Product advantages
Essentially, threaded rivets are hybrids of traditional nuts. But they should not be confused with exhaust vents. They have advantages, including:
- ease of installation work;
- you can reliably connect components made from fragile materials or those that have insignificant thickness (rolled sheet metal), because the rivet nut will not lead to deformation;
- if the total thickness of the products exceeds the length of the fasteners, then a one-sided fixation is made, without a through passage, and the quality of work will not be low.
Reliability of connections is achieved due to the threads located on the inside of the nuts, and on the outside of the bolts.
Types of threaded rivets
The range is quite wide, there are many classifications of fasteners. Thus, they can have a flat or countersunk head, a nut or screw thread, a round or hexagonal leg (does not allow rotation in the mounting sockets). If you take into account the purpose, then there may be:
- electrically conductive;
- having increased force (possibly indentation or stretching);
- for highly hermetic connections;
- with enlarged heads;
- with inch thread application;
- with special marks (for visual identification);
- with vibration isolation.
This list can be continued, but it is worth noting that the domestic industry produces a wide variety of rivets for different cases.
Materials used for production
The fasteners in question may have different sides. To get regular connections, buy nuts that have standard flanges. If you need to get a slight gap between the parts, it is better to use hardware with reduced or hidden sides. It is worth considering that before installation begins, the procedure of countersinking the holes into which the rivets will be placed is performed.
Threaded rivet nuts can be produced from several types of metal, in particular:
- Carbon steel. For the production of universal products and the creation of standard connections.
- Made of stainless steel. Production of hardware that will be used at high temperatures or in places with high humidity levels.
- Made of aluminum. Such rivets are distinguished by their low weight and excellent anti-corrosion properties.
- Made of bronze. This metal is used if fasteners with low spark generation rates are needed.
In some cases, neoprene polymer may be used. Products made from it are called self-installing, because installation work does not require riveting tools.
Types of rivets
For each type of rivet tool, only the same types of rivet fasteners are suitable.
Exhaust
A fastener that consists of two main parts. The first part is a hollow cylinder (rivet body) with through holes on both sides, and a shoulder (rivet head) on one side.
The body of the rivet is made of easily deformable metal. The diameter of the cylinder is the size of the fastening material. The second part is the rod (rivet core), twice as long as the rivet body itself. Made from high strength steel. The core extends through the entire body of the rivet and has a seal at one end called the shank head. The diameter of the rod head is slightly larger than the diameter of the rivet body. In appearance, the rivet shank resembles a nail.
Depending on their purpose, blind rivet fasteners are of the following types:
- Countersunk - the junction has a flat surface;
- Regular with collar - standard and most commonly used;
- Conventional ones with a large collar are used when connecting two materials of different softness.
- The enlarged collar allows the clamping force to be more evenly distributed on the joint surface and does not cause deformation of the material;
- Sealed rivets with gas-watertight housing. The name speaks for itself - used for airtight and watertight connections.
Threaded
However, like an exhaust hood, it consists of a hollow cylinder made of soft metal. There is a metric thread inside the body. Some types have a corrugated surface on the outside and on the shoulder. According to the shape of the body, rivet fasteners are divided into: round, hexagonal, corrugated.
A threaded rivet connects very thin materials where a pull-out fastening material would not provide a strong connection and resistance to vibration. This type of riveting is also used in places that are difficult to reach - ventilation and air conditioning systems, medical furniture, automotive parts and shelving.
The body of pull-out and threaded rivet fasteners is made of soft metals - copper, aluminum, an alloy of aluminum and silicon. The rods of the exhaust fastening material are made only of steel. The rivets are coated with zinc as protection against corrosion. If the parts are intended to be used in an aggressive external environment, then the rivets are made of stainless steel
Features of installation work
When you use mechanical special tools, significant physical effort will be required to obtain truly reliable connections of structural elements. The fact is that rivet nuts significantly counteract the tightening forces. A pneumatic riveter significantly simplifies the task , but its cost remains high.
If you have a special mechanical or pneumatic-hydraulic tool available, the installation process will be very simple:
- screwing the nuts directly onto the threaded rods in the riveter;
- the tool together with the hardware is turned until it stops in the hole made;
- the rod of the device is carefully pulled out, after which the fasteners are riveted independently;
- unscrewing the rod from ready-made connections.
Rivet nuts
At the ProfKrepezh company you can wholesale rivet nuts (rivet nuts, threaded rivets, rivet nuts).
The nut rivet is one of the new fastening elements, which has gained popularity and is widely used for its ease of installation, for its convenience and reliability when used in components of steel structures.
A nut rivet is a cylindrical, half-hexagonal or hexagonal body with an internal metric thread.
Purpose of a nut rivet
— to create a threaded detachable connection, one that can be easily disassembled and reassembled without disturbing the structure or its components (detachable connections include, for example, bolted, screwed, pinned, screwed, keyed);
- for use in components of steel structures, products for construction and general machine-building purposes, automotive industry, food industry, electrical industry.
Normative documents
A nut rivet is a cylindrical, half-hexagonal or hexagonal body with an internal thread for metric dimensions.
Threaded nut rivets should not be confused with blind rivets. Blind rivets are used to create a permanent connection!!!
The reason for such variety in names can be explained by the lack of GOST, ISO or DIN standard for nut rivets.
TU 1680-001-10702513-2019
Installation
It is made with a special tool - a riveter, which is used to install the rivet into a hole in the structure that is pre-drilled or punched with special equipment.
For reliable fastening, it is important to correctly make the mounting hole for the required type and size of rivet in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations
Particular attention should be paid to the thickness of the structural part into which the installation is being made. This is necessary for the correct expansion of the rivet (forming a “skirt” on the reverse side)
There are 2 rivet lengths: first and second length. The difference is in the range of thicknesses - smaller and larger.
The resulting deformed part (“skirt”) should be pressed tightly against the part, without gaps or distortions.
Next, a threaded rod or a regular bolt with a metric thread is screwed into the installed rivet with the required tightening torque, which directly holds the fastened parts of the structure together.
Advantages
Some of the main advantages of nut rivets are:
no need to further use: traditional bolts with a nut (especially an inconvenient option if there is difficulty in accessing the back side of the supporting structure - “blind” installation) or the use of welding, which requires the skills of a highly qualified specialist.
during installation, the pre-treated surface of the part is not damaged if it is coated or painted.
The result is a neat, aesthetic fastening point that provides a reliable connection, convenient and quick installation and dismantling of the attached structural element.
Rivet nut materials
Carbon structural steel with galvanic zinc coating for use in non-aggressive and slightly aggressive environments.
Corrosion-resistant (stainless) steel - alloy steel with a high content of chromium (at least 12%) and nickel for use in non-aggressive, slightly aggressive, moderately aggressive and highly aggressive environments.
Connection of profiled sheets
In principle, profiled sheets can be used anywhere. There are no strict restrictions as such. The main condition is the correct choice of product type and appropriate dimensions. One more nuance must be taken into account: you should definitely pay attention to such fastening elements if you plan to fasten structures, after completion of work with which access to their reverse side will be completely closed or very difficult.
For example, when working with a power (signal) cabinet, it will not be easy to dismantle the panel if the nuts screwed onto the screws turn.
Internal threads provide the opportunity to connect thin sheets of metal and steel, because the use of ordinary hardware will not give the desired result. Durability depends entirely on the parameters of the external sections. The larger the size of the fastener, the higher the reliability and strength. To connect parts whose thickness exceeds 4 mm, it is advisable to use rivets with M10 threads, 1-3 mm - M6, M8, up to 1 mm - M3.
Installation process
The algorithm for installing a threaded element can hardly be called overwhelming, but it is important to know certain nuances. If possible, it is better to use a factory riveter. If desired, you can assemble it yourself; one option will be discussed below. The first step is to determine the type of metal on which the rivet will be installed. Next, you need to know what the diameter of the bolt or module that will be fixed thanks to this rivet is. According to the specified diameter, the appropriate rivet is selected. Its outer diameter is measured and a drill is selected that will be one tenth in diameter larger than the rivet. This is necessary so that the latter fits into place without much effort or obstacles.
Electric or cordless drill. The metal is drilled in the required location. After this, the fastening element is inserted into the seat. If it needs to be placed in a certain position, then it is better to hold it with your hands. For hexagonal holes, you can use special punches if we are talking about thin metal. If the thickness of the metal is greater than the length of the fastener, then the hole must be drilled a little deeper than the fastener, but there is no need to make a through penetration. After this, a rivet maker core is selected that fits the thread to the element being installed. The handles are brought together or the bolt is rotated so that part of the rivet is deformed and fixed in the hole.
You should not apply too much force, as you can tear off the thread, which will later be used to fix the required part. It is necessary to ensure that the rivet is installed in the required position. After this, you can fix the required product using a screw or bolt.
DIY riveter
If the installation of threaded elements is required due to duty or work, then it makes sense to purchase a factory product that operates by hand force or based on a pneumatic mechanism. In most situations, the installation of such rivets is rarely required, so you can assemble the rivet gun yourself.
Bolt based
To assemble the entire structure, you will need a bolt similar to the one shown in the photo above. It can be taken from the crankshaft of a car engine. The diameter of the bolt must be such that a hole can be drilled inside it through which another bolt with a thread size that will match that used in the rivet will be inserted. The length of the second bolt must be at least 100 mm. The length of its thread should be as long as possible; if necessary, it can be additionally trimmed with a parallel tool.
Additionally, you will need a nut that will screw freely onto the thread of a bolt with a large diameter, as well as a collapsible bearing. The inner diameter of the bearing must be such that a long bolt, which will be used for clamping, can freely pass through it. The design is quite simple to assemble. To do this, you need to insert a long bolt inside a larger one in diameter. A nut is screwed onto the large bolt, and a collapsible bearing is placed onto the threads of the long bolt.
A rivet is screwed onto the long bolt and must be installed in the hole. You will need two keys to operate. One of them will hold the nut, and the second should rotate the bolt. You can simplify the task by welding a handle to the nut. The bolt rotates until the stop becomes significant. You shouldn't be too zealous. Once the result is achieved, you need to unscrew the long bolt. The bearing in this case is a stabilizer that prevents the bolt from biting inside the structure. There is a video about this riveter below.
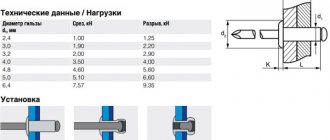
Dimensions
The selection of the optimal dimensions of a threaded rivet depends on several important factors. These include the type of hardware product, as well as the total thickness of the fastened elements of a particular structure. With the same thread parameters, the length will be determined by the type of fastener.
It is important to consider that most models are available in two versions - normal (standard) and extended. For example, a typical stainless steel rivet may have the following dimensions:
- Thread – from M4 to M10.
- Length – from 11 to 24 mm.
- The diameter of the rivet and hole is from 6 to 13 mm.
- The diameter of the collar is from 9 to 17 mm.
At the stage of selecting rivets, it is strongly recommended to use the corresponding tables, which indicate all their key parameters. Now you can easily find all the necessary information on specialized resources.