Cutting sheet and profile metal is required in almost all metalworking and machine-building enterprises, from a small metalworking workshop to a huge factory. Often you have to cut metal in a home workshop or directly on a construction site. Guillotine shears are one of the most convenient machines for cutting and cutting metal. There are several varieties and modifications, which will be discussed in more detail later.
Cutting metal on a guillotine is used when it is necessary to produce parts of a rectilinear configuration of a fairly large size - strips, rectangles, triangles with a side from several centimeters to several meters. The thickness of the metal is in the range of 2-60 mm, the width of the workpiece can reach 2 meters, and the length is practically unlimited.
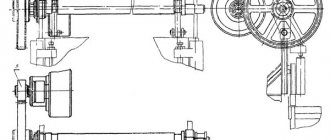
Main types of guillotine shears
Sample of a German hydraulic guillotine
Industrial workshops, private and home workshops specializing in metalworking are equipped with various types of guillotine shears, which differ in:
- type of drive;
- power;
- type of knives;
- productivity;
- maximum thickness of the metal being cut;
- the range of rental products they can work with;
- size of the processed sheet;
- the number of operations performed.
According to the type of drive, scissors are divided into:
- manual;
- hydraulic;
- pneumatic;
- electromechanical.
Guillotine shears for metal work on the principle of influencing metal simultaneously with a large pressure force and a sharp edge of a knife, operating on the principle of ordinary scissors. The two parts of the knife device are displaced relative to each other. They clamp the sheet or rolled product together and move its adjacent layers, cutting it with a sharp blade.
The guillotine cutting process combines two operations - cutting and breaking.
A good guillotine for cutting industrial metal provides up to 90% of the cut and about 10% of scrap.
Cutting edge with small gap
Cutting edge at optimal clearance
Influence of the gap size on the edge
In this case, the cut is smooth and requires virtually no processing. If the knives are dull or the gap is incorrectly set, then the cut/scrap ratio changes and a sharp protrusion appears on the lower edge - a burr, which indicates poor cutting quality.
The burr can easily cut your hands, especially when working with stainless steel. One of the main safety rules when working with guillotine-type scissors is the use of gloves made of thick fabric or with leather stripes. The appearance of burrs indicates the need to change the settings or sharpen the knives.
Hydraulic guillotine shears
Industrial machines for cutting metal, equipped with a hydraulic drive system, belong to the most powerful and productive types of guillotines. They are intended for serial or piece production of blanks with straight edges from metal sheets 2-20 mm thick with a cutting length of 1-3 m.
For large engineering companies, hydraulic guillotines are produced with the ability to cut sheets up to 6 m wide and more than 20 mm thick. They are distinguished by their large weight and size and are produced in single copies.
The hydraulic guillotine develops a force on the scissors of ≥ 400 MPa along the entire length of the sheet being cut. The machines are equipped with knives with both direct movement of the upper knife along vertical guides and with an arcuate trajectory (cantilever). The second option allows you to work with thicker sheets of metal or high-strength alloys with less hydraulic power. The cutting accuracy is not reduced.
The gaps between the knives are adjusted according to a special table in manual, semi-automatic or automatic mode. One of the most modern machines is the CNC hydraulic guillotine. Setting it up requires a minimum of time, and switching to the production of one of dozens of types of products is enough to press one button. All information about the settings is stored in the machine memory.
One of the main features of hydraulic shears is their noiselessness - the knives move smoothly, there are no shock effects characteristic of pneumatic and electromechanical guillotines.
Operational safety is ensured by the presence of photo sensors in the work area, protective screens and feed mechanism stroke limiters. Return of the beam to the top point is ensured by springs or gas-accumulating shock absorbers.
Electromechanical guillotine shears
This type of guillotine is widespread along with the hydraulic one. It is practically no different from a hydraulic guillotine in terms of productivity (up to 60 knife strokes per minute) but is noisier - the crank drive mechanism causes rapid movement of the knife and impact on the workpiece.
Electromechanical guillotine
Like the hydraulic guillotine, the electromechanical guillotine is intended for industrial use in workshops where high-performance precision cutting of straight workpieces of large size and thickness is required. However, metal cutting is also carried out using an electromechanical guillotine and in small-scale and artisanal production - a whole series of low-power scissors has been created for this purpose. They take up little space in the workshop and allow you to easily cut galvanized sheet steel, aluminum, copper, plastic and stainless steel up to 2-3 mm thick.
The drive to the upper beam with a knife is carried out using a crank mechanism on the power take-off shaft from an electric motor, which is activated by pressing a pedal or a button. As they rotate, the eccentrics transmit force to both ends of the knife beam, and the cutting force is distributed evenly. At the end of one revolution of the shaft, the beam returns to the upper position, and the workpiece is fed for the next cut.
Equipping electromechanical CNC guillotines allows you to turn them into one of the most accurate and productive machines for cutting and chopping metal. They are easy to maintain, have a reliable kinematic circuit and are cheaper than hydraulic ones. If you wish and have plumbing qualifications, you can make a guillotine cutter with an electric drive yourself in a home workshop or in a small production environment.
Principles of classification
Guillotine shears are distinguished by the following characteristics:
- By type of drive. In industrial production, as well as when cutting thick sheets, driven metal guillotines are more common. In this case, the control can be mechanical or hydraulic. In individual business practice, as well as in private workshops, manually driven machines are found.
- According to the execution of the main actuator. An electromechanical guillotine is most often equipped with a crank mechanism, while manual machines often have a lever mechanism.
- According to the method of pressing the workpiece to the supporting surface of the table. Guillotine shears can have mechanical (spring) or hydraulic clamping.
- According to the control method, cutting shears with non-automated feeding and removal of cut strips are distinguished, and automated complexes based on sheet shears, where all technological operations are carried out without human intervention.
Despite all the design and technological differences, these machines have one thing in common: the angle of inclination of the knives at which they cut. The fact is that at a zero inclination angle, penetration is carried out simultaneously across the entire width of the sheet, which causes increased energy costs and becomes the main reason for the increased drive power. Since the schedule of the technological operation of separating sheet metal has a peak of effort only at the beginning of the introduction of knives, and then rapidly decreases, it is much more profitable to ensure the gradual introduction of the tool into the workpiece. The force is significantly reduced, and the working displacement, although increased, is not much (due to the small thickness of the processed rolled profiles). Therefore, the knives of equipment for cutting sheet profiles are always inclined. The tilt angle ranges from 1.5...3.5°; it is larger for more powerful equipment. When cutting a harder product, for example, stainless steel, the gaps, on the contrary, are reduced. Increasing the gaps for ductile mild steel or copper degrades the quality and accuracy of the cut because the material being cut is pulled into the gap between the blades and forms burrs. Burrs are also a sign of a dull tool.
According to the classification accepted in our country, mechanically driven guillotine shears have the symbol H31__, H32__, H34__ or H33__ (the last two digits of the designation indicate the maximum thickness of the sheet metal being cut). Hydraulic shears are designated H37__. In practice, there is also marking of drive units for cutting sheet material according to its thickness and width. A typical example would be German-made machines, designated, for example, as follows: ScTR16×3150 (the first number is the maximum thickness, the second is the greatest width).
Pneumatic guillotines
A guillotine for cutting metal with a drive powered by compressed air exceeds hydraulic ones in productivity and is approximately equal to electromechanical ones. For its operation, a compressor or a central line with compressed air is required. Pneumatic guillotines are used in large metalworking shops for the production of large-scale parts.
Like electric and hydraulic machines, pneumatic guillotine shears belong to the stationary type of equipment. They are equipped with large work tables, retractable containers for collecting products and automated feeding mechanisms. Most pneumatic shears are equipped with CNC control - the speed of the pneumatics in combination with electronic control allows you to produce a large number of high-precision parts in a limited time.
Mechanically driven guillotines
Hydraulic driven units
A distinctive feature of such machines is the ability to cut fairly thick metal workpieces. Equipment manufacturers note in their operating instructions that for structural steels the maximum thickness can be up to 40 mm.
Similar devices on the edge of the blades develop a force of 200...400 tons. In this case, it is important to use thick knives that can transmit forces in the cutting zone.
Installation with hydraulic drive. The pumping station is located outside the machine
To operate a hydraulically driven guillotine, you must have a special pumping station. From it, oil is supplied through reinforced hoses to the actuators. Liquid pressure can reach up to 135...150 bar. Hydraulic cylinders transmit force to the actuator through a system of levers.
The main advantage of such guillotines is their quiet operation. The knives move without impact.
On the control panel, the operator specifies a number of parameters, the built-in computer will make the calculations itself:
- what gap is required between the knives;
- where to set the emphasis;
- at what speed should oil be supplied to the hydraulic system?
If it is indicated that several parts of the same type will be cut, then this parameter is also indicated. Then the material will be supplied automatically.
The operator and assistant can only:
- place the sheet of metal on the work table;
- align it with the guides;
- align with stops;
- indicate the number of the program by which you want to cut metal;
- set the number of required parts.
At the end of the cycle, on the back side of the machine there will be chopped blanks or parts that need to be taken to the semi-finished product site. Other employees of the company use them in the following production processes.
The price for such machines is high, amounting to several tens or even hundreds of thousands of euros. Guillotines of this type are made to order. In the future, the equipment manufacturer maintains it throughout the entire life cycle of the process unit, provides it with programs and offers original spare parts. If necessary, even a fairly old machine can be modernized. After modernization, it is ready to serve on equal terms with new units for quite a long time.
Video: cutting metal with a guillotine.
Food for thought. In the thirties of the twentieth century, DIP-250 and DIP-350 lathes were purchased in Germany. More than eighty years have passed. This equipment continues to be successfully used at a number of enterprises. After major repairs, gun barrels for modern guns and tanks are processed on similar machines. Machines can last quite a long time.
Video: CNC hydraulic guillotine.
Electromechanical guillotine shears
The most common type of machine is the electromechanical guillotine shear. A shaft with a flywheel constantly rotates in them. Through the crank mechanism, torque is transmitted to the active knife.
To make a cut you need:
- place a sheet of metal on the table;
- set the focus to the specified size;
- fix the workpiece on the table and press it against the stop;
- press the control pedal.
The metal will be cut according to the markings. By moving the sheet again to the stop, you can repeat the operation.
Electromechanical guillotine
These machines are quite lightweight. They equip small workshops and fairly large enterprises. They are characterized by high performance. You can cut up to 60 parts in a minute.
The disadvantage is the noise during operation. Here the metal is cut with a strong blow. You often have to send knives for sharpening. Edges tend to chip when subjected to impact loads.
It is necessary to frequently check the condition of the edges of finished products. If the formation of bent edges and burrs is observed, then the knives are removed and sent to a sharpening machine.
Video: operating principle of electromechanical guillotine shears.
Pneumatic guillotines
If there is a developed system of pneumatic pipelines, the enterprise uses equipment powered by compressed air. Pneumatic guillotines use air compressed by compressors to carry out basic production activities. They are equipped with pneumatic cylinders.
Installations of this type require a receiver. The volume of air used in the cycle can reach several liters, so a supply of working fluid is needed.
Pneumatic guillotine
The operation of such devices is somewhat louder than when using hydraulics. But there are also advantages. On such machines it is easier to install computer control. Therefore, a number of European countries producing technological equipment are focusing on creating just such guillotines. It is easier to configure here; programs for managing production operations are written relatively simply.
Training operators for such machines is also easy. After just 2-3 days of work, workers master the basic techniques of working on a guillotine. All that remains is to issue them a production task, indicate the placement of workpieces and areas for unloading semi-finished products.
Video: guillotine shears.
Manual guillotine for metal
Mechanical guillotine shears driven by a lever or pedal are undoubtedly the most common type of metal-cutting machines. With restrictions on the thickness of the metal being processed and its types, manual guillotine shears can be found in every workshop or workshop where work with sheet metal, fittings or rolled profiles is expected.
Mechanical guillotine machine
The mechanical guillotine cutter is equipped with two knives. The lower one, like a hydraulic or electric guillotine, is stationary. And the top one can move vertically downwards along guides, like in industrial installations, or rotate around an axis. The rotation point is located at one end of the knife beam, and the handle is at the other.
A manual mechanical guillotine can be equipped with a gearbox, which allows you to develop significant force on the knife, allowing you to cut sheets more than 1 mm thick and stainless steel. The foot guillotine is operated by a pedal, while the manual guillotine is operated by a lever. A combined drive is also possible. A mobile guillotine for cutting metal is installed on any flat surface that ensures the stability of the machine, and is used on construction sites, for example, for cutting roofing steel or corrugated sheeting.
In the second case, a manual saber-type guillotine, equipped with an arched knife, is most often used. In this case, the cutting point will be smoothly mixed by the cutting path and will not damage the metal of a complex profile. The manual saber guillotine is used for both transverse and longitudinal cutting of workpieces made of steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Guillotine cutting on manual machines is also possible when working with reinforcement, angles and profiles. If sheet cutting on a guillotine is possible on all types of machines, then a mini guillotine for metal for working with shaped steel must be equipped with a gearbox.
Table of characteristics of guillotine knives
Where to buy a metal guillotine
If you need a reliable, efficient and inexpensive manual guillotine for cutting metal, contact. The online store offers different types of such equipment, including:
- budget saber manual guillotines like the Stalex HS-1000 machine, priced from 30,700 rubles, which can be used for cutting steel sheets up to 1.5 mm thick and up to 1000 mm long;
- semi-professional options with a counterweight such as Stalex KHS-1250, which costs from 223,550 rubles and provides cutting of workpieces up to 1 mm thick with a cutting length of up to 1250 mm;
- industrial installations with pre-pressing before cutting, for example, Stalex 2500 priced from 656,950 rubles (maximum sheet thickness 1.25 mm, cutting length up to 2500 mm).
All machines are covered by the manufacturer's warranty.
Return to list