Precision is paramount | 04/14/2018
When cutting threads yourself - internal or external - you often need a thread gauge. It will help you select the correct thread profile parameters and avoid problems with the manufacture of the second part in the connection. Today, we will talk about the types and work with this simple tool.
What defects can be detected during inspection?
Inspection of threaded surfaces allows you to identify the following connection defects.
Torn cuts
. A defect occurs if the diameters of the hole and rod differ from the nominal ones. The reason may also be insufficient sharpness of the cutting tool. The problem can be prevented by careful control of all diameters and the use of cutting tools of a normal degree of sharpening.
Dull cut
. The defect appears if the nominal diameter is smaller than the hole diameter, but larger than the rod diameter. When cutting, the profile becomes incomplete. Precise measurement of diameters before cutting threads will allow you to avoid defects.
Thread taper.
The defect appears when the cutting tool cuts off excess metal. The problem is solved by correlating the established dimensions of the part and the tool.
Tight cutting
. If the dimensions of the part are not respected, and the tool has a rough thread, cutting occurs with difficulty. The defect can be prevented by first measuring the parameters of the workpiece and selecting the optimal size cutting tool.
Thread inspection devices
For comprehensive control and measurement
external metric threads use rigid limit ring gauges (GOST 17763-72 and GOST 17764-72), as well as threaded clamps. Internal threads are controlled using thread plug gauges (GOST 17756-72 and GOST 17759-72). When using threaded plug gauges and rings, the pass gauge acts as a complex meter. A no-go gauge is used to measure the limiting size of the average diameter.
Ring gauge M 1.1x0.25 6h PR for complex control and measurement of external metric threads
During element-by-element inspection
the outer diameter of the bolt is checked with any instruments that are usually used to control the diameter of shafts. And the inner diameter of the nut is used for hole control.
To control the average diameter, contact and non-contact methods are used. The first is based on the use of micrometer inserts or three wires.
Measuring mean diameter with thread micrometer inserts
A thread micrometer with inserts is used to measure the average diameter of a triangular thread with profile angles of 60 and 55 degrees. The measurement is carried out in the range from 0 to 350 mm. For each 25 mm interval, either a separate micrometer or special interchangeable anvils are used.
Threaded micrometer MVM-50 GRIFF with inserts for measuring average diameter
The standard kit includes two inserts: a prismatic one, which is placed instead of the micrometer heel, and a conical one, installed in the hole of the micrometer screw.
The micrometer can be equipped with one of five sets of inserts, which are selected depending on the pitch of the thread being tested: 0.4–0.5; 0.6–0.8; 1–1.5; 1.75–2.5; 3–4.5 mm.
Monitoring the thread pitch and profile angle using indicator measuring instruments
The thread pitch and profile angle are measured using microscopes and projectors. In this case, the average diameter of the internal thread is controlled:
- indicator devices with sliding half-plugs;
- indicator devices with sliding inserts;
- horizontal optimeters using measuring arcs with ball measuring tips.
It is convenient to measure the dimensions of parts during processing using an indicator device. Thanks to the special design of the stop bar, this device allows you to install the indicator holder in a convenient place. The device is universal and can be used both for boring and turning.
Indicator device for active dimensional monitoring during lathe processing
The use of indicators and setting rings with the nominal size of the hole being machined reduces the time for preliminary operations and ensures high accuracy in measuring the internal dimensions of the thread.
When processing holes, the cutter is adjusted according to the indicator to remove the first chip with an allowance of 0.1–0.2 mm per side. After this, the indicator readings are measured, and the first chips are removed. The resulting hole size is measured with an indicator device adjusted to the setting ring with the nominal hole size. When setting up, the indicator device is set to zero.
After measuring the hole, they determine which layer of metal needs to be removed to obtain the final size of the hole. Then, according to the indicator, the cutter is installed under the boring of the finishing hole. This measurement method simplifies boring holes according to accuracy classes 2 and 3.
If the batch of parts is large, it is more convenient to first perform preliminary boring of all products with an allowance of 0.3–0.5 mm per diameter, and then complete the finishing boring in one pass with a rigid cutter. The use of indicator devices allows you to work confidently and with great accuracy. However, the indicator does not eliminate the need to use maximum calibers. Measuring the thread with a gauge is a mandatory procedure that is required for final size control.
Safety rules when working with the device
Despite the simplicity of the tool, there are certain rules for its operation that must be strictly followed. The main provisions are as follows:
- The cleanliness of the device must be excellent, regardless of whether it is metric or inch. This will help extend its service life and avoid possible failure.
- To store the device, you need to get a strong and dense container with a hard surface. The ideal option would be a box or container.
- You cannot use other devices that are not intended for carrying out measuring manipulations instead.
- The workpiece with the markings made must be firmly fixed and in a stationary position. If this is not done, a significant measurement error may occur.
- The master, regardless of experience and skills, must wear special clothing to avoid the possibility of injury.
- It is strictly forbidden to operate a faulty product. The probes should be smooth, no scratches, chips or dents. The presence of defects will negatively affect the accuracy of the measured data and subsequent calculations.
It is worth noting that many problems arise due to the poor quality of the materials used in the manufacture of products. Long service life is guaranteed for steel structures. If you purchased an inexpensive product with a body made of plastic, expect it to fail prematurely. Plastic is not particularly durable, so with regular active use of the device, it can quickly fail.
Active control devices
One of the most progressive methods for measuring thread parameters is considered active. It is especially in demand in conditions of mass and large-scale production. Active control devices allow you to automatically monitor the progress of the technological process and provide the necessary processing accuracy.
Active control devices are usually included in the final processing cycle and, based on the results of the check, issue a command to adjust the cutting tool. There is a second way - to check the dimensions of the product during processing in order to immediately control the amount of movement, cutting conditions and other parameters. Active control devices of this type are used on machines with numerical control.
For automatic control and adjustment, contact and non-contact devices are used. In the first case, the tip of the device comes into contact with the product being measured and may cause errors. To exclude this possibility, the tips of active control devices are made of hard alloys and diamonds.
Measuring threads using the three-wire method
The three-wire method is often used to measure the average diameter of a thread. The diameter is determined by placing wires of the same size on the recesses of the threaded connections. The parameters of the resulting structure are measured with a micrometer. The final calculation results are greatly influenced by the profile error. To eliminate it, the wires are placed on the profile so that they are connected at the level where the width of the depressions is equal to the width of the protrusions.
Using the Three Wire Method to Measure Threads
In this case, the wires should be arranged as follows:
- The 1st lies on the depression on the left side;
- 2nd and 3rd on the depressions of the opposite side.
It is necessary to ensure that during measurement the part does not deform and the wires do not bend.
The size of all three wires used to measure the average thread diameter using this method is selected according to a special table, taking into account the pitch and angle of the thread profile. The ideal diameter is d = tan α /2c, where cs is the pitch, and α /2 is the profile angle of the thread being tested.
In addition to the average diameter, the diameter of the trapezoidal thread is measured using the three-wire method.
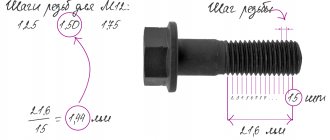
What is a thread gauge?
The tool is made in the form of a small set of toothed combs, each with its own pitch between adjacent protrusions. This step, as you might guess, corresponds to the thread pitch. Each comb is fixed in the housing and rotates along an axis. The configuration and ground surface of the dies makes it possible to easily use them when calculating the pitch of an external or internal thread.
Inch and metric thread gauges have the corresponding markings “D55” and “M60” on the body. Each comb on the front side has its own thread pitch designation.
Dies are produced in accordance with GOST 5950-85 using tool steels ХВ4, 8ХФ or У7. The material used in production is distinguished by a low coefficient of thermal expansion and reduced hardenability, which allows the tool to be used even with large temperature differences.
The profiles of the measuring combs themselves are created in such a way that when measuring, not only the pitch of the thread is determined, but also the number of threads (turns) of the thread and the filling level of the profile. The first is especially important when working with elements that have ground threads, which, as is known, in rare cases can be damaged after processing with a ground wheel.
Thread pitch measurement
To measure the thread pitch, use a caliper or ruler. To do this, determine the length of several steps and divide it by the number of steps. The pitch of internal and external threads is determined by a thread gauge. Each plate indicates the step size. In this case, the plates are selected so that the teeth fit tightly into the thread. Thanks to this, the pitch coincides with the pitch on the plate.
To measure the thread pitch, standard rulers with millimeter and inch graduations and thread gauges are used. The results of calculating the pitch with a ruler are inaccurate, so the main task when taking measurements is to find the number of turns that fall on a single thread pitch. Let's say if there are 5 turns per 1 inch, the pitch will be 1/5 inch. For convenience, results in inches are converted to millimeters.
To measure the thread pitch correctly, you need to be aware of the following tricks:
- you should measure not individual sections, but the entire part of the part profile;
- before measurement it is necessary to count the whole number of turns;
- The thread pitch is determined after measuring the depth and basic parameters of the threaded connection.
The result of the measurements will be the average step value. The error in the calculations depends on how correctly the thread is cut on the part.
The thread gauge provides the most accurate pitch measurements for pipe and tapered threads because it works with the tightest distances. The design includes plates made of iron alloys. Each plate has cutouts equal to the cutting profile and its pitch.
To determine the pitch size, a thread gauge is applied to the part. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the plate is parallel to the cutting axis and matches the size of the thread hole.
Scope of application
Any bolt requires a nut. To get the perfect kit, you need to correctly determine the diameter of the bolt. We are talking about the external size, which will be the initial value when selecting a connecting element. Some craftsmen use calipers to determine the diameter.
It is not enough to determine the correct diameter. You also need to find out the exact type of thread. It can be either inch or metric. Masters who constantly deal with such details determine everything accurately. The visual differences are pronounced. However, things are more complicated with the thread pitch size. Even a professional mechanic cannot install it accurately. In order not to guess, but to determine the value, you need to resort to the help of a tool.
The cutting step must be set in the following situations:
- To understand whether it is possible to increase the make-up length.
- When carrying out surface treatment of nuts and bolts.
- Establishing the possibility of cutting several turns of cutting.
- Identification of the stability indicator of the connections used, based on operating conditions.
The tool helps determine the type of slicing the user will encounter. The tool is in high demand among professional builders and manufacturers of all kinds of workpieces with threads. This device helps repairmen of various equipment. It makes it possible to determine the build quality.
Combs are a universal thing. They help not only to measure the pitch of the turns, but also to determine their number with the fill level of the profile.
Rules for using the device
Before determining the thread pitch, measure its diameter. This is a necessary condition, since not all cuts have the full range of steps. This applies most of all to small (up to 5 mm) and large (over 120 mm) cuts. Without a caliper it is impossible to determine the outer diameter. Once the indicator is established, it is worthwhile to figure out the step. In this case, a thread gauge will be an indispensable assistant. The measuring system does not cause any particular difficulties. The rules for using it are as follows:
- The device is picked up and a suitable plate with teeth is selected. It is applied to the threads of a bolt, nut or screw.
- The plate is selected until a complete match is established.
- As soon as the edges of the comb coincide with the cutting on the workpiece, the step value is set.
- The value is indicated on the side of the comb.
It is easiest to measure the external thread. To measure the internal pitch, the measurement area must be illuminated. In the same way, measurements of inch and metric markings on workpieces are carried out. If, when measuring metric cutting, the figure is 1.75 mm, this indicates that the distance between the vertices of the spiral is 1.75 mm. When receiving a value of 28 when cutting in inches, it means that there are 28 turns in one inch.
At the end of the work, the tool must be put in order. This involves cleaning the edges from dirt and dust that may settle during measuring manipulations.
Measuring the average diameter of a thread
To measure the average diameter of a thread, you must use a thread micrometer complete with different tips (one with a cone, the other with a cutout). The measurement limit is usually indicated on the measuring instruments themselves. Thus, the marking M 3–5 means that the kit allows you to measure threads in increments of 3; 3.5; 4; 4.5 and 5 mm.
Inserts for thread micrometer
A micrometer is used to measure the average thread diameter. Replaceable tool tips are inserted into the screw hole and allow for the most accurate measurements.
If averaged values are sufficient as a result, calipers can be used instead of a micrometer. By design, it consists of ball tips, the dimensions of which must match the type and pitch of the threaded connection. To find out the average diameter, the tips of the calipers must be aligned with the thread gauge. Then the procedure is repeated with the sides of the part. Threaded clamps are used to evaluate measurement results. And the accuracy of the diameter is checked by comparing the resulting thread with the template.
To control the average diameter of a thread consisting of a maximum of two turns, use the two-wire method. The measurement is carried out as follows: wires, the diameter of which coincides with one of the tabular units, are placed on the opposite protrusions and recesses of the thread. In this case, the distance between the ends of the wires shows the average diameter of the part. For each accuracy class, separate wires are created that comply with GOST 2475-88. When deriving final numbers, possible errors are taken into account, because the two-delay method does not allow achieving accurate values.
Another method for measuring the average thread diameter is to use a microscope. The device is applied to the side of the workpiece profile, and the eyepieces are pointed at the profile image on each side to determine its size. The values obtained as a result of measurements are added and divided by the number of sides. The resulting arithmetic mean is the average diameter of the threaded connection.
Rating of high-quality and inexpensive thread gauges
CALIBRON 201960
This practical and relatively inexpensive set of custom templates is a favorite among experienced professionals. With its help, a person can easily determine whether the thread matches the diameter. The range is calculated using millimeter measurements. Useful both at home and in professional workshops. Product weight 0.025 kg. Dimensions declared by the manufacturer are 75x15x15 mm. The error factor is 15 microns. The set consists of 17 different templates.
Average price – 595 rub.
CALIBRON 201960
Advantages:
- high quality of assembly and consumables;
- excellent equipment;
- time-tested brand;
- packaging that can be used for further storage;
- service life.
Flaws:
- Chinese assembly.
NORGAU 045142002
This high-quality and practical device can be used both at home and in workshops. The kit contains 24 templates of standard diameter. The upper measurement limit is 6 mm. The lower measurement limit is 0.25 mm. It is based on the use of high-strength hardened spring-type steel. Plastic screws and nickel plating are used to make the case. The product comes in a branded shockproof case. It is used for measuring both external and internal markings.
You can purchase the set at a price of 505 rubles.
NORGAU 045142002
Advantages:
- excellent equipment;
- shockproof case included;
- ergonomics;
- Taiwanese assembly;
- positive reviews.
Flaws:
- not identified.
STAYER PROFI 28041
A high-strength metal alloy is used to make this structure. The compact and easy-to-use device is equipped with two templates that are used to carry out standard measurements. It is based on the use of the metric system in increments of 0.5-1.75 mm. The set consists of 12 templates. Total weight – 30 g. Produced in Germany.
How much does the kit cost? The purchase will cost 305 rubles.
STAYER PROFI 28041
Advantages:
- copes well with the designated functionality;
- Excellent value for money and quality;
- strength;
- ergonomics;
- practicality;
- Two plates for pipe measurements are included in the kit.
Flaws:
- blades take a long time to develop.
GRIFF D55 D155005
This popular design is in high demand among domestic consumers, largely due to its affordable price. It is based on the use of the inch measuring system. Among other functions, it allows for measurements and auxiliary calculations regarding various elements and working parts. The design can also be used for standard measurements, but it will take some time to get used to. The device can be used not only by ordinary craftsmen, but also in production. The model is characterized by increased accuracy of measurements. The error rate is minimal, based on numerous reviews on the Internet. Due to its compact dimensions, the device is convenient to carry with you. The set contains 17 standard templates, the total weight of which is 30 g. Produced in the Middle Kingdom.
Average price – 180 rubles.
GRIFF D55 D155005
Advantages:
- 17 universal elements in the set;
- high build quality;
- affordable price;
- low error rate;
- compact dimensions;
- ergonomic shape.
Flaws:
- inch measuring system.
Avtodelo M60 40384 11083
This practical and inexpensive device will allow you to take the necessary measurements both at home and at work. In addition, you don’t need any professional skills to work with the tool. Used to carry out the necessary metric measurements. Characterized by increased cutting accuracy. The manufacturing process uses the stamping method, due to which the manufacturer managed to achieve high quality assembly. Cracks, chips and gaps were not identified, as well as other factors that contribute to a decrease in the accuracy rate. Calibrated steel is used to make the structure. The material is characterized by resistance to mechanical damage and premature wear. The set consists of 20 elements, the total weight of which is 15 g. Produced in Russia. The body is made of flimsy plastic.
You can buy it at a price of 100 rubles.
Avtodelo M60 40384 11083
Advantages:
- excellent build quality and auxiliary components;
- excellent equipment;
- compact dimensions;
- affordable price;
- The model is in demand among novice users.
Flaws:
- not identified.
Measuring the outer diameter of a thread
To measure external threads, micrometric instruments are used, the basis of which are microscrews. Control is carried out according to this scheme.
- Microscrews are applied to the thread profile. The position of the instrument is adjusted by rotating the micrometer several times.
- Record the size of the cutting profile for one side. The value is calculated based on the division value on the microscrew scale.
- The micrometer is applied to the opposite end of the profile and its size is calculated.
- The result of measuring the outer diameter of the thread is determined by subtracting the result of the second from the result of the first calculation.
Measuring the internal diameter of a thread
The internal thread is measured using calipers. The tool is installed on a template part using a thread gauge, and then compared with the original internal diameter of the threaded connection. To obtain accurate values, the caliper must be positioned at an angle to the axis being measured.
You can also use cylindrical thread gauges to measure the internal diameter of a thread. This is because the inner diameter has a smooth surface and is ideal for the shape of the tips used in these instruments. The results obtained are checked using plug gauges.
Inch thread spread
Despite the spread of the metric system in most countries of the world, the use of inch threads remains very wide. It is used to connect pipeline parts and all related equipment, including pumps, fittings, and plumbing fixtures. Therefore, inch threads are often called pipe threads. It is also used for the manufacture of many fasteners and equipment parts. Therefore, today there are many industries where inch threads are used.
One of the reasons for this state of affairs is that the industrial revolution originates from England, where the inch remains one of the main units of length measurement to this day. Today, the non-metric system, which uses inches, is used in the USA, Great Britain, and a number of other large industrial countries.
In addition, the spread of inch threads is also associated with the ease of use. Measuring tenths of a millimeter can be difficult and reduces accuracy. Inch threads are measured in 1/4 inch increments. This greatly simplifies the designation and accuracy of measurements of threaded elements, and also reduces the number of standard sizes.
Thread profile measurement
To measure the thread profile, a tool such as a microscope is used, and control is carried out using profiles. The procedure is carried out in the following sequence.
- A normal threaded ring measures the outer diameter.
- A ring is put on the screw, which demonstrates the accuracy of the thread by shaking.
- The diameter is coordinated using a standard threaded plug. At the same time, its protruding smooth end simultaneously serves as a tool for controlling the diameter of the threaded hole.
Where to buy thread measuring tools?
You can buy the necessary tools for measuring threads in the Rincom online store. Always in stock:
- calipers;
- probes;
- micrometers;
- calibers.
You can place an order with delivery throughout Russia directly on the website. It is possible to manufacture measuring instruments according to your drawings. The batch size of products is not limited. I