09/05/2019 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- Where are pipeline supports used?
- What types of supports for pipelines are there?
- What is the difference between fixed and sliding supports for pipelines?
- What standards and regulations are used in the manufacture of pipeline supports?
Pipeline supports are significant elements of the entire communications system. They take on the weight of the pipes, and then the entire load is distributed over the supporting structures or transferred directly to the soil. Thanks to the supports, it is possible to move the pipes in the longitudinal direction, fix them and protect them from premature abrasion. Today, manufacturers offer a wide selection of communications and corresponding supporting elements from various materials, all of them have their own technical characteristics - we’ll talk about this further.
Pipe supports: use cases
The main function of pipeline supports is to secure the communication in a certain position. They also prevent pipes from deforming under the influence of temperatures and vibrations. The fact is that vibrations often occur when transporting the working medium through the system.
It is extremely important to pay utmost attention to the installation process, since the reliability of communications depends on the supporting elements. If mistakes are made, they simply will not cope with the tasks assigned to them.
Let’s say right away that these products are used in a variety of fields and differ in type and purpose. So, installation of communications cannot be done without them:
- at enterprises;
- in housing and communal services;
- at nuclear power plants;
- at thermal power plants;
- in the gas and oil sectors.
If we are talking about a gas pipeline, then especially serious requirements are placed on the supports, including when the pipeline runs through regions that are unfavorable from a climatic point of view. It is equally important that the supporting structure protects the pipes from damage in the most vulnerable places, that is, at the fastening points.
The terminology of GOST 22130 defines supports as a structural element of the pipeline, that is, they cannot be called a transitional structure between pipes and foundations.
As we have already said, supporting elements are used when laying communications in a wide variety of industries. The necessary products are selected depending on their purpose in such a way that they allow the transmission of axial, transverse, vertical loads, torques to the soil or load-bearing structures.
Application
The beam bracket is designed to impart rigidity to the connection unit, so beam support is often used in the construction of roofing systems and various floors. Using screws to secure the supports, the individual structural elements are securely connected to each other and are able to withstand significant loads.
Fasteners used in construction
At the same time, the brackets are endowed with a number of advantages :
To install a wooden beam into a support, no special skill or knowledge of secret techniques is required. The use of a beam bracket does not lead to loss of building material. The use of special screws to secure the supports allows us to speak about the reliability of the entire building structure, which will not collapse under the weight of its own weight. Therefore, these products are used in frame, half-timbered and other construction options.
Purpose of pipeline supports
It is possible to achieve tightness and operational safety of the system only if two parameters are observed at once: the selection of high-quality pipes and the use of additional equipment, that is, supports for process pipelines.
VT-metall offers services:
According to the documentation, we are not talking about a separate construction part, but about a structural element of communication.
Let’s immediately name the useful functions of this component of the pipeline:
- Protection of the pipe from damage at the point of contact with the structure.
- Ensuring the pipes are positioned correctly.
- Load distribution along the entire length of the structure and its transfer to the ground.
- Elimination of vibrations, reduction of voltage in the system.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
The popular name “suspensions” has been assigned to supports for fixing pipes, but this term is not suitable for every type of fastening.
The fact is that all supporting structures existing today are divided into types based on:
- immobility/mobility;
- installation method.
If we talk about the installation method, then similar products can be:
- hanging;
- ordinary.
Suspended models are attached to ceilings, slabs and other means. They are considered movable supports for the pipeline, that is, they can move in two directions: across or along the axis of the structure. Whereas the stationary ones have a different task - they rigidly secure the pipe in a certain position.
Why are movable models needed?
- They reduce the stress coefficient in the system walls.
- The support reaction force of the pipeline is transmitted to the supporting structure, without changing the position of the point at which the transmission occurs.
Anchor corner supports
These supports (indicated by the letter U), and this is clear from the name, are placed when turning the overhead line. If the rotation angle is small, then the corner support has an intermediate support design. If the angle of rotation is large, then an anchor support is installed.
The support at the corner experiences equal loads from the tension of the wires of adjacent spans. The total force acts at the midpoint of the rotation angle.
Types of pipeline supports
1. Hull supports.
To connect structural elements in space, a box-shaped housing is often used. It is made of sheet steel or welded from individual elements. Body supports are mounted on a beam, have stiffening ribs, and are supplemented with cushions, clamps and yokes.
When using the housing, the pipe rises by 100–200 mm, making it convenient to fasten and maintain during operation. If we compare the cost of a bent angle and a range of rolled metal products, then purchasing the former turns out to be more profitable and reduces the cost of the entire structure.
2. Frameless supports.
This is a traditional model, which is a sheet steel cradle bent in accordance with the outer shape and diameter of the pipeline. Most often this element is called a “pillow”. It can also be equipped with a round, strip or tape clamp and a support plate, which has holes for fixing.
The design is simple, its production requires a minimum amount of materials, and it itself consists of a very small number of parts. For this reason, the open-frame model is called the most affordable one used in pipeline construction. For such support elements there are markings T11, HB, OPB.
3. Tubular supports.
If we talk about the design of this element, then we have a vertically located pipe, welded to a plate with holes for installation. To increase the contact area of the support pipe with the pipeline, a saddle-shaped cut is made at its upper end with a laser or cutter, which corresponds in shape to the main pipe.
When releasing such models, they are based on the OST 36-146-88 standard. This type is suitable for pipelines with a diameter in the range of 57–630 mm and medium temperatures up to +450 °C. There are currently four versions in total: A1, B1, A2, B2. Such products are marked TR; stainless steel, structural and carbon steel are used in their production.
4. T-bar supports.
T-bar elements can have different designs and are made of two types:
- Welded. In this case, a piece of the brand is installed on a single shelf, plates are welded at the ends, and a radius cut is made in their upper part in accordance with the diameter of the pipe for better fixation of the pipeline.
- Clamps. We are talking about strip or tape clamps that are welded on top of a piece of rolled metal, and holes for fastenings must be provided in its shelf.
These types of T-bar support structures are labeled as TP and TX. Various methods of connecting pipeline elements can be selected, thus achieving complete immobility of the unit or several degrees of freedom of the connection.
5. Clamp supports.
They occur when using both movable and fixed connection methods. Then the following types of fastening can be used:
- bar clamp;
- strip clamp;
- band clamp;
- flat clamp;
- rope clamp;
- mounting on the body;
- with frameless supporting structures;
- for welded and sliding supports for pipelines;
- the clamp is used as a guiding element.
The clamp tightly grips the pipe on all sides; gaskets made of dielectric and antifriction materials can be used with it. Also, with this fastening method, one degree of mobility of the pipeline along its axis can be achieved.
The classic model is an inverted U-shaped structure with or without stiffeners.
Clamp elements are used for pipelines with a diameter of 57–377 mm, while the yoke type is suitable for sizes 377–1420 mm. It is worth noting that assembly units can be marked differently, this is due to the fact that several standards are used in their production.
6. Welded supports.
Sliding and movable support structures are rigidly attached only to the base/stands or directly to the base and pipe. Welded support structures come in the following modifications:
- sliding guide;
- sliding motionless;
- steel;
- motionless;
- sliding;
- corner;
- on a beam with eyes.
For their production, they take rolled and bent angles, T-bars, channels, pipes or curved, welded bodies.
7. Supports for vertical pipelines.
According to OST 36-17-85, supports for technological vertical pipelines and piping of technological lines are manufactured. Most often we are talking about a strip, rod or yoke clamp, which is attached to a corner or in a bent body.
In the documentation, such structures are usually referred to as VP; usually these are fixed models. In this case, the main characteristics are considered to be material, diameter, face-to-face length, temperature and pressure of the working medium.
8. Rope supports.
A yoke is nothing more than a type of clamp, supplemented with special fasteners or studs. Yoke models are divided into types according to the design of the assembly unit and are:
- tubular;
- strip;
- case;
- stamped;
- stamped and welded.
This element is installed in this way: the pipe is laid on a cushion or cradle with holes for the studs, after which the yoke is pulled on top of the threaded connections. To make it easier to clamp the pipe, special mechanisms, claws, traverses, clamps or beams can be used.
9. Roller supports.
The design of this model stands out from the general background due to the following characteristics:
- two or more support platforms are provided;
- installation is carried out between the bearing supports;
- axial displacement of the pipeline by a specified amount is allowed;
- It is allowed to move the pipes sideways by 50 mm.
It is possible to produce one- and two-level elements, with one roller and several blocks, and the enterprises also produce clips for pipelines of energy facilities, steel and spring models. Rolling elements can significantly reduce the level of friction, and hence the wear rate of the elements of the entire structure. As a result, the service life increases, and assembly units are easier to repair.
10. Side supports.
The design of this element includes a plate and a support, which is necessarily equipped with several stiffening ribs for reinforcement. This model differs from the welded one only in its location in space, because it is mounted on a vertical surface, due to which it compensates for lateral loads, but does not perceive vertical forces.
Such elements are marked as T10 and are suitable for pipes with a diameter of 194–1,420 mm.
11. Frontal supports.
If we consider the location of the frontal models relative to the flow of the working medium and the body of the pipes, then they are installed in a transverse projection. These products are usually divided into types based on the material of manufacture and design:
- panel panels are made of reinforced concrete, often having several stiffening ribs;
- thrust ones are a pair of stops in a vertical or horizontal plane on both sides of the pipeline; they can also be four stops on all sides.
Double-supported frontal elements are installed when it comes to small axial loads, while four-supported ones are necessary for serious loads. If necessary, the entire structure can be reinforced with half rings and stiffeners.
12. Fixed supports.
This type of structure is necessary if it is necessary to exclude any mobility of communications relative to supports and foundations. Manufacturers offer the following design options designed for different operating conditions:
- "dead";
- for pipes in thermal insulation PPU;
- frontal and side thrust;
- yokes and clamps;
- hulled and unhulled;
- for vertical boxes;
- persistent reinforced;
- panel reinforced concrete;
- welded and steel.
To designate these pipeline elements, the abbreviation NOP is used. This type is suitable for installation with pipes with a diameter of 32–1,420 mm and is intended for conditions with increased operating loads.
13. Movable supports.
If it is necessary to achieve one or more degrees of mobility of the pipeline relative to the foundation or supporting structure, various movable models are used:
- clamp OPC;
- welded OPP;
- unframed OPB.
The rules for the manufacture of such supports for pipelines are established by GOST 14911-82, OST 36-94-83 and 36-146-88, in addition, the specifications of individual enterprises, drawing albums T-MM-26-05, and other documentation are taken into account.
14. Sliding supports.
This type of moving elements provides one degree of freedom in the axial direction. In this case, the following execution options exist:
- steel and welded;
- underlay and in a case for pipes in PPU thermal insulation;
- for pipelines of thermal and nuclear power plants;
- with flat clamp and bracket;
- sliding fixed and guides of several types;
- dielectric and yoke;
- clamp and frameless.
To resist rapid wear of pipes and system elements, anti-friction gaskets, rollers and blocks are used.
15. Adjustable feet.
They are chosen if precise vertical positioning of individual sections of the pipeline is necessary. Let us say right away that such structural elements necessarily have movable wedge stops. Assembly units are marked OR, and in their manufacture the standard TU 5263-003-93646692 is used. Another important element of such a supporting structure is the support. It is raised and lowered by moving the wedge stops, which are attached to the plate by bolted connections.
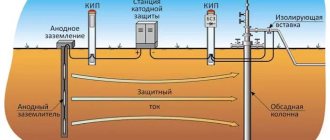
16. Dielectric supports.
Such elements are necessary to protect the pipeline from stray and induced currents. To do this, use a gasket made of any dielectric material, for example, paronite, which has anti-friction properties.
17. Supports for reinforcement.
OST 36-17-85 establishes standards for the production of structures for the installation of OKA pipeline fittings. From a technical point of view, these are four stiffeners that are cross-welded together and mounted on a support plate. In their upper part, the stiffeners follow the outer contour of the installed pipeline fittings.
18. Unloading supports.
This design is necessary to compensate for water hammer, vibration and mechanical loads that cannot be avoided during the operation of pumping and compressor equipment. Such an element consists of a pipe and has several degrees of freedom relative to the foundation. In its production, they rely on SNiP 3.05.05-84, and GPA markings are used.
Beam support: an integral element in the construction of wooden houses and structures
It's very cool to live in a country wooden house. However, first, it would be nice to build such a house! Today, wooden houses are assembled in a matter of days, however, the requirements for structures remain the same as in previous times.
It's no secret that one of the most ancient and sought-after materials in construction is timber. It is used to construct floor coverings, ceiling beams and other load-bearing elements. In addition, timber is an excellent material for wall structures. In any case, for installation work you will need a specialized fastening element such as a beam support.
Open beam support 50x140, used for vertical fastening of console beams
How does a fixed support for pipelines work?
Fixed structures are necessary in cases where rigid fastening of the system is required. In this way, it is possible to prevent its shifts in any of the possible directions.
Fixed elements are used in the installation of pipelines, which are installed in the following ways:
- external;
- internal (underground).
During the installation of sections of the system, the supporting structures are fixed using reinforced concrete frames. You need to understand that the latter are located at different distances from each other, dividing communications into segments. The length of the segment is related to the characteristics of the special compensators installed on it.
During both external and underground installation of communications, fixed elements are actively used. If a channelless method is used for laying underground, choose supports with high-quality waterproofing. Usually the role of the latter is played by a polyethylene shell. When it comes to external installation, galvanized waterproofing is preferred.
For a fixed installation method, the following elements are used:
- steel pipe;
- steel sheet obtained by hot rolling;
- polyurethane foam (PPU);
- heat-resistant tape;
- galvanized shell;
- centralizer;
- polyethylene shell.
For the manufacture of fixed steel supports for pipelines, the most durable and reliable grades of this metal are used.
The steel sheets used in this case can be of three types - it all depends on the quality:
- ordinary;
- low alloy;
- structural (considered the highest quality).
A centralizer is an element that simplifies the alignment of pipe ends before connecting pipeline elements. Today there are two types of centralizers:
- external;
- internal.
In accordance with the name, external ones perform alignment from the outside of the pipe and can be:
- link;
- eccentric;
- hydraulic jacks.
The first ones are necessary for centering pipes with a cross-section in the range of 57–2,224 mm. Unlike other models, they have increased resistance to low temperatures, since they are made from frost-resistant steel. Eccentric centralizers can be used when working with pipes of any cross-section. The latter type is used exclusively when aligning pipes with very large weights or when there are deformations on them. Such devices provide a force of 12 tons.
If we talk about internal centralizers, they are distinguished by one important feature: they allow long-term welding of pipes from the inside. As a result, the quality of seams is significantly improved. However, these products also have disadvantages, the main one of which is their heavy weight, that is, their transportation is impossible without special equipment.
Fixed support structures for pipelines are used in construction:
- main gas or oil pipelines;
- various types of communications at enterprises;
- pipelines to nuclear power plants and thermal power plants.
In addition, it is the fixed elements that are used in the construction of communications in regions with low temperatures, thus increasing the service life of the entire structure.
These elements are installed in systems used in completely different areas. They divide the entire system into separate segments in which bellows-type compensators are installed. The latter are designed to protect the pipeline from deformation that is possible when the ambient temperature drops.
Fixed supports of steel process pipelines are welded to platforms and mounted to the pipe using fasteners. To achieve the greatest reliability, metal plates are also welded close to the ends of the clamp.
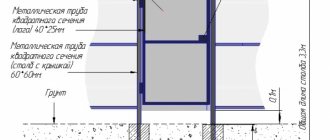
Beam support is an important detail during construction
Section: Educational program
The beam support (another name is the beam bracket) is positioned as a perforated fastener and is used when it is necessary to make a T-shaped connection of wooden materials. This product is a complex structure, combined from two metal corners and a plate cross member, on which the beam rests.
The beam bracket is a part made of thick metal coated with a layer of zinc. Each of the side shelves has many holes drilled at the factory and designed for the use of steel hardware such as self-tapping screws or rough nails. The two shelves at the base of the beam support also have multiple perforations, due to which the unit is attached to the transverse beam or concrete structures using anchors.
What are the benefits of sliding supports for pipelines?
Sliding models are necessary if communications pass along the surface of the earth. This ensures free movement of the pipeline in horizontal and vertical planes. Also, such devices protect the entire structure from premature abrasion.
It is impossible to do without sliding elements when installing systems that experience loads during seasonal temperature changes, because at this time the pipes expand and contract in two planes at once.
Thanks to sliding models, it is possible to achieve stability of communications and balance their movement in space that occurs when temperatures change.
The sliding model includes the following components:
- the base, the role of which is often played by a corner;
- semicircular metal pipe holder;
- pad;
- fasteners, that is, nuts and bolts.
Movable models are available in three types:
- hard;
- elastic;
- constant force designs.
Rigid models, in turn, are:
- guides;
- rigid suspensions;
- sliding supports.
The former do not allow communication to move downwards and horizontally. Suspensions of the second type allow you to achieve the greatest mobility of the entire structure. While the latter type eliminates the pipe moving down in the vertical direction. Elastic supports can boast such rigidity only if the pipe moves vertically. Then the following pattern works: the higher the load on the supporting element, the further the pipe moves. Note that the constant force support copes with any load, regardless of the displacement of the communication.
To protect this element of the system from rust, it is primed in several layers. Or it can be coated with primer enamel. But the highest degree of corrosion protection is provided by powder coating or galvanizing.
Typically, durable carbon steel is chosen as the material for the manufacture of such products. But it has to be replaced with low-alloy grades when it becomes known that the pipeline will be operated under conditions of large temperature fluctuations.
When classifying sliding supports for pipelines, it is not the price that is taken into account, but their design, therefore the following types are distinguished:
- on brackets (fastening elements);
- clamp;
- ball;
- dielectric;
- roller (roller).
Due to the rollers used in it, the roller design reduces the friction force between its base and the upper part. Note that friction is generated when the pipeline moves.
Dielectric sliding elements are chosen for pipes in the manufacture of which the following are used:
- carbon steel;
- low carbon steel.
Such structures require insulation from a special material - sheet paronite, which includes:
- rubber;
- asbestos;
- additional powder additives.
For the manufacture of ball sliding elements, steel is used, and they are considered a specific fastener. The fact is that with their help the pipe can move in two directions at once: longitudinal and transverse. Therefore, such models are most often installed at power plants and heating mains.
Typically, sliding type devices are isolated from metal casings using waterproofing. And the inner surface of the pipe and the waterproofing material are lubricated with a special graphite lubricant, which prevents friction. Next, weld the clamps and tighten them securely. It is important that when installing such structures you can do without special equipment, due to which the whole work takes much less time.
Main modifications
Among the fasteners for timber there are: open type supports, closed type, sliding type for rafters. A wide range of standard sizes and modifications of beam brackets means that each model should be used under appropriate conditions.
Open
The open-type beam bracket is positioned as a special platform with strips bent outward and crimped sides equipped with perforations of various diameters.
Its use allows :
In modern construction, an open support is considered the most optimal tool for effectively solving assigned problems. Therefore, these products are used as fasteners for connecting any elements of wooden structures in the same plane. Any hardware can be used to fasten them, from nails to self-tapping screws.
Important: since open-type beam brackets are produced in various standard sizes, the most suitable option must be used in each individual case. Also, attention should be paid to the fastening elements, selecting them according to the diameter of the existing perforation.
For the manufacture of open supports, high-quality steel is used, processed in a special way and having a thickness of about 2 mm. Compliance with the technological process in the manufacture of such elements gives the finished product high performance characteristics, allowing it to be used for outdoor work.
Closed
The design of the closed-type beam bracket received its name due to the fact that its fastening petals are bent inward. A closed support is used if it is necessary to connect a wooden beam to a brick or concrete base. In this case, both anchor bolts and other hardware (nails, for example) can be used.
Closed beam supports are produced from carbon steel using the cold stamping method, thereby obtaining both the fastening figure itself and its perforation. After this, the finished products are subjected to a galvanizing process, which gives them high performance characteristics :
The product’s ability to withstand heavy loads is achieved both by the strength properties of the metal and by the method of attachment to the timber. And stringent requirements for the manufacturing process allow the use of closed-type timber supports in the most severe weather conditions. Turning the fastening petals inward allows the closed support to compress the beam with great force, giving the connection unit high strength and reliability. These products are used when connecting load-bearing elements, using hardware as fasteners that correspond to the diameter of the perforation and the expected loads on the structure.
Sliding supports for rafters
To prevent deformation of the walls of a wooden structure, they resort to a sliding type of fastening of rafter elements. A sliding support for the rafters, which involves connecting their ends according to the principle of hinges, helps ensure mobility. This design consists of a corner with a loop, rigidly attached to the log of the upper crown, and of a special strip that is installed on the rafter leg.
Sliding type beam brackets are made of 2 mm thick galvanized steel with perforations. They are installed strictly parallel to the intended displacement and are most often used as fasteners for the Mauerlat, which has a number of advantages :
The use of movable supports is indicated for the operation of buildings made of chopped logs during the period of maximum shrinkage processes. Thus, you can easily avoid critical deformations of walls and other problems of a similar nature, the elimination of which may require serious investment.
Source
Distance between pipeline supports
However, it is not enough to know the types of supports for pipelines and buy all the necessary elements. For competent construction, you need to clearly understand the distance between these structures, because only in this case the system will work properly. The distance is set in accordance with the requirements specified in the relevant documentation, as well as on the basis of information about the scope of operation of the pipeline, its weight, and possible deflection during service.
The values are calculated based on data from the table “Design of Heat Networks” by A. A. Nikolaev. So, for horizontal placement, the table suggests the following calculation: with a minimum pipe diameter of 20 mm and a maximum working environment temperature of +60 ˚C, the supports should be 60 cm apart from each other. The rule works here: the larger the pipe diameter, the larger the pitch used.
The same calculation principle is used if vertical placement is planned. Let’s say the main line has a diameter of 40 mm and a temperature of +20 ˚С, then the length of one segment is 138 cm. If the network temperature reaches +70 ˚С, then the length of the segment is reduced to 113 cm.
When arranging fixed metal supports, the schematic characteristics of thermal communications are taken into account. Typically, such structures are installed near main branches, shut-off valves and in straight sections, taking into account the properties of the expansion joints installed there.
The distance between the fixed elements of the system is calculated as follows:
L = 0.9 × ∆L / (a × (t-tpo)), where
- ∆L – compensator capacity, in mm (values are taken from the table);
- a – coefficient of linear expansion of steel walls during temperature fluctuations, in mm/m˚С;
- L – length of the pipeline section for which the calculation is being made, in m;
- t – calculation of the temperature of the working environment during installation, in ˚С;
- tрo – ambient temperature;
- 0.9 – error value (equal to 10%).
To calculate the distance between the sliding fasteners, it is necessary to understand the scope of use of the entire system. The fact is that, for example, for a cold pipeline this step will be greater than for communications through which hot water flows.
Advantages and disadvantages
Manufacturers offer a wide range of fastening elements for interior finishing of wooden buildings and installation of roofs. Using such a mount has a number of advantages:
It is not recommended to use beam support fasteners when constructing external walls; in winter, the metal contributes to the creation of cold bridges; in conditions of high humidity, the metal can be susceptible to corrosion. The anti-corrosion coating is not designed for use of fasteners in conditions of high humidity.
Pipeline supports: norms and standards
At the moment, standards have been developed at the state level for two categories of such products:
- GOST 14911-82 “Parts of steel pipelines. The supports are movable. Types and main sizes." It applies to movable structures made of steel grades OPB (frameless), OPH (clamp), OPP (movable welded);
- GOST 16127-78 “Parts of steel pipelines. Pendants. Types and main sizes." It applies to pendants designated PM, PG, PMV, PGV.
If we talk about industry standards for assembly units for fastening gas pipeline pipes, then in Moscow there are 2.5 times more of them:
- OST 108.275.24 – pipelines of nuclear power plants and thermal power plants;
- OST 24.125.154 – pipelines for nuclear power plants and thermal power plants made of high-alloy and special steels;
- OST 36-94 – moving elements of technological lines;
- OST 36-104 – steel structures for systems working with media characterized by low temperatures;
- OST 36-146 – series KN, VP, TO, KhB, UP, ShP, TP, KH, KP, TX, TP for diameters 57 – 1420 mm.
There are also three subordinate TU standards relative to GOST. They are used in the production of the models we describe:
- TU 1468-012-04698606 – moving elements of process piping, used at a pressure of 10 MPa, temperatures from -70 °C to +450 °C, pipe diameters of 18–1620 mm;
- TU 1468-002-92040088 – suspension, supports and block modules for pipelines 32 MPa, DN 15–1600 mm;
- TU 1468-001-00151756 – sliding elements for diameters 100–1400 mm, temperatures from -70 °C, pressure 10 MPa.
There are also two series of assembly units of this type:
- 903-10: 4th edition - for structures mounted motionlessly, 5th edition - for movable modifications, 6th edition - for suspensions;
- 903-13: issue 6-95 – pendants, issue 7-95 – fixed elements, issue 8-95 – movable.
The album of drawings T-MM-26-05 includes options for the design of movable and dead structures of PS, ONS and OSS. In the documentation NTS 65-06 you can find working drawings and technical regulations intended for the manufacture of software and non-productive software.
The essence of installing beam supports
In the process of construction and installation activities, the connecting elements that cannot be avoided are fastening materials.
Today, perforated fasteners are often used in construction:
All this is an incomplete list for the use of metal fasteners, with holes made in them for ease of installation. As we will discuss below, there are two main types of supports: closed and open structures.
Mounting perforation in fasteners
In order for the supports for the beam to be effectively mounted between structures, already manufactured products are used, which should only be connected to the base and, in fact, the beam. This type of fastener is made of steel, which ensures high strength of the connection. (see also the article Joining timber along the length - connection options)
You should know! In order for the metal supports for the timber to be reliably protected from corrosion, a protective coating is applied to these fasteners, because the supports can support not only internal structures, but also the roof, and therefore are often located outside.
When installing outdoor awnings, a concrete floor is used instead of wood. Therefore, in such cases, special fasteners are also used, pre-fixed in the concrete base.
For such wood material, a support for timber 100x100 mm is used