Greetings to dear readers! In this material I tried to collect all the data about PIC solder. This Tin-Lead Solder is the most popular solder for mounting radio components and is used more often than others in radio engineering. I will try to explain why this is so and tell you about the types and technical characteristics of POS series solders. I’ll also tell you a terrible secret about POS-60 and POS-62 solders. Go!
Types of POS solders
First, let's remember what types of solders are made from alloys of the tin-lead group. The most popular are antimony-free solders POS-10, POS-40, POS-61 and POS-90. POS solder containing antimony is called POSSU. Antimony in the solder adds several percent to its strength.
When we talk about melting a mixture of tin and lead, we need to remember the definitions of solidus and liquidus . When any mixture of two or more metals is heated, the melting (transformation from solid to liquid phase) of the lightest particles occurs first. This temperature mark is called the solidus of the alloy.
With a further increase in temperature, more refractory components begin to melt. As soon as they melt, the liquidus . The PIC solder is now completely melted. This process is explained in more detail by a picture taken from a presentation on the topic of alloys.
Between these two points is a state of increased ductility of the solder . In this state, the solder can be pulled and deformed without losing integrity.
There are eutectic alloys - solders, in which the solidus and liquidus points coincide. This is very convenient when soldering and indicates the high quality of the solder.
About the composition of solder
The name of the solder of the tin-lead group indicates the tin content in it. For example, POS-40 contains 40% tin, and POS-61 contains almost 61% tin. The rest consists of lead and additional impurities. By appearance, you can estimate the composition . If the PIC solder is more matte and dark, then it contains more lead. If it is lighter and shiny, then there is more tin. This is best understood by comparison. Look at the photo to see what a sheet of tin and a sheet of lead look like.
The strength of solder depends not only on the alloy alloy, but also on the metal being soldered. For example, to solder copper or zinc, several percent of copper or zinc are added to the POS solder, respectively. This reduces chemical erosion of the metal and increases the surface strength of the joint.
Solder alloying
To improve performance characteristics, alloying of solder with the following substances is used:
- adhesion is improved by the addition of copper, cadmium, antimony, aluminum, silver and zinc;
- ductility and resistance to thermal cycling are improved by the addition of indium, silver, manganese, bismuth, and lithium;
- Nickel, cobalt, zinc, silicon, boron, iron add strength
- The corrosion resistance of solder is increased by nickel and copper;
- Heat resistance is increased by silicon, zirconium, tungsten, vanadium, cobalt, niobium, hafnium.
Solder paste
Soldering is most often carried out using solder and flux. In order to do the job well, it is necessary to choose the right grade of alloy for each specific task.
The paste differs from ordinary solder in that it contains two components at once: solder and flux, which significantly speeds up the process of soldering parts, especially when it comes to SMD elements.
Any paste is a thick, dense mixture of various substances. It has become widespread in industry. Electronics manufacturers actively use it in their production.
Types of solder pastes.
Depending on the composition of the paste, the following types are distinguished:
- washing;
- water soluble;
- halogen-containing;
- no-wash;
- halogen-free.
Its properties are determined by the type of flux that is added to it. If we are talking about the first type, then rosin is used. To clean the product from such a paste, a solvent is used.
It is important to choose the right paste depending on the job at hand. For example, if you have to solder a lot of small parts on a board, then it is better to give preference to a thicker paste.
For high-quality soldering, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work. The board should be cleaned and degreased. All contacts should be tinned using low-melting solder.
When working with SMD elements, it is necessary to apply a thin layer of paste. Otherwise, you can short-circuit the contacts of the microcircuits.
When using a large board, it is advisable to use bottom heating. This is best done using a soldering station. For these purposes, you can also use a hot air gun or other means to provide heating up to 150°C. If this is not taken care of, then she may be led away.
After finishing work, all excess paste is removed, which can be easily done using a soldering iron with various attachments.
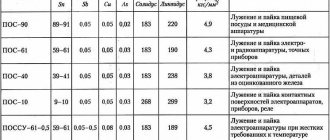
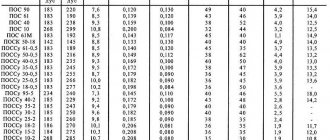
Technical characteristics of POS and POSSu solders
In order not to describe all the technical characteristics of solders of the tin-lead group, I will simply provide a table of parameters. It can be used to determine the melting point, density, electrical resistivity, thermal conductivity, tensile strength, elongation, impact strength and Brinell hardness of solders.
An analysis of the table shows that the most fusible among the list is cadmium with a melting point characteristic of 145 degrees Celsius. The strongest solder is POSSu 4-6 solder with a tensile strength of 6.5 kgf/sq.m. mm.
LABELING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1 On each piece of solder the following is stamped:
a) trademark of the manufacturer;
b) brand of solder;
c) heat number;
5.1a Solder ingots are transported without packaging in transport bags or in containers in accordance with GOST 18477-79. Packages of pigs must be tied with steel packaging tape measuring at least 0.8x30 mm in accordance with GOST 3560-73, fastened with a lock. It is allowed to use fastening means that ensure the safety of the package in accordance with GOST 21650-76. The weight of the package is no more than 1250 kg. It is allowed to increase the package up to 1500 kg, provided that loading and unloading is carried out on the access roads of the consignor and consignee, while the floor of the car along the path of the loader must be lined with metal sheets 3-4 mm thick.
Schemes for laying and fastening solder ingots into bags are given in Appendix 4. When transporting by air, the ingots are packed in thick board boxes of type II-1 in accordance with GOST 2991-85, dimensions in accordance with GOST 21140-88, lined on the inside with plastic film in accordance with GOST 10354-82. The gross weight of the boxes is no more than 60 kg.
5.1b The designation of the solder brand is applied on the front surface of the pig on the left side with numbers corresponding to the percentage of the main components without indicating the letter designation POS, POSS, POS, POSK. The heat number is stamped on the right side of the front surface of the pig.
Examples of solder markings:
Solder grade POS 90:90.
Solder grade POS 61M: 61M.
5.2 Transport marking - according to GOST 14192-77.
5.3 Solder ingots are transported by all types of transport in covered vehicles in accordance with the transportation rules in force for transport of this type and the conditions of loading and fastening approved by the Ministry of Railways of the USSR.
5.4 Solder should be stored indoors. If the specified storage conditions are observed, the consumer properties of tin-lead solders do not change during storage.
Annex 1
Information
Technical characteristics of POS-10 solder
POS 10 solder has a distinctive chemical composition. It contains 9-10% tin, about 89% lead, 0.2% bismuth, 0.1% antimony and other impurities in small quantities. POS-10 solder is used for soldering and tinning contact surfaces of electronics. For example, they solder relays and fill control plugs in radio electronics housings.
The POS-10 soldering temperature is 299 degrees Celsius. The solidus point is 268 degrees.
Advantages of POS-10 solder:
- high melting point is useful when soldering equipment cases.
Disadvantages of POS-10 solder:
- low strength and tensile strength of about 3.2 kgf/sq.mm.;
- high resistivity - 0.2 Ohm x sq.mm./m;
- high content of lead, which is hazardous to health.
Technical characteristics of POS-30 solder
Solder for soldering of the POS 30 brand is an intermediate link between POS 10 and POS 40. The composition of POS 30 solder is as follows: 30% tin and 69.5% lead. The rest is impurities and doping. Solder POS 30 can be easily replaced with POS 40, which is described below. The melting point (liquidus) is 238 degrees, and the plasticity temperature (solidus) is 183 degrees Celsius. According to the technical characteristics, POS 30 solder is most often used for soldering and tinning of zinc sheets and radiators.
Advantages of POS-30 solder:
- good adhesion;
- high strength.
Disadvantages of POS 30 brand solder:
- high lead content;
- often produced in rods.
Varieties
POS 30 solder is produced mainly in the form of wire. But there are several varieties, which are determined by the diameter of this product. The smallest wire diameter is the half-millimeter version. It is best suited for soldering wires and small parts. More common are medium ones, 1.5-2 mm thick. They are used for most procedures in home and industrial settings. The thickest solder is POS 30 wire with a thickness of 8 mm. It is used for repairing cases and soldering thick workpieces that require beveled edges to improve the quality of the joint.
Solder POS 3 in a reel
Technical characteristics of POS-40 solder
The chemical composition consists of 39-41% tin, 59% lead. The remaining impurities are in the same ratio as in POS-10. Soldering solder POS-40 is often used for soldering and tinning radio equipment casings made of galvanized iron with galvanized seams.
The soldering temperature of the solder is 238 degrees Celsius, and the solidus is 183 degrees.
Advantages of POS-40 solder:
- good ratio of ductility and melting point;
- because of this, it tolerates thermal cycling better than POS-61.
Disadvantages of POS-40 solder:
- high lead content, which is harmful to health;
- elevated liquidus temperature.
The terrible secret of POS-60 solder
Now the time has come for the terrible secret of POS 60 solder . According to GOST 21930-76 entitled “Tin-lead solders in ingots. Technical specifications" and GOST 21930-76 "Tin-lead solders in products. Technical specifications", solder such as POS-60 simply does not exist. GOST 21930-76 itself can. Here is the complete table from this GOST.
So “ POS-60 ” is jargon or a popular designation for “the solder that everyone solders with.” It seems to me that this is due to confusion in the designation of POS-61. Because when the tin content in the solder according to GOST is from 59 to 61%, it is more logical to call it POS-60 rather than POS-61.
Among the solders produced according to international standards there is Sn60Pb40 solder . This is a solder solder containing 60% tin and 40% lead. It could be called POS-60, if at least specifications for it were developed. According to international data describing the characteristics, the melting point of 60/40 solder is 191 degrees Celsius.
The same story with POS-62 type solder . Such lead solder according to GOST has not yet been invented. So, if they ask me “what is the melting temperature of POS-62 solder,” I know that the answer with the figure 184 degrees Celsius must be looked for in the imported solder catalog. For example, you can use the Kester solder catalog.
Types of solders
Solder is not always necessary to purchase. You can use an old radio component and assemble it from the board tracks using a soldering iron tip. This option is perfect for those who live far from the city, where it is not possible to purchase the material in a store.
Standard lead solders.
However, they are different and differ in their properties and characteristics. In this regard, every experienced master should understand this issue. To solder parts, it is necessary to use special alloys - solders.
The latter have a lower melting point than individual parts of the products.
Such alloys are divided into two main categories depending on their melting point: soft and hard. The first type is widely used in radio electronics, both by amateurs and professionals.
Low-melting solders include solders with a melting point of less than 450°C. They are made from: gallium, indium, tin, bismuth, lead and cadmium. High-temperature ones melt when heated above 450°C. In any case, it is usually an alloy consisting of several metals and impurities.
The most common option is a tin-lead alloy called PIC. The numbers after the abbreviation indicate the percentage of tin.
You can distinguish one alloy from another without knowing the brand. For example, with a higher tin content, a characteristic metallic luster appears, and with a higher lead concentration, the color becomes dark gray.
In addition, the melting point of POS does not exceed 265°C. Another distinctive feature of alloys with a higher proportion of lead is their ductility and the ability to be easily bent by hand.
Classification of alloys is carried out in accordance with GOST standards.
Physico-mechanical properties of solders.
The most common are:
- solder POS 90;
- POS 61;
- POS 40;
- POS 30.
In fact, there are significantly more markings. There are several dozen of them. Each is written in such a way that the composition of the alloy becomes clear from its name; all are manufactured in accordance with GOST 21930-76 tin-lead solder.
It is worth noting that the alloys differ from each other not only in their chemical composition. Depending on the form of release, they come in ingots, wire, a tube with rosin, or in a rod.
For example, POS 61 solder can be sold in rods or in the form of wire of various diameters. It is important to understand that the ratio of lead to tin affects the melting point. This parameter largely determines the choice of the required alloy.
In addition, the alloy can be produced with a flux, for example, with FRK525-2-T1, a low-activity halogen-free rosin flux.
This flux contains no halogens. Thanks to this fact, it has significantly less harm to the health of masters.
The use of alloys of various grades is determined by the scope of their application. POS thirty and forty are considered soft. Their melting point does not exceed 300°C. Used in joining galvanized products, tinning, repairing electrical appliances, etc.
Technical characteristics of POS-61 solder
The designation of solder, as we found out, is quite controversial, but you can’t argue against GOST. POS-61 is used for soldering and tinning of electronic components and printed circuit boards of precision instruments with highly hermetic seams, for which overheating is not allowed.
Composition of POS-61 solder
The chemical composition of POS-61 solder is as follows:
- Tin 59 - 61%;
- Antimony - no more than 0.1%;
- Copper - no more than 0.05%;
- Bismuth - no more than 0.02%;
- Arsenic - no more than 0.02%;
- Iron - no more than 0.02%;
- Nickel - no more than 0.02%;
- Sulfur - no more than 0.02%;
- Zinc - no more than 0.002%;
- Aluminum - no more than 0.002%;
- Lead - everything else - about 38.7 - 40.7%.
The soldering temperature of POS-61 solder is 220 degrees Celsius. Solidus is 183 degrees. I even shot a slow motion video of this solder melting on my Olympus Tough TG-860 at 240fps.
Solder POS 61 GOST 21931-76 has the following technical characteristics:
- Density determines weight and is equal to 8.5 g/cu. cm.;
- The electrical resistivity is 0.139 Ohm x mm2/m;
- Thermal conductivity is 0.12 kcal/cm x s x deg;
- Temporary tensile strength is 4.3 kgf/sq.mm.;
- The relative elongation is 46%.
Advantages of POS-61 brand solder:
- the best ratio of melting temperature and strength;
- good adhesion to metal surfaces;
- universal solder for soldering and most radio installation work;
- accessibility and prevalence;
- low cost;
- often produced in the form of wire, for example POS 61 T2A solder.
Disadvantages of POS-61 type solder:
- versatility reduces performance in special cases, for example when soldering zinc;
- melting temperature is not suitable for all devices;
- solder fumes (lead in it) are harmful to health.
Composition and characteristics
Chemical components
It was previously mentioned that PIC solder consists of an alloy of tin and lead. Tin has a lower melting point than lead, so by varying the percentage of these two components, you can select certain temperature characteristics. POS 60 has the following chemical compounds in its composition:
- Tin. The share is 59–60.5% of the total mass.
- Lead. The percentage content ranges from 39 to 40.5% by weight of POS.
- Impurities. They are represented by various elements such as copper, iron, antimony, nickel, zinc and others. Their mass fraction is no more than 0.3% of the total mass of the alloy.
Chemical composition of POS61 solder
The addition of copper or germanium significantly increases the wettability, as well as the strength of the solder joint; such an alloy is labeled POS-60M.
Other metals also influence the technical properties of the solder alloy.
Physical properties
The large amount of tin contained in this brand of solder directly affects its temperature characteristics and physical properties. Thus, POS 60 has the following properties:
- Melting point 183-190 degrees Celsius.
- Density 8.5 grams per cubic centimeter.
- The resistivity is 0.137 ohms per meter, which is 9–15% of the conductivity of copper.
- The tensile strength corresponds to the limit for soft solders and is equal to 50–70 MPa.
- The Brinell hardness is 14.9 PV.
- Thermal conductivity is 0.117 W/(m×k). Tensile strength is 4.3 kg/mm.
Physical properties of POS 60 and other solders
It is worth noting that tin and lead are identical in both softness and viscosity. Both of these metals have a characteristic of 1.5 on the Moss scale, so their percentage does not affect the physical properties of the solder.
Technical characteristics of POS-63 solder
Solder POS 63 is described in GOST and in the industry standard OCT 4G 0.033.200. POS-63 solder is understood as an alloy that consists of 63% tin and 37% lead. This is a kind of modernization of POS-61 solder, adjusted to the international standard J-STD 006B. Most are also labeled Sn63Pb37 . These are eutectic alloys with a melting point of 183 degrees Celsius.
POS-63 is used for soldering and tinning the leads of microcircuits and packaged radio components, printed circuit boards, wires and cables. In general, of modern solders, this is the most common. The technical characteristics of POS 63 solder are approximately the same as those of POS-61. But I haven’t found the exact values yet.
Advantages of POS-63 solder:
- the most common POS series solder;
- relatively low melting point;
- coincidence of solidus and liquidus points;
- low cost;
- supplied in the form of wire filled with flux.
Disadvantages of POS-63 solder:
- often counterfeited, especially by the Chinese;
- contains lead, which increases the cost of recycling electronic equipment in accordance with modern safety standards.
Technical characteristics of solder POSSu-61-0.5
Solder marking POSSu-61-0.5 indicates a type of antimony solder containing 61% tin, up to 0.5% antimony and about 38% lead. This solder is used for soldering and tinning of printed circuit boards and galvanized radio components under increased operating temperature requirements. But its melting point is 189 degrees.
Advantages of POSSu-61-0.5 solder:
- increased adhesion to the metal surface due to the antimony content;
- technical characteristics are almost the same as POS-61.
Disadvantages of POSSu-61-0.5 solder:
- difficult to find on sale;
- increased cost.
Technical characteristics of POS-90 solder
POS-90 brand solder consists of 90% tin and 10% lead. It also contains about 0.1% antimony and 0.05% copper. It is mainly used for soldering and tinning internal seams of food utensils and medical equipment. Yes, 10% lead can already be put into food products - surprisingly, everything is in accordance with GOST 1976. According to the technical characteristics, the melting temperature of solder type POS 90 is 220 degrees.
Advantages of POS-90 solder:
- low lead content;
- rarely counterfeited;
- low resistance;
- high strength.
Disadvantages of POS-90 brand solder:
- high cost (higher than pos-61);
- low plasticity.
Release forms
Depending on the scope of application, POS brand solder can have different release forms. So, for example, for tinning large areas, it is most convenient to use it in the form of a flat strip. Special lead-tin rods are produced for soldering various designs. They are convenient to solder with both a soldering iron and a gas torch. In radio electronics, rosin is used as a flux used in the soldering process; for this purpose, solder is produced in the form of a tube filled with rosin. This adds convenience during the installation of radio components as it does not require the application of additional flux.
Solder POS60 in the form of flux paste
Sometimes you can find POS-61 in the form of solder paste. It consists of alloy powder and flux and is used for surface mounting of electronic components using a soldering gun. Rarely used at home (and only by individual craftsmen) due to the need for special equipment.