A DC-DC converter or voltage inverter is a device that converts direct current of lower voltage into alternating current of higher voltage or vice versa. Such devices are variable voltage generators. It can be pulsed, pure or modified sinusoidal. Inverter converters are capable of acting as independent power sources and intermediate elements in the converter system.
Inverters contained in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) provide a stable supply of electricity to computer equipment and other equipment. In the event of an unexpected power outage, they instantly supply computers with electricity from the backup battery. This makes it possible to save data and shut down the PC correctly.
Large UPS systems use powerful inverters with larger battery capacity. They can provide autonomous power to equipment for a long time, and when normal network power supply is restored, they switch the equipment to it.
History of the appearance of the converter
In the late 1800s, American pioneer electrician Thomas Edison (1847−1931) left his laboratory to demonstrate that direct current (DC) was a better way of delivering electricity than alternating current (AC), which was the new system supported his Serbian rival Nikola Tesla (1856−1943). Edison tried all sorts of clever ways to convince people that AC was too dangerous, from electrocleaning an elephant to advocating the use of AC in the electric chair to control capital punishment. Regardless, Tesla's system won the day, and the world has been running pretty much on the grid ever since.
The only problem is that while many of our appliances are designed to operate with alternating current, low-power generators often produce direct current. This means that if you want to run something like an AC powered gadget from a DC battery in a mobile home, you will need a device that converts the DC to an AC inverter, as it is called.
Technical capabilities of inverter devices
Any inverter, being a welding machine, serves to ignite the welding arc and maintain its combustion in a stable state. Due to the features of its design, the inverter device copes with this task perfectly. In addition to the main function, modern inverter models are equipped with a number of additional options that make their use as convenient and comfortable as possible. These include:
- “Hot start” (this option allows you to ignite the welding arc faster, which is achieved by applying an additional electrical pulse to the electrode);
- “Arc force” (this function assumes that when the electrode suddenly approaches the surface of the parts being welded, the welding current automatically increases, which prevents the electrode from sticking in such a situation);
- “Anti-sticking” (this option works as follows: when the electrode sticks, the electric current stops flowing to it; it starts flowing only when the electrode is torn off from the surface of the parts being connected).
Front panel of the welding inverter "BIMark-170"
Some models of inverter devices are also equipped with overheating indicators and an automatic shutdown option if overheating does occur. This useful function protects such an expensive device as an inverter from burning out and, as a result, from costly repairs.
The additional options described above are especially useful for novice welders, as they help minimize the impact of a specialist’s skill level on the quality of welding.
Electricity DC and AC
When science teachers explain the basic idea of electricity as the flow of electrons, they usually talk about direct current (DC). We learn that electrons are a bit like a line of ants, walking along with packets of electrical energy in the same way that ants carry leaves. This is a pretty good analogy for something like a basic flashlight, where we have a circuit (a solid electrical loop) connecting a battery, a lamp, and a switch, and electrical energy is systematically transported from the battery to the lamp until all the battery's energy is depleted.
In larger appliances, electricity works differently. The power source, which comes from a wall outlet, is based on alternating current (AC), where the electricity switches between 50 and 60 times per second (in other words, at a frequency of 50 and 60 Hz). It's hard to understand how AC delivers energy when it's constantly changing its mind about where it's going. If the electrons coming out of the wall socket travel, say, a few millimeters down the cable, then they need to reverse the direction and go back, just like how do they ever get to the lamp on the table to make it light up?
The answer is actually quite simple. Imagine that the space between the lamp and the wall is filled with electrons. When you flip the switch , all the electrons filling the cable vibrate back and forth in the lamp filaments - and this rapid shuffling converts electrical energy into heat and lights the lamp. Electrons do not necessarily have to rotate in a circle to transfer energy: in AS they simply “run in place.”
Inverter UPS
The vast majority of electrical appliances in Russia that modern people use every day are designed for a voltage of 220V-230V.
Chemical voltage sources, batteries capable of storing a charge of electricity for a long time, provide a constant voltage that is too low to power household appliances: 2 volts, 6 volts, 12V, etc. Inverters convert direct voltage from batteries into alternating voltage 220V or 230V, depending on the design and settings. The work of all UPSs is based on this!
Video what is an inverter uninterruptible power supply and how it works
The battery life of the uninterruptible power supply will be proportional to the number and capacity of the batteries connected to the inverter input. But there are other factors that affect the operating time - you can read more here.
Batteries can store a supply of electrical energy for a long time, which allows you to keep a large amount of accumulated electricity in reserve for emergency situations, accumulated in the battery.
If there is a loss of electricity at the input to the distribution board, the inverter automation will instantly transfer the power of the electrical appliances connected to the inverter output to the battery (through an electronic circuit that converts a direct voltage of 12 Volts into an alternating voltage of 220 V with a given frequency (Hz)).
There is no switching in online systems - You can read more here.
The main advantages of electric inverters:
- This is environmental safety (no harmful environmental pollution)
- Low noise during operation, have a low noise level of the cooling fan several times compared to power plants...
- They do not require refueling or constant maintenance.
- They have high efficiency and low operating costs, tied to the cost of electricity.
- Continuous power supply, no pause (as in power plants) when switching to batteries.
- Possibility to increase battery life by increasing the number of batteries.
Main applications of inverters:
1) UPS for boilers (UPS for gas boilers)
2) UPS for pumps (UPS for long standby time)
3) Uninterruptible power supply for alarm and video surveillance systems (UPS for alarm and video surveillance systems)
Application example in a private home:
Consider the ECOVOLT PRO 1012 model.
A load power of 1000 W with a parameter value of cos = 0.8 allows you to connect electrical equipment with a total power of 1 kW.
An approximate calculation of the load power could be as follows:
- Gas boiler with piping – 300 W.
- Circulation pump 70 W,
- Emergency lighting – 300 W,
- TV – 200 W
(power values of electrical appliances may differ from those given here; exact values can be obtained from the equipment passport).
What is an inverter
One of the legacies of Tesla (and his business partner George Westinghouse, boss of the Westinghouse Electrical Company) is that most of the appliances we have in our homes are specifically designed to run on AC power. Appliances that require DC current but draw power from an AC outlet require an additional piece of equipment called a rectifier, typically made of electronic components called diodes, to convert AC to DC.
An inverter does the opposite job, and it's pretty easy to understand. Let's say you have a battery in a flashlight and the switch is closed, so the DC flows through the circuit always in the same direction as the race car around the track. Now, if you take the battery out and turn it around, assuming it's the other way, it will almost certainly still produce light and you won't notice any difference in the light you get - but the electrical current will flow in the opposite way.
Let's say you had lightning-fast hands and they were dexterous enough to turn the battery over 50-60 times per second. Then you would become a kind of mechanical inverter , turning the battery's DC power into AC power at a frequency of 50-60 Hz.
Of course, that's not how the inverters you buy at electrical stores work, although some are truly mechanical: they use electromagnetic switches that quickly switch to the current direction. Inverters like this often produce what's called a square-wave output: current either flows one way or the other way around, or it switches instantly between the two states.
Such sudden changes in direction are dangerous for some types of electrical equipment. At normal AC power, it gradually changes from one side to the other in the form of a sine wave.
Electronic inverters can be used to create this kind of smoothly varying AC output from a DC input. They use electronic components called inductors and capacitors to increase and decrease the output current than the sharp, square wave on/off output you get with a basic inverter.
Inverters can also be used with transformers to change a certain DC input voltage to a completely different AC output voltage (higher or lower), but the output power must always be less than the input power. The law of conservation of energy implies that an inverter and transformer cannot supply more energy than they consume, and some energy must be lost as heat as electricity flows through various electrical and electronic components. In practice, inverter efficiency often exceeds 90 percent, although basic physics tells us that some energy - whatever it is - is always lost somewhere.
How does an inverter-type welding machine work?
Due to its technical characteristics, the inverter can be used to perform welding with various types of electrodes. This device is distinguished by its compact size and light weight, which makes it very mobile, unlike heavy and large transformers. It is also convenient that such a welder can generate both direct and alternating current.
In order to understand what advantages an inverter has, you need to understand how it works. The operation of this device, which began to gain mass popularity only at the beginning of the 21st century, is based on a completely different principle compared to the operation of a conventional welding transformer.
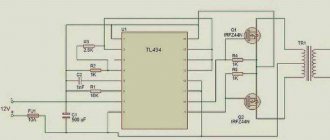
Schematic diagram of the welding inverter "Duga-200" (click to enlarge)
The alternating current supplied to the inverter from a regular electrical network is first rectified by passing through a diode bridge, which is equipped with the electrical circuit of the device. After rectification, the direct current is supplied to power transistors, which convert it back into alternating current, but with an increased frequency. To reduce the voltage of high-frequency alternating current and obtain the welding current of the required strength, a transformer is used in the electrical circuit of the inverter.
Since the voltage reduction of high-frequency current is not carried out according to the same principle as in a conventional welding machine, there is no need to use large transformers for this; a compact device is quite sufficient. After reducing the voltage and increasing the current to the required value, it is supplied to the output rectifier, in which it is converted to constant.
Inverter controls using the example of the Fast and the Furious device (click to enlarge)
The use of high-frequency current generated by the inverter not only makes it possible to significantly reduce the dimensions of the device, but also has a positive effect on the combustion process of the welding arc, which is highly stable. Such a welding machine is characterized by high efficiency, since it does not waste energy on heating the transformer iron.
Simplified diagram of the operation of a welding inverter
Thus, any inverter device consists of such structural elements as:
- a rectifier assembled on the basis of a diode bridge (this electrical circuit block is responsible for rectifying the alternating current coming from the electrical network);
- the inverter itself, which is a generator of high-frequency electrical pulses (the basis of this unit is made up of transistors that open and close at high frequencies);
- a step-down transformer, which solves the problem of lowering the high-frequency voltage and, accordingly, increasing the welding current;
- high-frequency output current rectifier (such a rectifier, like the input unit, is assembled on the basis of a diode bridge);
- a special electronic unit designed to control the operating modes of the inverter apparatus.
How the device works
Imagine being a DC battery and someone taps you on the shoulder and asks you to produce an AC battery instead. How would you do it? If all the current you produce flows in one direction, how about adding a simple switch to your output? Turning your current on and off can very quickly provide DC pulses that could do at least half the work. To make a proper AC , you will need a switch that allows you to completely cancel the current and do this about 50-60 times per second. Visualize yourself as a human battery, changing contacts back and forth more than 3,000 times per minute.
Essentially, an old-fashioned mechanical inverter boils down to a switching box connected to a transformer. And since electromagnetic devices that change low-voltage alternating current to high-voltage current or vice versa, using two coils of wire (called primary and secondary) wound around a common iron core.
In a mechanical inverter , either an electric motor or some other automatic switching mechanism reverses the incoming current back and forth basically simply by changing the contacts and generates an AC in secondary mode. The switching device works in the same way as in an electric doorbell. When power is connected, it magnetizes the switch, pulls it out, and turns it off very quickly. The spring will push the switch back, turning it on, and then repeat the process over and over again.
The switching frequency is set by control signals generated by the control circuit (controller). The controller can also solve additional tasks:
- Voltage regulation.
- Synchronization of key switching frequency.
- Protecting them from overloads.
Pulse width modulation
This algorithm for the operation of semiconductor switches, in contrast to the previous algorithm, forms a pause of a certain duration, which ultimately leads to a decrease in the effective value of un. To form a sinusoidal shape, pulse-width modulation PWM is used. We will consider the converter with PWM, or rather the algorithm of its operation, which includes PWM, separately.
It should also be noted that the considered algorithm for controlling semiconductor switches is called pulse-width WID control, which is often confused with PWM, although the difference is huge.
In converter technology, PWM has practically replaced WID, since it has a number of positive properties that increase the efficiency of the entire device and reduce the level of electromagnetic interference. Therefore, in the future we will consider a voltage inverter with PWM.
Material
Different materials can be used to make the converter housing:
- Aluminum.
- Steel.
- Plastic.
There are also combined options (aluminum with plastic and steel with plastic).
The aluminum case provides passive cooling better than others. Steel products have increased strength. The plastic version is only suitable for low-power inverters.
Expert opinion
Kuznetsov Vasily Stepanovich
Regardless of the housing material and type of cooling, the inverter should only be installed in an open space to ensure unimpeded heat dissipation.
Popular models
A lot of inverter models are produced in our country. They can be used both in industrial production and in domestic conditions. The following are considered popular:
- AIRLINE API-150−01 - the permissible power threshold of the device is 150 W. The case is made of durable plastic that can withstand high temperatures. The car inverter is connected from the cigarette lighter, which is located in the passenger compartment. You can connect several electrical appliances to this device, the total power of which is no more than 150 W. The device is protected against short circuits and surges in incoming voltage.
- Jet A JA-P11 - if there is no electrical power network nearby, then this device will help out in any situation. The maximum power of the device is about 300 W. There is protection against low supply voltage, overheating and overload.
- Titan HW-150E1 150 W - makes it possible to use electrical appliances up to 150 W. It is connected from the car cigarette lighter and the output voltage is 220-240 V. The weight of the device does not exceed 0.5 kg, which makes it very convenient on long trips.
Using stabilizers
Some inverter models are equipped with built-in stabilizers. This device allows you to maintain a constant voltage level in the network. This feature is useful, but the built-in options are usually limited. In addition, reliability is not always up to par. If there is no connection to the city power grid, you should not use an inverter with a built-in stabilizer, since diesel generators usually do not have sufficient power reserve. To achieve this, you will have to buy the most expensive equipment.
Price
The most significant impact on the cost of the converter is its power.
There are three main price segments:
- Initial . This includes low-power devices (up to 200 W) for powering small appliances. Plugs into the cigarette lighter. They produce a modified sine wave. Cost – up to 1400 rubles.
- Average . Inverters with a power of up to 800 W with a modified sine wave. Connects directly to the battery. Cost – 1400 – 5000 rubles.
- Supreme . Powerful devices (up to 5 kW) with modified or pure sine wave. Cost – from 5000 rub.
Additional protection
A modern inverter must have short circuit protection. It installs a safety device against accidental exposure to outside interference, especially when it comes to children.
Overload protection must be triggered in a timely manner to prevent overheating of the wiring and subsequent fire. The protection unit protects the converter from short circuits and high input voltage. For this purpose, there are indicators that show the state of the electrical network.
Additional sensors and installed voltmeters will help identify the corresponding malfunction. System temperature indicators located on the cooling radiator will allow you to control the fan when the readings exceed the permissible value.
In what areas is a 12-220 V voltage inverter used?
With stable use of the battery, its charge level gradually decreases. The converter stabilizes the voltage if there is no electricity.
A 12-220 V inverter, made by yourself, will allow you to improve engineering structures in any room. The power value of devices that convert current is selected according to the total values of the operated loads. Power consumption processes can be reactive or active. Reactive loads do not fully consume the amount of energy received, causing the apparent power value to be greater than its active value.
Pure sine wave inverters are used when connecting an element whose total power is 3 kW. Significant fuel savings are ensured by the use of voltage converters and mini-power plants.
The following consumers are connected to the inverter design:
- alarm system;
- boiler;
- pumping apparatus;
- computer system.