Device and parameters
An apparatus for cutting metal parts using gas consists of several elements. The master needs to know its structure in order to take certain measures in case of breakdown or jamming. Main details:
- handle;
- frame;
- channels for supplying flammable gas and oxygen;
- mouthpiece;
- a nozzle responsible for the formation of a burning jet.
In addition to the key elements, the metal cutter has gas supply regulators, a system of channels through which they pass through the body and reach the outlet openings. The dimensions of the apparatus for cutting metal parts are smaller than that of a grinder, however, the burner requires the connection of cylinders with consumables, which complicates the delivery of the equipment to the workplace.
Unit design
The design of most devices is similar. The main elements of air-arc and other cutters are:
- injector/ejector - mixing of elements occurs in it;
- inlets and nipples - for connecting oxygen and preheater gas;
- mixing chamber;
- valves - to regulate the flow of mixture elements;
- nozzle (nozzle) - tube tip, one or more.
The design of a gas cutter is the same for all types of products, but may undergo minor changes. More about this in the following sections.
The work of a gas cutter is not so difficult as it is dangerous. An ordinary cutter works like this:
- the user connects the device with oxygen and flammable gas cylinders, opens the valves (valves) to the desired pressure;
- oxygen and propane/acetylene/hydrogen are mixed into a single stream;
- the flow of the mixture simultaneously burns the metal and blows away the molten oxidized particles.
Gas cutter device
The scheme is similar for most devices for gas cutting or gas welding; differences are found only in ejector representatives. A technical data sheet or instructions for use are the best source of information on how best to operate a cutting tool. Now - about the types of equipment.
Gas cutter for metal: varieties
Gas cutters for metal are divided according to different criteria. For example, there is a classification based on the gas used, dimensions, type of cutting, design, and method of mixing consumables.
Acetylenic
It is a metal cutter that is used for cutting thick metal parts. Acetylene equipment is equipped with additional valves that allow you to set a high gas supply rate. There are industrial and portable models of cutters. Acetylene provides maximum flame temperature. This results in a greater depth of metal cutting.
Acetylene metal cutter
Propane
Propane-powered equipment is used for cutting alloys, non-ferrous and ferrous metals. The maximum cutting thickness is 300 mm. Propane cutters are more reliable, which ensures their durability during active use. Masters pay attention to the safety of such devices. They are often used when carrying out independent work in private workshops.
Portable cutting torch
You can buy a device for autonomous operation. Mini cutters fit in the palm of your hand. They are a metal canister of gas onto which a nozzle with a flammable substance supply system is screwed. You can compare a hand-held device with a turbo lighter. Using matches, a lighter or an installed ignition system, the gas is ignited and passes through special nozzles and nozzles, which form a thin stream of high-temperature flame. It does not go out in strong winds, which makes it easy to use a handheld cutter outdoors. To fill a small can, you can use a special refill nipple or buy a new full container.
Classification of devices
Gas cutters have many types and are classified according to the following criteria:
- type of cutting: surface and separation;
- purpose: manual and mechanized;
- type of fuel: acetylene, propane, methane, kerosene;
- design: presence or absence of an injector;
- oxygen supply: low and high pressure;
- mouthpiece type: multi-nozzle and slotted;
- power: low (< 10 cm of cut metal), medium (< 20 cm) and high (> 20 cm).
Today, different manufacturers produce more than a dozen modifications of such equipment, but structurally they differ little from each other. Such devices are characterized by the presence of a handle with valves for changing the supply of flame-forming gases, and a tip with a head in which the flame is formed.
The figure shows an example of a gas cutter from KRASS
Externally, the cutter and welding torch have much in common. As noted above, the main difference is that the latter oxygen supply does not have a cutting jet and a different head device. You can read more about burners in the article: gas-air burner for gas-flame processing of materials.
Advantages and disadvantages
If you need to cut a metal sheet, you can use different equipment and devices. This could be a roller knife, hand scissors, a grinder, a laser or water cutting machine. Each method has strengths and weaknesses. Advantages of gas cutters:
- Large cutting thickness. Depending on the type of equipment chosen, it is possible to cut a metal sheet with a thickness of 500 mm.
- Low price for burner, cylinders, connecting hoses.
Flaws:
- When a metal is heated strongly, it undergoes thermal deformation. Because of this, the structure of the material changes.
- Large cutting width, which is unacceptable if the exact dimensions are observed.
- If the sheet thickness is small, a flame cone is noticeable on the cut.
- Inability to work with stainless steel and non-ferrous metals.
- High cost per meter of cut sheet.
After cutting metal sheets using a gas torch, you need to additionally process the ends.
To make a quality cut, you need to control the distance between the torch nozzle and the surface of the material. To do this, you need to make a homemade carriage that will support the working part of the equipment in one position above the metal sheet.
Cutting torch
Operating principle and types of cutters
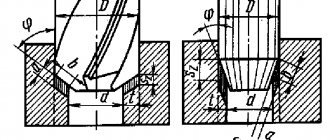
Regardless of the size of the autogen and the types of heating gas mixture, cutting can occur using the process of metal combustion in a stream of oxygen of a pure mixture, pumped through a special nozzle in the head of the working zone.
The main and fundamental feature of gas cutting is the combustion temperature, which must be no less than the melting temperature. Otherwise, the metal, without having time to flare up, will melt and flow all the time. Low-carbon fats must meet these conditions, but non-ferrous metals and cast iron do not.
A large number of alloy steels will also not be amenable to the gas cutting process - there are significant restrictions on the maximum indicator and permissible dosages of alloying components, carbon, impurities, the process of exceeding the combustion of which inside oxygen will become the most unstable or will cease to occur at all.
The cutting itself should be divided into two stages:
- Heating one part of a part to a temperature at which the metal begins to burn. In order to obtain a heating flame, part of the technical oxygen in a certain ratio is mixed with gas .
- The process of combustion (oxidation) of heated metal in a stream of oxygen and the general removal of the combustion product from the cutting zone.
If we start to consider the classification of only hand-held cutters, then this value will have the following features:
Type of fuel, power and method of producing a mixture of gases for a heating-type flame.
- Classification by type of flammable gas: propane-butane, methane, universal MAF, and acetylene.
- Power feature: small (cutting metal with a thickness of 3 to 100 mm) - marking P1, medium (up to 2-0 millimeters) - marking P2, higher (about 300 millimeters), marking - P3. There are special samples with a cutting thickness of about 500 millimeters.
- And if the first feature will only affect the overall temperature of the heating flame, as well as the power - the maximum thickness of the metal, then another feature will determine the design feature of the cutter.
Selection rules
When choosing a cutting torch, you need to consider a number of recommendations. You should pay attention to the following factors:
- Comfort is an important indicator that determines how long a technician can work with the device without fatigue. It is advisable to hold the burner in your hands. This will help you understand how comfortable it will be while working.
- Mouthpiece material - the outer part of this burner element should be made of chromium bronze. Pure copper with a red tint is acceptable.
- Connecting tubes must be made of brass.
- It is advisable to choose a burner without a decorative coating. The paint will cover possible defects in the assembly of the device.
- When working with oily or painted surfaces, you need to choose long cutters (up to 800 mm). This length will protect the brush from injury from the flame.
- Choose an aluminum handle. Plastic is less durable and wear-resistant.
- Flame temperature and gas flow rate affect the cutting thickness of metal parts. The cutting depth is indicated by special markings. For example, if you need to cut sheets up to 10 cm thick, the machine will be designated P. To cut sheets thicker than 10 cm, you need to select the P3 marking.
It is important to check the equipment before leaving the store. To avoid unnecessary problems in case of possible breakdowns of the gas burner, it is necessary to obtain a guarantee.
Gas cutting VS plasma cutting
application and differences
Plasma cutting has become widespread due to the accuracy and quality of the cut, but traditional gas cutting is still used in various technological processes. Oxygen cutting is still widely used for jobs that require a high degree of mobility and maneuverability, especially cutting thick steel workpieces.
Both processes have their advantages and limitations: material thickness, cut quality, maneuverability and component cost are just a few things to consider when making your choice. Below we will consider the advantages and features of each.
What is oxygen cutting?
In oxyfuel cutting, the flame of the oxygen-fuel mixture preheats the steel to its ignition temperature.
A stream of oxygen is directed at the metal, creating a chemical reaction to form iron oxide, also known as slag. A powerful flow of oxygen removes slag from the cut.
When using oxy-fuel torches, cut quality, preheat time and metal thickness depend on the type of fuel gas. The process uses one of four fuel gases in combination with oxygen: acetylene, propane, propylene and natural gas.
What is oxygen cutting used for?
Manual oxygen cutting is common in low-volume projects when the use of expensive units is not economically justified. For example, preparing parts for subsequent forging and stamping, in foundries, cutting pipes. Oxygen cutting is effective when working with thick steel and ferrous metals.
There are oxy-fuel torches that can be used for several processes such as cutting, welding and soldering.
Advantages of oxygen cutting:
- The undeniable advantage of this process is the low initial costs and portability of components compared to plasma cutting machines.
- The ability to quickly cut thicker steel, in addition to the versatility of the system.
What is plasma cutting?
At a basic level, plasma cutting is a process in which a high-velocity jet of ionized gas is delivered from the orifice of a constriction nozzle. High-speed ionized gas, plasma, conducts electricity from the torch of the plasma cutter to the workpiece. The plasma heats the workpiece, melting the material. Different gases are used for different types of metal: Ferrous metals and alloys are cut using active gases - oxygen. Inactive, inert gases: nitrogen, argon, are used when cutting non-ferrous metals and alloys.
A high-speed plasma flow created by a built-in or separately connected compressor mechanically blows away the molten metal, separating the material.
What is plasma cutting used for?
Plasma cutting is performed on any type of conductive metal, such as: non-ferrous metals, mild steel, aluminum and stainless steel. Using a plasma cutter, mild steel is cut faster than alloys.
Plasma cutting is ideal for cutting workpieces less than 25mm thick. Plasma cutting is great for unusual tasks, such as cutting metal foam: a metal with a cellular structure that is almost impossible to cut using oxyfuel cutting. Compared to mechanical means, plasma cutting is generally much faster and easier to perform non-linear cutting.
Advantages of plasma cutting:
- Pros of plasma cutting include ease of use, better edge quality, and faster moving speeds.
- Plasma cutting does not rely on oxidation, so it can cut aluminum, stainless steel and any other conductive metal.
- Work with any metals: ferrous, non-ferrous, refractory.
- Productivity when cutting metal of small and medium thickness is 3 times higher than manual oxygen cutting.
- Point, local heating of the surface, without unnecessary deformation and overheating of all parts.
- Safety because there are no flammable gas cylinders.
- Possibility of cutting complex shapes.
Needed for periodic repairs, maintenance or projects that require large volumes of cutting.
Setting up a cutting torch
After purchasing the equipment, you need to assemble and configure it. Stages of device assembly:
- It is necessary to install a reducer on two cylinders. Red is set to propane, blue to oxygen. Before screwing it on, you need to check the presence of rubber seals. The valves themselves must be free of oil or grease.
- Next you need to secure the gas supply hoses. They are screwed into the threads of the gearboxes. Secure with clamps. It is better to use metal fasteners.
- After connecting the hoses to the cylinders, you need to secure them to the burner according to the diagram specified in the instructions. It is included with the device.
When the assembly is completed, you can proceed to the configuration stage. In this case, you must follow some recommendations:
- When working with acetylene, you need to open the valve one full turn. The pressure should not exceed 1 atmosphere. It is advisable to set the pressure to 0.54 atmospheres.
- Next you need to blow out the hoses. To do this, you need to open the valve on the burner and wait for the sound to change.
- After adjusting the supply of additional consumables, you need to adjust the oxygen flow. The optimal pressure value is 2.0 atmospheres.
- Next, the hoses are purged by opening the valves on the cylinder and burner.
Typically, instructions for assembly, configuration, and further use are indicated on the packaging or in receipts that come with the gas apparatus.
According to the combustible gas used, cutters can be divided into propane, acetylene and universal
- Propane cutters use propane as the cutting gas. These burners are considered very reliable and safe to use, as well as durable.
- An acetylene gas cutter – in which the working gas used is acetylene, is capable of creating a high flame temperature (up to 3300 °C). This tool is used for cutting thick metal workpieces. It is also equipped with special valves for adjusting high-speed gas supply.
- In a universal cutter, combustible gas can be used in different types. Moreover, their price is not much higher than a propane or acetylene cutter.
Preparing for work
Before you start working with gas cutting equipment, you need to prepare. It includes actions that reduce the risk of damage to the device, workpiece, and injury. Preparation stages:
- Inspect the cylinders, connecting hoses, fasteners, and burner for damage. They must be intact, without visible defects.
- Sniff the surrounding air. This way you can detect a gas leak. Initially, you need to connect the hoses to the cylinders and the burner, clamp them with clamps. The flammable mixture should not burst out.
- Rubber seals must be intact. If cracks appear on them or their shape changes, it is necessary to immediately replace the gaskets with new ones.
- Before opening the oxygen valve, it is necessary to check the equipment for grease stains and oil leaks. Even small amounts of these substances can cause an explosion.
It is important to connect the hoses correctly without confusing the gas supply.
Preparing to use a cutting torch
In-nozzle mixing
In devices with intra-nozzle mixing, the mixture is formed in slotted channels between the outer sleeve and the inner mouthpiece. The supply of cutting oxygen is carried out by a lever valve, and the heating and combustible gas is supplied by regulators installed on the handle.
This equipment is available in 3 versions: for working with acetylene, propane and natural gas. Since the gas is mixed not at the handle, as in injection devices, but at the head, such devices have an increased level of safety. At the same time, this principle of operation requires a more complex design, which leads to an increase in the cost of the device. Also, for stable operation, an increased pressure of combustible gas is required - from 20 kPa.
Devices with intra-nozzle mixing
Instructions for use
Cutting metal with a cutter must follow the instructions. It consists of several stages that must follow strictly in arcs:
- Open the oxygen valve.
- Open the gas cylinder.
- Ignite the stream of gas mixture that comes out of the burner nozzle.
- Using the valve system, adjust the gas flow rate.
- Heat the metal surface until its color changes to straw.
- Metal cutting begins after opening the oxygen valve on the torch.
- To complete the cutting, you must first turn off the gas and then the oxygen.
The nozzle can be cooled in cold liquid.
Kerosene-oxygen cutters
Equipment for cutting metal that runs on kerosene has design differences from gas machines, since in order to produce a flame it is necessary to transform the liquid into a gaseous state. This process is carried out in an evaporator, in which the kerosene is heated using a special heating nozzle.
Fuel is supplied from the tank through an oil- and petrol-resistant hose under a pressure of 30 kPa. The container is equipped with a safety valve and a hand pump, and taking into account the design, it allows you to fill up to 8 liters of fuel. A device of this type is in demand when working in the field.
What you need to know when working with cutters
First you need to know the operating principle and classification of these devices. To do this, you can watch the video below:
- Each valve handwheel is marked with the gas whose flow it regulates.
- The arrows on the valve indicate the direction of opening and closing (“O” - opening, “Z” - closing).
- The gas index is indicated on the replaceable mouthpiece (“A” - acetylene, “P” - propane, “M” - methane).
- The oxygen fitting nut has a right-hand thread, and the fuel gas fitting has a left-hand thread.
- Parts in contact with acetylene before the mixing chamber are not made of copper and copper-containing alloys (>65%).
We also recommend watching a video on how to choose this device:
You can purchase high-quality cutters that perform gas cutting of metal (up to 30 cm), and also fill a propane cylinder at the best price.
Do-it-yourself cutting torch
Making a gas cutter with your own hands is not very difficult. Using a homemade machine you will not be able to cut thick sheets of metal, but it is suitable for thin sheets and low-melting alloys. Required materials:
- copper wire;
- droppers - 2 pieces;
- metal canister of gas for refilling lighters;
- needle for inflating balls;
- aquarium pump;
- soldering iron, consumables for it;
- needle file;
- nipple;
- compressor.
Making a homemade cutter:
- Bend the needle from the dropper. The optimal angle is 60 degrees.
- Make a hole on the side of the needle to inflate the swords. Pass the bent needle from the dropper through it. The tip should extend 2 mm.
- Wrap the holes with copper wire and go through them with a soldering iron.
- Attach the tubes from the droppers to the ends of the needles.
- A thick needle for inflating balls should be connected to a gas cartridge, a thin needle to a compressor.
To regulate the flow of gas supply, plastic jumpers are used, attached to the tubes from the droppers.
A metal cutting torch is used to cut thick metal sheets. With its help, you can make a cut to a depth of up to 50 cm. You can assemble the device yourself, but its capabilities will be much lower than that of a purchased cutter.
Using the cutter
Rules for general use:
- When working with a cutter, you should wear a special mask (or special glasses).
- You should first put on gloves and work clothes with fire-resistant (that is, non-flammable) properties.
- The autogen flame must face away from the supply hoses, and the hoses must not negatively affect the work of the entire cutter.
- Cylinders together with gas should be placed at a distance of no closer than five meters to the workplace. Metal cutting should be done either in open air or in a well-ventilated place.
After a long break or during the first launch of a new injection cutter, it is worth making sure that such channels are completely clean and that the oxygen inside the injector can create the required level to dilute the suction of combustible gas .
From the very beginning, when closing the valves on the cutter itself and on the cylinders with cutters, you should remove the hose along with the propane. Afterwards, you should install a special working division on the oxygen cylinder, and also open the valve on the cutter; this valve will begin to actively heat the oxygen and gas. The functionality of the injector should be checked by placing a finger on the flammable gas nipple - at this time the person should feel air being sucked into the nipple hole.
Cutting speed
If the cutting speed is low, the edges are melted; if the cutting speed is too high, the metal is not completely cut due to the lag of the oxygen jet.
In order for the molten slag to flow freely from the cutting zone, there must be free space L (mm) under the heated sheet,
where S is the thickness of the metal being cut, mm; Depending on the thickness of the metal being cut, the necessary internal and external mouthpieces are installed.