No welding takes place without the main element - the electrode. It is worth choosing a certain optimally suitable electrode for a specific welding machine. But there are types that are suitable for almost any brand of welding unit and have a number of advantages. Such convenient and easy-to-use electrodes include rutile ones, the main thing is that the welding seams after their operation are distinguished by accuracy and subtlety. What are rutile electrodes and when should they be used - in the text.
Rutile electrodes: what are they and what are they for?
All electrodes are made according to the same principle: a special coating is applied to a metal rod made of a special alloy. As a rule, the type of coating determines where the electrodes of this type will be used.
Rutile coated electrodes are designed for manual arc welding.
The coating is made primarily from titanium dioxide. This allows you to achieve high quality welding seams and also has a beneficial effect on the entire welding process. REFERENCE: This type of coating is one of the safest, as it does not emit harmful substances during combustion that can be inhaled by the welder.
Welding rods: types and characteristics
To work with reinforced products, you need rods coded “E” and hardness codes indicated by numbers: 38, 42, 46, 50, 55, 60, 70, 85, 100, 125, 150; 42A, 46A, 50A.
In the case when it is necessary to connect types of steel products that are resistant to thermal effects, consumables coded E-09 and E-10 are used. Many types of electrodes are suitable for welding high-alloy metal, their number is more than 40. The most commonly chosen electrodes are: E-12X13, E-06X13N, E-10X17T, E-12X11NMF, E-12X11NMF.
To connect materials with previously known characteristics, the following electrodes are used: E-10G2, E-12G4, E-10G3, E-16G2KhM, E-15G5, E-30G2KhM, the total number of types is 38.
Why so popular
Rutile electrodes are considered one of the best. They have a number of advantages, thanks to which a welder with any experience can obtain an even and high-quality seam.
- Can be used with both AC and DC current . The welding arc in any case maintains combustion stability.
- You can weld metal joints coated with a light layer of primer .
- Ideal for use when welding short seams or in awkward places. The arc is easy to ignite and just as easy to re .
- Allows you to form a seam with a high impact strength . This is achieved due to the increased alkalinity of the slag.
- The rutile welded seam has excellent durability and fatigue strength . Even under prolonged exposure to alternating loads, it retains its qualities.
- a low spatter coefficient is characteristic . This makes the welding process more convenient for the welder.
- Convenient to reuse the electrode. After welding is completed, carbon residue remains on the tip of the rod, which does not need to be cleaned off (unlike other types of coatings). The carbon deposits of rutile electrodes are a semiconductor, so you can continue working without additional problems.
- Less harm to health . During the combustion of rutile coating, no hazardous substances are released. Therefore, there is less negative impact on the welder’s respiratory system.
IMPORTANT: Low requirements for the hob. Even with strong surface moisture, the seam does not lose its properties. Welding is also allowed in the presence of a corrosion layer (up to 30%).
Types of welding materials
Electrodes used in manual arc welding are divided into:
- Non-melting.
They are made from different types of materials that differ in their refractoriness: tungsten, graphite, coal. Designed to ignite and maintain the welding arc. The joints between the workpieces are filled with additives created by manually applying a consumable that melts.
- Melting.
This type of electrode melts during welding operations on the surface of the structure. Made from steel, cast iron, copper or other metal. The specific type of raw material depends on the material. The rod performs the function of an additive and also plays the role of a cathode or anode. There are electrodes coated and uncoated.
Rutile electrode coating - characteristics
Electrodes with this type of coating can most often be of two main types: E42 and E46 (according to the state standard). The type must be indicated on the packaging label. Weld metal welded with E42 type electrodes has the following technical characteristics:
- Tensile strength - 410 MPa;
- Relative elongation - 22%;
- Impact strength - 80 J/cm2.
A seam welded with E46 electrodes has more durable characteristics:
- Tensile strength - 450 MPa;
- Relative elongation - 20%;
- Impact strength - 147 J/cm2.
In the manufacture of rutile electrodes, low-carbon welding wire (SV-08 or SV-08A) is used. A rutile coating is applied to it. The marking of such electrodes contains the letter “P”, which indicates the type of coating. As a rule, the letter “P” is always followed by two numbers:
- The first indicates in what spatial positions welding can be performed. Most rutile electrodes can be welded in any position.
- The second indicates the type of welding current: alternating or direct, its polarity and open circuit voltage.
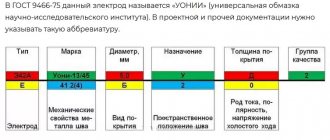
Marking
Depending on the manufacturer and the specific type of product, package markings may differ slightly. However, most rutile electrodes are labeled almost the same. Let's take a closer look at the example of marking MP-3 electrodes.
On their packaging you can see the following markings: E 46 – MR-3 – UD E 430 (3) - P26.
Let's look at everything in order:
- E46 - indicates the type according to GOST. This means that this model is designed for welding low-alloy and carbon steels. Tensile strength - 46 kgf/mm2.
- MP-3 is a brand from the manufacturer.
- U - indicates the purpose of the electrode. For welding carbon steels, tensile strength is 60 kgf/mm2.
- D is the coating thickness coefficient (thick).
- E - international marking. Indicates the type of electrode with a consumable coating.
- 43 - tensile strength (430 MPa).
- 0—relative elongation index (20%).
- (3) - temperature indicator -20°C. This is the minimum temperature at which the weld metal retains an impact strength of at least 34 J/cm2.
- P - type of coating. In our case - rutile.
- 2 - shows in what positions welding work can be carried out. This indicator means that you can cook in any direction except vertical “top to bottom”.
- 6 - for high-quality work you need to use a current of reverse polarity, constant. The open circuit voltage should be approximately 70V.
[ads-pc-2][ads-mob-2]
According to welding current parameters
Rods with a cross section of 4 mm. are selected for welding on simple welding devices. They are also used on the most productive and powerful units.
The length of this consumable is 35 and 45 cm. Suitable for welding thin workpieces up to 1 cm. Operates at a current of 220A. Welding consumables with a cross section from 5 to 12 mm. used only in welding work in the presence of additional lighting created by powerful lighting installations.
Aluminum rod FoxWeld AL Мg 5 (ER-5356) 1.6 mm 5 kg Source yandex.ru
Physico-chemical composition
Depending on the manufacturers and various modifications, the composition of the rutile coating may differ slightly. However, in most cases the composition is as follows:
- Rutile concentrate (titanium dioxide) - 48%.
- Feldspar - 20%.
- Ferromanganese - 15%.
- Magnesite - 15%.
- Dextrin - 2%.
Some types of electrodes may also contain additional elements: for example, cellulose. Such coatings are marked with the letters “RC”, which stands for “rutile-cellulose coating”.
Rutile electrodes: application
Due to its excellent qualities, rutile coatings are widely used in various conditions and are considered one of the most practical types. We list the main applications in which electrodes of this type do an excellent job:
- Welding of low carbon steel structures . The chemical composition of the coating allows you to effectively work with ferrous and low-alloy metals. In such cases, the seam is smooth and without cracks.
Welding of pipelines. Excellent for repairing pipes that carry liquids. In this case, it is difficult to completely dry the working surface of the metal. However, the welding arc of rutile electrodes burns stably even when drops of water enter the combustion zone.- Widely used for repairing parts or tools that wear out over time . Rutile electrodes make it possible to deposit welds of considerable thickness as efficiently as possible. Due to small splashing, material savings are achieved.
Rutile coated electrodes: pros and cons
Compared to other types of coatings, rutile has a number of advantages:
- Seam durability . Welded metal is not susceptible to cold or hot cracks.
- In contrast to the acid coating, the rutile welding arc burns with alternating current as intensely as with direct current.
- Easy to process areas where short seams are needed . If the main coating requires continuous welding, since the welding arc is difficult to re-ignite, then with rutile it is easier. The arc ignites easily, and there is no need to clean carbon deposits from the tip of the rod.
- It is not necessary to prepare the work surface . Other types of electrodes are susceptible to oxidation and rust, resulting in a weak weld. Rutile electrodes allow you to form a stable and durable seam, regardless of the quality of the surface.
- After welding, the slag is easily separated , and the surface of the weld practically does not require grinding.
There are also disadvantages:
- Not suitable for all designs. The small range of metals with which this type of coating can be used imposes certain restrictions on their operation. Such electrodes cannot be used for welding high-carbon steel .
- The properties deteriorate sharply with increasing voltage. Therefore, you will have to monitor compliance with the nominal indicator.
- It is necessary to carry out preparatory work - drying and calcination .
[ads-pc-4][ads-mob-4]
The best brands of rutile coated electrodes
ESAB-SVEL OK 46.00
Produced in Russia by the Swedish concern ESAB. This model is one of the best in its category and has the following advantages:
- Low requirements for preliminary preparation. Even damp products can be calcined at a temperature of 70-90°C.
- They are not afraid of moisture. The arc burns stably upon contact with a moistened surface.
- The minimum threshold of the required current, which is needed for reliable combustion, is significantly lower than that of other types of electrodes.
- Forms a strong and impact-resistant seam.
Lincoln Electric Omnia 46
They are produced by the American company Lincoln Electric, which has been producing electric welding products since 1927. Electrodes are affordable and are an excellent choice for beginners. The welding arc does not require precise control; if it is slightly extended, combustion stability is not lost.
When operating the Omnia 46, a relatively small amount of sparks are generated. A strong seam allows them to be used for welding critical structures (for example, pipelines operating under high pressure).
OZS-12
Electrodes of this brand have a NAKS certificate, which allows them to be used for welding work at critical and hazardous facilities. Among the advantages of the brand:
- The seam is made easily and smoothly, even without special welding skills.
- After cooling, a thin slag crust remains on the surface, which is easily separated.
But there is also a drawback . Despite the fact that rutile coatings are usually not susceptible to moisture, electrodes of this brand are sensitive to dampness . This entails additional requirements for storage, calcination (at a temperature of 150 ° C before each use), as well as cleaning the weld pool from large contaminants.
MR-3
MP-3 type electrodes are one of the most common. The Resanta brand managed to preserve all the advantages of rutile coating and avoid the disadvantages that are found in other manufacturers of products of this type.
MP-3 are easy to ignite, form a strong and even seam, and work effectively with different currents. The disadvantage is increased sensitivity to moisture. Before use, they must be calcined for at least an hour at a temperature of 150-170°C.
Manufacturers of welding electrodes
The Russian consumables market offers a wide selection of electrodes produced by domestic manufacturers. The technological capacity of production allows us to meet the needs of individuals and enterprises in various fields of activity.
Russian electrode manufacturers are divided into 3 categories:
- Large production facilities that supply the bulk of customers with materials.
- .
- Small businesses that manufacture products to meet their own needs.
We list several manufacturing companies producing electrodes:
- SVEL - Altai welding electrode plant.
A modern facility producing a wide range of coated products.
- Belorechensky electrode.
Welding materials are produced in accordance with state standards, and the products are certified.
- "Electrode-Boron".
Manufactures universal welding electrodes.
The products of Russian manufacturers are in demand in various fields of activity and are actively purchased not only in stores in our country, but also abroad.
Welding with rutile coated electrodes
Several nuances that must be taken into account when carrying out welding work:
- Check what material the electrode is made of. And now we are not talking about the coating, but about the rod itself. To achieve the highest quality weld, the metal of the rod must match the metal of the structure that is being welded.
- It is also important to consider the thickness of the electrodes. It must correspond to the thickness of the metal of the structure, although it may be thicker or thinner, which is compensated by the current strength and the skill of the welder.
Video
Watch a couple of videos where a craftsman shares his experience of working with rutile electrodes.
Video description
Explanation of electrode designations.
Below we will talk about the classification of electrode elements, their purpose and properties.
The purpose of the metal rod is to fuse the material being welded to a specific place where the workpiece is joined. The main part of the electrode serves to conduct current through itself. The end of the consumable melts under the influence of the elevated temperature of the welding arc. At the moment of melting of the end of the electrode, a complete product is formed together with the molten structure.
What does a consumable electrode consist of?
The welding electrode has a simple structure. Its main component is the rod; a special coating is made on the outside. The end that melts and comes into contact with the material being welded is made without coating.
Calcination of electrodes with rutile coating
Electrodes of this type require pre-calcination before use. Common requirements for calcination: at least an hour in an oven at temperatures up to 350°C.
These are general requirements, and exact guidelines vary by brand. Some models are slightly sensitive to moisture and can be calcined at relatively low temperatures (up to 90°C), or do not require calcination at all. Although there are brands that can become damp and lose their properties. The exact calcination mode is indicated by the manufacturer .