A real technical revolution has taken place in the world of welding. And this is an excellent fact, because this revolution consists of the appearance on the market of a huge number of new, convenient and safe devices for welding of various types. They allow even beginners to work effectively: the threshold for entering the profession has been lowered. This is a very positive development.
But every revolution brings new demands: you need to be aware. You need to know and understand new equipment and gadgets, understand the essence of new technologies, and be able to choose the best models of devices based on parameters that are important to you. We offer you to understand all the welding machines that exist today.
Classification and main types of welding machines
Classification of welding machines.
To begin with, let’s clarify all the known abbreviations associated with welding; we cannot do without them in the future.
- AC and DC: This is an English abbreviation that stands for alternating current and direct current respectively.
- TIG – manual welding with argon and tungsten electrode.
- MIG and MAG – semi-automatic arc welding with consumable electrode wire with the supply of inert or active gas.
- PV is a Russian abbreviation for “on duration,” indicating the time during which the device will operate without overheating.
- MMA – manual arc welding with stick electrodes.
The types of welding machines are as follows:
- transformers;
- rectifiers;
- semi-automatic;
- inverters;
- generators running on diesel fuel or gasoline.
Transformer - a veteran of retirement age
Many craftsmen consider transformers to be obsolete devices whose place is in recycling plants. There are other points of view. Let's try to figure it out.
This is truly the oldest professional welding machine used in welding. At the same time, it is the simplest in its design. The main task of the transformer is to convert electric current, or more precisely, to reduce the voltage to an acceptable level for welding.
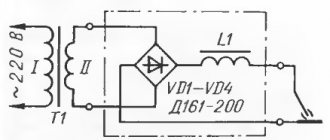
The design of the transformer is extremely simple: one of the most important elements is the core. There are two windings on it - primary and secondary. One of them works as static, the second moves relative to the first, and one winding moves against the background of the immobility of the other.
This process ensures a decrease in current. In this area there may be different options for the mechanism of action, but the main thing remains the same: reducing the current voltage so that the current supply to the arc is stable.
Welding transformer.
The peculiarity of transformers is only alternating current at the output. This fact does not speak in favor of the quality of the weld. The fact is that with alternating current, metal tends to splash in different directions. You need to cook using rutile or calcium fluoride electrodes, the diameter of the most optimal sections is about 1.5 - 2.5 mm.
Electrodes must be selected based on the maximum current and voltage in the device.
Like any other technical device, transformers have their advantages and disadvantages.
The positive properties of the welding transformer are as follows:
- They are simple in design and therefore easy to maintain.
- Extremely high reliability.
- Inexpensive in cost.
- They have quite high performance - up to 90% efficiency.
Now let's compare them with the disadvantages of a transformer:
- Massiveness: heavy weight and large dimensions.
- High energy consumption, since a lot is needed to preheat the device itself. Fan cooling also requires a lot of energy.
- High dependence on mains voltage: when it decreases, the quality of the output welding current decreases significantly.
And one more important factor. In order to cook using transformers, you need quite serious skills. This is not easy for beginners; they often have difficulty maintaining a high-quality arc.
So, what do we have with regard to transformers: serious dimensions, high energy consumption, preliminary welding skills are required. Arc stability and seam quality are not always ideal. But they are cheap in cost. Do they have prospects? Yes, of course, these prospects fade over time.
The most appropriate definition would be “outgoing devices.” Transformers are suitable for those for whom the criteria of low price, durability and reliability are most important.
WELDING CURRENT SOURCES
This is the main part of any welding machine, converting the mains voltage into direct or alternating current with specified parameters. Types of welding machines according to the type of current source are classified into:
Welding transformers
. Traditional and at the same time structurally the simplest source of welding current. Its main component is the transformer itself, which reduces the mains voltage to welding voltage. The current is regulated by various methods, the most common of which is by changing the distance between the primary and secondary windings. All transformers have one common feature - they produce alternating current at the output. In order to weld non-ferrous metals using a “trans” or improve the stability of the arc, it is necessary to introduce additional heavy and bulky elements into the design, and the transformer itself weighs quite a bit. At the same time, to perform critical work, special electrodes for alternating current are required.
The efficiency of the transformer is quite high (up to 90%), but part of the energy is spent on heating. For cooling, modern models also use fans of considerable power: after all, it is necessary to cool a device weighing several tens or even hundreds of kilograms. Currently, this type of welding power source is used infrequently, but transformers, in addition to efficiency, have two more important advantages: low price and durability, which is why they are still in demand.
Welding rectifiers
. Rectifiers are devices that convert alternating current into direct current. They consist of a step-down transformer, a rectifier (diode) unit, as well as regulation, starting and protection devices. This design, although more complex than a transformer, provides much more stable output characteristics of the welding current and electric arc. The quality of the seam is also much higher in the end. The price of rectifiers is not much different from the price of transformers, reliability is also high: there is practically nothing to break in them.
The main disadvantages are the same as those of a transformer - high weight, complexity of operation, and strong voltage drop in the network during the welding process.
Inverters
. This is the most modern type of welding machine. Unlike conventional welding machines, in which the power transformer operates at a mains voltage frequency of 50 Hz, the welding inverter uses high-frequency current (several tens of kilohertz). At the same time, to transmit the necessary energy, a transformer of much smaller size and weight is required, and welding takes place at a constant current of good quality, which also affects the quality of the seam. A conventional 160 A welding transformer weighs at least 18 kg, and a 160 A welding inverter power transformer weighs no more than 300 grams and is comparable in size to a pack of cigarettes, while the weight of the entire inverter, with the housing and all electronics, is 3–7 kg . The inverter consists of a rectifier, a line filter, a converter to high-frequency alternating voltage, a welding transformer, another rectifier and a control circuit. The welding inverter has a much wider range of welding current adjustment than a conventional machine, which is especially important when welding with thin electrodes. Another “plus” is that with inverters, as a rule, this adjustment is much more accurate and the output parameters are much more stable, which greatly simplifies the selection of the optimal operating mode.
All inverter devices are manufactured using one of two technologies - MOSFET or IGBT.
MOSFET technology was developed about half a century ago, IGBT - more modern and economical - has many advantages over MOSFETs. In Europe, where energy consumption regulations are becoming stricter every year, it is no longer possible to find MOSFET inverters for sale. We still see them quite often. MOSFET inverters are well proven, usually cost less and, despite their greater weight and size, are still quite popular, especially for simple welding work on ferrous metals. The production of MOSFET components is cheaper, but more of them are required: in a 200 A inverter you can find up to 24 identical MOSFET power transistors and a much smaller number of IGBT transistors (usually about a dozen). IGBT inverter devices are capable of operating at a significantly higher frequency (60–85 kHz) than MOSFETs, which further reduces the weight of the device. The thermal protection response temperature for IGBT transistors is about 90 °C versus 60 °C for MOSFETs, this directly affects the duration of continuous operation of the inverter. As for maintainability, the opinions of “servicemen” differ radically. Some believe that a compact inverter with fewer parts and power transistors is easier to repair, others believe that a device made using MOSFET technology with larger parts and a free layout is more repairable.
In addition, manufacturers produce various IGBT devices, sometimes with complex layouts and difficult access to individual parts. In any case, if you adhere to the opinion “the fewer parts, the less likely it is to break,” you should pay attention to IGBT inverters; moreover, due to the excellent parameters of the welding current, they are better at welding not only ferrous metals, but also cast iron and stainless steel. The leader in the production of inverter welding machines is Lincoln Electric.
By using an electronic feedback control system in inverters, it is possible to obtain output characteristics suitable for any welding method. The most important functions are Hot Start, Arc Force and Anti-Stick. At the beginning of work, the electronics provide an additional current pulse, which facilitates ignition of the arc (Hot Start function). If the electrode approaches the workpiece too quickly, Arc Force increases the welding current to prevent sticking. When stuck, the current is reduced or switched off, eliminating the possibility of “freezing” the electrode (Anti-Stick function).
To one degree or another, these functions are present in all inverters; more expensive models have the ability to adjust them (for example, Hot Start is not needed when welding thin sheets of metal; it’s easier to reduce it or turn it off completely).
Inverters also have disadvantages, but calling them such is a stretch. It is necessary to distinguish between using an inverter at home or at work.
The main enemy of electronic circuits is moisture and dust, especially metal dust. Therefore, it is not recommended to turn it on in dusty rooms and especially to operate the grinder next to the switched on inverter.
Of course, when it rains, work should be stopped; this is prohibited by safety regulations, and not only because it is harmful to the device. Professional models are better protected from dust and moisture, but they also cost accordingly. In any case, from time to time the device must be opened and thoroughly blown with compressed air.
Electronics are sensitive to the quality of the current, therefore, various protection elements are included in the inverter circuit: overheating sensors, fuses, and sometimes shutdown devices when the voltage drops below the permissible level, however, almost all devices can operate at voltages from 170 to 250 V. For protection against sudden voltage surge (above 270 V), many manufacturers install varistors (“tablets”), which split when the voltage rises sharply. After this, the damaged varistor should be replaced; this repair is simple and inexpensive. If you plan to operate autonomously from an electric generator, it is necessary to select a device with a built-in compensator for voltage drops in the supply network. Manufacturers warn separately about its presence; without it, the inverter can quickly fail.
The device should not be stored in an unheated room in winter - electronics require careful handling.
There is one more “disadvantage”: working on a transformer or rectifier is much more difficult than on an inverter, but those who have learned to work on “trance” will switch to an inverter without any problems, but the reverse transition is much more difficult - they will have to complete their studies.
The straightener is a real compromise
Straightener for welding.
This type of device is a pure technical compromise. They come in two types: silicon and selenium. In its design and principle of operation, it is exactly in the middle between a veteran of the welding movement transformer and a new generation device in the form of an inverter.
The rectifier design is based on the same transformer. But it is accompanied by additional elements: a rectifier unit, which can be either a thyristor or a diode. The main thing is that the rectifier helps to obtain constant current, unlike a transformer.
Direct current passes through the secondary winding towards the rectifier unit. If the unit is also equipped with a choke, the welding current and other indicators can be adjusted.
All additional accessories that equip the rectifier are aimed at only one thing: increasing the stability and continuity of the electric arc. After all, a good arc gives a high-quality seam as the final result.
And another very important advantage of the rectifier is its ease of operation: beginners without much experience can work on it.
Now the advantages of the rectifier point by point:
- Opportunity for beginners to operate the device.
- The result is high quality welding seam.
- Ability to cook cast iron and non-ferrous metals if you use suitable electrodes.
- You can cook stainless steel and low-alloy steels with special electrodes.
- Stable and continuous arc.
- Wide functionality that allows you to use rectifiers, including for home welding on the farm.
- Relatively cheap.
The disadvantages of rectifiers are almost the same as those of transformers: large dimensions, mains voltage drop and high dependence on it. It should be noted that many manufacturers of household electrical equipment are slowly reducing the production of rectifiers. So we can talk about the quiet maintenance of these devices in the future.
Argon arc welding machine - for whom the equipment is intended and the principle of its operation
A specialized type of welding equipment that is designed exclusively for working with non-ferrous metals is argon arc welding. Tungsten tips are used as electrodes, and inert gas (argon or helium) is used to protect the weld during operation.
Initially, we will consider the components of argon arc welding, as well as the principle of its operation. The equipment consists of a welding machine with an open circuit voltage of 60-70V, a contactor for transmitting voltage to the torch, an oscillator for converting the input voltage to 2000-6000 V and increasing the current frequency to 150-500 Hz, a cooling device, non-consumable electrodes, argon cylinder, as well as a ceramic burner.
Now let’s talk about how such equipment works and how it differs from other devices. In one hand you need to take a burner with a non-consumable electrode, and in the second you take a wire. There is a special button on the torch, when pressed, gas is supplied to the welding area. Moreover, the gas supply must be carried out 10-20 seconds before the arc appears. A tungsten electrode is installed in the burner, which should not protrude more than 5 mm. Place the electrode 2 mm against the surface to be welded and turn on the machine. As a result, the arc will ignite. To obtain a weld, the welder needs to feed wire into the arc zone.
This is interesting!
The arc is ignited by placing the electrode from the surface to be welded at a distance of 2 mm, but not less.
Contact of the electrode with the surface is contraindicated. During welding, gas will escape from the torch. The advantages of the devices in question include:
- Low heating temperature, which does not contribute to deformation of the shapes of welded parts made of non-ferrous metals
- Protection of the welding zone by means of inert gas, which has a positive effect on the absence of the development of oxidative processes
- High speed of metal welding work
- Ease of operation of the devices
- The ability to connect not only two homogeneous types of non-ferrous metals, but also dissimilar ones
Among the disadvantages of the devices under consideration, experts highlight:
- Reduced quality of the weld seam if work is carried out in a draft or wind
- Complex design of welding equipment, which complicates the features of setting modes
- The need to use additional devices for cooling the arc when operating with high current
Argon arc welding can occur in four modes. The most common is the manual mode, when the welder holds the torch in one hand and the wire in the other. There is also a mechanized type, which differs from the manual one in that the wire is fed into the welding zone automatically, similar to semi-automatic devices. More advanced types of argon arc devices are automatic and robotic.
This is interesting!
Argon arc welding is used when it is necessary to work with non-ferrous metals, and especially when it is necessary to connect two dissimilar materials. In this case, the use of only argon-arc devices will be effective.
Where there is a semi-automatic machine, there is argon
Semi-automatic welding machine.
Semiautomatic machines are specialized types of welding machines for electric arc welding under the protection of inert gases. Mostly it's argon, of course. An additional option for using semi-automatic machines is wire welding: this technology does not require gas protection.
The essence of the process is the exit of the wire from the hose in the holder with the simultaneous exit of the gas mixture. During welding, the wire is in a protective gas environment; it melts under the action of an electric arc. The current and wire feed speed are adjustable.
In terms of their design, semi-automatic devices are more complex than transformers or rectifiers. But they are more convenient to use. These are the favorite devices of craftsmen in auto repair shops, especially in body repair. Semi-automatic welders are also very popular among amateur and handicraft welders.
These are the parts that make up the design of a semi-automatic machine:
- Our old friend transformer.
- Another old friend is the rectifier.
- Special drive for wire feeding.
- Cylinder with inert gas.
- Gas burner with sleeve.
We have already written above that the semi-automatic machine is capable of welding without gas protection. In this case, the protective role is played by flux-cored wire. In principle, this is the same melting wire, but thanks to the flux component, it burns with the release of a cloud of protective gas. This cloud protects the weld pool from oxidation by air no worse than external argon or other inert gas.
The functions of the flux component of the welding wire do not end there. It contains elements that add stability to the electric arc. With this wonderful “fluxing” you don’t need a gas cylinder. But flux-cored wire costs much more than regular wire.
The choice of gas depends on the nature of the metal being welded. Iron cooks well with carbon dioxide. Steel prefers a gas mixture of argon and carbon dioxide. Well, it is best to work with aluminum under the protection of pure argon.
An important factor is the “legitimacy” of gas cylinders: you need to purchase only proven and reliable copies. There can be no talk of saving money on the quality of gas and gas mixtures for welding. Anything but gas.
Semi-automatic with gas cylinder.
Advantages of semi-automatic machines:
- There is practically no spattering of metal during welding.
- The result is high quality welding seam.
- The device is quite effective - it has high efficiency.
- Ability to weld thin sheet metal.
Well, there are much fewer disadvantages:
- High consumption of materials: wire, gas mixtures.
- Considerable cost, especially for flux-cored wire.
Gas welding kit
Gas welding is the creation of heat to melt metal through the combustion of flammable gas in an oxygen environment. At high temperatures (700-3000°C), the filler wire melts and the edges of the workpieces melt. A pool of molten metal is created, which, when cooled, forms a weld.
Fig. 10 Gas welding diagram
Application area:
- connection of steel with a thickness of up to 5mm;
- fusion of non-ferrous metals and alloys;
- joining of elements made of tool steel, requiring smooth heating and slow cooling;
- Welding cast iron is a feature of the chemical structure and properties of the material itself.
Advantages
- simplicity of the technological process;
- availability of energy carrier (gas) and oxidizer (air, oxygen);
- there is no need for a third-party energy source - the combustion process is a heat-generating operation;
- easy control over the parameters of the welding process - heating time, heat flow, cutting and welding speed.
Flaws
- low heating rate of the welding zone;
- due to the wide dispersion of the gas torch, the heating zone of the part increases significantly;
- there is no possibility of narrowing the torch - there is an irrational use of heat flow;
- as the thickness of the metal increases, labor productivity decreases - time is wasted on heating the processing zone;
- the economic effect is lower compared to an electric arc connection;
- impossibility of automating the process.
Rice. 11 Typical gas equipment for welding and cutting metal
It is advisable to purchase such equipment to solve your own household problems when combined with the provision of third-party gas welding services. Otherwise, it will simply gather dust in the warehouse.
And other "small" groups
In a large array of the most popular types and types of welding units, there are highly specialized and therefore quite small types of devices that must be mentioned, otherwise our review cannot be considered complete and comprehensive.
Spot welding devices
Spot welding is a very special process that belongs to contact technologies of the thermomechanical class.
It consists of several stages. First of all, metal blanks are placed between electrodes to begin simultaneous heating and deformation through pressure. What is the point? In an instant, we will answer. Heating occurs with an instantaneous current pulse, which heats the metal to the melting point. In this way, a liquid zone of metal is formed - common to both workpieces. The current is cut off and the area begins to cool and harden with continued pressure. This pressure lasts until the metal of the workpieces is completely crystallized.
Electrode welding.
The advantages of spot welding are the strength of the seam, efficiency and ease of execution. There is only one distinguishing property of a spot seam: it is in no way airtight. Therefore, the use of point technology is limited.
Devices for gas cutting and welding
Acetylene, hydrogen, natural gas are the main flammable heroes of this method. They burn well in the air. With their help, metal workpieces are heated to the melting point. If you smell carbide near the welder, then you are dealing with the acetylene method: it is produced from calcium carbide and water. This is the most popular gas in use.
This method is easy to implement, does not require expensive equipment and, most importantly, does not require mains electricity. But there are also disadvantages: there is no talk of accuracy, work productivity also leaves much to be desired: this method is exclusively manual.
Plasma welding devices
It's more cutting than welding.
But the principle of the process is the melting of metal using a plasma flow. The fact is that plasma, at its core, is a gas of charged particles that act as excellent conductors of current. The plasma is heated by the arc, which leads to increased ionization. The temperature eventually reaches crazy values - tens of thousands of degrees. Metal cutting occurs both due to the melting of the metal and due to the washing out of the metal from the working area by an ionized flow of the highest speed.
Spot welding machine
For individual operations during the assembly of structures, this type of equipment is becoming very popular. The device has a characteristic shape: two electrodes are located in the same plane and during operation heat pre-fixed parts and deform them at the point of contact, which gave rise to the name of this class of equipment.
This happens in a split second. An electric high-frequency current pulse melts metal in a small area, without the formation of scale, burning, or overheating of the part. For this reason, assembly is often done even from parts coated with paints and varnishes.
Inverter with its own features
The most advanced and popular model of apparatus, mainly thanks to which a revolution in welding took place. Just a few years ago they were regarded as technically expensive and not very convenient exotics. This is not at all the case today: accessibility and ease of use are the main qualities of a large group of modern inverters.
Other characteristics have also been significantly improved: reduction in size, excellent arc, optimization of energy intensity and process speed, minimal metal spatter, etc.
A very important “energy” nuance: in comparison with its welding predecessors, a transformer and a rectifier, the inverter machine consumes an order of magnitude less electricity. Thanks to its compactness and light weight, there is no need to waste energy on heating massive metal parts.
Additional savings occur due to quick ignition and even, stable burning of the electric arc.
The inverter is called a pulse device. It consists of a power transformer to reduce the mains voltage, a stabilizer to convert current and a set of electrical circuits. The mains voltage is supplied to the rectifier, after which the direct current is converted into alternating current at high frequency.
Subsequently, this high-frequency alternating current goes to a transformer, where it is again converted and sent to an arc with those characteristics that are ideal for welding here and now.
The fundamental novelty of inverter technology lies in the rather complex design of the device itself, which makes it possible for sequential current conversion processes as follows:
- Alternating current is supplied from a conventional electrical network, which is immediately transformed into alternating current in the rectifier. The rectifier operates on the basis of a diode bridge.
- The direct current obtained in the rectifier is directed to the inverter part, which plays the role of a generator of high-frequency electrical pulses. In this section, power transistors convert direct current back into alternating current, but with a completely different frequency - much higher than in the original network version.
- Now the high-frequency alternating current goes to the transformer in order to lower the voltage and at the same time increase the current. The result is a high-frequency current with a strength that is perfectly regulated.
- The finishing line for AC is the rectifier, which eventually converts the high-frequency AC into DC. This is what is used for welding.
What is needed for the welding process?
To combine metals into one whole, people figured out to heat them to a very high temperature, thereby achieving the fluidity of the material. Incandescence becomes possible due to the passage of current through the conductor-electrode. But alternating voltage is not constant, so the seam may be of poor quality and uneven.
The arc is regulated by changing the current strength. Therefore, direct current would be an ideal option for obtaining a uniform and high-quality seam. It can be obtained from batteries, chemical batteries or generators. But welding machines are connected to an alternating current network, and to reduce the voltage, their design includes transformers that can regulate its value.
Alternating current from the electrical network passes through the transformer of the welding machine, which becomes constant at the output. This is enough to create an electric arc. After this, the welding process becomes possible.
Inverter classification
Inverters are divided into types depending on different criteria.
If the first characteristic of welding machines is the technology of the welding process, then the classification is as follows:
- MMA inverters for manual operation;
- for semi-automatic MIG/MAG welding;
- in an environment with protective inert gas TIG;
- for plasma welding CUT.
MMA inverters
MMA welding.
Designed for manual welding using coated electrodes. These devices are beautiful to look at, and even more pleasant to work with: compact, light weight, reliable and easy to service. The resulting seams are neat and of the highest quality in all respects.
The capabilities of MMA devices are the widest, in any case, they are quite sufficient for handicraft and home needs - all simple work can be done with such a device. Therefore, MMA type inverter devices are the most beloved and popular for work at home or in a small production area. This is certainly a reliable welding inverter and the number one technological choice for “home” tasks.
Inverters – semi-automatic
The design of semi-automatic devices is more complicated. They are much more powerful and, accordingly, have larger dimensions, and this applies to both weight and size. This is understandable, semi-automatic machines are used in production, these are not home units at all - working with them at home will be quite problematic.
The main feature of inverter-type semi-automatic machines is the same as a regular semi-automatic machine. This is welding using wire, which is fed at a certain speed by a special device into the seam formation zone.
In an inert cloud
As for welding under the protection of inert gas, it is carried out using inverters - semi-automatic machines of an even more complex type. They are quite expensive and are also intended for industrial production; these are professional welding machines.
As we already know, semi-automatic machines require additional materials and equipment. Electrodes in this technology can be of two types: consumable and non-consumable tungsten.
Inverters for plasma welding and cutting
Despite the fact that this welding machine is classified in this place, it is not at all intended for classical welding work - it simply cannot be used for welding. These inverters are used in industries. The main feature is literally apothecary precision in cutting metal parts, regardless of thickness; they can cut very thick workpieces.
Equipment and accessories
Depending on the specific equipment model, equipment may vary. However, there is a necessary minimum that must be present in each kit:
- welding machine;
- 2 welding cables (about 2 meters long);
- warranty passport;
- instructions for use.
The kit may also contain additional elements:
- welding mask;
- carrying case;
- carrying handles;
- shoulder straps;
- brush for cleaning equipment.
Accessories
To facilitate the work of the welder and subsequent maintenance of the equipment, there are various types of accessories that can be divided into several groups:
Electrodes for welding machine:
- for welding carbon and low-alloy steel;
- for surfacing;
- for welding cast iron;
- for welding non-ferrous metals;
- for cutting;
- for welding high-alloy steel;
- for welding alloyed heat-resistant steel;
- for welding dissimilar metals.
Sprays and pastes. The compositions are intended for different purposes:
- fire protection of surfaces located in close proximity to welding operations;
- protection against splash adhesion;
- non-stick protection for gas burners and others.
Supporting materials:
- welder's mirror;
- construction pencils and talc chalk holders;
- rulers and squares.
Accessories also include:
- Burners.
- Plasma cutters.
- Electric holders.
- Grounding clamps.
- Welding cables.
How inverters are divided according to their functions
Argon welding diagram.
Classification of welding equipment can be carried out according to a variety of criteria. This also applies to inverters. Functionality is perhaps the most convenient criterion for dividing a huge number of models into understandable groups.
For everyday life
A home welding machine must have certain characteristics: compact, inexpensive, with wide functions. There are a great many of these inverters. Basically, they are all made in China, which need to be treated carefully and competently. What is this approach: buy in decent retail chains, carefully read the specifications.
Even if you buy a Chinese inverter of what you think is decent quality, be prepared for the fact that the cheapness of any device leads to its fragility. This classic rule applies not only to Chinese goods.
Professional inverters
They cost more and do more. These devices are designed for operations of varying complexity; they are powerful, with adjustable welding current characteristics, durable and reliable. All of them are designed for work on an industrial scale.
Specialized inverters
The name itself speaks for itself. We have already mentioned devices for spot welding or laser technology. They also have very high quality characteristics and are also designed for production operations.
Welding unit (generator)
For work “in the field” in the absence of a stationary electrical network, products that combine several functions are used:
- welding machine;
- electricity generator.
The welding unit consists of:
- internal combustion engine (diesel or gasoline);
- fuel tank;
- generator;
- welding inverter (transformer, rectifier);
- switching and control units.
Fig.9 General view of the generator
The engine produces torque that drives the generator. The latter generates electric current;
- convertible to 220V for connecting other consumers of electrical energy (via a socket on the body);
- supplied to welding equipment to generate the necessary parameters for welding work.
pros
- complete independence from an external power source - the electrical network;
- “2 in 1” function: generating electricity for the welding machine and other consumers;
- financial savings - one unit costs less than two separately;
- The device takes up less space than two separate ones.
The main advantage is its use in places with a complete lack of electricity. This fact is very important for choosing equipment when carrying out repair or construction work in the field.
Main characteristics of inverter devices
You need to be well versed in these characteristics. They will help you both in working with the inverter and in choosing a device when purchasing it, taking into account your experience, work plans and the thickness of your wallet.
Inverter characteristics.
The parameters for an inverter type welding machine are as follows:
- Mains voltage from a standard electrical network on which the inverter can operate. Usually these are two values: 380V and 220V. For the home, choose devices that operate with a voltage of 220V.
- The type of current produced at the inverter output.
- Current parameters at start. The quality and specifications of the electrodes depend on these values. More precisely, the diameter of the electrodes.
- The power of the device, on which the strength of the welding current at the output for the welding arc will depend.
- The ease of ignition of the welding arc, which depends on the open circuit voltage.
- Electrode diameters that should be used on a specific inverter.
- The lower and upper levels of the current received at the output of the device.
- Dimensions of the device - dimensions and weight. Remember the rule: the smaller the dimensions, the lower the power of the device, the lower the output current will be. If you are interested in an inverter with wide functionality, remove the “compactness” criterion from among the very first ones.
Inverters are very modern devices. They have a number of special options that are designed to make the welder's work easier. And ease of use always leads to improved quality of the final product, which in our case is a welding seam.
It is these new functions that make highly complex welding possible for people without much professional experience.
- “Hot start” is the supply of an additional electrical charge to the electrode, which greatly facilitates the ignition of the welding arc.
- Anti-stick is an essential feature, especially for those new to welding. At the slightest sign of sticking of the electrode, the current supply to it is automatically reduced.
- “Arc force” is the automatic supply of a higher current if the electrode end is in undesirable proximity to the surfaces of the metal workpieces being welded.
Rating of the best models
To make it easier for users to choose, professionals have compiled a rating of the best models of welding machines for use at home.
Bison “Master” M 1
This unit is recommended for use for manual arc welding with fusible electrodes. The device is characterized by high ignition speed and high productivity.
Advantages:
- Safety of use.
- Low power consumption.
- Availability of protection against voltage surges.
- Does not overheat during long periods of operation.
- High quality processing.
- Easy to use.
Flaws:
- High price.
Resanta SAI-190
This is an inverter type MMA welding machine. The device is characterized by the fact that it can be used even with a voltage drop. The unit is suitable for welding both thin and thick materials.
Advantages:
- Does not overheat during long periods of operation.
- High power, which is 5500 W.
- High-quality cooling system.
- Relatively silent operation.
- Compact dimensions.
Flaws:
- No carrying case.
Caliber Micro SVI-205
This is a household inverter, which is recommended for use for simple welding work. The device provides predominantly high-quality seams, but in this case everything depends on the type of material being processed.
Advantages:
- Light weight and compact size.
- Simplicity and ease of use.
- High quality processing.
- Easy to ignite.
- High performance.
Flaws:
- Short wire.
- The wire becomes hot during operation.
Aurora Stickmate 200
This is a universal model that can be used for different types of welding. The unit is equipped with the ForceArc function, which allows you to use the device without sticking the electrodes. In addition, this option ensures high quality seams. The device has another useful additional option: Antistick. It automatically reduces the current if the need arises. In this case, all relevant parameters are saved.
Advantages:
- Simplicity and ease of use.
- Easy to ignite.
- Availability of protection against voltage surges.
- Can be used with cables up to 50 m long.
- High-quality cooling system.
Flaws:
- Heavy weight.
A welding machine is an important tool when working with metals. There are a large number of types of such units, so the user can choose the option that fully satisfies his needs.
Features of inverters
High reliability in use does not exclude technical nuances or failures that you need to know and remember about.
Welding machine.
Malfunctions encountered while working with the inverter are as follows:
- the electric arc may lose combustion stability;
- the electric arc may simply disappear;
- strong spattering of metal may begin during welding;
- the electrode may stick to the surface of the metal workpieces being connected;
- the power supply to the device may turn off spontaneously;
- The device may suddenly become very hot.
The causes of such welding troubles can be various factors. The most common are the following:
- You have chosen the “wrong” electrode: its diameter does not suit the strength of the welding current received. As a result, arc stability suffers.
- If you incorrectly calculate the strength of the welding current, the metal will begin to splash with terrible force. Reduce the current, take electrodes with a smaller diameter - that’s what needs to be done to solve the problem, it’s simple.
- A common problem is low mains voltage, as a result of which even experienced craftsmen can experience a very undesirable phenomenon in the form of electrode sticking. The same picture will be given by too long electrical wires, which, due to their length, will certainly begin to overheat. Try to control both the length of the wires and the diameter of their cross-section - it should be at least 2.5 mm².
- A cable break is a primitive error, but nevertheless it occurs quite often. Incomplete contact between the surfaces of the electrode and the clamping device belongs to the same group of reasons for the disappearance of the welding arc.
- Excessive overheating of the device may occur due to prolonged use of the inverter without interruption. This situation is natural. If overheating occurs after a short period of operation, you need to check and replace the winding - most likely, it is worn out.
Malfunctions and repairs
Common malfunctions and breakdowns depend on the specific type of welding machine.
Malfunctions of welding transformers.
Poor contact in the terminal block to which the welding cables are connected. Leads to strong heating of the connection, destruction of insulation and short circuit. Eliminated by sorting out the heating connection, stripping the contact group and clamping them for tighter contact.
Spontaneous shutdown of equipment. Occurs immediately after the device is connected to the network due to protection activation. Probable causes are a short circuit in the high voltage circuit between the turns of the coils, as well as a malfunction of the capacitors. To repair, you must disconnect the device from the network and eliminate the defect by restoring the insulation or replacing the capacitors.
Excessive transformer hum. Often accompanied by overheating. The probable cause is loose bolts or overload of the transformer. Also, humming occurs due to a short circuit between cables or sheets of magnetic circuit.
The device gets very hot. Most often occurs due to exceeding the permissible load level.
The stated current and electrode diameter limits must be observed.
Otherwise, the equipment may be damaged.
Lack of welding current. Occurs due to low mains voltage or breakdown of the current regulator.
Consumes a large amount of current without load. The reason is the short circuit of the winding turns. Insulation needs to be restored. For the same reason, a sudden break in the welding arc is possible without the possibility of its recovery.
Malfunctions of welding inverters.
Transistor burnout. It is considered the weak point of inverters. In the event of equipment failure, it is the transistors that must be checked first. To check them you need to use a multimeter.
Damage to driver elements. Checked using an ohmmeter. If necessary, faulty elements can be replaced with suitable analogues.
Defective input and output rectifiers.
Control board faulty. The most complex piece of equipment. Performance is checked using an oscilloscope.
Arc instability. Occurs due to incorrect current setting.
Device overheating. Probable causes are long-term operation under heavy load, failure of the cooling system, or contamination of the board.
It is quite possible to repair transformers with your own hands. Welding inverters have a more complex design, and to repair them it is necessary not only to have the appropriate equipment, but also to have special knowledge and skills.
It should be remembered that repair and maintenance of welding equipment can cause serious harm to health. If you lack the necessary knowledge and experience for these purposes, it is better to turn to professionals.
How to choose a welding machine for your home
Versatility, compactness, light weight, ease of use, inexpensive price - this is the kind of welding machine you want to have at home as your own unit. Most buyers of home welding machines opt for inverter models.
This fact does not mean at all that transformers or rectifiers have stopped being purchased. And there are reasons for this. Let's figure out which welding machine is best for you “here and now”. The types of welding equipment are extremely diverse, so we make a choice taking into account all personal needs.
Choosing a home transformer:
- The most important thing you need to pay attention to when choosing a welding transformer for home work is the operating voltage of the step-down transformer. They are able to operate from a network with two characteristics: either three-phase or single-phase with values of 380/220V. There are universal use models that can connect to any type of network: 220V, three-phase network, phase voltage between two phases.
- The next most important parameter is the power of the transformer. In this regard, devices operating from a network with a voltage of 380V are optimal; they are much more powerful and almost do not cause voltage imbalances in the network. But not all consumers of home welding machines have the ability to connect to a three-phase network. It should be remembered that the power of the transformer cannot be higher than the maximum permissible power in your home network.
- The third criterion for choosing a transformer is the operating current parameters and the diameter of the required electrodes. If you are going to weld carbon steel, the range from 80A to 160A will be enough for you; choose electrodes from 1 to 6 mm. The final choice of electrode depends on the thickness of the edges of the metal workpieces.
- Well, the dimensions of the unit. As we know, transformers have very impressive ones. But this impressiveness should only concern you if you are going to move for welding work. Are you sure you will do this at home?
If you need a rectifier:
- Welding rectifiers require pulsed rectified current, then they make it possible to weld with a stable arc and without metal spattering. In addition, when used correctly, they save the consumption of expensive electrodes. The rectified current contributes to the formation of an even and thin weld seam.
- Requirements and wishes for mains current and voltage are almost the same as with transformers. They can operate with both types of alternating current; they are switched on either a single-phase bridge circuit or a three-phase one. A three-phase circuit is preferable when using a rectifier: with it the arc is more stable and the power is higher. Therefore, you should focus on connecting to a three-phase network of 380V.
- We check and evaluate the principle of adjusting welding modes, the diameter of the required electrodes, the upper and lower levels of welding currents.
Gas cutting and welding of parts - advantages of equipment
A separate type of welding equipment is gas. The principle of connecting parts is based on the fact that the metal melts with a high-temperature flame. To create a gas arc, through which metal melts, the following types of gases are used - hydrogen, natural gas, acetylene.
Why are these particular types of gases used? After all, they have the property of burning in air. The most popular type of gas is acetylene, which is produced by using calcium carbide with water. Gas combustion occurs while maintaining the temperature between 3200 and 3400 degrees Celsius.
The operating principle of gas welding equipment is based on supplying an open flame of combustible gas to the parts being connected. Due to the high combustion temperature of the gas, melting of metal workpieces is achieved. To adjust the flame, the holder has adjusting screws. The principle of operation of the device is similar to a gas burner or blowtorch, only a thin arc with a high heating temperature comes out of the holder through the nozzle.
The components of gas welding are:
- Cylinder with propane or other types of gases
- Oxygen cylinder acting as a catalyst
- Connecting hoses
- Gas cutting or holder, consisting of bronze, two valves, calibrated nozzle
- Ignition is carried out using a special piezoelectric element
The advantages of using the equipment in question include the following points:
- Simple design consisting of a gas cylinder and holder
- No need to connect equipment to the electrical network
- Ease of use
- The ability to not only connect parts, but also cut them
Unlike electrical devices, gas welding equipment is not capable of providing high speed work. In addition, the work is performed exclusively manually. As a rule, welding using gas is carried out mainly by specialists. The equipment cannot be called mobile, since gas cylinders are quite heavy and large.
Or is it still an inverter?
Of course, it contains all the wishes of a home welder: the widest functionality, various welding modes - everything for a person’s happiness. This type of welding equipment is extremely popular among the general public. The price, however, is high. But according to many, this game is truly worth the trouble.
What do we pay attention to when choosing it for home?
- The main criterion is also the voltage of the electrical network, these are the same 220V and 380V. And just as in previous cases, three-phase inverter models are more powerful. And its durability and service life depend on the power of the device. After all, the more power, the less the device overheats.
- The next criterion is the characteristics of currents and welding modes. Their choice will depend on only one thing - the thickness of the metal workpieces being welded. On the Internet you can find a lot of data on the dependence of the diameter of welding electrodes in millimeters on the value of the welding current in amperes. Typically, a current from 60A to 160A is sufficient for a home inverter. In addition, the ability to smoothly regulate the current value will allow you to further improve the quality of the weld.
- Another important factor that must be taken into account when choosing an inverter is mandatory. This is the duration of the PV switch-on, which shows the operating time of the device without interruption at maximum current values. Sometimes this indicator is called LO - load duration. The higher the on-time, the longer the inverter can operate without overheating. In general, the PV can be calculated based on the net welding time in relation to pauses for changing the electrode or preparing materials. If, for example, the inverter specification indicates a duty cycle of 80%, then the net time of the welding process will last exactly 4 minutes. Then you will have to pause for 1 minute.
- The next criterion is always indicated in the device passport - inverter power. This line indicates the level of rated welding current, when used, the inverter will not spontaneously turn off due to overheating. It is better to choose power with a reserve: if the need for rated current is 120A, choose a device with an indicator of 180A. This reserve will allow you to use long electrical cables and, most importantly, you will be able to work during power surges from the general network.
- DPN stands for “supply voltage range”. This parameter makes voltage drops of 20–30%, which are common in rural areas, painless.
- The best welding inverters are equipped with proprietary additional options that make the work of a novice welder easier, and should be especially important for you if you are a novice in welding. We are talking about AP - anti-stick, GS - hot start, FD - arc afterburner. Whether they are meaningful to you with your current experience is up to you and only you to decide.
As a summary, let's go through the main ideas of our review. The classification of welding machines is a harmonious and understandable system that will perfectly help you decide which welding machine will be the most optimal for your work at home.
There are few criteria determining the choice. If you take them into account, you will succeed: you will find a device that will suit you in terms of design complexity, breadth of functions, and cost.
We wish you a successful trip to the store, a competent salesperson and good assistants nearby.
Selecting a welder
Of course, you first need to decide for what (what kind of work) you will need welding equipment. And, based on this, select its functionality.
There are 3 groups of welders:
- Household. These are models powered from a 220V home outlet with a current of 160A. Such a device is capable of welding parts 0.5-6 mm. Suitable for use in a home workshop, garden or garage. Suitable for moderate use and medium welding speed.
- Semi-professional. The current strength of such devices is higher than that of household ones (from 200 to 300A). But they can also be powered from a household outlet or from a three-phase panel. Capable of welding and cutting metal of almost any thickness.
- Professional. Powerful tools that use current in excess of 300A, suitable for working with low-alloy and low-carbon parts.
For amateurs, weak models are suitable for everyday welding work.
An important criterion that you need to pay attention to is the time operating interval of the device (or the frequency of switching on).
For your information. For home work, you should not buy a device with high frequency. Practice shows that 80% is preparation (moving parts, replacing electrodes, cleaning scale and carbon deposits) and only 20% is welding itself. In addition, it is impossible to cook for hours without a break. The electrode burns out in a matter of minutes.
Polarity and voltage for operation can be different
Welding current
Welders work with alternating, direct or alternating and direct current. Variable, this is the home electrical network. It is characterized by a change in polarity, where “+” is replaced by “-” with a frequency of 50 Hz. There is no pole, so the welder cannot be connected incorrectly. Used for welding and cutting ferrous metals. The main disadvantage of this type of welding is the abundant splashing of molten metal drops due to the rapid change of polarities.
You might be interested in Measuring current with a multimeter
Direct current has a fixed direction. But it is necessary to ensure that the working equipment is connected correctly. However, the quality of the weld is noticeably better than with alternating current due to less spatter. This type of welding is used for non-ferrous metals and stainless steel. The production process of such welders is much more expensive due to the use of rectifiers in the design.
For your information. Welders using direct and alternating current are universal. The most expensive, but used for welding and cutting any metals.
Do not apply more than 100V to the electrode
Open circuit voltage
This voltage is called the EMF applied to the electrode. It is measured with the device turned on and not working (at idle speed). Denoted as Uxx. The unit of measurement is Volts (V). This value allows you to estimate how easily the welded arc will ignite and what its stability is. It must be remembered that this is a “double” quantity. On the one hand, the higher the voltage, the easier the ignition. The arc is more elastic, and the welding itself is more uniform. On the other hand, limiting the idle voltage is a requirement for operator safety. As a result, the lowest indicator is determined to be 40V, and the maximum is not higher than 100V.
The quality of the power source is important for a welder.
Supply voltage
The voltage is:
- Single-phase. Where there is one pair of contacts “0” and “phase” with a voltage of 220 V. It can be powered directly from a home outlet. Thanks to this, it has become widespread (sometimes, with more powerful equipment, it is better to power it directly from the distribution panel to avoid additional loads on the household electrical network).
- Three-phase. Where there are already three “phase” contacts and one grounding contact (aka “0”). The voltage is much higher and is 380V. This is already production equipment, the use of which in everyday life is difficult.
- Single-phase/three-phase. The device can use both 220V and 380V, depending on its purpose. One of the indicators of the voltage used will be the main one.
The power source for welding of any type is characterized by:
- ease of arc ignition;
- ability to ensure continuous combustion;
- control the upper value of the short circuit current;
- ensure electrical safety.
The dimensions of the steel sheet to be welded depend on the maximum amperage
Maximum current operating mode
When choosing a welder, the maximum current indicator is selected based on the thickness of the products with which you plan to work. It is measured in Amperes (indicated by Imax) and for home use a unit with characteristics of 160-180A is quite sufficient (processing metals up to 1 cm). If you plan (at least sometimes) to work with thicker metal, you can choose a model with parameters of 200A. There are special tips that clearly demonstrate the relationship between the current strength and the size of the metal part.
Table 1 Welding parameters
| Diameter of electrodes, mm. | Metal thickness, mm. | Welding current, A. |
| 1.5 mm | 1.2 - 2.0 mm | 30 - 75 A |
| 2.0 mm | 1.5 - 3.0 mm | 40 - 100 A |
| 2.5 mm | 1.5 - 5.0 mm | 50 - 120 A |
| 3.0 mm | 2.0 - 12.0 mm | 100 - 150 A |
| 4.0 mm | 4.0 - 20, mm | 120 - 200 A |
| 5.0 mm | 10 - 40 mm | 170 - 270 A |
Welding parameters must be selected according to the table