In not so long ago, the VGA connector was extremely widespread, and therefore users had no problems connecting various types of monitors to this connector. After all, at that time this interface was used by all modern monitor manufacturers. But today there are many other, more advanced connectors for connecting monitors, such as DVI, HDMI and Display Port.
The invention of new connectors was facilitated by the active development of computer technology. After the first LCD monitors appeared, the VGA connector immediately showed that its capabilities were no longer enough. In this regard, manufacturers began to actively make all kinds of adjustments to the original structure of the connectors in order to achieve extremely high quality images displayed on the screen. Thus, the DVI format initially appeared, and companies that produced equipment for entertainment and games also released their own format, as a result of which a replacement occurred: the VGA>HDMI connector. After some time, DisplayPort appeared.
What is VGA?
A VGA connector is an analog connector that is designed to connect a monitor to a computer. This standard first appeared back in 1987, when it was developed by IBM specifically for a series of new computers. The systems in this series used a video card that had the same name as the connector itself, and the resolution of this video card was small by today's standards (only 640x480 pixels). Thus, if you come across the concept of “VGA connector” or “VGA resolution” somewhere, you can roughly start from these numbers.
Despite the fact that this format appeared quite a long time ago, its use is still found today on many modern video card models. The maximum permissible resolution provided by VGA connectors is 1280x1024 pixels, while the frame refresh rate can reach 75 Hz.
If a larger image is displayed on the screen, then serious losses in quality will be noticeable. It is for this reason that over time other methods of digital data transmission are becoming more and more actively used.
Types and applications of a VGA to HDMI adapter - who benefits from buying it
To “make friends” between two incompatible ports, engineers developed special converters - adapters. They have fundamental design differences. The following commonly used options are distinguished:
| Modification | Appearance | Peculiarities |
| Cable |
Beware of scammers and unverified companies selling modifications of the first type. Often, unscrupulous manufacturers offer, under the guise of a quality product, two HDMI and VGA cable headbands connected in a primitive way, without taking into account the features of data conversion.
Adapters of this type have a wide range of applications:
- Connecting an old system unit to a modern monitor or TV, as well as reverse situations.
- Connecting an old projector to the digital input on a PC or similar equipment.
- Connecting multimedia devices (for example, game consoles) with television equipment and (less commonly) monitors.
Adapters of this type have a very wide scope of use and will be relevant for many years to come
VESA DDC
DDC is a specialized way to integrate a digital interface with a VGA connector and ensures a normal connection between the monitor and the video card. The first version of this standard appeared in 1994, and it included the EDID 1.0 format, defining several options for physical channels. The second version of this format, which appeared in 1996, separated EDID into a completely separate standard and also defined a new protocol, DDC2B+. A year later, a new version was released, which already introduced the updated DDC2Bi protocol, and also provided support for the VESA Plug and Display connector. Among other things, the final version included a connector for flat panel displays with separate hardware addresses.
In 1999, the DDC standard was completely replaced by E-DDC, and EDID today is nothing more than an auxiliary standard that defines the format of a compressed binary file that describes the properties, as well as graphic modes of the monitor, recorded in the memory chip by the manufacturer of this monitor.
Text modes
Characters in the standard test mode are formed in a 9x16 pixel cell, however, the use of fonts and other sizes is allowed: 8-9 pixels wide and 1-32 pixels high. Typically, the characters themselves are smaller in size because some of the space is used to create a gap between the characters. The function for selecting the font size in the BIOS is separate from the function for selecting the video mode, this allows you to use different combinations of modes with fonts. It is possible to load eight and simultaneously display two different fonts on the monitor.
VGA BIOS contains the following types of fonts, as well as functions for loading/activating them:
- 8×16 pixels (standard VGA font),
- 8×14 (for EGA compatibility),
- 8×8 (for CGA compatibility).
Typically, these fonts correspond to the CP437 code page. There is also support for software downloading of fonts. This allows you to use it, for example, for Russification.
DDC1
VGA connectors DDC1 allow the monitor to broadcast its characteristics to the computer one-way. Once the video card detects this information on the cable, it automatically reads it synchronously with the vertical sync pulses. For the time it takes to broadcast data, the vertical sync frequency may increase slightly (up to 25 kHz) if a DDC1-compatible monitor is detected.
Extenders [edit]
VGA expander
is an electronic device that increases the signal strength from a VGA port, most often from a computer. They are often used in schools, businesses, and homes when multiple monitors are connected to a single VGA port, or if the cable between the monitor and computer would be too long (often images appear blurry or have minor artifacts if the cable is run too far without an extender). VGA extenders are sometimes called VGA amplifiers.
DDC2
The VGA DDC2 monitor connector already provides two-way communication, that is, initially the monitor can broadcast its technical characteristics, after which the computer adapts to the parameters used by the monitor. The bidirectional data bus is a synchronous bus that is somewhat similar to Access.bus. This bus is based on I2C technology, which is also evidenced by the fact that they even use standard signals of this standard.
Modern computers provide a 15 kOhm load when we are talking about SCLK or SDA channels. On the first channel, the monitor must provide a kOhm load, while the DDC2B bus is a unidirectional option and provides only a single master on the bus, which will be the graphics adapter used. The monitor continues to function as a slave device on a standard 7-bit I2C bus, having an address of 50h and providing up to 256 bytes of EDID ROM. Due to the fact that this access is read-only, the first I2C will always be A1h.
Signal conversion devices
To convert digital signals into analog and vice versa, special devices such as a converter are used. When choosing the right adapter from VGA to HDMI or a reverse HDMI-VGA cable, first of all, attention is paid to the operating resolution at the input and output of the device and the screen refresh rate at this resolution.
HDMI-VGA adapter
The peculiarity of this conversion is that, along with converting video from digital to analog, it will be necessary to transmit the audio signal in a separate path.
The adapter must first of all ensure the transfer of information about the display used to the high-definition signal source. This information is contained in the middle of the transmission device. Since the digital stream contains Audio and Video signals, the HDMI output device must provide auxiliary information containing the audio mode, video mode and color standard type. The HDMI receiver decrypts the received data stream and transforms it into any color format YCbCr 4:4:4, YCbCr 4:2:2, RGB 4:4:4, according to the requirements of the DAC.
After the data stream is initially processed, it is decoded and sent to the pixel bus, and then to the DAC and audio codecs. The RGB pixel bus and unsynchronized pulses form the video DAC. The clock signals are output to a data buffer and from there directly to the analog display.
Read also: How to remove a TV from a wall bracket
The audio signal may be encoded using different compression methods, so additional processing may be required to extract it. Therefore, it is important to generate an EDID, which is extracted using an algorithm from the VGA device via the DDC information transmission channel. The obtained data must be processed and checked for the possibility of using high-frequency modes.
The processor is used to perform complex operations such as EDID readings, HDMI Rx programming and audio DAC. Due to the fact that the video DAC does not have I2C or SPI, it will not need to be controlled.
Thus, making an HDMI-VGA adapter with your own hands is not so easy. This will require knowledge not only in the field of electronics, but also in programming. The simplest adapter will consist of an HDMI receiver, a digital-to-analog converter, an audio codec, and a control microcontroller.
Considering that the price of a factory-made adapter is low, even if you find a circuit and buy the required radio elements, there will be no benefit in terms of price and labor costs. The easiest way is to purchase a ready-made adapter at a large store.
VGA-HDMI converter
The VGA to HDMI adapter also cannot be made by simply connecting the contacts. Conversion requires the presence of an active video converter. With the help of such a converter, it is easy to connect VGA signal sources to the latest panels using their HDMI input. Such converters are produced with a power supply designed for a constant voltage of five volts. In some models, power is provided via a USB cable.
The VGA-HDMI converter, in addition to video, must also transmit an audio signal. Such devices do not require settings and work immediately when turned on . Their circuitry contains: a VGA receiver, an analog-to-digital converter, an audio converter, and a control microcontroller.
E-DDC
The E-DDC Format VGA connector pinout has proven to be the most efficient version of this connector, and it is also the latest among all existing ones. It was first introduced in 1999 and was characterized by the fact that display information was stored in the device's memory, which occupied approximately 32 KB. It is worth noting the fact that in 2007 the E-DDC version was also approved, which provided support for standards such as DisplayID and DisplayPort.
Standard modes
- 320x200 pixels , 4 colors.
- 320x200 pixels , 16 colors.
- 320x200 pixels , 256 colors (new for VGA).
- 640×200 pixels , 2 colors.
- 640×200 pixels , 16 colors.
- 640×350 pixels , monochrome.
- 640x350 pixels , 16 colors.
- 640x480 pixels , 2 colors. At a resolution of 640x480, the pixel has a 1:1 aspect ratio.
- 640x480 pixels , 16 colors.
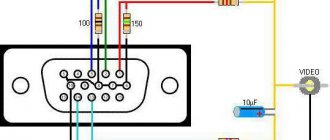
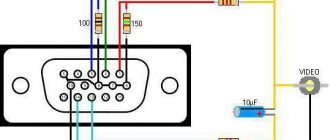
9-pin connector pinout
The pinout of a 9-pin VGA connector is as follows:
- Red video wire.
- Green video wire.
- Blue video wire.
- Horizontal sync wire.
- Vertical sync wire.
- Red common wire.
- Blue common wire.
- Green common wire.
- Common synchronization wire.
It is worth noting that if we are considering a standard VGA connector, the pinout will be slightly different, since there are 15 pins.
How to make an extension cord?
It often happens that you need to make a fairly long cable with a VGA connector, which will connect equipment, for example, in different rooms.
Of course, you can simply buy a long VGA-to-VGA connector cable, the pinout of which allows you to have the length you need, but in fact, the first thing that speaks against such a solution is its cost. For such a ready-made cable, the length of which is 15 meters, you will have to pay at least $20, depending on the quality of workmanship, not to mention the price of a cable whose length is even longer than the above.
The second problem, which applies to rooms where the final renovation has already been done, is that the only optimal option for stretching the cable is to run it behind the baseboard. At the same time, you really need to understand that the factory cable can be quite thick; in addition, it is also equipped with specialized thick ferrite rings, which makes it impossible to lay it behind the baseboard. If you need to stretch the cable through the wall into the next room, then in this case you will need to make a hole, the diameter of which will correspond to the width of the D-sub 15pin connector. To put it in more understandable terms, it is unlikely that anyone will be interested in a wiring harness for the VGA connector, for installation of which you will need to drill a hole with a diameter of about 40 mm.
S-Video (TV/OUT)
On older video cards, you sometimes find an S-Video connector, or, as it is also called, S-VHS. It is usually used to output an analog signal to outdated TVs, however, in terms of the quality of the transmitted image it is inferior to the more common VGA. When using a high-quality cable via S-Video, the image is transmitted without interference at a distance of up to 20 meters. Currently extremely rare (on video cards).
We do it ourselves
Thus, there are two factors that represent the main disadvantages of using a ready-made cable - its cost, as well as its dimensions. It is for this reason that a completely independent VGA connector is a much more suitable option.
In this case, we will broadcast the signal in this format from the computer to the monitor through a shielded pair of 5/6 categories, since this solution is a much cheaper and more effective option. In this case, FTP Cat.5e will be used, which is not equipped with active transceivers. The cost in this case will be approximately $0.30 for each meter, and therefore for a complete cable 15 meters long you will need to spend no more than $4.5, which, of course, is an order of magnitude less compared to $20, and if we talk about an even longer length, then the cost will ultimately vary even more.
Of course, in the VGA interface, 13 of 15 pins provide for the transmission of an analog component video signal, while horizontal and vertical sync signals, as well as other service information and control signals, will be of much worse quality. At the same time, shielded twisted pair FTP Cat.5e provides only 8 conductors, but this is quite enough to transfer video data to the monitor from a computer.
DVI (variations: DVI-I, DVI-A and DVI-D)
Used to transmit a digital signal, replacing VGA. Used to connect high-resolution monitors, televisions, as well as modern digital projectors and plasma panels. The maximum cable length is 10 meters.
The higher the resolution of the image, the shorter the distance it can be transmitted without loss of quality (without the use of special equipment).
There are three types of DVI ports: DVI-D (digital), DVI-A (analog) and DVI-I (combo):
- DVI-D An exclusively digital connection avoids losses in picture quality (especially noticeable at high resolutions). Provides undistorted picture output due to the fact that the video signal does not undergo double analog/digital conversion, but is transmitted directly in digital form, as is.
- DVI-A. An extremely rare type of analog connection via a DVI port, which is essentially no different from VGA. It is practically not found in nature.
- DVI-I. Universal, combines the two previous types at once. As a rule, it is no longer possible to find a VGA port on modern video cards, but they all have DVI-I. Having a special adapter, you can connect a VGA monitor to this port.
To transmit digital data, either Single-Link or Dual-Link format is used. Single-Link DVI uses a single TMDS transmitter, while Dual-Link doubles the bandwidth and allows screen resolutions higher than 1920 x 1200, such as 2560 x 1600. Therefore, for large monitors with high resolution, or intended for stereo image output, you definitely need at least DVI Dual-Link, or HDMI version 1.3 (more on this below).
Making it easier
The best option is to use a VGA-RJ45 adapter without soldering, since in this case it will be enough to crimp the ends of the twisted pair with a shielded modular connector. If you have no desire to start soldering, then a pair of such adapters will cost you no more than $5. If you want to save money, or maybe you don’t have the opportunity to find such an adapter at the moment, then in this case you have only one option left - soldering.
Thus, you yourself can choose what is more convenient for you to do and how to make such an extension cord for yourself. If necessary, any types of adapters can also be soldered, one of the most popular of which is the “tulip” adapter.
How many FPS are output via HDMI cable?
0. HDMI v2 interface. 0 can transmit 3820 x 2160 pixel resolution video signals at up to 60 frames per second and up to 32 channels of uncompressed multi-channel digital audio, all over the same high-speed HDMI cables that have been around for years.
Interesting materials:
Where is the remote control in Xiaomi? Where are the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve centers located in the spinal cord? Where is the exchange link on Steam? Where is the link to exchange on Steam? Where is the trade url on steam? Where are the stickers on WhatsApp? Where is the QR code in VK? Where are Page Options in Word 2016? Where is the message archive on WhatsApp? Where is OKVED in the statement?