Metal drawing and its types
Main types of rotary metal drawing:
Step molding
A sheet blank in the shape of a circle is fixed between the mandrel and the support. The mandrel must match the internal configuration of the product. The drive begins to rotate the blank, and controlled forming pressure is carried out by a special passive roller driven by the rotation of the blank. Pressure is applied in both longitudinal and radial planes. The roller presses the metal against the mandrel and moves along a complex curve, either towards the edge of the blank or back.
The clamping is carried out in several passes, in steps. At the end of the treatment, a series of smoothing movements of the roller are carried out with reduced pressure to obtain a high-quality surface.
Projection - One-Pass Molding
Extraction is carried out in one pass. The roller moves parallel to the mandrel, depending on the angle of its installation, the wall of the blank is thinned more or less, its material moves under the influence of the roller in the axial direction.
Projection - One-Pass Molding
The method is characterized by efficiency and dimensional accuracy, as well as a high class of the resulting surface.
Rolling with or without mandrel
In this case, the outer diameter of the workpiece is reduced with a simultaneous thickening of its wall due to the redistribution of the material. Rolling is carried out towards the center, in several passes.
Rolling with or without mandrel
As an option, the part is formed by individual segments of the mandrel using a roller with an offset center. Cutting, additional profiling or flanging are carried out as final operations.
Combined
For parts with complex configurations, stepwise forming, rolling, profiling and cutting are used together in various combinations.
UNV3-02 machine for torsion, twisting and forging with attached block for rolling
The RV is produced from a workpiece mounted on a rotating mandrel by rollers, satellite-rotating from the workpiece, which move along the generatrix of the mandrel with the required specified clearance.
When the rollers come into contact with the workpiece, a large specific pressure arises at the point of contact, under the influence of which the metal of the workpiece plastically flows into the gap between the roller and the mandrel, forming a part.
The inner surface of the part takes the shape of the outer surface of the mandrel, and the outer contour of the part follows the trajectory of movement of the working edge of the roller.
On modern rotary drawing mills, rolling can be carried out with one, two or three rollers.
The presence of tensile forces in the molded area of the workpiece during the entire drawing process and the fact that the molded part of the workpiece is always on the mandrel reduces the possibility of longitudinal bending of the part even in the presence of slight runout of the mandrel or slight variation in the thickness of the workpiece.
Shaping methods [edit | edit code ]
There are two main methods of Rotary hood:
- Direct, in which the direction of material flow coincides with the direction of movement of the roller;
- Reverse, in which the direction of material flow is opposite to the direction of movement of the roller.
In direct rotary drawing, the outer contour of the mandrel must follow the inner contour of the drawn part with technological allowances, so the length of the mandrel must be greater than the length of the part, which complicates the design of the mandrel, makes it heavy and expensive, and makes adjustment more labor-intensive.
The direct method of rotary drawing is recommended for shaping thin-walled and long cylindrical parts, as well as all types of parts of conical and ogive shapes.
When using the reverse method, the mandrel must correspond to the internal contour of the workpiece, so the mandrel can be several times shorter than the part.
However, with this method there is a danger of longitudinal bending of the extruded part after it leaves the mandrel, which imposes particularly stringent requirements on the thickness difference of the workpiece, runout of the mandrel and rollers, and on the accuracy of setting the gap between the mandrel and all rollers.
The reverse method can be used for shaping relatively thick-walled and short precision blanks of cylindrical parts or blanks of parts.
The rotary drawing process can be divided into processing without thinning, with thinning and sheeting.
When extruding without thinning over several successive passes of the tool, the wall thickness does not change or decreases slightly. A more or less significant reduction in the maximum diameter of the workpiece is obtained when processing without thinning.
When processing with thinning and rolling, the outer diameter of the workpiece (or inner diameter of the pipes) and the resulting part remains unchanged, and the wall thickness is more or less significantly reduced; due to this, the length of the resulting part along the axis of rotation increases.
With rotary drawing, the workpiece is installed between a mandrel mounted on the spindle and the tailstock clamp.
Roll dressing and cleaning
- More than 3500 installed equipment worldwide
- Industry 4.0 Developer and manufacturer of unique technological solutions
- Made in Germany High quality and reliable equipment
In 1928, in the Baden town of Haueneberstein (Germany - Baden-Württemberg), Albert Reiss founded a tinsmith workshop, which became the founder of the machine tool company ARKU Maschinenbau GmbH. A small family business produced sheet metal products.
In the mid-60s, ARKU moved into the production of sheet metal straightening machines. The first straightening machines were used to make the levers for the letters of printing presses. The company conducts active research activities in the field of plastic deformation of metals.
In the 70s, metalworking saw a transition to sheet metal in rolls. In parallel, ARKU is increasing the production rate of coil processing lines. Serial production of sheet-straightening machines is launched. Since the 1980s, ARKU has defined two main areas of its activity: the production of straightening machines and complete lines for the processing of coiled metal.
During the 90s, the trend towards industrial processing of sheets from coils strengthened its position.
ARKU's technical innovations in this area, such as the compact CompactFeed® sheet processing line, the unique EcoPlan® drive system, and the high-performance FlatMaster® hydraulic sheet straightening machines, have made the company the leading European manufacturer of sheet metal straightening technology and complete coil processing lines. In 2010, ARKU's production portfolio was supplemented by a new technological direction - high-performance grinding machines ARKU EdgeBreaker® and EdgeRacer®.
ARKU's headquarters are located in the region of Karlsruhe, famous for its technical thought. Production is located in Baden-Baden. The company adheres to a strategy of active development of new products, constantly improving and introducing new technological solutions in the field of metal sheet processing. More than 3,500 ARKU sheet straightening machines are installed and used worldwide.
In 2005, the Russian representative office of ARKU Maschinenbau GmbH was organized on the basis of TKTs Centrum LLC in Moscow, providing a full range of services for the supply of equipment, maintenance and technical support to Russian Customers.
Parts processed on pressing and rolling machines and machines [edit | edit code ]
The rotary drawing process was at one time used to a limited extent to produce parts such as bodies of rotation with a conical or cylindrical generatrix; Now this method is often used to produce parts with a curved forming surface when the roller moves using a CNC-controlled hydraulic support. The parts are edging, molded with special rollers, and annular grooves and ribs are extruded.
Many parts that were previously produced by cutting from bar material, forgings and stampings, and with a constant wall thickness by deep drawing, are successfully processed on rotary machines and lathes.
When processing preheated workpieces, the diameters of the parts reach up to 7 m, and the thickness of the workpieces reaches 30 mm and above.
Read also: What dowels for timber 150 150
Rotary metal drawing process
As a rule, a sheet plate in the shape of a circle is used as a blank. In addition, for some parts other flat shapes are used - an oval or an ellipse, as well as complex curvilinear closed contours. Blanks are also used - sections of pipes, most often round.
Preparatory operations for unique parts and small series are performed on round cutters. In the case of large series, cutting is more efficiently performed on hydraulic cutting machines, due to the fact that laser or plasma cutting is associated with high temperature exposure in the cutting area. This may impair the ductility of the material.
Drawing sheet metal parts
Rotary drawing is a widespread method of metal processing; it is used for the production of thin-walled hollow parts in the form of bodies of rotation.
Rotary metal drawing
It is carried out by applying pressure to a rotating sheet or hollow workpiece, resulting in the shape of a mandrel.
Rotary metal drawing process
As a rule, a sheet plate in the shape of a circle is used as a blank. In addition, for some parts other flat shapes are used - an oval or an ellipse, as well as complex curvilinear closed contours. Blanks are also used - sections of pipes, most often round.
Preparatory operations for unique parts and small series are performed on round cutters. In the case of large series, cutting is more efficiently performed on hydraulic cutting machines, due to the fact that laser or plasma cutting is associated with high temperature exposure in the cutting area. This may impair the ductility of the material.
Rotary drawing technology is used in the production of pipe-shaped products with varying diameters and wall thicknesses. In addition, it is possible to form stiffening ribs on the outside. Rotary metal drawing is also used in complex technological processes in conjunction with stamping, welding, riveting and metalworking operations.
Sheet metal bending die
The production of parts using stamping occupies a leading place in metal forming technology and is used in various industries.
Of particular importance is the stamping of metal products from rolled sheets. It is based on plastic deformation of metal without heating it using special stamps. This method of plastic deformation of parts is widely used for the manufacture of parts of different sizes and complex shapes with great accuracy, which cannot be achieved using other processing methods.
They are used for assembling large-sized products in the engineering industry, in the automotive and shipbuilding industries, as well as in the instrument-making industry and everyday life, where various miniature parts are often required.
Technology of stamping parts from metal sheets and its types
Stamping is the process of giving parts the desired shape and obtaining the size specified by documents by mechanically acting on them using pressure. The main direction of stamping is the production of parts from blanks, which are used as rolled sheets. Under the action of a compressive force, the workpiece undergoes deformation and acquires the desired configuration.
There is a distinction between stamping performed by the hot method with heating of the workpiece and the cold method without preheating it. Stamping of sheet metal parts is carried out without preheating them.
Pressure deformation with heating of a workpiece is used in the manufacture of parts from metal that does not have sufficient ductility, and is mainly used in the production of small batches of volumetric products from metal sheets with a thickness of within 5 millimeters.
This takes into account the degree of warping of the part during cooling, as well as its shrinkage during deformation processing, which affects its size. To eliminate deviations from the required dimensions for parts obtained by hot stamping, large tolerances are made.
Methods for rotary drawing of metal
The variety of techniques for rotary drawing of metal comes down to one of two types:
- Straight. The metal moves along the forming roller.
- Back. The metal moves against the movement of the forming roller.
Direct method
The outer contour of the punch corresponds to the inner contour of the future product (taking into account the necessary allowances). Because of this, the mandrel is made longer than the product. The design of the punch becomes more complicated, the weight, cost and labor intensity of debugging the technological process increases.
Direct method of rotary drawing of metal
This method is applicable for molding parts in the form of a cone and cylinder with a large ratio of length to diameter and diameter to wall thickness.
Back
In this case, the mandrel must match in size and shape with the inner surface of the workpiece, which makes it possible to make the mandrel much shorter than the future product.
Thick-walled rotary hood
The method is used in the production of products with a small length-to-diameter ratio and relatively thick walls.
Rotary metal drawing operations are also divided into forming:
- With thinning, the outer size is maintained, the wall thickness is reduced.
- Without thinning - the wall thickness is maintained during processing, but the outer diameter changes.
- With rolling, the outer diameter is maintained, the wall thickness increases.
Main types of rotary metal drawing
The workpiece is secured between the mandrel fixed to the drive and the caliper clamp.
Rotary drawing technologies
Metal forming technologies, which are dealt with by the Technological Center Research and Production Enterprise, are becoming increasingly important in the manufacture of parts due to the economical use of metal and the possibility of obtaining optimal mechanical properties of parts. Cost-effective and flexible rotary extrusion methods are promising.
FEATURES OF THE ROTARY HOOD
Rotary drawing is a process of local cyclic deformation of a rotating flat or hollow workpiece with a deforming tool in the form of one or several rollers and is a real alternative to conventional sheet stamping in the manufacture of axisymmetric parts. Tools in the pressing method are most often not tied to the geometry of the parts. In this regard, this method is sufficiently economical and extremely flexible, which allows the pressing method to be promising not only in the field of mass production, but also in the production of a limited number of parts and the production of single prototypes.
The rotary drawing process is more amenable to automation than most other form-building operations of sheet stamping, because equipment is used that, in its kinematic design and control system, is similar to universal metal-cutting machines of the turning-milling group, and it is possible to combine several operations on one equipment up to production finished part. In addition, this equipment is quite versatile and allows the production of parts of various complex shapes and sizes.
ADVANTAGES OF A ROTARY HOOD
- Relatively simple and inexpensive technological equipment and tools.
- Achieving significantly higher plastic deformations (more than 90%) without heat treatment compared to other cold sheet metal forming operations.
- Quite low energy consumption and power of the equipment used.
- Possibility of forming parts from hard-to-deform alloys.
- Implementation of local heating of the source of plastic deformation.
- Implementation of combining on one machine from one installation the main and finishing operations (smoothing the surface, trimming the flange, cutting off the allowance or bottom, bending or curling the edges, creasing, etc.).
- Combination of several basic operations (drawing, rolling, crimping, distributing, flanging) in one automated cycle.
- Obtaining a part with a given variable wall section; processing of parts from sheet, stamped, forged, cast or welded workpieces, thereby obtaining an improved metal structure - the hardness and tensile strength of the part material increases up to 2 times compared to the workpiece material.
- Possibility of adjusting the accuracy of the resulting workpiece (part) by appropriate selection of processing modes.
- Ensuring high surface cleanliness of the part corresponding to finishing operations - surface roughness up to Ra 0.32.
ECONOMIC ADVANTAGES OF ROTARY HOODS
- Small time and material costs for production preparation.
- High economic efficiency when producing parts in small batches.
- Reducing the parts processing cycle and reducing costs by reducing the number of transitions and concentrating operations on one workplace.
- Increasing the metal utilization rate.
- Quick reconfiguration for the production of new parts.
- High automation of rotary drawing on automated equipment, allowing efficient use of the process in mass production.
Traditional rotary drawing operations, previously used primarily for the manufacture of critical high-precision parts of space and military equipment, thanks to the creation of their fairly reliable mathematical models with appropriate methodological and software, have the opportunity to be effectively used in flexible modern production. The use of rotary drawing technologies in industry makes it possible to produce many axisymmetric parts of various machines and mechanisms with high performance properties, with minimal production costs, contributing to the development of automated production.
Machines for rotary drawing of metal
To implement the technology, the following types of machines are used:
- Pressing and rolling machines for rotary drawing of metal.
- Rotary forging machines.
- Round cutters.
On manual lathes, molding is performed by the muscular strength of the worker. Used to produce unique products or especially small series. For medium and large series, pressing and rolling (rolling) machines with numerical control are used. Hydraulics or electric drives, controlled by a controller according to a program loaded into the central CNC unit, allow precise control of the force and direction of the clamp, as well as the direction of movement of the roller, including the most complex curved trajectories. Such machines ensure absolute identity of products in a series, which is especially important for jet engine parts and other high-tech products
Scheme of forging on rotary machines
Rotary forging machines allow you to form conical-shaped products from pipes by crimping the pipe with a special tool - a forging die. The peculiarity and main advantage lies in the unique ability to produce products that have:
- the length is many times greater than the diameter.
- along the length, the diameter and opening angle of the cone can be repeatedly changed.
- knurling of stiffeners is required.
Circular cutters are designed for cutting rolled sheets into flat pieces in the shape of a circle or ellipse. Also used are both manual and electro-hydraulic.
Rotary drawing machines
Equipment for producing a hollow axisymmetric part from a rotating workpiece, deformed by rollers along a rotating mandrel.
Principle of operation
Rotary drawing is made from a workpiece mounted on a rotating mandrel by rollers.
When the rollers come into contact with the workpiece, a large specific pressure arises at the point of contact, under the influence of which the metal of the workpiece flows plastically into the gap between the roller and the mandrel, forming a part.
The inner surface of the part takes the shape of the outer surface of the mandrel, and the outer contour of the part follows the trajectory of movement of the working edge of the roller.
Finished goods
DishesDiffusersCupsGeyser coffee makersGas cylindersCoffee TurksReflectorsCans
The range of possible parts produced on a rolling machine is huge: from metal utensils to lighting fixtures made of various types of metal, such as copper, silver, tin, aluminum, steel, stainless steel.
Advantages
Centralized control Low noise level Automatic lubrication system Addition of working devices High wear resistance High precision of operations Control safety Rolling away the part from two opposite sides Processing of thick materials up to 10 mm Heating at the point of deformation of the part Quick change of tools Cutters for trimming the workpiece Low cost of equipment Use in private enterprises and large factories
Equipment
The rotary drawing machine provides enormous potential for the production of complex parts in the form of a cylinder, cone, parabola, pipe, etc., which are manufactured in large quantities in one working cycle.
The machine tests products, trims and rounds edges, as well as compresses and presses products.
The machine is equipped with a CNC system that ensures maximum accuracy of both external and internal dimensions of the part.
The machine has precision tools, impeccable sensors and automatic measuring technology for the production of high-quality products of complex shapes.
Characteristics
| Max. workpiece diameter | 600 mm |
| Distance between centers | 800 mm |
| Spindle size DIN 55027 | Size 6HD |
| Main spindle motor power (spindle servo) | 15 kW |
| Motor rotation speed (servo spindle speed control) | 2000 rpm |
| X-axis movement | ø600 |
| Z axis movement | 600 mm |
| Tailstock movement | 300+500 mm |
| Ejector stroke | 200 mm |
| Moving the Retaining Plate | 300 mm |
| Turret position | 4+4 |
| Sheet thickness (aluminium) | 0.6–6.0 mm |
| Sheet thickness (copper) | 0.6–5.0 mm |
| Sheet thickness (non-alloy steel) | 0.6–3.0 mm |
| Sheet thickness (stainless steel) | 0.6–2.5 mm |
| Weight | 6500 kg |
| Dimensions L*W*H | 4300×2200×2000 |
Standard equipment
- Inclined machine body, durable cast iron, FC-30;
- Reinforced roller guide (HIWIN, Taiwan);
- Reinforced ball screw with a lead nut consisting of two half-nuts (HIWIN, Taiwan);
- Programmable tailstock with hydraulic control;
- Built-in lubrication control system;
- Centering device;
- Air conditioning of the control unit;
- Protective cover ensuring complete closure;
- Two four positions of pressing tools;
- Standard pressing tools (one set with roller holder and rollers);
- Standard tool box;
- Impact resistant iron pad;
- Computer numerical control system (SIEMENS828DSL):
- Servo control on several axes;
- Development of the second level by ProsperCNC of extrusion functions;
- Frequency speed control, constant speed function;
- Workflow map on the monitor;
- Simple, convenient programming process;
- Helical interpolation function;
- Mold and mandrel processing functions.
Scope of application of rotary metal drawing
The method is used to produce:
- jet engine parts in weapons systems;
- tank bottoms and covers;
- various screens in radio engineering, including radar screens;
- thin-walled vessels of complex shape: cans, teapots, cylinders, kettles;
- parts of construction mixer bodies;
- parts of fans and exhaust hoods.
Products made by rotary drawing
The method is also used in the production of contemporary art objects and in the studio for customizing unique motorcycles and cars.
Rotary metal drawing
Rotary drawing is a widespread method of metal processing; it is used for the production of thin-walled hollow parts in the form of bodies of rotation.
Rotary metal drawing
It is carried out by applying pressure to a rotating sheet or hollow workpiece, resulting in the shape of a mandrel.
Metal drawing and its types
Main types of rotary metal drawing:
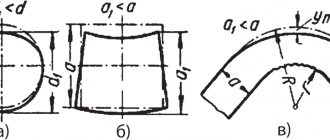
Step molding
A sheet blank in the shape of a circle is fixed between the mandrel and the support. The mandrel must match the internal configuration of the product.
The drive begins to rotate the blank, and controlled forming pressure is carried out by a special passive roller driven by the rotation of the blank. Pressure is applied in both longitudinal and radial planes.
The roller presses the metal against the mandrel and moves along a complex curve, either towards the edge of the blank or back.
The clamping is carried out in several passes, in steps. At the end of the treatment, a series of smoothing movements of the roller are carried out with reduced pressure to obtain a high-quality surface.
Projection - One-Pass Molding
Extraction is carried out in one pass. The roller moves parallel to the mandrel, depending on the angle of its installation, the wall of the blank is thinned more or less, its material moves under the influence of the roller in the axial direction.
Projection - One-Pass Molding
The method is characterized by efficiency and dimensional accuracy, as well as a high class of the resulting surface.
Rolling with or without mandrel
In this case, the outer diameter of the workpiece is reduced with a simultaneous thickening of its wall due to the redistribution of the material. Rolling is carried out towards the center, in several passes.
Rolling with or without mandrel
As an option, the part is formed by individual segments of the mandrel using a roller with an offset center. Cutting, additional profiling or flanging are carried out as final operations.
Combined
For parts with complex configurations, stepwise forming, rolling, profiling and cutting are used together in various combinations.
As a rule, a sheet plate in the shape of a circle is used as a blank. In addition, for some parts other flat shapes are used - an oval or an ellipse, as well as complex curvilinear closed contours. Blanks are also used - sections of pipes, most often round.
Preparatory operations for unique parts and small series are performed on round cutters. In the case of large series, cutting is more efficiently performed on hydraulic cutting machines, due to the fact that laser or plasma cutting is associated with high temperature exposure in the cutting area. This may impair the ductility of the material.
Rotary metal drawing process
Rotary drawing technology is used in the production of pipe-shaped products with varying diameters and wall thicknesses. In addition, it is possible to form stiffening ribs on the outside. Rotary metal drawing is also used in complex technological processes in conjunction with stamping, welding, riveting and metalworking operations.
Methods for rotary drawing of metal
The variety of techniques for rotary drawing of metal comes down to one of two types:
- Straight. The metal moves along the forming roller.
- Back. The metal moves against the movement of the forming roller.
Direct method
The outer contour of the punch corresponds to the inner contour of the future product (taking into account the necessary allowances). Because of this, the mandrel is made longer than the product. The design of the punch becomes more complicated, the weight, cost and labor intensity of debugging the technological process increases.
Direct method of rotary drawing of metal
This method is applicable for molding parts in the form of a cone and cylinder with a large ratio of length to diameter and diameter to wall thickness.
Back
In this case, the mandrel must match in size and shape with the inner surface of the workpiece, which makes it possible to make the mandrel much shorter than the future product.
Thick-walled rotary hood
The method is used in the production of products with a small length-to-diameter ratio and relatively thick walls.
Rotary metal drawing operations are also divided into forming:
- With thinning, the outer size is maintained, the wall thickness is reduced.
- Without thinning - the wall thickness is maintained during processing, but the outer diameter changes.
- With rolling, the outer diameter is maintained, the wall thickness increases.
Main types of rotary metal drawing
The workpiece is secured between the mandrel fixed to the drive and the caliper clamp.
Machines for rotary drawing of metal
To implement the technology, the following types of machines are used:
- Pressing and rolling machines for rotary drawing of metal.
- Rotary forging machines.
- Round cutters.
On manual lathes, molding is performed by the muscular strength of the worker. Used to produce unique products or especially small series. For medium and large series, pressing and rolling (rolling) machines with numerical control are used.
Hydraulics or electric drives, controlled by a controller according to a program loaded into the central CNC unit, allow precise control of the force and direction of the clamp, as well as the direction of movement of the roller, including the most complex curved trajectories.
Such machines ensure absolute identity of products in a series, which is especially important for jet engine parts and other high-tech products
Scheme of forging on rotary machines
Rotary forging machines allow you to form conical-shaped products from pipes by crimping the pipe with a special tool - a forging die. The peculiarity and main advantage lies in the unique ability to produce products that have:
- the length is many times greater than the diameter.
- along the length, the diameter and opening angle of the cone can be repeatedly changed.
- knurling of stiffeners is required.
Round cutters
Circular cutters are designed for cutting rolled sheets into flat pieces in the shape of a circle or ellipse. Also used are both manual and electro-hydraulic.
Scope of application of rotary metal drawing
The method is used to produce:
- jet engine parts in weapons systems;
- tank bottoms and covers;
- various screens in radio engineering, including radar screens;
- thin-walled vessels of complex shape: cans, teapots, cylinders, kettles;
- parts of construction mixer bodies;
- parts of fans and exhaust hoods.
Products made by rotary drawing
The method is also used in the production of contemporary art objects and in the studio for customizing unique motorcycles and cars.
What are the features of CNC pressing and rolling machine?
Would you like to know more about CNC press-forming machines? Find out about rotary hoods, classification, features and advantages of such units.
Pressing and rolling machines with numerical control are equipment used for processing sheet metal blanks. Pressing and rolling processing of a roller is a modern method carried out on CNC pressing and rolling machines.
This method involves the use of devices that have hydraulic and electro-hydraulic supporting parts of the metal-cutting device. They move the pressure rollers, which are the main tools in the processing of parts.
Scope of application, operating principle and types of pressing and rolling machines (rotary drawing)
Rotary hood - a method of metal processing by rotation by rolling out sheet metal or a hollow workpiece (for example, a pipe) with a roller tool around a mandrel. This method is used for the manufacture of hollow cylindrical products or products with a variable radius (convex and concave), for example: caps, lids, containers, rings, various cones, etc.Rotary drawing is one of the most ancient methods of sheet metal processing.
Pressing and rolling machines (rotary drawing machines) are similar in operating principle and type to lathes. The main difference is the higher rotation speed of the workpiece.
Pressure -rolling machines come in three types: manual tabletop and floor-mounted, and CNC rotary drawing machines.
Tabletop pressing and rolling machines (rotary drawing)
Floor-mounted pressing and rolling machines (rotary drawing)
Pressing and rolling machines (rotary drawing) with CNC (CNC)
The operating principle of all types of rotary drawing machines is identical.
The most common type of tool is the roller tool:
The following types of tools are also used on manual rotary drawing machines for the manufacture of various products:
The following types of tools are used on CNC machines:
For products of non-standard shape, the tool is manufactured individually along with the equipment.
The main advantage of metal forming using the rotary drawing method is the low cost of equipment in contrast to other types of processing, such as stamping, etc. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to use pressing and rolling machines not only for large production volumes, but also for single and small-scale production in small workshops.
When processing on manual pressing and rolling machines, the equipment can be made of wood!
Types of products produced using rotary drawing technology (pressing and rolling machines): production of metal utensils, shades of metal lamps, containers, production of ventilation diffusers, incl. nozzle ventilation diffusers, etc..
Some of the most popular areas of use in the production of rotary drawing machines now are:
Video of work on a pressing and rolling machine (rotary drawing):
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the equipment for rotary hood:
Manual pressing and rolling machines
CNC press rolling machines (rotary drawing machines)
back
What is a rotary hood
A method for processing sheet-type metal products, in which a three-dimensional part is transformed into a hollow one with an axisymmetric appearance, is called rotary drawing. It involves significant deformation and thinning of the walls of the spare parts. This method of processing sheet metal by drawing has ancient roots. In modern manipulation of steel blanks, it is carried out by a pressing and rolling machine.
Using the rotary drawing method, these devices are capable of producing household items with thin walls and complex shapes. A set of such devices is presented:
- teapots;
- scoops;
- sponges;
- vessels;
- coffee pots.
Classification of CNC machine tools
Pressure-rotary drawing has many of the properties and functions of turning analogues. In contrast, pressure-rotary devices have a higher operating speed. There are three types of devices of this type:
- manual tabletop;
- manual floor;
- with a rotary hood.
Rotary drawing is accompanied by additional actions such as rolling, expanding and welding. The rolling machine is capable of both producing a solid part using the rolling method, and completing the drawing and production of spare parts made using other equipment. The most popular products of this kind, for example, are tubular spare parts with various combinations of cross-sections.
The machines can be used not only for processing metal parts, but also copper ones that have a conical shape. The advantage of CNC devices is that the process is less labor-intensive than using presses. Modern technologies make it possible to monitor the operation of devices remotely. Round metal plates are used as the main raw material for working on a rotary pressing machine.
But the devices can also cope with workpieces that have a more complex geometric shape. Additional methods of working with the product are circular and hydrojet cutting. Examples of plasma and laser cutting in this case are less effective, since they can increase the temperature, which will change the plastic qualities of the spare part.
Do-it-yourself rotary hood or “pressure”
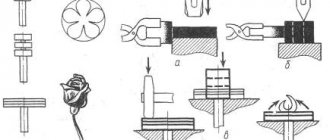
A tool for working on a pressing and rolling machine or for rotary drawing of non-ferrous metals on any lathe looks like this:
The duck nose or sheep nose are most actively used in work, although this largely depends on what kind of product is being rolled out. And the simplest tool to make to begin your exploits in winepressing looks like this:
It can be made from tool steel round timber 16..30mm, depending on what machine you will work on and what dimensions your product will be. Using a sharpening machine or grinder, give the tip the required shape, grind, harden and polish to a mirror surface. All flaws and shortcomings after grinding and polishing the tool will be transferred and multiplied on the workpiece in work! An unhardened tool will quickly acquire surface damage - scratches and spoil the surface of the workpiece. When working with such a tool, for obvious reasons, it is necessary to use lubricants. You can use stamp lubricant, wax, soap (for aluminum), etc. The main task is to ensure sliding, the longest possible stay of the lubricant on the workpiece during work and the ease of cleaning it after finishing work.
The next step in mastering the “pressure” with your own hands can be a straight hand tool with roller attachments:
It is necessary for rolling sharp corners (using triangular rollers), rolling edges and flanging (using rollers with a groove on the surface), in addition, it can be used to work not only with non-ferrous metals, but also with harder black metals (according to ability to draw cold-rolled steel up to 2 mm thick, strength groups K260V, K270V, K310V, K330V, K350V - deep - G, DX53D - Molded steel, corrosion-resistant, quality for deep drawing, DX54D - Molded steel, corrosion-resistant, quality for extra deep drawing hoods, DX56D - Molded steel, corrosion-resistant - Quality for extremely deep drawing, etc.), stainless steel. (304), etc... (the leftmost tool in the photo is equipped with a carbide tip and is used for trimming edges).
A tool for working with ferrous metal must be more powerful. Pressing steel with a thickness of 1 mm or more without a lever is quite a labor-intensive task, not to mention working with metal 2 or 3 mm thick, and even more so with stainless steel. Also, the pressure tool for working with h/m must be roller, because the hardness of the workpiece becomes close to the hardness of the tool, and the forces applied during rolling increase significantly and as a result, when you try to roll out with a simple tool, it heats up, becomes damaged and damages the workpiece. In addition to the actual lever used to increase the operator’s pressure on the part, such a tool allows you to not have to worry about holding the rolling roller in a vertical position, reduces runout, and the increased weight of the tool rests on the support stand.
As an example, I will give a drawing and photographs of a finished lever tool for pressing and rolling. You can modify and optimize it to suit your needs and at your own discretion:
Support stand:
Pressing lever with roller + “fingers”
Swing arm:
Photo of the finished tool:
To make work easier, this tool is also good for working with non-ferrous metals. The disadvantages of a tool with a lever would be that it is less sensitive, so when working with silver jewelry, it is better to use a straight tool.
Various models of pressing and rolling machines can be viewed here.
Also see the article about composite mandrels for the production of “closed” forms using a rotary hood
Advantages of machines of this type
All types of rotary pressing machines have the same principle of use. The roller tool is the most commonly used. When working with this equipment, it is possible to produce unique spare parts of complex shapes, while simultaneously carrying out equipment. The machine is equipped at a low price. For other types of metal manipulation, the price of equipment will be significantly higher.
Among the main advantages of units with a rotary hood are:
- possibility of mass, small-scale and single production;
- possibility of operation in large and small workshops;
- possibility of manufacturing wooden equipment;
- production of parts for the economic, chemical and food industries;
- economical use.
Why are prices for rotary hoods discussed individually?
Despite the fact that the equipment is focused on mass production, the production of parts by drawing is still a complex process.
If the product is unique and not standard, it is necessary to create a sketch of it, think over the deformation technology, select a tool, and, if necessary, make the same specific mandrel. All this requires time and effort, and a whole group of specialists. Therefore, the cost of the service is usually discussed individually. In the price list (the “Cost” tab) you will see samples of products and average prices for one unit, but determine the final cost of the project individually when discussing with the contractor.
Inexpensive metal drawing services
Do you need a custom rotary hood? This is where you can choose the right offer so that your order is completed efficiently and without wasting time. Our advantages:
- professional personnel;
- prices available for Moscow and regions;
- excellent technical equipment of production;
- compliance with all standards and requirements laid down by guests;
- guaranteed quality result.
Send us an application and we will make a preliminary calculation of the project on the day of your request. We are waiting for your orders!
Features of the package
Models of CNC machines have a high productivity rate. Thanks to numerical control, they have an automatic production mode. By using such a machine, you can provide yourself with a number of advantages. One of them is the presence of two tool rollers, which simultaneously exert increased pressure.
The configuration of the above models consists of examples:
- circle-centering device;
- optional manipulator;
- double type tool head;
- 4+4 positioning mechanism;
- hydroelectric power stations;
- additional roller with a compensator.
The thickness of aluminum blanks for processing should be from 0.6 to 4 millimeters. For steel blanks - from 0.6 to 2.5 millimeters. For workpieces made of corrosion-resistant steel - from 0.6 to 1.5 millimeters. The specified characteristics are relevant only for original models.