In a workshop, a wide variety of tools, machines and installations are used to work with wood products.
Some woodworking machines for the home workshop are used very often, while others are designed to perform only some specific, highly specialized work. It should be noted that working with wood at home is very different from working in a woodworking or carpentry shop. This article will provide an overview of some of the popular wood shop machines and their purpose.
Types of woodworking machines
Without widespread mechanization of technological processes today, it is difficult to imagine not only the harvesting, but also the processing of wood. The entire production cycle, right up to the launch of finished construction, furniture or other products on the market, is inextricably linked with the use of woodworking machines of various types, configurations and purposes. And it is impossible to fully understand the features of this cycle without thoroughly studying its technical basis. So, the main types of woodworking machines are:
Sawing machines
This group includes devices designed for sawing logs and blanks, shaping flat elements and performing other work related to dividing material in one plane along a given path. The most common representatives of sawing machines are:
- Sawmills are machines that carry out longitudinal and transverse sawing with linear saws that perform reciprocating movements relative to the workpiece. Previously, they were widely used in the logging industry, but today these positions are being ceded to circular saws and band saws due to their bulkiness, inefficiency and difficulty in maintenance.
- Circular saws are manual and automatic machines that perform longitudinal and transverse sawing with circular saws in vertical and inclined planes along a straight path. They are used primarily for shaping virgin lumber. They are classified according to power, productivity, number of saws, their diameter and height (maximum cutting thickness).
- Belt machines are manual and automatic machines, the working element of which is a rotating cutting belt moving along a trajectory simulating endless linear motion. They are used both for the initial preparation of material and for its further sawing. Easier and cheaper to maintain than circular saws, but less accurate and productive.
Sawing
They are used to cut workpieces and give them a certain shape. Divided into the following categories:
- sawmills for cross-cutting and longitudinal sawing with linear saws. Movements are reciprocating. Bulky units that require complex maintenance are now not as popular as the next two options;
- circular saws. Needed for performing transverse and longitudinal cutting with circular saws vertically and obliquely. They are used to shape primary lumber;
- belt based on a tape that rotates and moves along a linear path. Suitable for harvesting at the initial stages and sawing material later.
Planing machines
Planing machines are designed to remove the top layers of wood by moving a cutting tool buried in it. This allows you to adjust the thickness of the material and shape the surface of the workpiece in accordance with its purpose. The main types of planing machines include:
- Thicknessers are single-sided - they process only the upper plane of the workpiece, and are designed to work primarily with massive, large-sized elements. They are distinguished by their simple design, which is why they are more common.
- Thicknessers are double-sided - they process the upper and lower planes of the workpiece simultaneously.
- Thicknessers are special - they can process the workpiece simultaneously from three or four sides, therefore, in addition to adjusting the thickness, they are involved in giving it a certain shape.
- Planers - planing in one plane and chamfering at specified angles.
Lathes
Elements made on a lathe have the form of bodies of revolution and are formed from straight blanks using the method of sequential circular removal of a layer of material. The final processing product is used in construction and furniture production as fastening, cabinet and decorative elements. Woodworking lathes are classified according to power and maximum dimensions of the workpiece processed; an important criterion is the degree of production automation. Depending on it there are:
- Manual lathes - installation and adjustment of feeds, speeds and other parameters
- is carried out directly by the turner in each specific case; the technological process requires his constant participation.
- Automated lathes - equipped with a copying device for working according to templates, may have some autonomously calculated parameters, but are operated by a person.
- Automatic lathes do not require human participation in the production process, perform work in accordance with the embedded software, and can make flexible changes to the progress of work in accordance with logical algorithms. Extremely expensive equipment used in large industries.
Olympiad tasks on technology for grade 9. Boys
I. Technology is the science of:
1. public and social processes; 2. physical and mechanical processes in metals; 3. transformations of materials, energy and information; 4. biological phenomena on Earth; 5. chemical processes in production.
II. Woodworking machines are classified as:
1. energy; 2. transport; 3. technological; 4. auxiliary.
III. Establish a correspondence between Russian scientists-inventors and their inventions/discoveries:
1. Nartov A.K. 2. Lomonosov M.V. 3. Polzunov I.I. 4. Yablochkov P.N.
a) scientist, inventor of electric lighting; b) an inventor who developed and manufactured a pocket watch; c) the mechanic who designed the suspension bridge; d) a scientist who discovered the law of conservation of matter and motion; e) mechanic, gave a description of more than 20 types of lathes, inventor of a machine with a mechanical support; f) inventor of the first steam engine in Russia.
IV. The technological properties of metals include:
1. elasticity; 2. density; 3. hardenability; 4. strength; 5. color.
V. For the manufacture of marking tools (punch punches, scribers), steel grades are used:
1. 11Р6М5; 2. 95X; 3. 70G; 4. U8.
VI. Type of heat treatment - hardening is used for:
1. increasing plasticity; 2. elimination of casting defects; 3. obtaining ultimate hardness; 4. decrease in strength; 5. relieving internal stress.
VII. In machine designs, a collapsible connection is:
1. hairpin; 2. adhesive; 3. welded; 4. rivet.
VIII. Removing a small layer of metal using a file is called an operation:
1. felling; 2. filing; 3. pressing; 4. planing.
IX. To cut sheet steel, use a chisel with a pointed angle:
1. 35˚ — 45˚; 2. 45˚ — 55˚; 3. 60˚ — 70˚; 4. 80˚ – 90˚.
X. Determine and record the size of the part measured with a caliper if the division value is 0.1 mm:
XI. The hardness of wood is the ability of a material to:
1. restore its original shape after the load is removed; 2. withstand certain loads without destruction; 3. bend under load without destruction; 4. resist the introduction of other bodies into it.
XII. Type of wood material obtained by removing a thin layer of wood:
1. chipboard (chipboard); 2. edged board; 3. furniture panel; 4. veneer; 5. plywood.
XIII. Cutting tools for wood processing are made from:
1. iron; 2. solid bronze; 3. carbon structural steel; 4. alloyed (W, V, Cr) tool steels.
XIV. Match the parts of the planer with their names:
A. knife b. wedge c. sole d. last d. taphole f. bed g. cheeks h. handle-horn and. shoulder insert
XV. Saw teeth for mixed sawing with hand saws have the following shape:
1. an isosceles triangle with an apex angle of 60°; 2. an isosceles triangle with an angle of 90°, directed towards the sawing; 3. semicircle; 4. rhombus.
XVI. A rectangular wooden rod used to fasten bars together is called:
1. dowel; 2. pin; 3. dowel; 4. hairpin.
XVII. For drilling through and blind holes of large diameter, a drill is used:
1. feather; 2. center; 3. ring; 4. spiral.
XVIII. The elements of a tenon joint are called:
1. socket and block; 2. block and tenon; 3. spike and eye; 4. eye and socket.
XIX. The most durable wear-resistant surface film on wood gives:
1. bayts; 2. non-aqueous stain; 3. alkyd varnish; 4. nitrocellulose varnish; 5. wax primer.
XX. Match the types of joinery joints with their image in the figure:
a) on the mustache; b) simple “overlay lock”; c) corner box; d) cross; e) tee overlay; f) thorny; g) straight with a straight joint; e) straight into the overlay.
XXI. The sources of electric current are:
1. galvanic cells; 2. batteries; 3. electric generators; 4. all of the above.
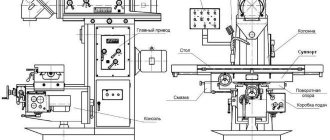
XXII. Match the main parts/assemblies of the drilling machine shown in the figure with their names
a) belt drive; b) electric motor; c) manual feed handle; d) rack and pinion transmission; e) cartridge; f) column; g) handle for securing the spindle head; h) bed; i) spindle head lifting mechanism; j) spindle.
XXIII. A protective device that automatically turns off an electrical circuit in the event of a short circuit is called:
1. fuse; 2. breaker; 3. refractory insert; 4. switch.
XXIV. The electric motor commutator consists of insulated plates made of:
1. zinc; 2. copper; 3. steel; 4. aluminum; 5. from any dielectric material.
XXV. Match the symbols of the elements of electrical circuits with their names:
a) direct current source; b) alternating current source; c) resistor; e) diode; e) inductor; g) transistor; h) capacitor; i) light bulb.
XXVI. Environmentally friendly material used in furniture production:
1. particle board; 2. fiberboard; 3. glued furniture board; 4. waterproof plywood; 5. Laminated particle board.
XXVII. The occurrence of “ozone holes” is influenced by gas emissions from enterprises into the atmosphere:
1. sulfur dioxide; 2. carbon dioxide; 3. neon; 4. freon; 5. mercury.
XXVIII. Requirements for the designed product by the consumer:
1. functional; 2. ergonomic; 3. aesthetic; 4. economic; 5. all of the above.
XXIX. The implementation of a creative project begins with:
1. putting forward project ideas; 2. product design development; 3. development of technological documentation for the product; 4. collecting information for project implementation; 5. identifying the project problem.
XXX. The image of an object on a plane using rays parallel to each other is called:
1. central projection; 2. oblique projection; 3. parallel projection.
XXXI. The image of parts in three types is called:
1. axonometry; 2. sketch; 3. technical drawing; 4. drawing.
XXXII. Establish a correspondence between the axonometric image of the part and the views:
XXXIII. In accordance with the formula “I want” – “I can” – “I must”, determine a rational sequence of actions for the correct choice of profession:
a) find out your professional interests, inclinations and abilities; b) study the chosen profession, find out how to acquire it; c) find out what professions are required in the labor market in the city or region.
XXXIV. The profession of the “man-nature” type includes:
1. forestry teacher in an educational institution; 2. agronomist; 3. designer; 4. tractor driver.
XXXV. In school woodworking workshops it is prohibited to use:
1. lighting fixtures; 2. oil radiators; 3. varnishes and paints based on nitro; 4. all of the above.
Answers:
| I. | 3 |
| II. | 3 |
| III. | 1-d, 2-d, 3-e, 4-a |
| IV. | 3 |
| V. | 4 |
| VI. | 3 |
| VII. | 1 |
| VIII. | 2 |
| IX. | 3 |
| X. | 89.4 mm |
| XI. | 4 |
| XII. | 4 |
| XIII. | 4 |
| XIV. | 1-z, 2-d, 3-b, 4-a, 5-c |
| XV. | 2 |
| XVI. | 3 |
| XVII. | 1 |
| XVIII. | 3 |
| XIX. | 3 |
| XX. | 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th |
| XXI. | 4 |
| XXII. | 1-z, 2-d, 3-c, 4-b, 5-a |
| XXIII. | 1 |
| XXIV. | 2 |
| XXV. | 1-i, 2-d, 3-c, 4-a, 5-z, 6-g |
| XXVI. | 3 |
| XXVII. | 4 |
| XXVIII. | 5 |
| XXIX. | 5 |
| XXX. | 3 |
| XXXI. | 2 |
| XXXII. | 2 |
| XXXIII. | 1-c, 2-a, 3-b |
| XXXIV. | 2 |
| XXXV. | 3 |
Drilling machines
Wood is a soft material that does not require much effort when drilling. Therefore, most of the work related to the creation of through or blind holes in wooden workpieces is carried out using hand-held power tools. Drilling machines are used to drill holes of considerable depth when working with hard wood or in cases where special precision is required. In addition to the standard classification by power and permissible workpiece parameters, they are classified by the number of spindles (single and multi-spindle) and by configuration:
Machine for drilling holes.
- Vertical drilling machines - linear movement of the rotating spindle is permissible exclusively in the vertical plane.
- Horizontal drilling machines - linear movement of the rotating spindle is permissible exclusively in the horizontal plane.
- Horizontal drilling for deep drilling - have runout control and additional axial stabilization, which increases drilling accuracy.
- Radial drilling - allow changing the direction of drilling at a certain angle by tilting the spindle radially in the plane of its axis.
The progress of modern machine tool building has significantly reduced the need for drilling machines due to the development of turning and milling machines, which today, in addition to their main purpose, are capable of performing a number of precise drilling operations.
Milling
Needed for processing wood using a milling cutter. You can work with flat surfaces with patterns, shaped variations, produce cylindrical and spherical parts, make grooves, splines, grooves, etc. Woodworking machines of this type are ideal for carrying out fine carpentry work.
Among them are:
- universal - for small and light parts. The rotation angle is adjustable in the horizontal plane;
- widely universal - equipped with a spindle head that rotates at any angle in mutually perpendicular planes;
- horizontal - there is no turning mechanism;
- vertical cantilever - the spindle is located vertically;
- non-cantilever - for working with vertical, horizontal and inclined planes;
- longitudinal - for dimensional workpieces. Massive units are used in large enterprises.
Grinding machines
The process of sanding wood involves removing the top layer of material using an abrasive (usually paper or fabric backed) to smooth out surface irregularities and reduce roughness. It can be done using hand-held power tools, but in large industries it is impossible to do without grinding machines. The most common of them are:
- Surface grinding machines - perform grinding work in one, usually the upper horizontal, plane; they are used for the final processing of lumber, as well as building and furniture elements of simple shape.
- Grinding machines for objects of rotation - have a radial trajectory of movement of the working body, designed for the final processing of elements made by turning.
- Edge grinding machines - have a complex trajectory of movement of the working body, designed for the final processing of shaped joinery and furniture elements.
- Special grinding machines are mechanisms that perform a number of additional works in addition to the main technological grinding process (measurement, calibration, etc.)
Copying machine
Copying machines (usually made in the “copy-milling” or “lathe-copy” models) are designed to create a copy of a sample of a wooden product that is as close as possible to the original. Such devices allow you to perform work quite quickly, sometimes making several copies of a part at the same time. These machines use a pattern copying technique. This technology allows you to achieve the same shape for all elements of a particular part, as well as accurately copy this part one or more times. Thus, the possibility of technological errors is practically eliminated, since most stages of lumber processing are carried out automatically.
It should be noted that copying machines are quite compact in size, but at the same time they are highly durable even with frequent use; they operate for a long time without breakdowns or repairs if the devices are serviced on time. Moreover, copy-milling machines make it possible to produce elements similar to each other with maximum precision.
Bending machines
An unusual type of woodworking machine that does not involve removing layers of material. The purpose of bending machines is to give wooden elements a special shape that is unattainable by other methods. Structurally, they are hydraulic presses equipped with specialized clamps and
forming heads, and also, optionally, means for preparing the material for molding.
Bending wooden blanks on bending machines allows you to create complex, elegant parts, which is widely used in the production of exclusive furniture.
Types of woodworking machines and their purpose
Types of woodworking machines and their purpose
Woodworking enterprises need special machines that differ mainly in functionality and power. There are machines for household, professional and industrial use. Sawing, drilling, milling, planing, turning and other wood processing processes require specialized technical equipment, so each type of installation deserves separate consideration.
Combined machines
Combined machines are devices that are often used for processing wood at home. This is very convenient, since it is often not possible to equip a home workshop with many working installations.
A combination machine can perform many functions at the same time, for example:
- sawing;
- milling;
- grooving;
- resuscitation;
- planing.
Industrial combined machines for wood processing can be divided into two categories:
- household;
- professional.
The main differences between these two types are dimensions, motor parameters, and supply voltage.
Moreover, some woodworking machines of a combined type can be made homemade and used just as successfully at home.
As can be seen from the material described in this article, there are special installations for various types of wood processing, each of which copes with its own task. Some of them may be partially interchangeable with each other's functionality. Some machines, for example, copying machines, are designed only to perform a specific job. A separate type of woodworking machines for home workshops is combined. Their functionality is wider, and their scope of application extends to many stages of wood processing. These devices are most often chosen for work at home.
Timber machines
Timber machines are used mainly for sawing thin logs and balance beams into unedged boards, slabs and carriages. The machine is distinguished by a reinforced frame design, high productivity and a set of other advantages:
- Double-shaft sawing system.
- Improved alignment of the log during sawing.
- Possibility of sawing logs with beams or “in sections”.
- Possibility of equipping with saws of smaller diameter.
- High yield of lumber.
Logs are used as blanks. Equipping a production facility with timber cutting machines can significantly simplify and speed up the process of obtaining timber, as well as unedged boards. The operator sets the required parameters of the final product. The possibility of using the machine as a separate unit or as part of a woodworking production line is noted.
Multi-rip machines
Multi-saw machines are an easy-to-use technical tool used for cutting wooden workpieces. The tool is used primarily in sawmills and industrial enterprises whose activities are related to wood processing. The advantages of a multi-rip machine include:
- Easy installation.
- Convenient operation.
- Long service life, reliability.
- A reinforced foundation is not needed.
- High performance.
- Extreme precision in wood processing.
Jointer
A jointer is equipment that is used to process wooden workpieces. Different jointers have different characteristics, but their main purpose is to process wood before it is processed on other machines.
These wood processing machines can be of 2 types:
- one-sided;
- bilateral.
For single-sided work, work is performed only on one side of the wooden element; for double-sided, it is possible to simultaneously process two sides (adjacent).
In addition, such machines are divided according to the type of workpiece feeding:
- automatic;
- manual.
A machine with an automatic material feeding method uses a special conveyor mechanism or a built-in automatic feeder.
Cross cutting machines
Wood is a natural material that does not lose its relevance even in the context of the modern variety of building materials. Cross-cutting machines are well known to craftsmen involved in wood processing, interior decoration and furniture production. Its design resembles a circular saw, but its placement on the frame allows you to obtain perfectly accurate cuts.
It will not be possible to make a perfectly even cut of the material with the established parameters when using hand tools. Advantages of using a cross-cutting machine in a workshop or enterprise:
- Obtaining a perfectly accurate cut of wood.
- There is no need for additional processing.
- The installation is suitable for woodworking companies, logging shops and organizations producing building materials.
- High performance.
- Suitable characteristics for setting up the production process.
Craftsmen, craftsmen and ordinary woodworking enthusiasts can purchase a cross-cutting machine.
Dividing machines
Dividing machines include equipment designed for cutting slabs, thick boards, and timber. The distinctive properties of the installations are their design and operating principle. Main features and advantages of dividing machines:
- Availability of main engine load indicator.
- Stepless speed control.
- There is a feed speed indicator.
- Convenient selection of the appropriate operating mode.
This type of equipment is equipped with circular or band saws, and the material is supplied by a specialized conveyor with a pusher.
Tenoning machines
The equipment is necessary in the woodworking industry as an indispensable device for fixing parts “on a tenon”. Manufacturing molded products, processing windows and doors, creating furniture panels, splicing wooden elements - there are many products manufactured using this installation. Tenoning machines are used to a greater extent to automate mass production.
NPF "Tehpromservice" offers all types of machines for equipping workshops, as well as large production facilities. The cost of equipment is determined by its purpose, functionality and technical characteristics.
Woodworking machines: types, features
Woodworking machines can be classified depending on the range of tasks performed, namely:
- universal, combined, which perform a wide range of tasks. They can replace several specialized machines;
- specialized, carrying out a specific type of processing;
- special, processing only the same type of parts (for example, for lining).
Useful: sawmill equipment.
Special ones, in turn, are divided according to the type of operation performed into the following types:
- debarking machines (designed for cleaning bark. They can be rotary, caliper and hydraulic. The former are most often used.);
- sawmill frames (they cut logs in the longitudinal direction with one or several saws. They can be general purpose, intended for stationary workshops, and special - for valuable wood species and plywood production);
- band saws (used for cutting wood materials. They are divided into dividing, carpentry, and log saws. The former can do vertical and horizontal cutting, the material is fed by mechanization. The latter - only horizontal and manual feed);
- circular saws (cut lumber, blanks and sheets of plywood or various types of slabs. They can be for transverse cutting, longitudinal or mixed type);
- longitudinal milling (form the longitudinal surfaces of block and panel parts. They are jointing, thicknessing and four-sided);
- milling (they mill various surfaces along contours, cut tenons and springs, process edges. They can be with a lower spindle or an upper one);
- tenon-cutting (they form tenons and springs on adjacent parts when they are connected at an angle into boxes or frames. They are one-sided and two-sided);
- drilling, drilling-grooving and slotting (they make holes (through and not through), select nests, remove knots that are sealed with plugs. They can be subdivided by the type of cutting tool, the type of specific operation, depending on the location of the spindles and their number) ;
- lathes (used for processing rotating parts. There can be center lathes, lobe lathes and round-rod lathes (centerless);
- grinding (used at the end of processing, smoothing out any irregularities).
Woodworking machines have several ways to feed material. Accordingly, they can be cyclical or incoming. The former work on the principle of intermittent supply of material to the cutting tool or vice versa. In the receiving areas there is a continuous supply of material, that is, processing is in motion. Also, to determine the type and subtype of a woodworking machine, it is customary to use their letter indexing:
Circular machine
Circular saws have some similarities with sawing equipment. The purposes of the wood circular saw are:
- Dissolving lumber both lengthwise and crosswise.
- Production of wooden beams.
- Cutting plywood.
- Manufacturing of glazing beads.
A circular saw is a wood cutting machine that you can make yourself.
Based on the type of construction, circular saws can be divided into three categories:
- Tabletop. Used in domestic conditions. The weight of such a machine varies up to 25 kg. You can install such a device on any work surface, for example, on a table.
- With stand. This machine is also portable, but is equipped with a special stand that allows you to process long boards.
- Stationary. Most often, such woodworking machines are used in industrial production. It is the stationarity, that is, the immobility and stability of the structure that makes it possible to perform work on such a device very accurately and efficiently.
For all of the above circular saws, it is necessary to choose different cutting discs.
Woodworking machines and their operation
A woodworking machine is a working machine on which parts are made and products made from wood and wood materials of the required shapes, sizes and processing accuracy are processed.
There are general-purpose (universal) and special-purpose (narrow-purpose) machines. According to the method of wood processing, woodworking machines are divided into circular saws, band saws, longitudinal milling machines (planing, surface planing and four-sided), milling, tenoning, drilling, drilling and grooving, slotting, grinding, and combined machines.
A woodworking machine has motor, transmission and actuator mechanisms. Propulsion mechanisms include electric, hydraulic and pneumatic drives, which ensure the movement (operation) of actuators (cutting and feeding). Transmission mechanisms transfer motion from motor to actuator mechanisms.
The design of woodworking machines depends on their purpose. With different designs, they have a number of structural elements of the same purpose: a frame, a table, a drive, feeding and cutting mechanisms, controls, monitoring devices, protective fences, which facilitates their manufacture, operation and repair. Elements of machine tools are divided into main and auxiliary.
Thicknesser
The main purpose of a wood planer is to smooth the surface of a wood element. In addition, such machines are used to calibrate all similar products to the same size.
The design of various installations allows cutting both along and across the wood.
The device has a working surface in the form of a table. It consists of 2 parts. One of them supplies the wooden element, and the other receives it. Between these surfaces there is a special shaft in the form of a knife, which is used for slicing. After cutting, the wooden element arrives at the receiving table. In this part of the machine there are special rollers that support the beam.
When choosing such a device, you should pay attention to the method of supplying lumber to the working area. Some models provide only manual feeding, while in others this can happen automatically.
Types and structure of woodworking machines
The main elements of machine tools provide processing (cutting) and supply of materials and workpieces to the cutting tool or to them. Auxiliary elements of machine tools include devices for sharpening cutting tools, settings, lubrication, and waste removal. All elements are mounted on the frame (base) of the machine.
Cutting mechanisms (shafts, spindles, chucks) are used to install and fasten cutting tools (saws, cutter heads, cutters, drills). Such mechanisms are placed on supports, which can be movable or fixed. To feed material or a workpiece into the machine, tables, guide rulers, squares, stops, clamps and other devices are used.
Protective barriers and safety devices come in the form of caps, casings, lids, fan shields. These elements protect the machine operator from accidental contact with the rotating and progressively moving mechanisms of the machine. The guards are interlocked with the machine drive and when they are unlocked, shifted or removed, the machine does not start working. Fences can serve as receivers for an exhaust system (pipelines) to remove wood waste (sawdust, shavings, dust) from machines.
The machine controls are buttons, handles, handwheels, and pedals. In computer numerical control (CNC) machines, a keyboard unit is provided to enter the necessary data, and information about the process and processing accuracy is displayed using a digital device or display.
According to the degree of mechanization and automation, machines can be semi-mechanized, mechanized, semi-automatic and automatic. In semi-mechanized machines, the process of processing the material or workpiece is mechanized, and their feeding to the cutting tool is manual. Mechanized machines have mechanized processes for feeding material or workpieces and their processing, but there is no automation. Semi-automatic machines automate a set of work operations only within one processing cycle, while automatic machines automate all work operations.
Modern automatic machines and lines are software configured and controlled using electronic computers (computers).
Circular saws
Circular saws are used for cutting lumber (boards and bars), plywood and wood boards into blanks. The cutting tools of such machines are steel circular (circular) saws. For cross-cutting (across the wood fibers) of boards and bars into blanks (pieces), cross-cutting machines are used: articulated-pendulum TsME-ZA AND with linear movement of the saw support TsPA-40. The machines perform positional processing when a rotating circular saw moves onto a stationary material. For finishing trimming of workpieces, two-saw end levelers Ts2K12-1, Ts2K20-1, Ts2K12F-1, Ts2K20F-1 are used.
vote
Article rating