Solder POS-61: technical characteristics, melting point, application
It’s rare that a boy didn’t try soldering during his school years. Schoolchildren learned the first basics of joining metal parts in a young radio amateur club. For many, the smell of rosin and the shine of molten tin remain in their memory for the rest of their lives. Despite the fact that we worked with a primitive 25 W soldering iron using tin and rosin, the process was fascinating.
With the development of the soldering technological process, modern soldering irons, fluxes and special metal alloys with low melting points, the so-called solders, appeared. The market leader is the product POS-61. Stands for tin-lead solder, tin content - 61%. The melting temperature of POS-61 solder ranges from 184 to 193 degrees.
General information about soldering
What is more important in a soldering job: the tool or the material? Everything is important: the soldering iron, the solder, and the flux. The variety of soldering irons is related to the object of soldering. Massive parts are heated with powerful soldering irons, and microscopic circuits of chips are heated with low-power ones. Professional soldering workers use several types of these heating tools.
Classification of soldering irons by power:
- A soldering iron with a nichrome insert with a power of 25 watts is a common household tool used by craftsmen, radio amateurs, and electronics engineers. They are still popular to this day, quite cheap, and last up to 10 years. A metal insert in the form of a copper rod, the tip of which is cut at 60 degrees. It is used in 90% of cases that arise in business situations; even many repair shops use them.
- The second type is more powerful with a 40-watt heater and a nichrome insert, twice as heavy and larger than its 25-watt counterpart. Used for more complex work. The tip is sharpened into a wedge, similar to a screwdriver, but it cannot be used for screwing screws. This sharpening is made for the convenience of soldering massive parts, for heating up to 190 C. They are used by professionals, but not recommended for home use.
- The third type is a gas soldering iron, three in one. The soldering iron itself has a copper core sharpened for a needle. The second function is a hair dryer that can heat an object up to 600 degrees. Gas burner - in this case the nozzle is changed, the tool performs the functions of a gas burner, heats the parts to a temperature of 1300 degrees.
- The fourth type is a modern ceramic soldering iron. Champion compared to all presented instruments. It has a very thin tip, capable of soldering millimeter dots, and is used to perform very precise work. Power - 100 watts. It is equipped with a soldering station with a temperature range from 200 to 480 degrees. Among specialists it is used as a universal tool.
Chemicals for work
Due to the fact that the soldering iron tip is clean and dry, and the soldering technology involves fluxes, a set of chemicals is required. For high-quality work, the following list of fluxes is recommended:
- Rosin is a universal and popular substance, without which no soldering worker will start working. Application is mandatory. Sold dry.
- Flux LTI-120 is a chemically active substance that contains orthophosphoric acid for removing oxides from metal. The principle of action is the same as that of ordinary rosin. Used to work with oxidized metal. There is no need to rinse off after completing the process.
- Flux F-38M is an active acidic substance that must be washed off after work. Used for soldering nichrome, aluminum, stainless steel. Washable with low-fat gasoline.
- Soldering acid, a cheaper version of F-38M flux. It is used in exceptional cases, as it tends to corrode metal. Helps with soldering stainless steel, bronze, nickel, nichrome.
- Glycerin is an oily liquid, does not have oxidizing properties, is safe, and does not harm products. Wash off with plain water.
- Homemade flux - add 200 grams of ethyl alcohol to 200 grams of isobutyl alcohol; vodka is not suitable as it contains water. 50 grams of glycerin and 100 grams of rosin are added to the alcohol mixture. The result is a concentrated solution that has inactive properties and is washed off with water.
- TT indicator flux . Gel density. It has a paste-like structure, does not flow, and does not require cleaning. The manufacturer's recommendation is on the label: do not wash off, protects contacts from oxidation.
Characteristics of POS-61
Solder is a mixture of tin, lead and rosin. The market offers solders for every metal and its alloys. The most popular alloy is tin-based. The melting point of POS-60 tin is 232 degrees.
Technical characteristics of POS-61 solder:
- Metal tin - 61%.
- Lead - 38%.
- Rosin - 1.0%.
The temperature of transition to the liquid state is 190 degrees.
It is a 2 mm thick tube filled with rosin. Sold by weight. Packaged on a roll. The label contains instructions with markings indicating the diameter of the tube, the percentage composition of the components and the weight.
Soldering copper, steel and aluminum
Copper does not require any special conditions, special flux or highly qualified soldering specialist. Copper heats up well due to its high thermal conductivity coefficient.
It does not form a dense oxide film, like aluminum does under the influence of atmospheric oxygen. The surface is cleaned of oxide without the use of chemicals.
The soldering process is as follows:
- thoroughly clean the surface with sandpaper to a bright metallic shine;
- Coat the joint of the parts with flux - soldering acid zinc, chlorine;
- withstand soldering temperature of 200 degrees.
Soldering steel products is technologically simple. For this, you can even use low-melting solders, for example, POS-61 or pure tin. For high-quality connection of steel parts into a single whole, it is recommended to tin the contact point with tin.
Subsequently, the following list of operations is performed:
- clean the surface with a file or emery cloth;
- apply zinc chloride as a flux;
- heat the soldering area to a temperature of 200 degrees;
- apply POS-61;
- heat with a soldering iron until the tin becomes liquid.
Aluminum is a metal that is difficult to solder. Craftsmen try to solder using cold soldering. This is a crazy idea; aluminum cannot be soldered using this method.
Another popular way is to use tin as solder and machine oil as flux.
The process is as follows: thoroughly clean the surface, lightly wipe with a rag with a drop of oil, warm it well with a soldering iron and apply POS-60 solder with a tin melting point of 230 degrees. Tin spreads in a thin film and combines with the metal.
Melting various materials
The craftsman may well need to solder copper - for example, we are talking about heating pipes or other products made from this non-ferrous metal.
You can work with a soldering iron with copper and its various alloys using different solders, both soft and hard. At the same time, the temperature of soldering copper elements with soft solders is 250-300 ℃, and with hard solders – 700-900 ℃.
What should be the temperature of the soldering iron tip if you need to solder, say, polypropylene products? In this case, the optimal temperature will be +260 ℃, and the conditional permissible range is from +255 to +280 ℃.
But it is worth noting that if you overheat the soldering iron above 271 ℃ and reduce the heating time of the tool, the surface of the soldering zone will warm up much more than the inside. This means that the resulting sealing film will be very thin.
Technical characteristics and melting temperature of POS 61 solder
POS 61 solder is the most popular filler material made on the basis of a tin-lead mixture. Its low melting point makes it popular for repairing electronic circuits, printed circuit boards and other devices that do not tolerate significant temperature changes.
In addition, the composition has proven itself well as a means for sealing cracks and holes in various metal products.
Description
Tin-lead solder POS 61 is ideal for use in domestic conditions . This is facilitated by the low fusibility of the composition due to the high tin content. Its melting point does not exceed 200 degrees Celsius.
Due to the high fluidity of the molten composition, the solder fills all cracks and cavities, providing high-quality joint characteristics. The composition used belongs to the universal category. It can be used to solder products made from the following metals:
- steel;
- copper;
- brass;
- bronze;
There is an analogue of this solder on the domestic market - POS 60. The mass fraction of tin in its composition is only one percent less.
The foreign analogue is Sn63Pb37, which contains 63% tin and 37% lead. The technical characteristics and scope of application of the material are practically no different from POS 61.
Material characteristics
Let's look at the main technical characteristics of POS 61 solder:
- density – 8.5 g/cm3;
- impact strength – 3.9 kg/cm2;
- tensile mechanical strength – 43 MPa;
- relative elongation – 45%;
Chemical composition
The main chemical elements of solder are:
- Tin . Under ideal manufacturing conditions, the tin content in the composition is 61% of the total mass. According to the requirements of regulatory documents, its mass fraction must be at least 59%.
- Lead . Its percentage is 38-39%, depending on the presence of auxiliary additives. For example, POSSU 61-05 solder, in addition to tin and lead, contains only 0.5% antimony.
In addition to antimony, the composition may include the following chemical elements that improve the quality of the compound:
- iron;
- bismuth;
- nickel;
- sulfur;
- zinc;
- aluminum.
Temperature parameters
The soldering temperature of POS 61 is 240 Cº . In this case, the composition begins to melt at a temperature of 184 Cº, and complete transition to the liquid state of aggregation occurs at 194 Cº (± 2 Cº, depending on the content of auxiliary chemical elements).
Of all the lead-tin solders, POS-61 is the lowest melting point.
Decoding
Explanation of the abbreviation:
- POS – tin-lead solder;
- 61 – mass fraction of tin in the composition.
Varieties
Regardless of the release form, the composition of the material and the ratio of the main components remain unchanged. The most common varieties are:
- Wire. Its diameter ranges from 1 to 7 mm, depending on the application. The step size is 0.5 mm. Delivery is carried out in compact coils or coils, which are unwound during operation. This form of release is the most popular.
- Solder with rosin POS 61 is produced in the form of thin tubes with filler, twisted in a spiral. Pine rosin plays the role of flux during soldering work. Its advantage is its neutral composition, which does not require removal after completion of the working cycle, unlike acid-based fluxes. Other types of POS 61 solders are produced without rosin.
- Ribbon. A distinctive feature is the ability to quickly repair cable and wire materials. Tape solder is characterized by a low antimony content.
- Rods. Their length does not exceed 40 cm. The maximum diameter is 8 mm. This release form is ideal for tinning the temperature rod of a soldering iron. Some craftsmen prefer to make rods themselves, casting them into special molds.
For large production enterprises, POS 61 is supplied in the form of massive ingots weighing up to 25 kg. This reduces the cost of consumables and soldering work.
Use in everyday life and at work
In addition to unique technical characteristics and high performance qualities, POS 61 solder has another advantage - affordable price . These factors caused the spread of this material, which has found many applications, both in everyday life and in industry.
Among radio amateurs, solder has long established itself as a reliable assistant. The low melting point eliminates the possibility of overheating of radio components and microcircuit elements, which is a decisive factor when choosing a suitable consumable material.
At various enterprises, POS 61 is used for soldering strands of copper wires. The solder contains copper, which has a beneficial effect on the intensity of wire dissolution.
When sealing cracks in metal vessels, a gas burner is used as a working tool. The molten composition easily penetrates into all cracks, reliably sealing the holes.
The low melting point leaves its mark on the work front. Solder cannot be used to repair products whose operation is associated with high-temperature influences. This will cause rapid wear of the connection.
Designation in regulatory documents
In the process of manufacturing solder, manufacturing enterprises are required to follow the requirements of interstate standard 21931-76. It contains instructions on the product range, as well as acceptance rules and testing methods for finished products.
Popular companies
The most popular manufacturers, proven suppliers of high-quality soldering consumables, are:
- Metal Compounds Plant;
- Technological lines;
- Kievtsvetmet;
- Plant of metals and alloys;
- Ukr-specialsplav.
Conclusion
POS 61 solder is the most popular material for repairing various temperature-sensitive products. High quality characteristics are the reason for its spread, both in everyday life and in industry.
Radio amateur Vladimir Gennadievich Nosov. Experience – 20 years: “For soldering microcircuits I use only POS 61 solder. It melts perfectly with a household soldering iron with a power of 60 W, providing a high-quality and durable connection.”
Low-melting solder pos 61: its technical characteristics, composition and application
In technical production, as well as at the everyday level, there are times when it is necessary to create a strong connection between two different parts of the workpiece.
These could be pipes, radio components on a printed circuit board or circuit board, or electrical wires. For this, special filler materials are used, and the most common are various solders.
This article will give a general description of solders, and a more detailed overview of the group of tin-lead filler materials.
The main requirement for the solder used is a lower melting temperature than the melting temperature of the workpiece.
different together .
In this regard, there are different types of materials that differ from each other in physical and chemical properties and are part of the alloy components.
So, there are two groups of solders: soft and hard. Soft ones are those whose melting point is below 300 degrees, therefore, the melting of hard solders will be above this value.
One of the most common filler materials is POS - tin-lead. There are several materials in this category, depending on the percentage composition of tin in the alloy, which is indicated by a number. They are characterized by a relatively low melting point and low strength.
This somewhat limits their scope of application. For example, these solders are convenient to use in radio installation and are undesirable for use in parts that experience great physical stress.
Pos 61
The melting point of pos 61 is 183 degrees, which is the starting point. Complete melting is achieved at a temperature of about 190 degrees, which allows you to work with it using any household soldering iron or professional soldering station. Soldering temperature is 240 degrees. This is the lowest melting point solder of the entire group of tin-lead solders.
Compound
This filler material belongs to the soft category, contains 61% tin, 38-39% lead and may contain an acceptable percentage of impurities in the form of antimony, nickel, iron, sulfur and bismuth.
Within the tin-lead group, this material is the purest solder in composition and is more suitable for electrical installation and tinning, since due to the copper content in it, it reduces the rate of dissolution of copper wires and tracks and wears out the soldering iron tip less, and the relatively low melting temperature does not harm printed circuit board.
A few soldering rules
There is one unshakable rule: the temperature of the soldering iron must be higher than the melting temperature of the solder.
Moreover, the solder material must be completely melted before it fills the empty spaces and is evenly distributed over the surface.
If the soldering iron tip is too overheated, the solder will oxidize and the soldering seam will not be of very high quality. By the way, oxides can appear on the soldering iron itself, and in order to get rid of them, experts advise purchasing a so-called tip activator - a really very useful thing.
And if the soldering iron tip is not just overheated, but burns out, then the solder material will no longer stick to it at all. “Cold” soldering (that is, when the temperature of the soldering iron tip is less than optimal) will also not give the expected result.
If the solder material does not melt to a fluid state, the soldering area becomes dull and rough, and the connection is not very strong.
And one more important rule, suitable for any soldering: the temperature of the elements being soldered must certainly be the same.
All about POS solder
Greetings to dear readers! In this material I tried to collect all the data about PIC solder.
This Tin-Lead Solder is the most popular solder for mounting radio components and is used more often than others in radio engineering.
I will try to explain why this is so and tell you about the types and technical characteristics of POS series solders. I’ll also tell you a terrible secret about POS-60 and POS-62 solders. Go!
Types of POS solders
First, let's remember what types of solders are made from alloys of the tin-lead group. The most popular are antimony-free solders POS-10, POS-40, POS-61 and POS-90. POS solder containing antimony is called POSSU. Antimony in the solder adds several percent to its strength.
When we talk about melting a mixture of tin and lead, we need to remember the definitions of solidus and liquidus . When any mixture of two or more metals is heated, the melting (transformation from solid to liquid phase) of the lightest particles occurs first. This temperature mark is called the solidus of the alloy.
With a further increase in temperature, more refractory components begin to melt. As soon as they melt, the liquidus . The PIC solder is now completely melted. This process is explained in more detail by a picture taken from a presentation on the topic of alloys.
Between these two points is a state of increased ductility of the solder . In this state, the solder can be pulled and deformed without losing integrity.
There are eutectic alloys - solders, in which the solidus and liquidus points coincide. This is very convenient when soldering and indicates the high quality of the solder.
About the composition of solder
The name of the solder of the tin-lead group indicates the tin content in it. For example, POS-40 contains 40% tin, and POS-61 contains almost 61% tin. The rest consists of lead and additional impurities.
By appearance, you can estimate the composition of the solder by eye. If the PIC solder is more matte and dark, then it contains more lead. If it is lighter and shiny, then there is more tin. This is best understood by comparison.
Look at the photo to see what a sheet of tin and a sheet of lead look like.
The strength of solder depends not only on the alloy alloy, but also on the metal being soldered. For example, to solder copper or zinc, several percent of copper or zinc are added to the POS solder, respectively. This reduces chemical erosion of the metal and increases the surface strength of the joint.
Solder alloying
To improve performance characteristics, alloying of solder with the following substances is used:
- adhesion is improved by the addition of copper, cadmium, antimony, aluminum, silver and zinc;
- ductility and resistance to thermal cycling are improved by the addition of indium, silver, manganese, bismuth, and lithium;
- Nickel, cobalt, zinc, silicon, boron, iron add strength
- The corrosion resistance of solder is increased by nickel and copper;
- Heat resistance is increased by silicon, zirconium, tungsten, vanadium, cobalt, niobium, hafnium.
Technical characteristics of POS and POSSu solders
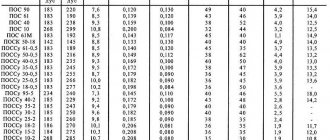
In order not to describe all the technical characteristics of solders of the tin-lead group, I will simply provide a table of parameters. It can be used to determine the melting point, density, electrical resistivity, thermal conductivity, tensile strength, elongation, impact strength and Brinell hardness of solders.
Analysis of the table shows that the most fusible among the list is cadmium solder POSK 50-18 with a melting point characteristic of 145 degrees Celsius. The strongest solder is POSSu 4-6 solder with a tensile strength of 6.5 kgf/sq.m. mm.
Technical characteristics of POS-10 solder
POS 10 solder has a distinctive chemical composition. It contains 9-10% tin, about 89% lead, 0.2% bismuth, 0.1% antimony and other impurities in small quantities. POS-10 solder is used for soldering and tinning contact surfaces of electronics. For example, they solder relays and fill control plugs in radio electronics housings.
The POS-10 soldering temperature is 299 degrees Celsius. The solidus point is 268 degrees.
Advantages of POS-10 solder:
- high melting point is useful when soldering equipment cases.
Disadvantages of POS-10 solder:
- low strength and tensile strength of about 3.2 kgf/sq.mm.;
- high resistivity - 0.2 Ohm x sq.mm./m;
- high content of lead, which is hazardous to health.
Technical characteristics of POS-30 solder
Solder for soldering of the POS 30 brand is an intermediate link between POS 10 and POS 40. The composition of POS 30 solder is as follows: 30% tin and 69.5% lead. The rest is impurities and doping.
Solder POS 30 can be easily replaced with POS 40, which is described below. The melting point (liquidus) is 238 degrees, and the plasticity temperature (solidus) is 183 degrees Celsius.
According to the technical characteristics, POS 30 solder is most often used for soldering and tinning of zinc sheets and radiators.
Advantages of POS-30 solder:
- good adhesion;
- high strength.
Disadvantages of POS 30 brand solder:
- high lead content;
- often produced in rods.
Technical characteristics of POS-40 solder
According to the chemical composition, POS 40 solder consists of 39-41% tin, 59% lead. The remaining impurities are in the same ratio as in POS-10. Soldering solder POS-40 is often used for soldering and tinning radio equipment casings made of galvanized iron with galvanized seams.
The soldering temperature of POS-40 solder is 238 degrees Celsius, and the solidus is 183 degrees.
Advantages of POS-40 solder:
- good ratio of ductility and melting point;
- because of this, it tolerates thermal cycling better than POS-61.
Disadvantages of POS-40 solder:
- high lead content, which is harmful to health;
- elevated liquidus temperature.
The terrible secret of POS-60 solder
Now the time has come for the terrible secret of POS 60 solder . According to GOST 21930-76 entitled “Tin-lead solders in ingots. Technical specifications" and GOST 21930-76 "Tin-lead solders in products. Technical specifications", solder such as POS-60 simply does not exist. download and view GOST 21930-76 itself . Here is the complete table from this GOST.
So “ POS-60 ” is jargon or a popular designation for “the solder that everyone solders with.” It seems to me that this is due to confusion in the designation of POS-61. Because when the tin content in the solder according to GOST is from 59 to 61%, it is more logical to call it POS-60 rather than POS-61.
Among the solders produced according to international standards there is Sn60Pb40 solder . This is a solder solder containing 60% tin and 40% lead. It could be called POS-60, if at least specifications for it were developed. According to international data describing the characteristics, the melting point of 60/40 solder is 191 degrees Celsius.
The same story with POS-62 type solder . Such lead solder according to GOST has not yet been invented. So, if they ask me “what is the melting temperature of POS-62 solder,” I know that the answer with the figure 184 degrees Celsius must be looked for in the imported solder catalog. For example, you can use the Kester solder catalog.
Technical characteristics of POS-61 solder
The designation of POS-61 brand solder, as we found out, is quite controversial, but you can’t argue against GOST. POS-61 is used for soldering and tinning of electronic components and printed circuit boards of precision instruments with highly hermetic seams, for which overheating is not allowed.
Composition of POS-61 solder
The chemical composition of POS-61 solder is as follows:
- Tin 59 - 61%;
- Antimony - no more than 0.1%;
- Copper - no more than 0.05%;
- Bismuth - no more than 0.02%;
- Arsenic - no more than 0.02%;
- Iron - no more than 0.02%;
- Nickel - no more than 0.02%;
- Sulfur - no more than 0.02%;
- Zinc - no more than 0.002%;
- Aluminum - no more than 0.002%;
- Lead - everything else - about 38.7 - 40.7%.
The soldering temperature of POS-61 solder is 220 degrees Celsius. Solidus is 183 degrees. I even shot a slow motion video of this solder melting on my Olympus Tough TG-860 at 240fps.
Solder POS 61 GOST 21931-76 has the following technical characteristics:
- Density determines the weight of POS-61 solder and is equal to 8.5 g/cu. cm.;
- The electrical resistivity is 0.139 Ohm x mm2/m;
- Thermal conductivity is 0.12 kcal/cm x s x deg;
- Temporary tensile strength is 4.3 kgf/sq.mm.;
- The relative elongation is 46%.
Advantages of POS-61 brand solder:
- the best ratio of melting temperature and strength;
- good adhesion to metal surfaces;
- universal solder for soldering and most radio installation work;
- accessibility and prevalence;
- low cost;
- often produced in the form of wire, for example POS 61 T2A solder.
Disadvantages of POS-61 type solder:
- versatility reduces performance in special cases, for example when soldering zinc;
- melting temperature is not suitable for all devices;
- solder fumes (lead in it) are harmful to health.
Technical characteristics of POS-63 solder
Solder POS 63 is described in GOST and in the industry standard OCT 4G 0.033.200. POS-63 solder is understood as an alloy that consists of 63% tin and 37% lead.
This is a kind of modernization of POS-61 solder, adjusted to the international standard J-STD 006B. Most good Chinese solders are also labeled Sn63Pb37 .
These are eutectic alloys with a melting point of 183 degrees Celsius.
POS-63 is used for soldering and tinning the leads of microcircuits and packaged radio components, printed circuit boards, wires and cables. In general, of modern solders, this is the most common. The technical characteristics of POS 63 solder are approximately the same as those of POS-61. But I haven’t found the exact values yet.
Advantages of POS-63 solder:
- the most common POS series solder;
- relatively low melting point;
- coincidence of solidus and liquidus points;
- low cost;
- supplied in the form of wire filled with flux.
Disadvantages of POS-63 solder:
- often counterfeited, especially by the Chinese;
- contains lead, which increases the cost of recycling electronic equipment in accordance with modern safety standards.
Technical characteristics of solder POSSu-61-0.5
Solder marking POSSu-61-0.5 indicates a type of antimony solder containing 61% tin, up to 0.5% antimony and about 38% lead. This solder is used for soldering and tinning of printed circuit boards and galvanized radio components under increased operating temperature requirements. But its melting point is 189 degrees.
Advantages of POSSu-61-0.5 solder:
- increased adhesion to the metal surface due to the antimony content;
- technical characteristics are almost the same as POS-61.
Disadvantages of POSSu-61-0.5 solder:
- difficult to find on sale;
- increased cost.
Technical characteristics of POS-90 solder
POS-90 brand solder consists of 90% tin and 10% lead. It also contains about 0.1% antimony and 0.05% copper.
It is mainly used for soldering and tinning internal seams of food utensils and medical equipment. Yes, 10% lead can already be put into food products - surprisingly, everything is in accordance with GOST 1976.
According to the technical characteristics, the melting temperature of solder type POS 90 is 220 degrees.
Advantages of POS-90 solder:
- low lead content;
- rarely counterfeited;
- low resistance;
- high strength.
Disadvantages of POS-90 brand solder:
- high cost (higher than pos-61);
- low plasticity.