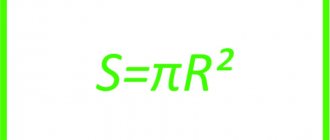Pipe area is a concept used when calculating three different product parameters - external surface, internal surface and cross-section. When carrying out calculations related to a section, in some cases it is necessary to deal with the so-called live section. By calculating the area, it is possible to determine the amount of materials required and the level of costs required for the installation and full functioning of the pipeline.
Calculation of such an indicator as pipe area may be necessary during the construction of a pipeline, as well as its insulation, painting and other activities.
Coolant movement speed
It is immediately worth noting that the minimum speed of water movement in the heating system pipeline cannot fall below 0.2-0.25 m/sec. If the speed at some point turns out to be lower, the coolant will gradually begin to release air - and this, in turn, will cause air locks to appear in the system. Such traffic jams always lead to a decrease in the performance of the system, up to its failure.
Conclusion
Having collected the values of all the necessary parameters, it is enough to substitute them into the formula to find out the required pipe diameter for the heating system. To simplify your work, you should use special tables that indicate formulas for calculations and describe in detail all the indicators used in them.
By simple calculations you can determine the optimal pipe size for a particular situation. A clear understanding of what pipe diameter to choose for heating will allow you to create an extremely high-quality and functional design that will provide the house with sufficient heat.
Some physical features
The cross-sectional area of the pipe determines the speed of movement of liquids and gases that are transported through it. You need to choose the optimal diameter. Internal pressure is no less important. The feasibility of choosing a section depends on its size.
The calculation takes into account not only pressure, but also the temperature of the medium, its nature and properties. Knowing formulas does not relieve you from the need to study theory. Calculation of sewerage, water supply, gas supply and heating pipes is based on information from reference books. It is important that all necessary conditions are met when choosing a section. Its value also depends on the characteristics of the material used.
Table of rolled metal surface areas
Surface area of 1 ton of rolled steel.
Click on the position you are interested in.
| Profile name, number and section thickness, mm | Surface area of 1 ton profile, m2 | Profile name, number and section thickness, mm | Surface area of 1 ton profile, m2 |
| 1. Sheet steel and open bent profiles. The surface is given as a total on both sides. | |||
| Sheet thickness | Square | Sheet thickness | Square |
| 2,0 | 127,6 | 12,0 | 21,5 |
| 2,2 | 115,9 | 14,0 | 18,4 |
| 2,5 | 102,3 | 16,0 | 16,2 |
| 2,8 | 91,2 | 18,0 | 14,4 |
| 3,0 | 85,0 | 20,0 | 13,0 |
| 3,2 | 79,9 | 22,0 | 11,8 |
| 3,5 | 73,0 | 25,0 | 10,4 |
| 4,0 | 63,9 | 28,0 | 9,4 |
| 5,0 | 51,1 | 30,0 | 8,7 |
| 6,0 | 42,7 | 32,0 | 8,2 |
| 7,0 | 36,6 | 36,0 | 7,3 |
| 8,0 | 32,1 | 40,0 | 6,6 |
| 9,0 | 28,5 | 45,0 | 5,9 |
| 10,0 | 23,4 | 50,0 | 5,4 |
| 11,0 | 21,5 | 55,0 | 4,9 |
| 2. Closed bent square, rectangular and pipe profiles. The surface is given on the outside. | |||
| Wall thickness | Square | Wall thickness | Square |
| 2,0 | 65,2 | 12,0 | 10,8 |
| 2,5 | 52,1 | 4,0 | 9,3 |
| 3,0 | 43,5 | 16,0 | 8,1 |
| 3,5 | 37,3 | 7,0 | 7,6 |
| 4,0 | 32,9 | 18,0 | 7,5 |
| 5,0 | 26,5 | 20,0 | 6,7 |
| 6,0 | 22,0 | 22,0 | 6,1 |
| 7,0 | 19,0 | 25,0 | 5,5 |
| 8,0 | 16,6 | 28,0 | 5,0 |
| 9,0 | 14,5 | 30,0 | 4,7 |
| 10,0 | 13,1 | 32,0 | 4,4 |
| 11,0 | 11,8 | 40,0 | 3,5 |
| 3. Angular steel, equal flange. The surface is given as a total on all sides. | |||
| Shelf thickness | Square | Shelf thickness | Square |
| 3 | 86,5 | 14 | 19,0 |
| 4 | 65,0 | 16 | 16,6 |
| 5 | 52,0 | 18 | 14,9 |
| 6 | 44,0 | 20 | 13,3 |
| 7 | 37,0 | 22 | 12,0 |
| 8 | 33,0 | 25 | 10,6 |
| 9 | 29,5 | 28 | 9,6 |
| 10 | 26,3 | 30 | 9,0 |
| 12 | 22,0 |
| 4. Hot rolled channels. The surface is given from all sides. | |||
| Profile no. | Square | Profile no. | Square |
| 5 | 47,1 | 20 | 38,3 |
| 6,5 | 46,4 | 20A | 36,4 |
| 8 | 45,4 | 22 | 36,6 |
| 10 | 44,7 | 22A | 34,9 |
| 12 | 43,1 | 24 | 35,0 |
| 14 | 41,6 | 24A | 33,3 |
| 14A | 39,7 | 27 | 33,2 |
| 16 | 40,5 | 30 | 31,4 |
| 16A | 38,7 | 33 | 29,6 |
| 18 | 39,3 | 36 | 27,7 |
| 18A | 37,7 | 40 | 26,1 |
| 5. I-beams. The surface is given as a total on all sides. | |||
| Profile no. | Square | Profile No. | Square |
| 10 | 44,4 | 27 | 33,0 |
| 12 | 43,1 | 30 | 31,2 |
| 14 | 41,8 | 36 | 26,7 |
| 16 | 40,5 | 40 | 24,9 |
| 18 | 39,1 | 45 | 23,2 |
| 20 | 38,1 | 50 | 21,4 |
| 22 | 36,7 | 55 | 19,7 |
| 24 | 34,4 | 60 | 18,1 |
| 6. I-beams for monorails. The surface is given as a total on all sides. | |||
| Profile no. | Square | Profile No. | Square |
| 24M | 24,0 | 36M | 21,4 |
| 30M | 22,3 | 45M | 19,3 |
| 7. Beams with parallel flange edges. The surface is given as a total on all sides. | |||
| Profile no. | Square | Profile no. | Square |
| 20B | 49,1 | 50B2 | 22,8 |
| 20B1 | 39,4 | 50B3 | 20,9 |
| 20B2 | 36,7 | 55B | 26,7 |
| 20B3 | 33,6 | 55B1 | 22,6 |
| 23B | 45,9 | 55B2 | 20,8 |
| 23B1 | 38,0 | 55B3 | 19,1 |
| 23B2 | 35,3 | 60B | 24,4 |
| 23B3 | 32,0 | 60B1 | 20,5 |
| 26B | 43,2 | 60B2 | 18,6 |
| 26B1 | 35,9 | 60B3 | 17,2 |
| 26B2 | 33,3 | 70B | 21,0 |
| 26B3 | 30,4 | 70B1 | 19,1 |
| 30B | 40,7 | 70B2 | 17,4 |
| 30B1 | 35,4 | 70B3 | 15,9 |
| 30B2 | 33,0 | 70B4 | 14,6 |
| 30B3 | 30,1 | 80B | 19,3 |
| 35B | 37,8 | 80B1 | 17,2 |
| 35B1 | 34,4 | 80B2 | 15,5 |
| 35B2 | 31,1 | 80B3 | 14,2 |
| 35B3 | 28,4 | 80B4 | 13,1 |
| 40B | 34,9 | 90B | 17,8 |
| 40B1 | 30,8 | 90B1 | 15,7 |
| 40B2 | 27,8 | 90B2 | 14,5 |
| 40B3 | 25,5 | 90B3 | 13,2 |
| 45B | 32,3 | 90B4 | 12,0 |
| 45B1 | 27,5 | 100B | 16,7 |
| 45B2 | 24,9 | 100B1 | 14,4 |
| 45B3 | 22,8 | 100B2 | 13,0 |
| 50B | 29,3 | 100B3 | 11,7 |
| 50B1 | 24,8 | 100B4 | 10,6 |
| 8. Wide-panel I-beams. The surface is given as a total on all sides. | |||
| Profile no. | Square | Profile no. | Square |
| 20Ш | 38,9 | 50Ш4 | 14,2 |
| 20Ш1 | 33,8 | 50Ш5 | 12,9 |
| 20Ш2 | 31,2 | 60Ш | 21,4 |
| 23Ш | 37,9 | 60Ш1 | 17,4 |
| 23Ш1 | 30,9 | 60Ш2 | 16,0 |
| 23Ш2 | 27,8 | 60Ш3 | 14,6 |
| 26Ш | 33,2 | 60Ш4 | 13,1 |
| 26Ш1 | 28,6 | 60Ш5 | 11,8 |
| 26SH2 | 25,9 | 60Ш6 | 10,7 |
| 30Ш | 30,1 | 70Ш1 | 15,8 |
| 30Ш1 | 26,0 | 70Ш2 | 14,4 |
| 30Ш2 | 23,4 | 70Ш3 | 13,1 |
| 30Ш3 | 21,1 | 70Ш4 | 12,0 |
| 30Ш4 | 19,4 | 70Ш5 | 11,0 |
| 35Ш | 26,8 | 70Ш6 | 10,3 |
| 35Ш1 | 22,7 | 70Ш7 | 9,5 |
| 35Ш2 | 20,8 | 70Ш8 | 8,8 |
| 35Ш3 | 19,1 | 80Ш | 17,4 |
| 40Ш | 23,2 | 80Ш1 | 14,4 |
| 40Ш1 | 20,4 | 80Ш2 | 13,2 |
| 40Ш2 | 18,9 | 80Ш3 | 12,1 |
| 40Ш3 | 17,9 | 90Ш | 15,7 |
| 40Ш4 | 16,2 | 90Ш1 | 13,1 |
| 50Sh | 22,6 | 90Ш2 | 12,1 |
| 50Ш1 | 19,4 | 90Ш3 | 11,1 |
| 50Ш2 | 17,4 | 100Sh | 14,2 |
| 50Ш3 | 15,7 | 100Ш1 | 12,3 |
| 9. Column I-beams. The surface is given as a total on all sides. | |||
| Profile no. | Square | Profile no. | Square |
| 20K | 32,3 | 35K1 | 19,3 |
| 20K1 | 29,3 | 35K2 | 17,3 |
| 20K2 | 26,1 | 35K3 | 15,6 |
| 20K3 | 23,7 | 35K4 | 14,2 |
| 20K4 | 21,7 | 35K5 | 13,0 |
| 23K | 31,6 | 35K6 | 11,9 |
| 23K1 | 27,5 | 35K7 | 10,9 |
| 23K2 | 25,7 | 35K8 | 10,0 |
| 23K3 | 23,2 | 40K | 19,9 |
| 23K4 | 21,2 | 40K1 | 17,5 |
| 26K1 | 26,1 | 40K2 | 16,0 |
| 26K2 | 23,3 | 40K3 | 14,5 |
| 26K3 | 20,9 | 40K4 | 13,1 |
| 26K4 | 19,2 | 40K5 | 11,8 |
| 26K5 | 17,6 | 40K6 | 10,8 |
| 30K1 | 21,4 | 40K7 | 9,8 |
| 30K2 | 19,9 | 40K8 | 9,0 |
| 30K3 | 18,3 | 40K9 | 8,2 |
| 30K4 | 16,7 | 40K10 | 7,8 |
| 30K5 | 15,2 | 40K11 | 6,2 |
| 30K6 | 14,1 | 40K12 | 5,2 |
| 30K7 | 12,8 | 40K13 | 4,4 |
| 30K8 | 11,7 | 40K14 | 3,7 |
| 10. Round steel, reinforcement, rod. | |||
| Diameter | Square | Diameter | Square |
| 5,0 | 102,0 | 45,0 | 11,3 |
| 6,0 | 84,9 | 48,0 | 10,6 |
| 6,5 | 78,5 | 50,0 | 10,2 |
| 7,0 | 72,8 | 53,0 | 9,6 |
| 8,0 | 63,6 | 56,0 | 9,1 |
| 9,0 | 56,7 | 60,0 | 8,5 |
| 10,0 | 50,9 | 65,0 | 7,8 |
| 11,0 | 46,3 | 70,0 | 7,3 |
| 12,0 | 42,5 | 75,0 | 6,8 |
| 13,0 | 39,3 | 80,0 | 6,4 |
| 14,0 | 36,3 | 85,0 | 6,0 |
| 15,0 | 33,9 | 90,0 | 5,7 |
| 16,0 | 31,8 | 95,0 | 5,4 |
| 17,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 | 5,1 |
| 18,0 | 28,3 | 105,0 | 4,9 |
| 19,0 | 26,8 | 110,0 | 4,6 |
| 20,0 | 25,4 | 120,0 | 4,2 |
| 21,0 | 24,3 | 125,0 | 4,1 |
| 22,0 | 23,2 | 130,0 | 3,9 |
| 24,0 | 21,2 | 140,0 | 3,6 |
| 25,0 | 20,4 | 150,0 | 3,4 |
| 26,0 | 19,6 | 160,0 | 3,2 |
| 28,0 | 18,2 | 170,0 | 3,0 |
| 30,0 | 17,0 | 180,0 | 2,8 |
| 32,0 | 15,9 | 190,0 | 2,7 |
| 34,0 | 15,0 | 200,0 | 2,5 |
| 36,0 | 14,2 | 210,0 | 2,4 |
| 38,0 | 13,4 | 220,0 | 2,3 |
| 40,0 | 12,7 | 240,0 | 2,1 |
| 42,0 | 12,1 | 250,0 | 2,0 |
Name of the profile, number and section thickness, mmSurface area of 1 ton of profile, m2
Measuring pipes using photography (copy method)
This non-standard method is used when there is complete inaccessibility to a pipe of any size. A ruler or any other object is applied to the pipe being measured, the dimensions of which are known in advance to any master (often in this case they use a matchbox, the length of which is 5 cm, or a coin). Next, this section of the pipe with the attached object is photographed (in addition to a camera, in modern conditions it is also possible to use a mobile phone). The following size calculations are made from photographs: the visual thickness in mm is measured in the photograph, and then converted into real values, taking into account the scale of the photographs.
Why are geometric calculations needed?
Before you begin to measure or find out the original dimensions, you need to understand for what purposes the calculations made will serve.
There are several such goals:
- Calculation of thermodynamic parameters of the system . The formula for the surface area of a pipe is necessary when calculating the heat transfer of an individual pipe, section of pipeline or, for example, a heated floor. In order to find out these parameters, it is necessary to calculate the total area of the product or system from which heat is transferred to the environment.
- Calculation of heat loss in the direction “heat source-heating device” . In this case, the greatest loss of thermal energy occurs in the longest section with the largest area of contact with the environment, that is, again in the pipes. Therefore, as in the previous case, having learned the heat transfer surface area, it is possible, based on this value and the amount of heat generated at the starting point, to plan the number and size of heating devices in the future system.
Comparison of one-pipe and two-pipe systems
We have already found out how to calculate heating pipes and what diameter is needed for both types of systems. For closed circuits, with a room area of 120 m2 or more, this figure is 32 mm for polypropylene. In this case, the nominal bore for products with a nominal pressure of 20 and 25 atmospheres is 21.2 mm. For products with a nominal pressure of 10 atmospheres, the nominal bore is 20.4 mm and the outer diameter is 25 mm.
- Efficiency - definitely, “hitches” heat the room more efficiently than single-pipe ones;
- saving money - all that can be saved on Leningradka is some segment of the contour and that’s it.
The number of tees will be the same, and the same number of taps, but more adapters may be required. Imagine a circuit from which two pipes extend at a short interval. One of them goes to the radiator inlet, and the second returns the coolant back to the system. It turns out that the section between the pipes is a bypass. In order for the circulation in the battery to be better, the bypass must be made of a smaller diameter than the main heating circuit. It follows from this that a couple more units of fittings will be required. It turns out that we spend less money on pipes and more on fittings, resulting in no savings, and the efficiency is lower.
As a result, we can conclude from this that the stories about how good and cheap a single-pipe heating system is are simply unfounded.
Pressure type of main line
The design is a system that supplies and removes transported liquid from computing equipment. When feeding, large pumps are used to feed and pump out material from the pipes.
A serious advantage over free-flow communication is the possibility of delivery over vast distances, without serious losses in time. In addition, a huge advantage of these structures is the large slope, which allows the construction of highways with a smaller diameter, which not only reduces the financial costs of production, but also facilitates the calculation of parameters.
The initial parameters are regulated according to GOST 539-80
| Conditional pass | Wall thickness | Pipe length | |
| VT7 | VT10 | ||
| 101 | 104 | 130 | 2977 |
| 154 | 158 | 189 | 3020 |
| 220 | 227 | 265 | 3103 |
| 278 | 284 | 308 | 3200 |
| 361 | 369 | 399 | 3300 |
| 430 | 441 | 470 | 3566 |
Tip 1: How to calculate the pipe diameter
If you are faced with the task of calculating the diameter of a pipe, then you can do this with the support of primitive geometric calculations. Any pipe is a cylinder and has two diameters - external and internal, they differ by twice the thickness of the pipe wall. The calculation can be made using various methods, depending on the available data.
Instructions
1. In the most general case, the diameter s of a pipe with a wall thickness T can be calculated by measuring the circumference of its cross-section. Let this length be equal to L. Then, according to the formula for the circumference, its diameter will be equal to d1 = L / P, where L is the circumference of the pipe section, P = 3.14 Thus, D1 is the outer diameter.
Thermodynamic parameters
The purpose of these physical and chemical quantities is to carry out accurate calculations of heat absorption and heat release of individual sections of highways. Having learned the costs, it is possible not only to develop a scheme for a new design that involves less losses in the transport of matter, but also to draw up a new financial plan for production and volume of products.
Heat network
In order to carry out the necessary calculations, it is necessary to create an individual formula based on operating with the total area of the structure.
Metal pipe weight calculator
Calculation of pipe weight primarily depends on the type of pipe metal. So, when calculating the weight of a round pipe, a completely different formula is used than when calculating profile pipes. Therefore, first of all, indicate the type of profile. Then indicate the name of the alloy or steel and the dimensional characteristics of the rolled product. The result will be calculated automatically.
Note! The result is approximate and cannot be used when calculating structures related to human life. To obtain more accurate figures for the mass of pipes, use the “GOST tables of steel pipe weights” in the reference section
Calculation of the weight of a profile pipe
To calculate the mass of a square pipe, the calculator uses the formula:
where ro is the density of the metal, S is the size of the pipe wall, A is the overall dimension of the side, L is the length of the pipe.
To calculate the mass of a rectangular pipe, the calculator uses the formula:
where ro is the density of the metal, S is the size of the pipe wall, AB is the overall dimensions of the sides, L is the length of the pipe.
Where to begin
Paint consumption depends not only on the size of the pipe, but also on the material used to make it and on the shape.
Most often you can find pipes in the shape of a cylinder. But there are other types:
- In the shape of a rectangle. Outwardly, they look like ordinary timber. Otherwise called profile.
- Cone-shaped. The name speaks for itself. Very rarely used. Their scope of application is pressure injection systems.
- Corrugated.
- For sewerage equipment. They are large cement rings.
The dimensions of pipes of each type correspond to the requirements stated for them in special documents.
Steel pipe weight calculation
If you are not a pipe professional, but you need to find out how much a steel pipe will weigh, then don’t despair. You will be able to calculate the weight of a rectangular steel pipe or any other pipe using modern technologies in the form of the World Wide Web, where you can use online programs that contain tables for calculating the weight of different steel pipes.
Find out the weight of the pipe using the formula
If you do not have access to the Internet, then there are formulas for calculating the specific gravity of pipes. You need to know that it is customary to calculate the weight of one meter of steel pipe in kilograms. There are two calculation formulas and practice shows that both of them are effective and produce results that are not much different from each other. Formulas are used to calculate a larger number of pipe sizes; for example, the weight of a round electric-welded steel pipe is no different from a seamless pipe and depends only on the wall thickness.
1. Variant of the first formula: Mn = ((Dn – Tc)/40.5)*Tc. Du is the diameter of the pipe, indicated in millimeters, Tc is the thickness of its wall in millimeters, and Mn will be the result. The result will show you how much one meter of pipe weighs in kilograms.
2. Option of the second formula: Mn = (Dy – Tc)*Tc*0.0246615. In this case, Du will also be the diameter of the pipe in millimeters, Tc – the thickness of the pipe wall in millimeters. The result Mn will show the weight in kilograms of one linear meter of pipe.
Find out the weight of the pipe using a calculator on the Internet
Currently, there is a fairly large assortment of rolled steel products. Sometimes certain difficulties arise if you need to find out, for example, the weight of a profile steel pipe. The above formulas will not work here, since in order to find out the weight of a square steel or the same profile pipe, you will also need to take into account the cross-section of the pipes: rectangular or square. For this purpose, there are programs that allow you to easily calculate the required weight of the pipe. The calculator can be easily downloaded from the Internet and you will always have with you figures on the characteristics of pipes of different sizes. To use the calculator, you need to know the thickness of the pipe wall and its cross-section. Finding such a calculator is not at all difficult, just use any search engine.
When are pipe weight calculations necessary?
The main reasons here are the following:
- to calculate the strength of the erected structure. If, for example, the frame of a modular building is mounted from a profile or round pipe, then the weight of the useful load will also press on the base - window openings, people in the house, furniture, and the like. This also includes the weight of the upper levels of the frame. Quite often, the load-bearing skeleton of a building weighs much more than everything in the building.
— pipes and other rolled metal products are purchased by weight. If you don’t know the weight, the storekeeper will never agree to measure one and a half kilometers of main pipes for you with a tape measure,
— It may be difficult to load pipes onto vehicles if you do not know their weight. It is much easier with plastic pipes; it is enough to know the cubic capacity and compare it with the capacity of the vehicle on which transportation will be carried out. But when transporting steel pipes, everything is different. Here you need to calculate everything accurately, since such pipes weigh ten times more, and vehicles simply will not budge from reloading.
Steel pipe weight calculation
If you are not a pipe professional, but you need to find out how much a steel pipe will weigh, then don’t despair. You can calculate the weight
Steel pipe weight: calculation calculator and formulas
Pipes, both round and profile, are sold at retail by the meter. However, when calculating future building structures, as well as when hiring a carrier, it is necessary to know the exact weight of the product. The steel pipe calculator calculates the weight of a pipe based on theoretical principles and allows you to calculate the mass of all existing types of pipes made from different grades of steel.
Round steel pipes
Purpose of the calculator
In order to find out the exact mass of a product, you need to calculate its volume, find out the grade of steel, then use GOST tables to determine its density. This is not an easy task, and its solution takes a lot of time. To save the builder from having to rummage through technical literature on his own, an online calculator was created.
Steel pipe weight calculator
This calculator takes into account all the elements that affect the determination of mass, so inaccuracies in calculations are minimized. When counting manually, the same data will be used as in the calculator on the site, but the time will be spent ten times more. At the same time, manual counting is fraught with technical errors, while automation does not have this drawback.
Principles and elements of calculation
Determining the weight of steel pipes using a calculator is based on the data contained in GOST standards. The programmers included the possibility of calculations depending on the following parameters:
- pipe cross-sectional shape – round, square or rectangular;
- outer diameter (for a round pipe) or side length (for a profile pipe);
- wall thickness, which is determined in accordance with the technical data sheet of the product;
- steel grade;
- product length in meters.
Section of steel pipes
From a physics course we know that the mass of an object is equal to its volume multiplied by the density of the material from which it is made. The volume is equal to the cross-sectional area multiplied by the height of the product. In the case of pipes, their length is taken as the height of the product. When making calculations, the greatest difficulty is the calculation of the cross-sectional area, since it has a complex geometric configuration.
The calculator calculates the weight of a square steel pipe using the following formula:
A rectangular pipe is calculated as follows:
The calculator calculates the weight of a round steel pipe using an algorithm described by the following formula:
π is a constant value, equal to 3.14, used when calculating the area of a circle.
Where to get the source data?
GOSTs contain information on the range and parameters of all standard types of pipes. In addition to dimensions, the calculations include a parameter such as steel density.
Density of steel of various grades
The letter designations in the steel grade indicate one or another impurity. Chemical elements that are added to steel have the following designations:
Designations of elements in alloys
Tolerances for calculations
Any inaccuracies that will be made when calculating the mass of pipes will be within the tolerances provided for by GOSTs. These inaccuracies will be higher for substandard products, and the mass of pipes of the highest quality will be calculated with maximum accuracy.
Profile steel pipe
The scatter is explained by the peculiarities of production. Pipes that meet quality requirements have constant wall thickness and perfect welds. The so-called substandard has flaws, which, however, allow the pipes to be used in construction, not necessarily for their intended purpose. These flaws affect the mass, which is reflected in the form of inaccuracies in the calculations.
Information
After completing the installation of pipe communications, above-ground or underground pipelines, the need arises to paint the pipes. This is done to avoid corrosion and destruction of steel pipelines. The online calculator will help you calculate the area of the pipe, as well as the paint consumption for painting the pipe surface. The program will quickly and without errors determine the area to be painted on the pipe; you just need to enter the available dimensions into the calculator menu bar.
Calculator functions for calculating pipes
The pipe area calculator for painting is an online program consisting of the following blocks:
- two lines for entering pipe sizes;
- additional function “Count paint consumption”;
- two lines of output of finished calculation results;
- reference information with a pipe sketch, formula and explanation of symbols.
The pipe painting calculator allows you to calculate:
- pipe surface area;
- required amount of paint.
In addition, the finished result can be saved as a PDF file or printed with one click.
How the calculator works
To get a ready-made calculation of the pipe area and paint consumption, you need to enter the following data in the program menu lines:
- indicate the outer diameter, in mm;
- indicate the length, in meters;
To obtain the amount of paint required, you need to tick the “Calculate paint consumption” box and:
- indicate paint consumption based on the average consumption rate (i), in g/m2;
After this, the calculator will automatically produce the finished result: calculation of the pipe area in square meters; the amount of paint required in grams.
IMPORTANT! In order to use the pipeline for a long time and without repairs, several rules must be followed: remove rust, degrease the surface of the pipe, apply at least two layers of paint: base primer and main finish. You can avoid all these procedures, with the exception of degreasing, and use a special 3in1 rust paint, which includes primer, paint and a rust converter.
Pipe (water and gas) is a type of rolled metal, a long hollow welded product of round cross-section. It is used for water and gas pipelines, heating systems, as well as for the manufacture of parts for water and gas pipelines.
Source
Examples of practical applications of pipe volume calculations
Let's try to analyze the sequence of actions when performing calculations related to the volume of pipes using several specific situations.
Example No. 1
In a country house, it is planned to replace the water in the heating system with an analogue that does not harden in the cold - propylene glycol. It is necessary to calculate the volume of coolant required.
The heating system consists of a 70-liter jacketed stove, three bimetallic radiators of 7 sections each, as well as 85 meters of PN25 polypropylene pipes (25 x 4.2).
Standard pipes PN25 (25 x 4.2), most often used when organizing a heating circuit, have an internal diameter of 16.6 mm. Since the volume of liquid must be calculated in liters, we will use decimeters as a unit of measurement. The ratios are as follows: 1m = 10 dm and 1mm = 0.01 dm. Therefore, d = 0.166 dm and L = 850 dm.
Next, we calculate the total volume of pipes. To do this we use the formula:
And we get:
- We know the volume of the boiler jacket; it is equal to V2 = 70 l.
- Also in the passport of the bimetallic radiator we find data that the volume of one section of this product is 0.28 liters. The total volume of all three radiators comes out:
Now, knowing the total volume of liquid required to fill this heating system, you can safely, using a reserve of 15%, order 110 liters of propylene glycol.
Example No. 2
Often, at production and farming facilities, instead of standard batteries, they install radiators of their own production, operating on the register principle. It is required to calculate the volume of such a radiator, consisting of 5 pipes and three pairs of jumpers.
- We measure the length of each pipe. In our case, they are equal and amount to 2.2 meters, and the length of each jumper is 0.15 m.
- If possible, measure the outer diameter from the end side; it is 114 mm. Using tables of standard values, we calculate that the wall thickness for such a pipe is 4.5 mm. Using a flexible ruler, we measure the circumference of the jumper pipe, let it be equal to 200 mm, from here we find the outer diameter, it is equal to 32 mm, then similarly, using the reference book, we determine the wall thickness, for a given diameter it is equal to 3 mm.
- Determine the internal diameter of the pipes:
Next, we determine the cross-sectional area of both pipes:
We determine the volume of each type using the total length of the pipes:
We calculate the total volume of a homemade radiator:
For more information, we convert cubic millimeters to liters, we get V = 96 liters.
Types of pipe sections.
To lay water supply or sewerage systems in construction, pipes of various shapes and sections are used. For classic water supply, round, square, rectangular, triangular, elliptical and other pipes can be used. For sewerage, pipes of round, semicircular, elliptical, semi-elliptical, ovoid, rectangular, trapezoidal and other shapes and sections are used.
The most popular are pipes with a round cross-section. The production of such pipes is low-cost, they have good technical characteristics, as well as a number of excellent technical and operational qualities.
To calculate the weight of a pipe or the length of a pipe, you can use a pipe calculator.
The types of pipeline sections can be different:
The following are the cross-sectional shapes of gravity pipes and channels, such as:
- a) – Round,
- b) – Semicircular,
- c) – Tent,
- d) – Banquet,
- e) – Ovoid (ovonal),
- e) – Elliptical,
- g) – Semicircular with straight inserts;
- e) – Ovoid inverted,
- i) – Tray,
- j) – Pentagonal,
- l) – Rectangular,
- m) – Trapezoidal
Calculation of pipeline cross-section.
The formula for the cross-sectional area of a pipe will depend on what the shape of this section is. To calculate the cross-section of a pipeline, it is necessary to calculate the area of a circle with a diameter that is equal to the outer diameter of the pipe, and then subtract the thickness of its walls.
The area of a circle is calculated by the formula: S = Pi*(R^2) or S=Pi*(D/2-N)^2,
- R is the radius of the circle, equal to half its internal diameter;
- S is the desired value;
- Pi is the number pi, which is usually rounded to 3.14.
- D and N are the outer diameter and wall thickness of the pipe.
As an example, we calculate the internal cross-sectional area of a round pipeline with an internal diameter of 100 mm.
The radius of this pipe will be 50 mm, or 0.05 m.
The area of the pipe will be 3.14 x 0.05^2 = 0.00785 m2.
Attention: when calculating the permeability of gravity pipelines (for example, domestic sewage), take into account not the total, but the so-called live flow cross-section, which is limited by the average water level
- a) – total cross-section,
- b) – live flow cross-section in a partially filled pipe,
- c) – live cross-section of the flow in the tray.
All necessary data on the internal diameter of VGP pipes, which are used when installing internal communications, can be found in GOST 3262-75, according to which these pipes are manufactured.
Features of pipes with different sections.
Round pipes are very easily cleaned of sediment formed by hydraulic means using balls and cylinders
As the diameter of a circular pipe increases, soil pressure and temporary external loads increase rapidly. To reduce the force in the walls of the pipes, the vault is given a semi-elliptical cross-section.
Sometimes an ovoid cross-section can be used; a pipe of such a cross-section is capable of high static and dynamic loads, but such a pipe also has disadvantages: installation of pipes with such a cross-section requires a greater channel height and laying depth than for round-section pipes with the same throughput.
In addition, in pipes with an elliptical cross-section, sediment forms much faster, which settles on the walls. In places where quicksand are present and the soil is very wet, tray-shaped pipes can be used. This allows sewer networks to be laid at a shallower depth.
Financial operations
A clear financial structure, as well as the presence of a specific production plan, allows the company to accurately purchase products for industrial production. The second stage is the correct distribution of structures along trade routes, covering the costs of replenishing costs, or repairing problem areas of highways.
Without calculating the pipe area, it is difficult to calculate other parameters, so this parameter plays a key role in industrial calculations.