Forming tools
According to their purpose they are divided into two main types
- Stamping boards
- Shovels and shovels for earth
- Sita
- Tampers: with a blunt end for compacting the surface and with a narrow end for places with difficult terrain.
Universal pneumatic rammers with a replaceable tip are also used. Manual tamper A scraper, or rule, for leveling the mixture and removing its excess - Stuffing caps. Thin sharp rods are used to pierce thin gas outlet channels in the ground
- Mallets - used for holding sub-models together and for beating them out.
- The flutter is a board resting on the edges of the mold. Compacts the ground when using models made of low-strength materials.
- Brushes. Clean the surface from any remaining soil
Finishing
- Smoothing irons - for correcting blemishes
Cutting and piercing tools Coating brushes Containers - buckets or bags for storing and applying powder coatings.
The following main advantages of chill casting are highlighted:
1. Increased labor productivity as a result of the elimination of labor-intensive operations of mixture preparation, molding, and cleaning of castings from burnt marks. Therefore, the use of chill casting, according to various metallurgical enterprises, makes it possible to increase labor productivity in the foundry by 2–3 times, reduce capital costs during the construction of new workshops and reconstruction of existing ones by reducing the required production space, costs for equipment, treatment facilities, etc. .d.
2. Improving the quality of the casting due to the use of a metal mold, increasing the stability of quality indicators: mechanical properties, structure, density, roughness, dimensional accuracy of castings.
3. Elimination or reduction of the volume of operations harmful to health, knocking out molds, cleaning castings from burnt marks, cutting them off, general improvement and improvement of working conditions, less environmental pollution.
4. Mechanization and automation of the casting manufacturing process, due to the repeated use of the mold. To obtain castings of a given quality, it is easier to automatically regulate the technological parameters of the process. Automation of the process makes it possible to improve the quality of castings, increase production efficiency, and change the nature of the work of the foundry operator managing the operation of such complexes.
Advantages of our factory
creates only high-quality products. The foundry equipment of our enterprise is automated, which allows, after creating a prototype, eliminating all its defects, to organize the production of high-quality castings in a timely manner. Molds and equipment for models are created on high-precision machines. Experienced engineers and technologists of our plant, using modern foundry equipment, perform melting of the sixth class of accuracy (maximum). Our plant has reasonable prices and payment terms. Processing of received applications is carried out promptly. Delivery of finished products is made to all cities of Russia and the CIS.
Aluminum die casting
Chill casting is widely used for the production of shaped castings from low-melting non-ferrous alloys, including aluminum. This technology produces parts for car engines, housings for pumps and filters, wheels for vehicles, and parts for household appliances.
The designs of molds for aluminum casting can be one-piece for the production of simple parts or collapsible, having different parting planes. From one-piece molds, finished parts are shaken out or knocked out of the mold. Among the main elements of the design of chill molds are:
In addition to the main ones, the design of chill molds may include additional elements (pan, cooling pipe, bushings, casing, pins and others). Molten aluminum enters the chill mold through a gating system.
Casting aluminum in cokels is one of the popular methods of casting metal parts with precise parameters; it is economical due to the fact that operations for preparing casting mixtures and cleaning castings are eliminated; in addition, it is a productive method of non-ferrous casting.
The chill mold is reusable. Due to the fact that the metal cools in the mold for a relatively long time, to produce a large batch of parts, a large number of molds are needed and used simultaneously.
Aluminum die casting is an accelerated technological method that produces many parts from one die in a short period of time. The resulting high-precision products do not require subsequent mechanical modification, which reduces metal consumption and reduces the labor costs of key workers.
Design features of the mold
A mold for casting is a multi-turn mold made of metal. Despite the fact that such molds can be used to produce castings of different shapes, their fundamental design is the same. The casting mold consists of half-molds, a plate, various inserts and casting cores. With the help of the latter, the casting is formed. Pins are used to center and connect it. Immediately before pouring, the half-forms are secured using special locks. The metal melt is fed into the mold through a gating system.
Casting into metal molds (molds)
As the mold fills, excess air is removed through the air ducts.
In foundry production, another type of mold is used - they are called shakeout molds. These molds are distinguished by the fact that they are one-piece and are used for castings of simple shapes.
Defects in castings made of non-ferrous alloys and methods for their prevention
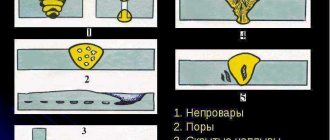
Common characteristic defects of castings during chill casting are:
- underfilling and non-filling at low temperature of the melt and chill mold before pouring, insufficient pouring speed, high gas content of rods and paints, poor ventilation of the chill mold;
- shrinkage defects (sinks, sink marks, porosity, cracks) due to insufficient power supply to massive casting units, excessively high temperature of the melt and die, local overheating of the die, irrational design of the gating system;
- cracks due to untimely detonation of a metal rod or insert, high pouring temperature, low-tech casting design;
- slag inclusions when using contaminated charge materials, insufficient refining of the alloy before pouring, improper operation of the gating system;
- gas porosity due to disruption of the smelting process (use of mixtures contaminated with moisture and oil, excessively high overheating, insufficient refining or deoxidation of the alloy).
Specific defects in castings made of magnesium alloys are defects of shrinkage origin (porosity, cracks, looseness), caused by a wide temperature range of their solidification. To eliminate these defects, it is necessary to fine-tune and strictly adhere to technological conditions - melt and chill temperature, use of paint, etc. Often, castings made of magnesium alloys, due to poor performance of the gating system, are affected by slag inclusions, which leads to corrosion of the casting during its operation and storage. Such defects are eliminated by careful fine-tuning of the gating system.
Specific defects in castings from copper alloys are: gas porosity due to poor refining and cleaning of the alloy from slag particles, secondary oxide films when casting aluminum bronzes due to the division of the melt flow into jets and its oxidation in the mold, cracks due to poor deoxidation of the alloys during melting.
- ← Section 3.3
- Section 3.3.2 →
Pros and cons of the die casting process
Chill casting has clear advantages over other types of similar processes, including sand casting, since it:
- makes it possible to reuse forms;
- reduces costs for molding materials;
- allows you to obtain castings of increased accuracy, with smaller allowances for machining;
- provides a cleaner casting surface, reduces the surface roughness of the workpiece;
- allows you to improve the quality, strength and other mechanical properties of castings;
- allows you to automate and mechanize the process;
- is more economical and efficient.
While this process has clear advantages over other casting methods, it is worth noting some disadvantages:
- the labor intensity and complexity of the process of making molds;
- high cost of manufacturing molds, which increases depending on the complexity of the mold configuration;
- limited number of castings, since the mold is not eternal and has limited wear resistance;
- impossibility of producing castings with thinner walls, cast iron “bleaching”, difficulties in producing steel castings (gas porosity);
- inflexibility of forms, which sometimes leads to deformations and cracks in the workpieces, warping of the walls of the die during casting;
- the need to use rods, ventilation ducts, gas outlets, and thermal insulating coatings.
Content
- 1 General information
- 2 Casting principle
- 3 Application
- 4 Basic operations of the technological process
- 5 Features of formation and quality of castings
- 6 Production efficiency and application scope
- 7 The following main advantages of chill casting are highlighted:
- 8 It should also be noted the main disadvantages of chill casting:
- 9 Classification of mold designs.
- 10 The main structural elements of molds include:
- 11 Chilling machines
- 12 See also
Application area of die casting
Thanks to die casting, mass production not only in the Russian Federation, but throughout the world is provided with cast parts by more than 40%, compared to other types of casting.
The die casting method produces castings from cast iron, steel and its alloys, magnesium, aluminum and their alloys. all possible purposes and weights. Various parts are turned from castings, which are widely used in mechanical engineering, carriage building, automotive industry, tractor manufacturing, when laying gas pipelines, etc.
All branches of industry and engineering production use parts made by die casting: pistons, blocks, cylinders, electric motor housings, bearing cheeks, flanges, frames, fittings, screws, gears and many other parts of machines and mechanisms.
Modern industry needs a huge number of parts, most of which are cast. They can weigh from a few grams to hundreds of kilograms.
Casting into reusable metal molds – chill molds – is one of the most progressive and effective types of casting, as they can withstand from several pours to tens of thousands of uses (manufacturing of aluminum parts).
The possibility of modernization, mechanization and automation of chill casting allows us to completely cover the shortage of cast products in industry and minimize the use of heavy manual labor.
Rating: /5 – votes
Classification of mold designs.
Depending on the location there are:
One-piece, or shake-out. This type is used under conditions where the design of the casting allows it to be removed from the mold without its connector. Chills with a vertical parting plane. Consist of two or more halves. The casting can be located entirely in one of the halves, in two halves, simultaneously in two halves of the mold and in the bottom plate.
Chills with horizontal split. This type is used mainly for simple configurations, as well as for producing large-sized castings. Chills with a complex (combined) parting surface. Used for the manufacture of castings of complex configurations. Depending on the cooling method, chills are distinguished with air, liquid and combined cooling. Air cooling is used for low heat-loaded chill molds. Water cooling is usually used for highly heat-loaded molds, as well as to increase the cooling rate of the casting or its individual parts.
Types of molding
They are determined by the type of model and the chosen casting method.
According to a simple model
The model is placed face up on the board. Center it relative to the flask. Cover with a facing mixture, then add filler in layers, carefully compacting each layer. Add soil to the flask until it is filled. Having removed the upper flask, take out the model and create a gating system. The flasks are collected together, secured and dried.
According to split model
The method significantly simplifies the technology and increases the accuracy of manufacturing the casting mold. A part of the model without spikes is placed on the board, the lower flask is installed and the ground is shaped. Upon completion, the structure is turned over, the second part is attached to the model, the upper flask is attached and it is stuffed.
With false cover
For particularly complex product geometry, I use false pins. It does not come into contact with the melt, but plays the role of a figured fake board.
Forming methods
Lumpy
It is used for artistic casting, especially sculptural compositions. The model is furnished with several independent flasks, their edges touching. Sometimes a casting is divided into segments that are relatively simple in configuration, they are modeled and cast independently, and then the finished castings are connected.
Template
It is produced by casting products of a certain shape into the ground. Distinguish
- Bodies of rotation (cylindrical, conical and elliptical)
- Rectangular or prismatic.
The formation of the earth is carried out by a template of the appropriate configuration, driven by a powerful spindle for bodies of rotation or moving along special guides for prismatic shapes.
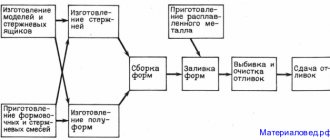
Basic operations of the technological process
The general diagram of technological operations performed during chill casting is shown in Fig. 4. The need to perform some of them depends on specific conditions - design features of the casting, casting properties of materials, features of the production process and other factors. For example, operations associated with the production of sand cores and heat treatment of castings may be completely absent. The need to carry out other operations may arise only after several casting cycles (in particular, applying a protective coating).
Rice. 4 — Sequence of technological operations of the process
Before pouring the melt, the chill mold is prepared for work: the surface of the working cavity and the connector are thoroughly cleaned of traces of dirt, rust, soot, and oil; check the ease of movement of moving parts, the accuracy of their centering and the reliability of fastening. Then a layer of fire-resistant cladding coating and chill paint is applied to the surface of the working cavity and metal rods. The composition of linings and paints depends mainly on the alloy being poured, and the thickness of their application depends on the required cooling rate of the casting: the thicker the layer of refractory coating, the slower the casting cools. At the same time, a layer of refractory coating protects the working surface of the mold from a sharp increase in its temperature during pouring, melting and setting with the casting metal. Thus, facings and paints perform two functions: they protect the surface from sudden heating and setting with the casting and allow you to regulate the cooling rate of the casting, and therefore the processes of its solidification, which affect the properties of the casting metal. Before applying the refractory coating, the mold is heated with gas burners or electric heaters to a temperature of about 150°C-180°C. Paints are applied to the molding parts, usually in the form of an aqueous suspension using a spray gun; paint is applied to the runner and gating system with a brush. Drops of the aqueous suspension, falling on the surface of the heated chill mold, evaporate, and the refractory component covers the surface in an even layer.
After applying the refractory coating, the mold is heated to operating temperature, depending mainly on the composition of the alloy being poured, the wall thickness of the casting, its dimensions and the required properties. Typically, the heating temperature before pouring for aluminum alloys is 250-300°C. Then sand or ceramic rods are installed, if necessary to obtain the casting; The chill mold halves are connected and secured with special clamps, and when installed on a chill mold using its locking mechanism, after which the melt is poured. Often during the process of solidification and cooling of the casting, after the casting has acquired sufficient strength, the metal rods are “undermined”, i.e. partially removed from the casting before it is removed from the die. This is done in order to reduce the compression of the metal rod by the shrinking casting and ensure its removal from the casting. After the casting has cooled to a given temperature, the mold is opened, the metal rod is finally removed and the casting is removed. The sand core is knocked out of the casting, the sprues and profits are cut, and preliminary quality control of the casting is carried out. Before the next pouring, inspect the working surface of the die and the parting plane. Typically, fireproof paint is applied to the working surface 1 - 2 times per shift, occasionally restoring it in places where it peels off from the working surface of the chill mold. After this, if necessary, which is more often the case when casting thin-walled castings or alloys with low fluidity, the chill mold is heated to operating temperature, since it cools during the removal of the casting and painting of the working surface. If the casting is quite massive, then, on the contrary, the mold can be heated by its heat to a temperature higher than the required working temperature, and it is cooled before the next casting.
The chill casting process is a low-operation process. Manipulative operations are quite simple and short-term, and the longest operation in terms of duration is cooling the casting in the mold to a given temperature. Almost all operations can be performed by machine mechanisms or automatic installations, which is a significant advantage of the method, and, of course, the most important advantage is that the labor-intensive and material-intensive process of making the mold is eliminated: the mold is used repeatedly.
Features of formation and quality of castings.
Chill is a metal mold that, compared to sand, has significantly greater thermal conductivity, heat capacity, and strength, but practically zero gas permeability and gas content. These properties of the die material determine the features of its interaction with the casting metal discussed below:
- High efficiency of thermal interaction between the casting and the mold: the melt and the solidifying casting are cooled in the mold faster than in a sand mold, i.e. at the same hydrostatic head and temperature of the poured melt, the fillability is usually worse than that of a sand mold. This complicates the production of castings from alloys with reduced fluidity in molds and limits the minimum wall thickness and dimensions of the castings. The average wall thickness of die castings made of aluminum alloys is 3-7 mm. At the same time, the increased cooling rate contributes to the production of dense castings with a fine-grained structure, which increases the strength and ductility of the cast alloys. However, in cast iron castings produced in chill molds, due to the characteristics of crystallization, carbides are often formed, which negatively affect the properties of cast iron: impact strength and wear resistance are reduced, hardness in the bleached surface layer increases sharply, which makes it difficult to process such castings by cutting and leads to the need to subject them to thermal processing (annealing) to remove chill.
- The chill mold is practically unyielding and more intensively prevents shrinkage of the casting, which makes it difficult to remove it from the mold and can cause the appearance of internal stresses, warping and cracks in the casting. However, the dimensions of the working cavity of the chill mold can be made much more accurately than in a sand mold. During casting, there are no errors caused by pushing away the model, elastic and residual deformations of the sand mold, which reduce the accuracy of its working cavity and, accordingly, the casting. Therefore, castings in molds are more accurate.
- The physical and chemical interaction of the casting metal is minimal, which helps to improve the quality of the casting surface. Chill castings do not burn. The surface roughness of castings is determined by the compositions of linings and paints applied to the surface of the working cavity of the mold, and corresponds to the values of Rz = 80-20 microns, but may be less.
- The chill mold is practically gas-tight, but its gas content is minimal and is determined mainly by the compositions of fire-resistant coatings applied to the surface of the working cavity. However, gas holes in chill castings are not a rare phenomenon. The reasons for their appearance are different, but in any case, the location of the casting in the mold, the method of supplying the melt and the ventilation system must ensure the removal of air and gases from the mold during pouring.
Application area of die casting
Thanks to die casting, mass production not only in the Russian Federation, but throughout the world is provided with cast parts by more than 40%, compared to other types of casting.
The die casting method produces castings from cast iron, steel and its alloys, magnesium, aluminum and their alloys. all possible purposes and weights. Various parts are turned from castings, which are widely used in mechanical engineering, carriage building, automotive industry, tractor manufacturing, when laying gas pipelines, etc.
All branches of industry and engineering production use parts made by die casting: pistons, blocks, cylinders, electric motor housings, bearing cheeks, flanges, frames, fittings, screws, gears and many other parts of machines and mechanisms.
Modern industry needs a huge number of parts, most of which are cast. They can weigh from a few grams to hundreds of kilograms.
Casting into reusable metal molds – chill molds – is one of the most progressive and effective types of casting, as they can withstand from several pours to tens of thousands of uses (manufacturing of aluminum parts).
The possibility of modernization, mechanization and automation of chill casting allows us to completely cover the shortage of cast products in industry and minimize the use of heavy manual labor.
Source
The process of making the mold and the materials used
When making molds, the designer must be guided by the grades of the alloy that will be poured into the mold being manufactured. Of course, he must also take into account the size of the parts obtained as a result of casting into this tooling.
Thus, when manufacturing parts with small dimensions from non-ferrous metals, cast iron and some other materials, it is recommended to use gray cast iron 20 or 25 for the production of casting molds. Other types of materials are also used for the production of molds. It should be noted that the stronger the material, for example, 15L steel, the higher the dimensional stability. For certain grades of metal, molds are made from aluminum, but before using these molds, the working surfaces are anodized.
The production of molds is carried out using die-forging equipment. But modern equipment operating under computer control, for example, a turning and milling center, makes it possible to produce particularly precise shapes.
General characteristics of the metal
The main components of the bronze alloy are copper and tin. There are additives in the form of metals and non-metals, but they are contained in small quantities. Depending on the percentage presence of copper, the alloy changes color. It comes in red, yellow or steel grey.
An important characteristic of a bronze alloy is its ductility. At the same time, the material has sufficient hardness
Taking these qualities into account and changing the content of components, an alloy with different characteristics is obtained. One can be forged, the other is used as a starting material for castings.
Art casting "Kupina"
Melting points
An important characteristic of a bronze alloy is its melting point. Its maximum value reaches 1350 degrees
It varies depending on the presence of additives that increase the refractoriness of bronze. This includes aluminum, titanium or zinc. When the percentage composition of alloying components changes, the melting point of bronze varies within the range of 975–1350 degrees.
Considering that bronze has viscosity, heating is carried out to a temperature exceeding the melting of the alloy by 100 degrees.
Original salad “Cows in oranges”
Another salad with decoration. It turns out delicate, but with a bright orange accent.
KBJU per 100 g: 122.4/13/6.4/2.5
What you need:
- 300 g boiled chicken fillet
- 100 g cheese
- 1 processed cheese
- 4 boiled eggs
- 1 orange
- pp-mayonnaise
For decoration:
- 2 boiled eggs
- slightly boiled carrots
- greenery
Let's prepare it step by step:
- This is a layered salad, grease each layer with pp mayonnaise.
- Place the first layer of finely chopped chicken.
- Then - orange slices; no need to grease them.
- Place grated egg whites on top of the orange.
- The next layer is cheese and processed cheese.
- Lastly, add the finely grated egg yolks.
- Decorate the salad with finely chopped herbs, make cows from egg whites as in the photo.
- Salad ready!
Chill casting is a precision technology for the production of aluminum castings.
Chill casting (reusable metal mold) is a fairly expensive, but proven and accurate casting technology used in the production of castings from aluminum alloys.
Despite the high initial cost of equipment, chill casting technology has a number of main advantages compared to other technologies, namely:
- castings are obtained with a denser structure;
- the appearance of castings and surface cleanliness are significantly improved;
- the accuracy of castings and the identity of their dimensions increases;
- the metal consumption of the casting and the cost of machining are reduced due to the reduction of casting allowances;
- the yield of suitable casting increases;
- operations with molding sands are eliminated;
- with large-scale production, the cost of production is reduced;
- The productivity of foundry workers is significantly increased.
For the manufacture of molds, PRACTIC Plus specialists mainly use gray or high-strength cast iron, as well as carbon or alloy steels. Gray cast iron, used for molds, is resistant to thermal loads, inexpensive and easy to process. Steel molds are more expensive to manufacture, but more durable than cast iron ones, since they are not afraid of shock loads. Metal rods, guides and pushers for opening the mold and pushing out castings are always made of steel, since they experience increased tensile stresses.
The main indicator of a mold is its durability. During operation, the working surfaces of the chill molds are subjected to rapid heating and cooling, as a result of which thermal stresses arise in them, leading to warping and surface cracks - cracks. The durability of cast iron and steel molds when producing castings from aluminum alloys is 50-100 thousand pours. To increase the durability of the molds, the working surfaces are coated with paints. With the help of paints, welding of metal to the walls of the mold is also eliminated, high-quality surfaces are obtained and the direction of solidification of castings is regulated. When it comes into contact with metal, the paint sublimes, creating a gas and soot layer between the liquid metal and the die, which prevents the liquid metal from welding to the die. The paint is applied with a brush or spray once or twice a shift, depending on the design and operating mode, onto a mold heated to 100-200 °C.
During the casting process, a very important technological parameter is the temperature regime of the die. To obtain high-quality castings from aluminum alloys, the chill temperature must be maintained within 200–350 °C. PRACTIC Plus specialists warm up and maintain the temperature of the chill mold (dispersal of the chill mold) using gas burners, and control the temperature regime using infrared thermometers (pyrometers) or thermocouples. Cooling of the chill mold is carried out by natural heat transfer to the environment through the walls of the chill mold. If necessary, our specialists will design and manufacture molds cooled externally with water (water-cooled) through specially designed channels. The durability of water-cooled molds is higher than that of non-water-cooled ones.
When casting castings with complex configurations, PRACTIC Plus specialists use various movable metal rods and inserts. Mobility is necessary for timely removal of the rod from the casting. If the internal contours of the casting are complex, then the rods are made of several parts. We also use sand cores to produce castings with complex internal configurations. They are installed in the mold each time before pouring when assembling the mold using sign parts.
At "PRACTIC Plus" they are made of oxide either cast or from rolled forgings by machining. Cast molds are cheaper because minimal machining is required. The opening (opening) of the molds is carried out manually or mechanized using mechanical, pneumatic and hydraulic drives, which are also designed and manufactured by PRACTIC Plus specialists. The surfaces of the connectors are processed according to the 6th accuracy class. The individual parts of the mold are centered using pins and bushings. Ventilation channels are provided to remove gas and air from the die cavity.
The PRACTIC Plus company considers orders for the production of aluminum castings of any configuration and series, weighing up to 50 kg.
The price of casting depends on the complexity of the part and is calculated individually.
For additional information, please call: (067) 437-90-70, or the contacts listed on the website.
General information
The mold consists of: (Fig. 1)
Figure 1. Composition of the chill mold
1 - pouring bowl, 2 - gating system, 3 - molding system, 4.5 - guide columns and bushings, 6 - profit, 7 - right and left half-molds.
More complex mold (Fig. 2)
Fig 2. Complex chill molds
A chill mold is a metal mold that is filled with a melt under the influence of gravitational forces. Unlike a one-time sand mold, the chill mold can be used many times. With this casting method, the use is either completely eliminated, or a small amount of sand mixtures is used only for the production of one-time cores. In this regard, the loading of the molding area, the volume of molding sand during the production of castings, and the costs of delivery and preparation of molding sands are reduced. In addition, chill casting has the following advantages - increased dimensional accuracy of castings, high productivity of the process, reusability of casting molds, the ability to automate the process, economical use of production space, the possibility of combined use of chill molds and complex sand cores, stability of the density and structure of castings, high mechanical and operational properties.
What is metal casting and how can you make money from it?
Casting is one of the methods of processing various metals. With it you can create objects of different sizes and configurations. This is the simplest and most affordable method, which is carried out using special equipment. Now many manufacturers offer mini construction.
Mini foundry
This means that an individual project of the production complex will be developed, the layout of the workshops, the placement of equipment, and the provision of all necessary communications.
Why is it beneficial to pay attention to ready-made turnkey complexes? Because:
- manufacturers accurately calculate the required production area;
- place communications as efficiently as possible;
- provide a full range of equipment setup services;
- By purchasing, you can immediately begin the production process.
Technical characteristics of foundry equipment If the choice is made in favor of such a complex, then the next step in organizing a business will be to search for customers. Die-cast metal products are in great demand in almost all industries:
Sheet metal bending
- machine tool industry;
- automotive industry;
- instrument making;
- production of household appliances;
- shipbuilding;
- production of medical and dental equipment;
- jewelry art;
- production of home and garden decor items;
- construction materials industry.
The advantages of a mini-factory are its compact size and the ability to produce products in small batches. Often large enterprises are forced to refuse small wholesale customers, since reconfiguring equipment is quite problematic.
A mini-factory is an automated complex: in order to switch to a new type of manufactured products or metal blanks, you only need to make changes to the software package and make new molds. And the cost of non-standard parts made to order is several times higher than standard production.
Foundry
Another advantage of the mini ones is that they are designed so that they can process all types of metals, while the large-scale lines have separate workshops for this.
2.1. The essence of foundry
The production of cast products has been known since ancient times. In China, India, Babylon, Egypt, Greece, and Rome, items of weapons, religious worship, art, and household items were cast. In the 13th–15th centuries, Byzantium, Venice, Genoa, and Florence were famous for cast products.
In the Russian state in the 14th…15th centuries, bronze and cast iron cannons, cannonballs and bells were cast. In 1586, A. Chokhov cast the “Tsar Cannon” (Fig. 1.9). “Tsarpushka” is a cast iron weighing about 39 tons (barrel diameter - 890 mm, length - 4 m, caliber - 887 mm). To fire a stone cannonball, a gunpowder charge weighing 84 kg was required. The estimated speed of the cannonball leaving the barrel was 230 m/s, and the speed of the cannonball at a distance of 1,000 m from the gun was 180 m/s. Later, other remarkable examples of foundry art were created in Russia. Thus, in 1735, the “Tsar Bell” (Fig. 1.10) weighing over 200 tons was cast by father and son Motorin, in 1782 - the monument to Peter I “The Bronze Horseman” (weighing 22 tons) by E. Falconet, in 1816 G . - a monument to Minin and Pozharsky by V.P. Ekimov, in 1850 - sculptural groups of the Anichkov Bridge (Fig. 1.11) in St. Petersburg by P.K. Klodt and others. In 1894, a cast-iron casting of a chabot for a blacksmith was made at a factory in Perm hammer weighing 620 tons.
Rice. 1.9
.
Tsar Cannon Fig. 1.10. Tsar Bell Fig. 1.11. Sculptures of Anichkov Bridge
Foundry production
- a branch of mechanical engineering engaged in the production of shaped blanks or parts by pouring molten metal into a special mold, the cavity of which has the configuration of the blank or part.
When cooled, the poured metal hardens and, in its solid state, retains the configuration of the cavity into which it was poured. The final product of a foundry (blank or part) is called casting
.
Total global production of castings in 2011 amounted to 75 million tons. At the same time, 70% of castings come from mechanical engineering, where the mass of cast parts of their total mass is 50%. In the machine tool industry, 80% of all parts are made from cast blanks, and in agricultural engineering and tractor manufacturing - up to 60%.
The casting method is used to produce engine blocks, cylinder heads, pistons and piston rings, crankshafts, gearbox housings and covers, gear wheels, frames of machine tools and rolling mills, turbine blades, caterpillar tracks, excavator buckets and other parts that are difficult or impossible to obtain by other methods. metal processing (in particular, pressure and cutting).
Casting technology allows:
1) to obtain products of complex shapes and various sizes (internal combustion engine cylinder blocks, metal-cutting machine beds, shaped artistic castings);
2) manufacture products with minimal processing allowances (camera parts, internal combustion engine pistons). At the same time, the metal utilization factor (CMM) is at least 70%, and for injection molding - 95%;
3) manufacture products from alloys with low ductility and low machinability (excavator buckets, tracks, etc.).
For the production of castings, casting in sand-clay molds and special methods are used (lost wax casting, shell molds, chill molds, pressure casting, centrifugal casting, etc.).
When choosing a casting method, the production volume, requirements for the geometric shape of the product and surface cleanliness, the chemical composition of the metal being poured, the shape of the casting, economic considerations and other factors are taken into account.
Regardless of the casting method, in all cases a casting mold is needed to obtain a casting. Casting shape
is a structure consisting of elements that form a working
a cavity, the filling of which with a melt ensures the production of a casting of a given size and configuration.
When making castings, the casting mold is the main tool. The form provides, firstly, the necessary configuration and dimensions of the casting, secondly, the specified accuracy and quality of its surface, and thirdly, a certain cooling rate of the poured metal, which contributes to the formation of the required structure and corresponding properties of the casting.
Casting molds are divided according to the number of fills into one-time and multiple, according to the material - sand, sand-cement, gypsum, metal, highly refractory materials, etc.
The main operations of the technological process for manufacturing castings are: making a casting mold, melting metal and pouring into a mold, removing castings from a mold.