Screws, screws, self-tapping screws, bolts and nuts - all this is combined under one name “construction fasteners” or, in other words, “hardware”. Their main task is to fasten various parts of industrial and domestic structures. Depending on the specifics of production and purpose, all fasteners have their own characteristics.
The most common part among all threaded connecting elements is the screw. It is worth starting with the distinctive characteristics of all threaded hardware in order to understand how a screw differs from a bolt and screw.
What is a screw, screw, self-tapping screw, bolt, washer and nut, what does it look like, what is it intended for?
A washer is a fastener that is auxiliary and is placed under the head of the nut. The main purpose of such a product is to increase the pressure area and also prevent the destruction of other fasteners. In addition, the washer prevents the fastener from loosening and makes it more resistant to various types of mechanical stress.
Washer
A screw is a fastening element, which is a type of screw, differs from it in that it has a thick rod, external thread, and a pointed tip. This makes it easier and easier to enter a hard surface. Namely, in wood or concrete. Most often, special holes are made for screws, which are filled with relatively soft material. Usually this is a tree.
Screw
A screw is also a fastener, a type of which is a self-tapping screw or screw. The main feature of the fastener is that it is a rod with an external thread and a head large enough for screwing. Most often, special holes are made on the head so that the screws can be tightened with a screwdriver. Or they make special notches to screw in the products using a special key.
Screw
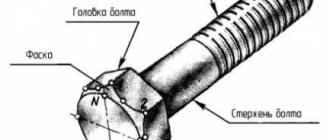
A bolt is a fastener that is a cylinder with a fairly high hexagonal head. Most often it works together with a nut in pairs, and is used to connect some parts.
Bolt
A nut is a fastener that has a thread inside it and is used in conjunction with a screw or bolt. Typically, nuts are made in a hexagonal shape so that they can be secured with a wrench.
screw
Extra options
The bolt may be threaded along its entire length or only partially. It may also have additional elements, such as a toe or a wreath.
- Its shank can be equal to or close to the thread diameter.
- Bolt types can also be classified according to their embedment or socket criteria.
- The socket with a hex head is most often used, but in its place you can also find a cross-shaped notch or groove.
- On the other hand, the most common screw ends are flat, lenticular, truncated, tapered, and recessed.
Instead of a flat end shank, a hex bolt may have a biconvex end.
What is the difference between a bolt and a screw: comparison, photo
A screw and a bolt look very similar to each other, and many can confuse them. But they are used in completely different industries. The fact is that there is a peculiarity in the design, because of this, a bolt is mainly used to fasten parts using a nut. That is, there will be a bolt on one side and some part in the middle. On the other side there will be a nut that will hold it all together.
Bolt and nut
A screw differs from a bolt in that it is not used together with a nut, but is most often used separately. That is, in the part itself there is a thread into which the screw is screwed. This way the connection is made, that is, additional nuts for the screw are not used.
Anti-vandal screw
Foreign analogues of washer-grower GOST 6402
Of the world-recognized standards for Grover washers, the following can be noted:
- Grovers DIN 127. Products with rectangular sections. 2 forms are made - A (sharpened cuts) and B (smooth cuts). Hardness from 44 to 51 HRC. Sizes from M2 to M100;
- Grovers DIN 128A(B), 137A(B), 432;
- Grovers DIN7980. They have a square cross section. Hardness 44 - 51 HRC. Designed for SCREWS for high strength connections.
A comparative table of compliance with GOST, DIN, ISO can be viewed (https://getpocket.com/read/3347360666).
What is the difference between a screw and a bolt and a screw: comparison, photo
A screw differs from a screw and bolt in that it has a thinner thread and a pointed tip. Used without nut and washer. Most often, its surface is self-tapping, that is, when a certain force is applied, the self-tapping screw can be screwed into a wooden surface, without cutting a preliminary thread. Screws and bolts are not used for these purposes because they do not have a pointed tip and do not have a self-tapping characteristic.
Plumbing screw Bolt
Screws
Shapes and materials
Bolts typically have hex heads that are initially larger than the nut's hole and shank to avoid locking problems. The head can also be shaped like a button.
Stainless steel nuts and bolts are the most common. However, now the following materials are used for various industries:
- Classic steel;
- Brass;
- Stainless alloys;
- Bronze;
- Titanium;
- Silumin and telfon (for elements not subject to particularly heavy loads);
- Glass and porcelain (for electrical insulators, given their very low electrical conductivity).
Bolted connections are very useful when it is necessary to withstand external tensile and shear forces and remove them without damaging components.
A set of bolted elements constitutes an elastic system, the stiffness of which depends on the stiffness of both components.
Several tables are available for bolt sizing information. It is necessary to identify the specific item to search for because the term "bolt" refers to a wide range of components that vary in purpose, size, shape, tolerance, material, surface finish, specifications and even quality.
What is the difference between a screw and a self-tapping screw: comparison, photo
The self-tapping screw itself is a type of screw, but differs in some ways. The fact is that the technology for making self-tapping screws is somewhat more complicated. Since harder, more durable materials are used for manufacturing, which can destroy the surface with a certain force. For example, a self-tapping screw can be screwed in without making a separate hole, just apply some effort. Screwed in from a certain force. This way the screw will fit tightly into the surface of the wood or other material. In order to insert a screw, you must first make a hole on the surface.
Screw
That is, the screw itself cannot be screwed in without making an additional hole. Since the material is quite fragile and the edge is not so strong. They are not so sharp, so screwing without an additional hole is quite difficult. In addition, the screw is not as tall and has a smaller thread pitch. In this case, the tip of the self-tapping screw is sharper than that of a screw.
Self-tapping screws
Alternative options for locking
In the process of tightening the screw pair, the twisted ring is compressed and takes the shape of an ordinary washer. The friction force is higher, but the tension effect will still not be very large.
After one-time use, the ring loses most of its qualities and its use for fastening moving elements, especially on critical parts, is unacceptable.
Therefore, even if you use a part included in the catalog of the best growers, the risk of reducing the fastening strength still remains. An alternative can be found - there are several such options:
- self-locking nut;
- Belleville nut with spring effect;
- nuts of crown type and with a cylindrical belt;
- toothed flange;
- locking washers and with antennae, etc.
The use of screw-type washers helps to ensure a more durable fastening and significantly reduces the risk of parts coming loose. For different base materials and screwing directions, you can select the appropriate type of ring or replace it with an alternative locking method.
What is the difference between a nut and a bolt: comparison, photo
A nut differs from a bolt in that they are two fasteners that are used in pairs. That is, the nut has an internal thread, and the bolt has an external thread. Accordingly, the nut is screwed onto the bolt. In this way, the structural elements are connected.
Bolt nut
What is the difference between a nut and a washer: comparison, photo
The nut is also significantly different from the washer. The fact is that the nut has a thread inside. A washer is a component that is typically used to seal the joint between a bolt and a nut. That is, it is inserted immediately before screwing on the nut. This helps improve the connection. This minimizes the possibility of unscrewing, unscrewing the nut and removing it from the surface of the bolt. There are different types of washers, both flat and shaped. They are also called growers. Additional pressure improves the adhesion of the bolt and nut and makes the connection of the parts more reliable.
Nut Washer
As you can see, there are many fasteners and parts that are used to connect components, mechanisms and structures. They have a large number of differences and are used in each specific case.
Basic classifications
There is a generally accepted system for classifying fasteners:
- high-strength threaded products;
- fasteners for mass use;
- fasteners for shockless fixation and one-sided installation;
- elements for hermetic structures;
- fasteners necessary for fastening polymer composite materials.
Note that the classification is conditional, and it is impossible to unambiguously fit all hardware to these parameters. The simplest example is riveting. The peculiarities of its design mean that it is categorized as a fastener for impact-free, one-sided fixation, but there are products designed or capable of fastening polymer and composite materials, and this is another category from the list.
There are several other types of classification. For example, by type of construction. There are two sections here:
- detachable. That is, all fasteners consisting of two or more parts.
- and permanent ones, such as nails and rivets.
It also makes sense to separate hardware according to purpose. Some elements are designed to work in aggressive environments, such as underwater, while others are designed to work under high loads. That is, the same fastener can have different areas of application, and different technologies and materials are used for their manufacture.
For threaded connections, a division based on thread pitch also applies. A bolt of the same size can be either with a fine thread, that is, a large number of turns, or with a large one. And the last type of classification is by size. There is no strict standard prescribing specific fastener sizes, but there is a generally accepted system of standards. In this sense, it will not be possible to divide hardware into groups.