Shore hardness measurement
Shor's name was Albert. He was an American industrialist who lived in the 20th century. I developed a hardness scale in order to make my work easier and make the enterprise successful.
The plant produced low-modulus materials. They are characterized by low longitudinal elasticity. This results in high elasticity, even at room temperatures. These are polymers, vulcanization products, rubbers, and some plastics. It is for them that the Shor method was created.
Shore hardness of materials is an empirical method. This means that he is experienced, aimed at studying facts, observation.
The indicator turns out to be “disconnected”. There is no connection with the fundamental characteristics of the test sample. But its hardness affects its performance parameters. So, the Shore hardness of rubber is of interest, for example, to motorists.
They rely on the scale when buying tires. Their hardness standard is from 50 to 75 Shore units. The softer the rubber, the better its grip on the road.
However, the pliability of the material leads to its rapid wear and heating. Soft rubber is noisy and quickly loses its shape. The Shore number allows you to select the ideal tires for specific conditions and needs.
Only now, only about 30% of manufacturers indicate the scale indicator on their tires. The presence of a note indicates a responsible approach to business and the quality of the product. problem in determining Shore hardness . There would be a desire. The apparatus for the experiments is simple, as is the scheme for conducting them.
The only negative is a decent spread of results. But a more convenient method has not yet been invented. Let's move from theory to practice?
Independent Expertise Volgograd
Property valuation
Today, the concept of appraisal activity implies, in most cases, an assessment of the market value of real estate.
Examination of window blocks
Business valuation
Determining the market value of a business includes the valuation of all assets.
Handwriting examination
Handwriting examination is one of the types of personal identification.
Auto-assessment in case of an accident
There are many situations in which an auto examination is required, and the procedure for carrying out an auto examination should be trusted to professionals.
What is Shore hardness of rubber?
Each tire manufacturer has its own technologies and recipes for the production of compounds from which tire treads are made, and one manufacturer most likely has several such recipes. Of course, no one will tell you the chemical composition and the recipe itself, but you can learn something about the composition of the rubber, for example, from the Shore hardness index of the rubber, or from the marketing positioning of the tire on the market by its manufacturer.
To simplify the situation as much as possible, there are certain maximum and minimum hardness levels of the rubber compound suitable for tire production, and it is within this range that manufacturers vary. The hardness of rubber is measured using special instruments - Shore durometers and is expressed, accordingly, in conventional Shore units .
A scale and method for determining the hardness of low-modulus materials (plastics, elastomers, rubbers, etc.) were proposed by Albert F. Shore - hence the name. The principle of determining Shore hardness is quite simple - a special rod is pressed into a material sample with a given force and under given conditions. The depth of indentation determines the hardness of the material (in inverse proportion - the deeper, the softer). The rubber mixture from which the tread of car tires is made, as a rule, has a hardness in the range of 50-70 Shore units.
What is affected by the hardness and composition of rubber?
First of all, the hardness of the rubber mixture from which the tire tread is made determines the quality of traction with the road surface: the softer the rubber (lower hardness), the better, other things being equal, the traction. But there are significant side effects that prevent manufacturers from making car tires too soft and force them to develop balanced tire models tailored to certain operating conditions. Here are the main side effects:
Disadvantages of soft rubber (all other things being equal):
Soft rubber wears out faster .
Soft tires hold their shape worse , which reduces directional stability and stability in corners and turns.
Soft tires are noisier .
Soft rubber heats up more , and therefore has reduced speed limits.
Advantages of soft rubber (all other things being equal):
Shorter braking distance and better acceleration dynamics.
Better grip on wet road surfaces.
It has slightly better handling due to better grip on the road surface.
More comfortable on poor road surfaces
It should be noted right away that the hardness of rubber is not always declared by the manufacturer and this parameter for a specific tire model can only be found out from the test results, and even then, only if the model participated in the test. As a rule, hardness is tied to other parameters, for example, the so-called hard rubber mixture is usually made from a solid rubber mixture. high-speed tires, and from softer ones - the so-called. rain.
Specialists of the Independent Expertise organization are ready to help both individuals and legal entities in determining various types of assessment and examination.
If, after studying this section, you still have unresolved questions or you want to personally communicate with our specialists or order an independent examination of tire quality , all the information necessary for this can be obtained in the “Contacts” section.
We look forward to your call and thank you in advance for your trust.
Tire quality examination is carried out
Volgograd, st. Irkutskaya, 7 (youth stop, separate entrance from the end of the building). 400074,
The conclusion of an independent expert organization has the status of an official document of evidentiary value and can be used in court.
Source
Shore measurement principle
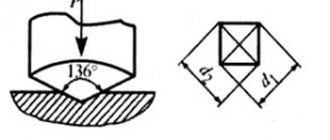
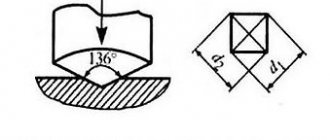
Shore had to develop the hardness device himself. This happened in 1920. The device is called a durometer. It has a support platform with a hole in the center, an indenter, that is, a presser, and a calibrated spring that applies a certain force to it.
The last element of the machine is the indicator. It determines the degree to which the indenter “nose” extends beyond the supporting surface.
The device has several measuring scales. There are two main ones, A and D. The breakdown is necessary for the accuracy of the experiments, because the subjects are materials with different hardnesses. Soft ones are checked on scale A, and more elastic ones - on D.
Measuring Shore hardness requires attention to external conditions. Some polymers react, for example, to air humidity, or soften under the influence of direct sunlight. It is necessary to exclude factors that influence the parameters of the material. There are ISO standards for this.
Requirements also apply to the thickness of the test sample. It should not be less than 6 millimeters. The width of the material should allow for an indentation from any of the edges of at least 12 millimeters. The smoothness of the subject is also important.
Rough materials may not adhere tightly to the supporting surface, which will distort the measurement results.
To determine, for example, the Shore hardness of polyurethane , the durometer is installed vertically. The “nose” of the indenter, in this case, must be 12 millimeters from the edge of the sample.
You need to press the supporting surface to the sample as quickly as possible, without pushing, keeping the parallel between the planes. All that remains is to apply pressure to the supporting surface to ensure reliable contact with the material being tested. For this purpose, a load is used. But, manual bench press is also allowed.
Instantaneous measurement is carried out in 1 second. However, usually the readings are taken after 15 seconds. To be sure, take 5 measurements in different places on the surface.
The average value is the hardness number. It can be from 0 to 100. This is the Shore hardness scale. Let's try to apply measurements not only when choosing car tires.
Devices
Equipment for determining Shore hardness was created by the inventor of the method itself. Depending on the method, a durometer or scleroscope is used.
A device called a durometer is used to determine the Shore hardness by indentation. These devices come in several types. Class D and A appliances include the following parts:
As additional equipment, durometers are equipped with a device for securing the load. It is centered along the axis of the indenter and allows you to create a certain clamping force.
As for the types of durometers, they are differentiated based on the scales used for different materials. There are 12 scales in total. The most common options among them are types D and A. Type A is characterized by its focus on softer materials. Devices of this type are therefore characterized by less pressing force and greater measurement accuracy. It should be noted that the force created by the durometer is calculated using special formulas.
Schematic diagram of Shore's scleroscope
Scleroscopes are represented by devices equipped with a spherical striker. They are also differentiated into several types based on scales. The most common are C and D. Thus, type C device has a hollow tube with a window mounted on a tripod with a sample stage. The latter has a scale on it. Inside the tube there is a striker with a mass of 2.5 g and a radius of 1.25 mm, held by a locking-release device mounted on top of the tube. The rebound height is recorded visually. Type D devices have a heavier firing pin (36 g) and an electronic or mechanical device for recording the magnitude of the rebound. The striker is usually equipped with a diamond tip, although options with a blunt steel tip are used for testing soft materials.
Separately, it should be noted that due to the presence of several scales for each of the devices for determining Shore hardness, a conversion table from one to another has been created.
Application of Shore measurement
Shore hardness is a table that can indicate the nuances of using products. So, if the eraser indicator is 20 units, then it is artistic. Creators need soft erasers that do not damage drawing paper and can delicately shade, for example, pencil sketches.
For office purposes, schools, or offices, erasers with a hardness of about 50 Shore units are better suited. When buying sealant for construction or housework, it is important to know whether it will be easy to open. For example, we fixed some seams in the bathroom.
If the sealant darkens or cracks, it will have to be scraped out. This is more difficult than cleaning regular grout. The softer and more pliable the sealant, the easier it will be, so to speak, to dismantle it.
The sealant should have a Shore hardness of 10-25 units. Otherwise, the product is not of high quality.
For bicycle tubes, acceptable Shore hardness units are much lower than for car tires. For a bike, 30 points is enough.
Skateboard wheels are cut. Even mild variations should have 75 units. For hard skateboard wheels, the figure is completely equal to the recommendations for solid forklift tires - 95-98 units.
For comparison, plastic construction helmets for protection during work guarantee only 75 points. Purchasing low-quality headgear with a Shore hardness of 40-60 can cost your life.
Rebound method
This method is used primarily in cases where it is necessary to determine the hardness of metal parts. The indicator in this case is proportional to the height to which the scleroscope striker will bounce when it falls freely onto the surface of the material under study.
Both listed methods have the same name and identical designation of scales, but are fundamentally different in terms of measurements and data obtained. Their results are not related to each other and do not have a direct relationship.
Hardness tester Equotip 550 UCI
The Equotip line of metal hardness testers from the Swiss company Proceq is represented by models that implement different methods of hardness measurement, thereby achieving versatility in their use in various industries. Proceq hardness testers are registered in the register of measuring instruments of the Russian Federation and have positive reviews from Russian specialists: (review from Tekhdiagnostika OJSC, review from Magnitogorsk Iron and Steel Works OJSC). Proceq metal hardness testers are designed and assembled in Switzerland. The warranty period for all devices in the line is 2 years with the possibility of extension to 3 years.
The Proceq line of metal hardness testers can be divided into three groups:
Combined hardness tester T-UD2
The combined hardness tester NOVOTEST T-UD2 is an entry-level model in the NOVOTEST line of hardness testers and is designed for measuring the hardness of structural and carbon steels, incl. alloyed and stainless, as well as other metals and alloys that differ in their properties from structural and carbon steels - cast iron, aluminum, brass, bronze, copper, etc. - using custom calibrations according to a known model.
The T-UD2 hardness tester is equipped with two types of transducers: dynamic (Liba) - for measuring the hardness of massive parts, materials with a coarse-grained structure, cast iron and non-ferrous metals, and ultrasonic (contract impedance) - for measuring the hardness of small objects, products with a thin wall, complex shape, surface hardened layers.
Notes
- It should be distinguished from a “scleroscope” - a device for measuring hardness using the rebound method.
- ↑ Pressing force of the supporting surface of the durometer on the test sample. The standards provide different units of measurement for this parameter, so they are indicated not in the title, but in the corresponding rows of the table. There are minor differences between different standards - these are given in parentheses.
- Standard PV 3931
- Standard a: temperature 23±2 °C, relative humidity 50%, pressure 86-106 kPa.
- Range of values ±5 units.
- Rubber rings that are used to tie around stacks of banknotes, small bags, attach prescriptions to bottles of medicines, etc.
- TU 38.106.209-90
- For example, the wheel of a luggage trolley, hand luggage (suitcase).
- ↑ The test sample is impacted (pressed) by the end surface of a solid cylinder.
Ultrasonic hardness tester T-U2
The NOVOTEST T-U2 ultrasonic hardness tester is a modification of the entry-level model in the NOVOTEST line of hardness testers - the NOVOTEST T-UD2 universal combined hardness tester with an ultrasonic sensor. The T-U2 device is intended for measuring the hardness of metals and their alloys: structural and carbon steels, as well as non-ferrous metals and alloys acceptable for the ultrasonic method using custom calibrations based on a known sample.
In addition, it is possible to measure the tensile strength of objects based on pearlitic carbon steels, which makes it possible to automatically convert from the Brinell scale (HB) in accordance with GOST 22791-77. The hardness tester uses the ultrasonic method of hardness measurement (contract impedance) standardized according to ASTM A 1038, which, unlike the dynamic method, allows you to work with small objects, products with a thin wall, complex shapes, and surface hardened layers.