Everyone knows the Phillips screwdriver. Many people know that they differ in size, and if the size of the screw and the bit do not match, then when screwing in they can be torn off. But not everyone knows that Phillips screwdrivers are divided into two types:
- Phillips (PH);
- Pozidriv (PZ).
Of course, these are not all types of splines, there are several dozen of them, but the rest are rarely used:
Types of screwdrivers.
PH is a standard Phillips screwdriver. The PZ has additional serrations and a different tip shape. The PZ provides a stronger grip and is gradually replacing the outdated Phillips tip.
Philips has two slots that are located at right angles to each other. Its main disadvantage is the risk of damage to the screws, since the force is adjusted in a narrow area.
Pozidriv is an improved Phillips profile. Its difference lies in the additional cross, narrower and less deep. This shape fits into the fastener better, and the risk of thread breakage is reduced several times.
Of course, you can drive screws with any screwdriver, but due to the different shape of the tip and slot, the tool will sit unevenly and there will be backlash. Because of this, the risk of breaking the screw increases, the bit deteriorates faster, and the quality and speed of work decreases. When using the right screwdriver, it's easy to immediately feel the difference.
It is very easy to distinguish between PH and PZ screws. PZ has additional notches, but PH does not.
Screwdrivers and bits are even easier to distinguish. When purchasing, the type of tip is always indicated on the price tag or packaging.
In addition, the type, size and length of the working part are often already indicated on the screwdriver itself.
The designation PH1x80mm makes it clear that you are holding a screwdriver with a Phillips tip of the first size and a long working part of 80 mm. The first and second sizes are most often used.
The PZ has virtually no bevel on the cross, while the PH has it at an angle.
Video instruction:
How to choose a quality screwdriver
You shouldn’t expect good metal and an ergonomic handle from cheap products; it’s better to initially choose screwdrivers from well-known brands. This is 2-3 times more expensive, but then you can use one screwdriver for many years, which is better than changing Chinese products every six months. The screwdriver should fit comfortably in your hand and not press on your palm. Even the slightest inconvenience during the work process can reward you with bloody blisters. When applying a lot of force, a low-quality steel screwdriver will quickly lose its shape and begin to spin on the slot of the screw head. It is quite difficult to check the quality of steel when purchasing; usually, the more comfortable the handle, the higher the quality of the steel. The price is appropriate.
Self-tapping screws for PH and PZ
How PH self-tapping screws differ from PZ is something every craftsman who does housework needs to know. Not to mention the installers who cover the balconies.
Most self-tapping screws have a cross head. There are two types of cross holes in the self-tapping screw PH and PZ.
How to understand which screw needs which bit?
The self-tapping screw can be small or large, with a hidden head or an external one. There is an instruction on the head of any self-tapping screw.
If there is a regular cross on the head, then you need a Ph bit.
If the cross has the characteristic four notches at 45°, then this screw needs a Pz bit.
Screwdriver manufacturers
- Stanley is an American company with production in Thailand. A wide range of screwdrivers of fairly good quality.
- STAYER is a Russian company that produces budget instruments. It produces quite good screwdrivers in its price category.
- Wiha produces premium tools. Screwdrivers from this company are expensive, but high quality
- JONNESWAY is a Taiwanese manufacturer that produces very high quality screwdrivers
- Hama is a company from Germany, production in China. The products of this company are highly reliable
A high-quality screwdriver will last for many years if used correctly. You just have to follow a few simple rules: use a different screwdriver for each screw and do not use the screwdriver as a lever or chisel.
Recommendations for choosing bits
A good bat can perform many more fastener tightening operations than its simplified counterpart. To choose the desired tool, you need to contact a retailer whose employees you trust and get the necessary recommendations. If this is not possible, choose bits from well-known manufacturers - Bosch, Makita, DeWALT, Milwaukee.
Pay attention to the presence of a hardening titanium nitride coating, and also, if possible, to the material of the product. The best way to choose is to try out one or two pieces of equipment in your own business. This way you will not only determine the quality of the product yourself, but will also be able to give recommendations to your friends. Perhaps you will settle on an inexpensive option that has clear economic or technical advantages over the originals of famous companies.
High-quality screwdriver attachments can always be purchased at the Stroybat online store for professional fasteners.
Kernel
Screwdriver shafts can vary in length, diameter, shape and strength. The strength characteristics of a rod are characterized by its hardness. According to GOST, it should be in the range of 47-52 HRC. If the hardness is lower, the rod may bend, if higher, it may crack. It is possible to ensure satisfactory hardness by using high-alloy chrome-vanadium steel; in this case, “CR-V” or “chrome-vanadium” may be written on the rod. But such an inscription does not always guarantee quality, because it is not difficult for unscrupulous manufacturers to apply it. Conversely, famous manufacturers do not always write what, in their opinion, goes without saying. To ensure corrosion resistance, various protective coatings are sometimes applied to the rods. Sometimes the rods are covered with rubber or plastic, this makes the work of electricians easier, but it makes the rod thicker than the tip, so it is not always possible to reach the head of the fastener, which is deeply recessed into the part.
The length of the rod is usually 100-200 mm. For working in tight spaces, screwdrivers with a short shaft and a shortened handle are produced. If the fastener is located in a hard-to-reach place, it is more advisable to use a screwdriver with a long shaft and take a telescopic screwdriver with an adjustable extension of the shaft.
The diameter of the rod depends on the size of the tip and the loads for which the tool is designed. The cross-section of the rod can be not only round, but also hexagonal or square. This shape allows you to grip the rod with a wrench and provide more torque.
We must not forget that the rod must not only be durable, it must be securely fixed in the handle. This factor cannot be controlled visually, so unscrupulous manufacturers often pay insufficient attention to fixing the rod, and over time it begins to rotate. You can safely throw away such a screwdriver, because it will not be possible to revive it.
Sometimes the shaft of a screwdriver extends through the entire handle and ends at a heel that can be struck with a hammer. This screwdriver will come in handy if you need to unscrew a screw with a painted slot.
Pozidriv [edit | edit code]
Pozidriv (POZ >[7], the brand name is Pozidriv
) is a registered trademark [8] denoting the type of cross-slot of threaded fasteners and screwdrivers for them.
History [edit | edit code]
This type of spline was patented in 1962 by the British company GKN
[9] .
Description [edit | edit code ]
Phillips Phillips head.
and is used primarily in the production of screws and self-tapping screws. In mechanical engineering and metalworking, Pozidriv is used much less frequently.
A distinctive feature of the slot is the thin ray-shaped lines emanating from the inner corners.
Differences from Phillips slot [edit | edit code]
Unlike the previously invented Phillips
, the edges of the side surfaces of the Pozidriv screwdriver that go into the depths do not become thinner, but run parallel to each other. In this case (of course, provided that a Podriv screwdriver is used), the axial force pushing the screwdriver out of the slot is insignificant.
When used, the screwdriver is practically not pushed out of the slot - a more stable grip is formed, which reduces the wear of the mating elements and the likelihood of damage (the so-called “breakdown”) of the screwdriver slot and the fastener. Also, it becomes possible to apply more torque to the tool (achieving more torque).
External resemblance to Phillips
- because of this, they can be easily confused, and when using a screwdriver that does not match the slot of the fastener, incomplete contact of the working surfaces occurs - this significantly increases the mechanical stress on individual sections of the slots, leading to their premature wear (mainly on the screwdriver), or damage.
The slot is significantly deeper than Phillips
, therefore it is used only where screws have large heads for reasons of strength - in construction and furniture production.
Markings and sizes [edit | edit code]
Screwdrivers are marked with letters PZ
with spline number - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5.
Varieties [ edit | edit code ]
- POZISQUARE [10] - Pozidriv combination with a square slot.
Friason [ edit | edit code]
Frearson
- a rather rare and almost forgotten type of slot.
Also known as Reed & Prince
. Similar to Phillips, but has a sharp end and a larger V-shape angle (75°). One advantage over Phillips is that one screwdriver or bit fits all screw sizes. Found in imported marine equipment. The lack of fillets on the cross slot allows for more force to be applied, unlike the rounded conical shapes of Phillips, which were designed to push the tool out at high torque.
Phillips [edit | edit code]
Phillips (eng. Phillips) is a registered trademark [1] denoting the oldest and most famous type of Phillips recess of threaded fasteners and screwdrivers for them.
History [edit | edit code]
The straight slot has existed, according to some sources, since the 15th century. However, this slot has disadvantages, which were especially evident during the mass assembly of cars and airplanes:
- The screwdriver or screwdriver slips out of the slot, scratching the parts being connected.
- When working with a mechanical screwdriver, there is a risk of breaking the slot or thread (ratchets that accurately measure torque did not yet exist at the time of the invention of the Phillips screwdriver).
In 1933, American John P. Thompson developed screws that solved both problems: they automatically centered the tip and pushed it out when the screw was tightened. Engineer Henry Phillips bought Thompson's patent and founded the Phillips Screw Company. Henry Phillips developed the technology for producing such screws, but was unable to implement it at home. Only in 1937 did he manage to interest the management of the American Screw Company. Such screws were first used in the production of Cadillacs. During World War II, such screws began to be used in the production of military equipment [2].
Thompson was not the first inventor to try to improve the design of the screw: for example, back in 1909, a screw with a square slot was patented by the Canadian Peter L. Robertson. It became widespread mainly in Canada. According to half a legend, Henry Ford at one time experimented with Robertson screws and found that their use significantly speeded up the assembly of cars, but received a refusal from the inventor to sell him a patent, as a result of which he switched to an alternative proposal from Phillips - because of which, according to this According to legend, the Phillips slot, not Robertson, became widespread. However, on Canadian-built Ford cars in the 1920s and 30s, all interior trim elements were attached with Robertson screws.
Features [ edit | edit code ]
Markings and sizes [edit | edit code]
Screwdrivers are marked with letters PH
with slot number - 000 (1.5 mm), 00 (2 mm), 0 (3 mm), 1 (4.5/4 mm), 2 (6 mm), 3 (8 mm), 4 (10 mm) [ 3].
Varieties [ edit | edit code ]
- ACR RIBBED PHILLIPS [4] .
Cross slot with straight serrations against ejection (ACR technology = anti-cam-out recess); distinctive marking - ACR. Compatible with all Phillips screwdrivers.
- PHILLIPS II [5] - an improved version of Phillips.
Cross-shaped slot with inclined notches against ejection; distinctive marking - ACR2. Designed to meet increasingly fast assembly processes where the screwdriver may be ejected from the screw, resulting in damage to the surface of the part; facilitates tightening in difficult installation positions and reduces pressure on the spline - resulting in reduced worker fatigue.
- PHILLIPS SQUARE-DRIVE [6] - Phillips combination with a square spline.
Cross slot with notches (ACR technology) combined with a square slot; distinctive marking - PSD = PHILLIPS SQUARE-DRIV Allows significantly higher torque. Only three screwdriver sizes cover the most popular size ranges.
Why Phillips is not related to the Dutch company Philips
Fun fact - Phillips fasteners are often confused with the Dutch company Philips.
So here it is. The Phillips cross-shaped fastening profile has nothing to do with Philips, which produces household appliances, lighting solutions and medical equipment. Although their names are similar.
For reference, the Dutch company was founded in 1891 by Gerard Philips together with his father Frederick. It was originally called Philips & Co, located in Eindhoven in the Netherlands and was engaged in the production of electric lamps.
Little trick to remember: double L
in the title it’s about fasteners (
Phillips
), the single
L
is about the Netherlands and household appliances (
Philips
).
Types of screwdriver tips
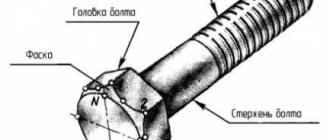
Any simple screwdriver consists of three elements: a handle (plastic, wood or rubber), a metal rod and a working tip. The latter has protrusions corresponding to the slots in the head of the screws or self-tapping screws. The screwdriver is held by the handle and rotated along the axis. It is important that the handle does not slip in your hands.
When screwing in and unscrewing, an increased load is placed on the tip, so the edges on it gradually lick off and stop clinging to the slots in the fastening element. To extend the service life of the screwdriver, the tip is made of durable alloys and hardened.
Chrome vanadium molybdenum steel is usually used. Let's consider the types of fastener slots for which various screwdrivers are produced.
Straight (flat) slot - SL
One of the most ancient types of slots. The slot shape is used in self-tapping screws and screws on products that do not require strong tightening (low-critical designs).
It is inconvenient to work with screwdrivers with self-tapping screws with a straight slot, since the tip constantly moves to the side and slips out, scratching the surrounding surfaces.
Screwdrivers for working with flat slots can be sharpened to a classic or radius shape. In the first case, it will be two faces that meet at a slight angle to a flat flat end. In the second, there is a small protrusion inside that prevents the tip from moving from the center of the screw head.
In terms of twisting, radius sharpening is preferable because it increases productivity. But it’s inconvenient for her to insert a sting into a crack to bend, pry or wedge something.
Cross splines
Screwdrivers got this name because of the shape of the protrusions in the tip, which are based on a cross. Sometimes they may be called simply “cross” or “plus” masters.
Phillips - PH
The slot was almost the only cross-shaped one that was widely used in the USSR. Corresponds to GOST 10653-86 and is designated as type N. According to the ANSI standard, it is designated as Type I Cross Recess.
The spline type was developed by J. Thompson, but the patent was later sold to Henry Phillips. It was his company, Phillips Screw Company, who perfected the spline design and took credit for its advancement.
Thanks to this slot design, the problem of the screwdriver shifting when tightening was solved, and such fasteners could be used with electric and pneumatic tools.
A modern tool for Phillips splines is designated PH and can be numbered 0000, 000, 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4. The number indicates the conventional geometric size, written in increasing order.
PH slotted screwdriver.
Pozidriv – PZ
A more complex modification of the launch vehicle is designated Type IA according to the ANSI standard. GOST 10753-86 classifies it as type Z. The patent for this spline shape was filed in 1962 and belongs to GKN Screws and Fasteners.
The design of the slot involves a main cross-shaped intersection of the slots at right angles and additional grooves located at 45º from them. This configuration increases strength and increases contact points with the working part of the screwdriver. There is less ejection with high torque, which is why this shape is more often used on power tools. But the production of additional notches makes the fastener production process more expensive.
Screwdrivers for such slots are designated PZ or Pozidriv. A number from 0 to 5 is indicated next to it, indicating the conditional size in ascending order. An incorrectly selected number leads to a mismatch between the screwdriver and the fastener head, which affects the ease of operation and quality of fastening.
Podriv and Phillips screwdrivers and slotted bits are not interchangeable. In addition to additional risks, the difference exists in the grooves themselves. In Phillips they are sharpened with a small radius, while in PZ they are parallel. Using a PH bit in a head with PZ splines will not allow the tip to fit tightly into the seat, and vice versa - a posidriv bit with its flat edges will break the PH slot.
Screwdriver for PZ slots.
Friason
The name is taken from English Frearson. According to the ANSI standard, it is designated as Type II Cross Recess. May also be called Reed and Prince.
The design is similar to Phillips, but differs in the point of intersection of the edges. If the launch vehicle has a rounded angle of convergence, here it is completely straight. There is no conventional division into sizes - one screwdriver is suitable for all screws with this type of slot.
Due to the clear angle and large blades, it is possible to transmit increased torque. The self-tapping screw does not eject from the head. Due to the reliability of fastening, screws with such slots are used on foreign marine equipment.
Friason slotted bit.
Supadriv
The spline configuration was developed by the same company that developed the PZ standard. Screwdrivers for them are interchangeable and can be used without harm to both the tool and the fasteners. According to the configuration, the main cross-shaped intersection and additional 45-degree risks are also used here. The difference is a wider center, allowing axial movement of the screwdriver tip.
Phillips II
The second generation of launch vehicles is compatible with the first. The difference between PH2 and its predecessor lies in the notches inside the cross-shaped recess. They form a kind of teeth that connect to the mating side in the tip of the tool.
This design increases the adhesion force between the screwdriver and the slots, which reduces the pushing effect. To identify the type of spline, two parallel marks are applied to the head. Screwdrivers and bits are marked with the ACR brand.
Bit for PH2 slot.
French slot
Standardized by the Bureau de normalization de l'aéronautique et de l'espace as BNAE NFL22-070. Structurally, it has a stepped design. A large cross is made from the edge, and closer to the middle it narrows to a small one. Change does not happen gradually, but in steps.
Splined bit BNAE NFL22-070
JIS B 1012
This spline is designed in Japan and used in Japanese equipment. The angle of convergence of intersecting slots is straight, but without a sharp part. Due to the strong bevel, it was possible to minimize the ejection of the screwdriver.
If you insert a PH screwdriver into the head of the JIS B 1012 fastener, the slots will be damaged, so JIS B 1012 is indicated by an additional dot on the head. When working with a Japanese slot, it is better to buy a corresponding JIS screwdriver, which is commercially available.
The invention and authorship of the cross slot is an unusual story
A new type of cross-shaped slot was invented in 1933 by the American inventor John P. Thompson. But large manufacturers of hardware did not appreciate the invention.
Only 2 years later, in 1935, engineer Henry F. Phillips became interested in his invention.
Henry Phillips, the man whose name is named after the most common type of fastener in the world.
/photo geni.com/
He bought the rights to the cross slot from Thompson. After which I spent about a year polishing the design of the profile and screwdriver.
In 1936, Phillips patented a modified Phillips spline. As a result, the tip of the screwdriver or screwdriver was centered strictly in the center of the fastener. And when tightening, the tool simply popped out of the head of the bolt or screw without damaging the fastener.
Even the numbers and copies of his patents have been preserved: US Patent #2,046,343, US Patent #2,046,837 - 2,046,840.
Henry Phillips patent US2046837-0 for a Phillips slot. /photo Google Patents/
Henry Phillips patent US2046840-0 for a Phillips slot. /photo Google Patents/
Confident of the success of the new Phillips screw, Henry Phillips founded the Phillips Screw Company. The company, by the way, still exists and is the copyright holder for all types of Phillips splines.
The first major customer to introduce Phillips screws and bolts on its assembly lines was General Motors. The automaker has launched a new type of fastener on the Cadillac assembly line.
The success of Phillips fasteners was so resounding that by 1940, virtually all American fastener manufacturers (more than 85%) were lining up with the Phillips Screw Company to purchase a production license.
And the name Henry Phillips became a household name and was forever attached to the cross slot.
By the way, in the Russian nomenclature there is a separate GOST for a Phillips slot - .
Types of screwdrivers by slot type, design and purpose
Screwdrivers are used both in large industries and in everyday life. But there are dozens of types of similar instruments with different designs and purposes. Choosing the wrong screwdriver model can damage the fastener and make it completely unusable. Let's look at the types of screwdrivers and their names, as well as the shape and features of use, so that later you can easily select the right tool yourself.