a carefully drilled through hole, exactly at the point where the load is applied, and the device will never slip off the handle.
Working with a homemade torque wrench
Torque Control Tools
The main tool for controlling tightening torque is a torque wrench. This is the name of a wrench that has a dynamometer (a device for measuring torque) built into it. The following types of devices exist:
- Indicator - when tightening, displays the applied force digitally or using an arrow. The error is 6–8%.
The indicator torque wrench is inexpensive, but has the largest error - Digital is a subtype of indicator, but uses an LCD display to display the moment. Supports sound notification capabilities, uploading data to a computer, etc. The error is up to 1%.
Digital torque wrench - the most accurate - Limit - when the specified torque is reached, it stops tightening using a click mechanism. The error is up to 4%.
The limit (snap) torque wrench is easy to use
For non-professional use or a small car service, an indicator or limit key is suitable as the most affordable ones. Digital will be in demand in large car service centers.
How to choose the force to tighten the connection correctly
When working with a limit type key, in order to achieve the required torque, you should:
- Before starting tightening, select the required tightening force, for example, 50 Nm. The force is set on the main scale of the device, but not 50, but 48 Nm.
- On the auxiliary scale the force is set to 2 Nm, which in total will give us the required 50 Nm.
- Using a socket of the required size, tighten the nut. When the force reaches 50 Nm, a click will be heard and tightening will stop.
Control of force when working with an indicator type key is carried out visually.
In addition to the torque wrench, you can find torque screwdrivers and screwdrivers on sale; they work on the same principle. When choosing a torque wrench, remember that the tightening torque you need should be 25% less than the maximum allowable for the wrench. Using the key “to the limit”, you will quickly disable it. And also be sure to read the instructions for its use.
Well, you can check the correct tightening of the connection with a protractor.
How to use a homemade torque wrench
Typically, a torque wrench is a fairly expensive tool. Its purchase is unlikely to be justified for private use. However, the simplest device is easy to make yourself. For this you will need:
- ordinary spring scales with a hook and a round scale, allowing you to weigh up to 20 kg (the so-called steelyard);
- a piece of rather thick pipe (2.5 cm) about half a meter long.
Having secured the hook of the scales to the end of the pipe, insert a wrench into the other end and pull the scales, tightening the nut. In this case, to create a torque of 10 Nm, a force of 2 kg will be required. Using this diagram, you can calculate in advance how much force in kilograms you will need to apply to tighten it.
Of course, a homemade key will have a fairly large error, but it’s still better than nothing.
Video: how to make a torque wrench with your own hands
Varieties
Tighten the nuts; is a torque wrench necessary?
Before choosing torque wrenches for cars, you should study the available product options. This will help you get to know the devices better, and roughly understand what you need and what characteristics or capabilities you should count on when purchasing it.
It is customary to distinguish 3 types of torque wrenches. But you can add one more device to this list, which is an adapter key.
- Switches. When it comes to which torque wrench you should choose for repairing your own car in a garage, many are inclined to the simplest and most affordable option in the form of a pointer device. This key has a simple design and low cost. But the low price hides the corresponding quality. In terms of accuracy, they are much inferior to competitors, having an error of up to 10%. In this case, you should not count on a maximum tightening torque of more than 280 Nm. This key is not in demand among professional auto mechanics. But if you are doing work in the garage, and the procedure itself does not require increased accuracy, a pointer tool should be sufficient.
- Clicky. They are the ultimate. When choosing a torque wrench for car maintenance, motorists often lean towards click tools. Structurally, it includes a clutch with a given torque, which begins to operate when the specified tightening parameters are exceeded. For such tools, the torque range can vary from 40 to 360 Nm, which already significantly exceeds the capabilities of a standard pointer device. This range greatly simplifies the selection of a specific tool with the required characteristics. Click devices can be divided into household and professional ones. For the former, the error indicators do not exceed 5%, while for the latter it is even at a level of up to 3%. But in cost they are superior to switch analogues.
- Electronic. If there are increased demands on the car, it will be much more correct to choose an electronic torque wrench. This is the best tool for car maintenance, although it is rarely found in the garages of ordinary motorists. This is a professional-level device with the highest technical characteristics. The tightening scale here is electronic, and when the desired value is reached, a sound signal is heard, often supplemented by LED indicators. The range starts at 20 Nm. But the most significant feature of such a key is considered to be an error that does not go beyond 1%. The only, but significant reason to refuse to purchase an electronic device is the price. It is really high, which is why such devices are used mainly in car repair shops and service stations.
- Adapter keys. This is a special electronic device that can hardly be considered a type of electronic torque wrench. The device is equipped with a mechanical drive, to which you can connect a ratchet, and install heads and other attachments on the adapter. Dynamometer adapters are equipped with various components. There are sets of several adapters that differ in range. The device has a digital display and additional buttons for settings. The operating principle is similar to electronic keys. There is a battery inside the box. At the same time, the price is significantly lower than that of electronic torque wrenches.
Arrow torque wrench
The driver himself must decide which torque wrench he should choose for further maintenance of his own passenger car.
If you literally carry out some work on the machine several times a year, when you need 1-2 uses of such a key, there is definitely no need to spend a lot of money on buying an electronic device. It’s much easier and cheaper to go to a car service center. But for such periodic work, click devices are perfect. They are much better than pointers, have a good percentage of error, and at the same time cost adequate money.
Standard tightening torques for cylinder head bolts
To know for sure how much torque to tighten a particular threaded connection, you can use the following data.
Table: tightening torques for connections depending on thread diameter
| Nominal thread diameter | Turnkey size of head, bolt (nut), mm | Thread pitch, mm | Strength classes according to GOST 1759–70 | ||||
| Bolt | |||||||
| 5.8 | 6.8 | 8.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |||
| screw | |||||||
| 4;5;6 | 5;6 | 6;8 | 8;10 | 10;12 | |||
| 6 | 10 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 1,25 | 1,6 |
| 8 | 12 — 14 | 1,25 | 1,6 | 1,8 | 2,5 | 3,6 | 4,0 |
| 10 | 14 — 17 | 1,25 | 3,2 | 3,6 | 5,6 | 7,0 | 9,0 |
| 12 | 17 — 19 | 1,25 | 5,6 | 6,2 | 10,0 | 12,5 | 16,0 |
| 14 | 19 — 22 | 1.5 | 8,0 | 10,0 | 16,0 | 20,0 | 25,0 |
| 16 | 22 — 24 | 1,5 | 11,0 | 14,0 | 22,0 | 32,0 | 36,0 |
| 18 | 24 — 27 | 1,5 | 16,0 | 20,0 | 32,0 | 44,0 | 50,0 |
| 20 | 27 — 30 | 1,5 | 22,0 | 28,0 | 50,0 | 62,0 | 70,0 |
| 22 | 30 — 32 | 1,5 | 28,0 | 36,0 | 62,0 | 80,0 | 90,0 |
| 24 | 32 — 36 | 1,5 | 36,0 | 44,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 | — |
Practical application: how to use the tool correctly
Indicator devices do not cause any difficulties. You just read the readings and see the torque. But the click mechanism requires getting used to and correct understanding of the scale markings. Rough readings are marked on the fixed shaft of the handle. Precise divisions on the turning part.
The illustration shows marks at 98 Nm and 2 Nm (on the rotary handle). The values are added up: the final value is 100 Nm. To tighten the car wheel bolts with such a torque wrench (for example, a value of 120 Nm), you need to set 112 Nm on the fixed handle and 8 Nm on the rotating part.
If you understand the general principle, using the tool will be convenient.
There are various marking options:
In this case, for all types of handles there is a general rule: the locking wheel is unscrewed at the end, the value is set, after which the mechanism is tightened again. Most torque wrenches of this type are even simpler.
The ratchet does not spin, you just hear a loud click. Fundamentally, this does not change anything: you just need to stop puffing after the characteristic sound.
The tightening torques for bolts and nuts are indicated in the vehicle repair and maintenance instructions. The table is not universal: fasteners with the same metric dimension may have different indicators on different units.
Even the tightening torque of wheel bolts on cars of the same manufacturer (assembled on the same platform) may differ. For example, the Volkswagen Passat is 120 Nm, and the single-platform Volkswagen Sharan is 170 Nm.
It is highly advisable to comply with the factory settings, otherwise components and parts may be damaged. But there are situations when information is not available. In such cases, a table for tightening bolts with a torque wrench will help.
| Thread/pitch mm | Strength class | ||||
| 4.6 | 5.8 | 8.8 | 10.9 | 12.9 | |
| 5/0.8 | 2,1 | 3,5 | 5,5 | 7,8 | 9,3 |
| 6/1.0 | 3,6 | 5,9 | 9,4 | 13,4 | 16,3 |
| 8/1.25 | 8,5 | 14,4 | 23,0 | 31,7 | 38,4 |
| 10/1.5 | 16,3 | 27,8 | 45,1 | 62,4 | 75,8 |
| 12/1.75 | 28,8 | 49,0 | 77,8 | 109,4 | 130,6 |
| 14/2.0 | 46,1 | 76,8 | 122,9 | 173,8 | 208,3 |
| 16/2.0 | 71,0 | 118,1 | 189,1 | 265,9 | 319,7 |
| 18/2.5 | 98,9 | 165,1 | 264,0 | 370,6 | 444,5 |
| 20/2.5 | 138,2 | 230,4 | 369,6 | 519,4 | 623,0 |
| 22/2.5 | 186,2 | 311,0 | 497,3 | 698,9 | 839,0 |
| 24/3.0 | 239,0 | 399,4 | 638,4 | 897,6 | 1075,2 |
| 27/3.0 | 345,6 | 576,0 | 922,6 | 1296,0 | 1555,2 |
| 30/3.5 | 472,3 | 786,2 | 1257,6 | 1766,4 | 2121,6 |
| 33/3.5 | 636,5 | 1056,0 | 1699,2 | 2380,8 | 2860,8 |
| 36/4.0 | 820,8 | 1363,2 | 2188,8 | 3081,6 | 3696,0 |
| 39/4.0 | 1056,0 | 1756,8 | … | 3955,2 | 4742,4 |
The dependence is indicated not only on the diameter and thread pitch. One of the important characteristics is the strength class. This limitation is associated with the so-called fluidity of the metal, when deformation can lead to failure of at least the thread, and at most the bolt head (stud rod).
Important! The values indicated in the table refer only to the strength of the fastening elements.
It is unacceptable to use this guide when installing components and parts of a car, and especially wheel rims! The tightening torques for fasteners set by the manufacturer are not only related to the strength of the bolts.
The geometry of the part and the tightness of the gasket may suffer. The operating conditions of bearings and seals will change.
Main threaded connections in the engine
List of main engine threaded connections and features of their tightening:
- Cylinder head (cylinder head). A very important unit, therefore, when attaching it to the block, it is important to observe not only the tightening torque, but also the order in which the bolts are tightened. As a rule, the cylinder head is tightened with a fairly large torque, starting from the center of the block to the edges in several passes. Be sure to check this information in the vehicle's owner's manual (the numbers and order may be different for each engine model)!
- Valve lid. Due to the small diameter of the valve cover studs, extreme care should be taken when tightening them and not exceeding the required torque. Also check the tightening order and torque in the manual.
- Spark plugs and glow plugs. They are tightened in any order, but very carefully, since if the threads in the engine are damaged, expensive repairs will be required.
- When tightening the injectors, also be careful: due to their small diameter, it is easy to damage the threads.
- The engine mounts should be tightened after the engine is fully installed, when it is already resting on them with its weight. If you tighten the cushions before the engine is completely resting on them and the jack is removed, the cushions will quickly tear during operation.
This cylinder head tightening procedure is most often used for inline four-cylinder engines.
What does the cylinder head consist of?
The cylinder head is designed the same on any type of engine. It consists of:
- housing (head), in which the channels of the oil and cooling systems pass;
- intake and exhaust valves;
- one or two camshafts.
The housing is the main element of the cylinder head. It circulates lubricant and coolant and is the basis for camshafts and valves. If the cylinder head housing is correctly secured to the engine block, then all engine systems operate normally. If the cylinder head is not tightened evenly, then there is a high probability of cracks forming in the head housing. The cylinder head is made of aluminum, and the mounting bolts are made of steel. Therefore, the thermal expansion of the head and bolts is not the same. If any part of the cylinder head is not tightened well, this will lead to stress in it, because one part of the head will increase more than the other.
Bel-Esprit › Blog › Tightening without using a torque wrench
A method of tightening without using a torque wrench (taken from the Internet, with a small editorial edit by me) I wondered: “How to tighten a bolted joint without a torque wrench to the required torque if you don’t have a key on your property”? This can be done, I tried it personally yesterday. You will need: 1) an open-end or double-sided socket wrench, in my case it was a bendable screwdriver for bits with a cavity in the handle into which a meter-long piece of pipe was inserted;
2) spring canter (scales) with a limit of up to 20 kg. I took the electronic ones bought on Ali. Now let's remember our school knowledge. The tightening torque is a certain force applied to a 1 meter long lever. For example, we need to tighten the nut with a torque of 2 kgf*m. To do this, we need to measure the length of the spanner in meters. For example, the length of the key was 0.25 meters. Divide 1 by 0.25. We get the number 4. We multiply four by the required tightening force (2 kgf*m) and we get the number 8 kg. Since I am a philologist, and not a mathematician, I simplified my calculations and the efforts made with a meter-long piece of pipe: it is easier for a girl to count and twist) Next, we install a screwdriver/wrench on a bolt or nut, we cling to the other end of the wrench with the hook of a spring scale and pull the ring scales until the required kg are reached. Thus, in a simple way without the presence of a torque wrench, the bolted connection is tightened to the required torque. Yes, it looks unprofessional when you insert a pipe into a screwdriver, hook a scale to the end of the pipe and pull, looking at the dial (I would even say stupidly), but the price tag of at least 2500 rubles for a torque wrench justifies the moment of shame V=).
Source: www.drive2.ru
Main mistakes when making a key
Any high-precision tool cannot be manufactured completely without errors, since the master has neither accurate designs nor drawings at hand, and all this can lead to incorrect measurements and subsequent breakdown of car parts. However, many professionals have answers on this matter, offering car enthusiasts a number of recommendations in order to minimize errors and inaccuracies, in particular:
- You should not use soft metal as a lever, which can easily bend when pressed, because the force applied to the steelyard, without maintaining orthogonality, will not give the desired result, and the purpose of the device will be completely lost.
- You should not choose a cheap steelyard, because the accuracy of its measurements is very questionable, and the spring quickly stretches and fails. So, as of December 2022, the cost of scales should be in the region of 400-500.0 rubles. This is not much compared to the price of the torque wrench itself - about 3-4 thousand rubles, and it is better to change the low-quality component immediately.
- When attaching the nozzle to the nut, you need to take into account that it must be perpendicular to the axis of operation of the lever, otherwise the measurement will not work.
- Most steelyards have only an informational function and do not in any way limit the actions of the master, who can easily get distracted and tighten the bolt without paying attention to the scale reading.
You might be interested in this About High Jack jacks: features of the rack and pinion mechanism, selection criteria
Thus, when using a homemade product, the master bears much more responsibility, because the device cannot have the same automatic force reduction functions as a purchased analogue.
Service station
A homemade device is best used to control bolt tension if in doubt. If it is necessary to control the tightening on any complex component part, the car owner should still contact a service station for diagnostics and repairs, and should not replace important components in his garage, because unauthorized intervention can cost much more than the money saved on the key.
The importance of correct tightening of cylinder head bolts or nuts
The cylinder head (cylinder head) is one of the most important components of a car. It closes the cylinder block. It contains camshafts, valve covers and other parts of the gas distribution mechanism. The cylinder head is constantly exposed to enormous variable forces of pressure and temperature. Therefore, special requirements are imposed on its threaded fastening.
The block head must constantly experience a compression force, which is set by a certain tightening torque of the threaded fastener. In order for the compression force to be evenly distributed over the interface between the head and the cylinder block, a large number of tightening bolts or studs with nuts are provided. The uniform pressing of the cylinder head to the cylinder block is ensured by a specific pattern for tightening the threaded connections. To seal the joint, a head gasket is used, made of a special material that is resistant to high temperatures. When the head fastening is tightened, it shrinks in thousandths of a millimeter, which ensures reliable sealing of the joint.
Compliance with the correct order of tightening the cylinder head bolts ensures that it is pressed correctly to the cylinder block
Consequences of retightening the cylinder head bolts
If the threaded connections of the block head are tightened with a force exceeding the nominal force, then the tensile force that acts on the bolt or stud will begin to destroy the threads in the block or pull out the body of the fastener. The so-called yield point occurs, when with a further increase in the tightening force, the pressing force begins to decrease. Result: rapid burnout of the gasket at the point of worst compression.
If the threads in the holes of the block are severely damaged, then they will no longer be able to provide the necessary pressure on the head at the correct tightening torque. It will need to be restored, and this is an additional cost. Experienced motor repairmen in practice feel the maximum tightening force that a threaded connection can withstand. They will never allow defects from overtightening bolts or nuts.
Working with a torque wrench
What happens if you don’t tighten the cylinder head bolts enough?
If the head is fastened with minimal force, this will lead to weak pressing of it to the surface of the cylinder block. Microscopic gaps form between the gasket and the adjacent planes of the block and head, which will certainly lead to burning of the sealing material.
Checking the flatness of the block head with a special ruler
Insufficient tightening of the mounting bolts does not ensure a normal fit of the head, which can cause warping of its joint surface.
Tighten the bolts correctly
Any threaded connection is designed for a certain tightening torque. It is regulated by industry quality standards, for example, “OST 37.001.050–73 Tightening of threaded connections. Tightening standards" and guidelines from vehicle manufacturers. Foreign manufacturers use other standards, but they are basically similar to domestic ones. The information below will be presented based on Russian standards.
To what extent can threaded connections be tightened?
Why is it important to maintain the correct tightening torque? Only proper tightening will ensure reliable fixation of the part, on the one hand, and prevent damage to the thread and/or the part itself, on the other hand.
Let's look at what happens when the tightening torque is exceeded using the example of a bolt and nut:
- Immediate thread deformation. Due to too much applied force, deformation and breakage of the threads on the part occurs. The bolt or nut is not subject to further use; in addition, certain difficulties will arise when trying to unscrew the nut for replacement. You will most likely need to use a drill or metal saw to cut off the nut.
- Damage to metal hidden from view. It may seem that the nut is tightened correctly, but due to exceeding the yield strength, irreversible changes occur in the bolt or nut: deformation, disruption of the metal crystal lattice. Such a case is especially dangerous because it is not immediately noticeable, but after some time a crack in the bolt can lead to dire consequences.
Tightening the cylinder head bolts with a torque wrench
The yield strength is a mechanical characteristic of a material that characterizes the stress at which strain continues to increase without increasing the load. Designation σт.
Unit of measurement: Pascal [Pa] or multiples [MPa].
This is an important parameter with which permissible stresses for ductile materials are calculated.
After passing the yield point, irreversible changes begin to occur in the metal of the sample, the crystal lattice of the metal is rearranged, and significant plastic deformations appear.
Wikipedia
If, on the contrary, you do not tighten the nut with the appropriate torque, after a while it will simply unscrew, which can also lead to undesirable consequences. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to tighten threaded connections not “with all your strength”, not by hand, but wisely, using special equipment.
Types of wrenches for correct tightening of threaded connections
The threaded connection must be tightened with such force as to prevent:
- loose fit of mating surfaces of fastened parts;
- thread breakage;
- mechanical destruction of the bolt body;
- turning the edges of a nut or bolt head;
- destruction of engraving washers.
Any material from which the block is made (cylinder head, mounting bolts) has its own strength limit. It is the lowest tensile strength of the weakest link in the fastening unit that determines the greatest tightening force. The weakest link in fastening the cylinder head is the bolts (studs) and threads in the holes of the block. Their weakness is determined not so much by the strength of the material they are made of, but by their incomparable dimensions (diameter) with the dimensions and weight of the block and cylinder head. It is clear that to destroy a solid cast iron block or a massive duralumin head you need to put in much more effort than to break a thin bolt made of high-strength alloy steel.
How much effort do you need to apply?
The threshold or limit value of the strength of critical parts is usually given in the engine data sheet. The values of the maximum tightening forces for the cylinder head bolts are also given there. To perform tightening with the required force, use special torque wrenches.
According to the method of regulation and indication, torque wrenches are divided into the following categories:
- Unregulated with constant tightening torque. They are used for tightening cylinder heads on conveyors during engine assembly. Their advantages are high reliability.
- Adjustable for maximum tightening torque. These are so-called ratchets with the ability to set a certain tightening torque. When this force is reached, the ratchet is activated and further tightening becomes impossible. The ratchet attachment is often equipped with reverse. In this case, it can not only tighten bolts and nuts, but also unscrew them. Many socket sets come with a ratchet.
- With scale and pointer. This wrench can be used to tighten threaded connections with different torques. The main conditions: you need a lot of free space and the ability to conveniently observe the scale. Included in the tool kit of mechanics.
- Digital display in a compact device that measures the applied force. A very accurate, reliable, easy-to-use tool. With its help, you can tighten the cylinder head bolts with an accuracy of hundredths of Nm directly on the car engine.
- Combination of adjustable tightening force with control via digital or dial indicator. Such wrenches protect the threads from applying excessive tightening force, while at the same time allowing you to control the torque using an indicating device.
Replacing the oil pressure sensor
To install a new sensor, you will need the following tools and consumables: two wrenches for “21”, an open-end wrench for “22” with an adapter, a rubber protective cap, an O-ring and block (usually included in the kit), a wire terminal for the sensor contact. Before replacement, you must remove the negative terminal from the battery. Operating procedure:
Remove the rubber protective cap from the top of the sensor and disconnect the wiring terminals. Unscrew the sensor from the fitting using a “21” wrench, carefully holding the tip of the fitting with a key of the same size. Remove the sensor. An O-ring and a metal washer are installed at the connection between the sensor and the fitting, which must be replaced if they are worn. The new sensor is installed in the reverse order.
Tightening torque and tightening order of cylinder head bolts
Different engine models require different torques to tighten the cylinder head. There are also differences in the order of tightening the mounting bolts. All this information is indicated in the engine passport. Let us once again emphasize the importance of correct tightening and compliance with the magnitude of its torque.
The procedure for tightening the cylinder head bolts
Tightening the cylinder head fastening always begins with the middle bolts. This rule must be observed because it is necessary to ensure the tightest fit of the mating surfaces. Each valve engine cylinder head must be installed without distortion or unnecessary metal stress. Tightening of threaded connections must be done in several passes. It is important to maintain a constant force for each bolt in each pass.
Torque Limits for Bolts
What is lingering force and how do you know it?
The tightening torque is an indicator of the force that must be applied to threaded connections during the process of screwing them. If the fastener was tightened with a little force than was necessary, then under the influence of various mechanical factors the threaded connection may not withstand, the tightness of the fastened parts is lost, which entails serious consequences. Also, with excessive force, the threaded connection or fastened parts can simply collapse, which will lead to thread failure or the appearance of cracks in structural elements.
Each size and strength class of threaded connections has a certain tightening torque when working with a torque wrench, which is indicated in a special table. In this case, the designation of the strength class of the product is located on its head.
Is it possible to properly tighten cylinder head threaded connections without a torque wrench?
Tightening threaded connections in the absence of the appropriate equipment is absolutely not worth it for car enthusiasts who decide to independently change the head gasket or grind the valves.
Experienced repairmen who are able to feel in practice the strength limit of any bolt do not always use a torque wrench when tightening. But such ability does not come immediately. To do this, you need to work with torque wrenches for several years.
But even experienced specialists tighten the cylinder head bolts on expensive brands of passenger cars with a torque wrench, because this operation directly affects the longevity of the power unit. In an emergency situation, when it is not possible to use a torque wrench, you can use the option with a mechanical or electronic cantor. In the video below, an experienced mechanic explains to viewers how to properly tighten a cylinder head without a key. It is worth keeping in mind that the correctness of the work should be checked using a protractor.
Video: how to check the tightness of the cylinder head
Tightening the cylinder head bolts on used cars is a responsible, difficult, and specific task. Responsible, because the normal and long-lasting operation of the engine depends on proper tightening. Difficult, because this work is not very convenient to perform due to cramped conditions and insufficient visibility. Specific - because the bolts need to be tightened in several passes, according to a certain pattern, using a special torque tool.
Source: autoclub.su
General rules for performing work, methods used
There are a number of general rules that must be followed when installing the block head:
- It is important to strictly observe the tightening torque. For these purposes, a special tool is used - a torque wrench. It is not recommended to perform this operation with regular keys;
- The head bolts must be pulled smoothly, jerking is not allowed. Since the tightening force on the last approaches is significant, extending the wrench arm with a pipe can simplify the procedure and ensure smooth, uniform tightening;
- Before installing the bolts, you need to carefully inspect the condition of the threads on them. There should be no dirt or foreign particles on the coils.
- The threads of fasteners should be lubricated with engine oil before tightening. But you should not pour grease into the holes for the bolts (especially for “blind” holes), since in the future it will not allow the fasteners to be fully tightened.
Despite the fact that each engine has its own characteristics of tightening the cylinder head, the general technology of this operation is the same. In general, two methods are used to tighten fasteners:
- In several approaches, bringing the tightening force to the required value;
- Tightening the fasteners to a certain force (in one or more approaches), and then tightening the bolts twice to a certain angle.
The tightening method is selected based on the type of bolts.
The first method is used when using non-stretching bolts (these are not used now, but they can be found on old cars). But often this type of fasteners requires tightening after a certain period of engine operation in order to compensate for the shrinkage of the cylinder head gasket. But such fasteners are allowed for reuse, and more than once.
The second method of tightening the block is relevant for most modern cars. And all due to the use of tensile bolts (the so-called TTY type).
Such fasteners, due to elastic deformation, are able to compensate for thermal expansion of the head and shrinkage of the gasket, but for this they need to be put into deformation mode (in fact, just stretched a little).
To do this, it is necessary to tighten the bolts twice to a certain angle. On some cars this angle is 45 degrees, on others it is 90 degrees.
But after the elements are put into elastic deformation mode, they will no longer be able to return to their original state, and therefore their reuse is not allowed due to the high probability of destruction.