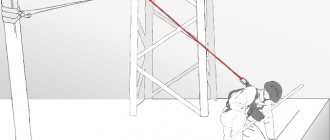
Workers falling from heights and falling objects when working at heights are one of the leading causes of serious injury or fatality in the workplace. Therefore, it is extremely important to be able to correctly select the necessary models of personal protective equipment against falls from a height and correctly assemble them into full-fledged safety systems.
In Russia, there are several documents that describe personal protection systems against falls from a height (safety systems). This is order 155 N dated March 28, 2014 on the approval of the Rules on labor protection when working at height (as amended on December 20, 2022)
and
GOST R 58208-2018/EN 363:2008 “System of occupational safety standards (SSBT).
Personal protective equipment against falls from height. Personal fall protection systems. General technical requirements" . It is worth noting that the Rules are a mandatory document for compliance by the employer and employee, while GOST is more of an advisory nature, however, the recommendations and examples given in the standard are based on generally accepted practice in the use of personal fall protection systems. We will focus on both documents, since the standard is a more recent document, and many points are described in more detail.
Here are some excerpts from the Labor Safety Rules when working at height, where requirements or descriptions of safety systems for working at height are found:
- clause 48: If it is impossible to use protective fences, it is allowed to work at height using safety systems.
- clause 86: Systems for ensuring the safety of work at height are divided into the following types:
- restraining systems - positioning systems - safety systems - rescue and evacuation systems. — rope access systems are distinguished separately.- clause 87: Systems for ensuring safety of work at height must:
a) correspond to the existing conditions in the workplace, the nature and type of work performed; b) take into account the ergonomic requirements and health status of the employee; c) after the necessary adjustment, correspond to the gender, height and size of the employee.- clause 88: Safety systems for working at height are designed:
a) to hold a worker in such a way that a fall from a height is prevented (retention or positioning systems); b) to safely stop a fall (safety system) and reduce the severity of the consequences of stopping a fall; c) for rescue and evacuation.- clause 89: The employer, in accordance with standard standards for issuing PPE and based on the results of an assessment of working conditions, provides the employee with a system for ensuring the safety of work at height, combining compatible PPE against falls from a height as elements, components or subsystems.
- clause 98: Safety systems for working at height consist of:
a) anchor device; b) harness (safety, for holding, for positioning, for sitting); c) connecting and shock-absorbing subsystem (slings, ropes, carabiners, shock absorbers, retractable type protection device, slider type fall protection device on a flexible or rigid anchor line).
When connecting components to form a personal fall protection system, the following aspects should be considered, among other things:
- suitability of the components for their intended use in the system, taking into account all phases of use (e.g. reaching a working position, working process);
- features of the workplace (for example, the tilt of the workplace, the location of the anchor device);
- characteristics of the user for whom the system is intended (for example, his qualifications);
- compatibility of components (for example, interaction of anchor devices with other components);
- ergonomic considerations (eg, proper selection of harness or attachment device to minimize discomfort and stress on the body).
Let's look at each system in more detail.
Who should be assigned to work at height groups?
From the beginning of this year, groups of work at height are required to be assigned to all workers for whom there is a significant risk of falling from a height of over 1.8 meters, regardless of whether they use stationary, suspended, portable scaffolding or not, since in the new edition of the rules this the division was removed. It is also important to note that when reading the rules on working at height, it is necessary to pay attention to other labor protection rules. For example, in the new rules on labor protection in river and sea transport, there is no concept of a height of 1.8 meters; there is an important condition that “there are risks of falling.”
It is important for the employer to completely eliminate the need to carry out work at height, and if this is not possible, production tasks with a significant risk of people falling require the management of the enterprise to carry out a number of occupational safety measures:
- provide all high-rise work sites with barriers at least 1.1 meters high;
- When carrying out work at height, use reliable scaffolding and scaffolding, hanging cradles, various machines and lifting mechanisms;
- provide people with effective PPE.
An assessment of occupational risks for high-altitude workers should be carried out immediately after the new rules come into force and the new data should be immediately introduced into the organization’s OSH documentation. It should be understood that the employer is now required to conduct a risk assessment, including when working at height. Although there is still no uniform methodology for assessing professional risks in the country, this provision is enshrined in Article 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is important to note that in POTS there is a clear division into work with a high risk of falling from a height, as well as similar work with a low risk. This is exactly what the employer must determine, since he is responsible for the completeness and quality of the risk assessment.
The employer has the right to independently develop additional safety rules when working at height (if they do not conflict with the new occupational safety requirements) and bring them to the knowledge of employees in the form of oral briefings and written instructions. He also has the right to make video and audio recordings of the work process to resolve controversial situations, and to maintain electronic document flow in the company.
PPR is at its best according to the new rules
According to the new rules, high-altitude activities must be accompanied by the preparation of a work performance plan (WPP). The contents of this document are regulated by Appendix No. 6 of POTRV. It indicates all the features of the construction site, the schedule for the supply of materials, the movement of personnel around the territory, technological maps, safety measures, information about protective equipment and insurance, and much more. Simply put, this is a clear instruction when working at height according to the new rules, valid at a specific enterprise for a specific workplace.
The development of PPR at altitude is carried out by the organization itself or the services of third-party organizations with appropriate qualifications are used.
The manager is obliged to appoint an official responsible for approving the work plan and monitoring its implementation. The new rules also stipulate that the PPR must be located directly at the construction site.
What types of work at height require a permit?
For production tasks associated with a high risk of employee falls, it is necessary to issue a work permit, which indicates references to the current PPR or Labor Code.
A person responsible for safety at a high-altitude facility is appointed, who conducts safety briefings for working at height with each member of the team. He also carries out preliminary preparation of work sites, admission of employees, issuance of PPE approved in the OHSMS and documentation of all work performed in a log.
The mandatory requirement to appoint a responsible person for work at height appeared in the new rules of 2022.
Tolerance groups for work at height
In the new edition of the labor protection rules, workers who are allowed to perform work at height with a work permit are divided into three groups.
Group 1 – ordinary team members working under the supervision of a foreman or as part of a group.
Group 2 – foremen and foremen.
Group 3 includes:
- superintendent of works at height;
- employee issuing and servicing personal protective equipment;
- OT specialist;
- an employee who issues permits for work at height;
- a person obliged to ensure the urgent evacuation of workers in case of unforeseen situations;
- instructors teaching work at height;
- persons taking the qualifying examination;
- other people who have access to high-altitude work sites.
Representatives of the third group are allowed to work at height only if they have the necessary qualifications. But for this, in accordance with the new rules introduced in 2022, they are required to additionally obtain a group 1 or 2 certificate. Qualification must be confirmed every 3 years.
Training to perform work at height
Persons receiving permission to perform any work at height are required to have not only theoretical, but also practical skills to carry it out correctly and safely. The labor protection rules introduced in 2022 made it unacceptable to obtain qualifications remotely or by correspondence, in the form of self-study without an experienced instructor.
Assigning access groups is impossible within an enterprise or organization; this is done by certified training centers. High-altitude training is carried out by specialists who have Group 2 access to such work and practical experience of at least a year.
High-quality training with practical exercises is very important, because if an accident occurs, after which a person is killed or seriously injured, the statistics of his training will be taken into account in the investigation. In case of poor quality training, responsibility is transferred from the employer to the center.
Permission to carry out work at heights in adverse weather conditions
Since 2022, permission has appeared for work at heights, which were previously prohibited:
- in low visibility due to rain, snow, fog;
- in open areas with strong wind speeds above 15 m/s;
- in case of ice, icing of building and other structures, wires;
- on “sailing” structures with wind force over 10 m/s.
Naturally, work at height in conditions of increased danger is carried out in case of emergency, with a permit, preliminary instructions and under the control of the person responsible for safety. Management is obliged to implement all necessary measures to reduce the risk of workers falling, since it is the manager who is responsible for such work.
Harness requirements
Let us remind you that high-rise work includes any kind of work performed at a height of over two meters - construction and steeplejack without support (at a height of over five meters), installation and roofing work, lowering and ascent, etc. Mandatory requirements for a personal safety harness include:
- Technical requirements regulated by GOST R EN 361-2008 standards: composition of single- or multi-fiber synthetic materials, their tensile strength, compatibility of woven tape and sewing threads with the fabric of slings and belts.
- To visually control the integrity, the woven tapes and sewing threads that provide the connection are made in contrast to the base color of the straps.
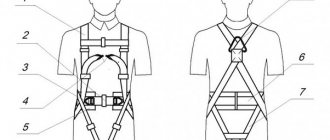
- A safety harness is a design with the obligatory presence of straps in the hip and shoulder areas (not to be confused with a mounting belt, which does not have such structural elements).
- The harness must be able to adjust the straps according to the volume of the body - only correct and tight fixation of the system on the body will prevent serious injury in the event of an emergency.
- The fixation of the straps must be absolutely reliable, excluding the possibility of arbitrary loosening.
- The width of the basic straps should be at least 4 cm, and the auxiliary ones – at least 2 cm: this will prevent the straps from cutting into the muscle tissue in the event of a sudden stop during a high-altitude fall.
- The harness must be made of a material that can withstand a weight significantly greater than the weight of a person, while the structure itself should not be heavy - polyamide is often used as such a material.
- Convenience and ease of use of the harness, a correctly adjusted size will allow a person to easily prepare for work and navigate, if necessary, in a difficult situation.
Only the exact fulfillment of these requirements can ensure high-quality work that is optimal in terms of time and labor costs, and, possibly, save human lives.
Certification of PPE and collective safety systems for work at height
This year's new rules regulate the mandatory certification of anchor devices, which was not the case before. Other requirements for safety equipment and systems:
- Safety helmets must be securely attached to the head in the correct position;
- the force that the safety harness transmits to a falling person cannot exceed 6 kN;
- minimum load for elements of safety systems with a retractor – 12 kN;
- elements of safety systems when working at height must cope with a static load of at least 15 kN, and their synthetic slings - at least 22 kN;
- PPE that prevents falls should not come apart spontaneously, allow a person to fall, or injure his back in any position, even unnatural ones;
- PPE that prevents falls must withstand the dynamic load from a load weighing 100 kg when it falls from different heights: 1, 2 and 4 meters;
- the carbine cannot open spontaneously or injure hands while working at height;
- the materials of the connecting components must be protected from corrosion and cannot touch the human body, excluding his hands.
Personal rescue devices (PRDs) are required by regulations to achieve maximum effectiveness when used by any user on any construction site. At any time, they must ensure a smooth descent at a speed of no higher than 2 m/s, without rotation or jamming. MIS are not reused.
Positioning system
A work positioning system is a personal fall protection system that allows the user to work in a position in which he or she is supported by the elements of the system.
When is it used?
It is used in cases where the worker has support for his feet, but to maintain balance he needs to hold onto the support with his hands. The positioning system allows you to free your hands to perform work, keeping the worker in a comfortable supported position. Typically, when performing work, all components of the positioning system are loaded by the worker and have no slack.
Restrictions
Can only be used in conjunction with a safety harness.
As with the use of a fall arrest system, consideration must be given to the type of work being performed and the use of suitable lanyards and harnesses. For example, when performing hot work, use slings and harnesses made of non-flammable materials.
Layout examples
Using a positioning lanyard installed around the support
Components:
- Combined harness (with positioning capability)
- Lanyard with length adjuster
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Convenient location in the work area. Disadvantages:
It is necessary to monitor the integrity of the sling and, if necessary, install protectors. The support surface may be sharp. Inability to move vertically.
Using a positioning lanyard installed at one end
Components:
- Combined harness (with positioning capability)
- Lanyard with length adjuster
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Convenient location in the work area. Possibility of adjusting the working position in height. Disadvantages:
Less mobility in the horizontal plane.
New labor safety requirements for the evacuation and rescue plan for injured workers
An action plan in case of accidents, manifestations of occupational diseases, accidents or other emergency situations associated with high-altitude work must be developed and prescribed in the enterprise's occupational safety management system. It includes the following mandatory items:
- Rules and algorithms by which decisions are made to stop or resume work at height.
- Ways to urgently contact emergency services and the work manager.
- The location of a safe shelter for evacuated people, the path to it.
- Means for rescuing victims, including in the event of a fall from a height. Their locations and methods of use.
- Paths for ascent or descent of victims when working at height.
- Providing medical care to the wounded.
Permission to use power tools on portable ladders
If in previous years this type of work at height with pneumatic, electric or other tools with moving parts was prohibited, then the new labor protection rules allowed it, but with the following reservations:
- a work manager responsible for their safety is appointed;
- PPR is being developed;
- an outfit is issued for all team members;
- Before starting work at height, instructions are provided;
- the measures listed in the PPR are applied to reduce the danger of working at height.
What is a safety harness?
A safety harness, necessary to fully ensure the safety of even highly qualified high-altitude specialists, is an individual element of insurance. Reliable coverage of the body and fixation of a person in the event of a possible fall are ensured by durable slings, adjustable straps and reliable fastening buckles. The leg and shoulder straps tightly secure the person's body and do not allow him to slip out of the safety system, no matter what position he finds himself in. However, it should be remembered: a safety harness is not an absolute guarantor of human safety - methods for protecting human life and health must be used comprehensively, safety requirements must be strictly observed, and the specialist’s qualifications must be of a high level.
The safety harness can be used not only for professional high-altitude work of any kind (installation, fire fighting, emergency response, etc.), but also for hiking, rock climbing and mountaineering. The main function of safety equipment is both to prevent unauthorized descent and to stop a person from falling from a height.
Other changes
- According to the new rules, wooden stairs must now undergo safety tests every six months, metal ones - at least once a year. After checking, a date stamp is placed on the stepladder and this data is entered into the protocol. The specialist responsible for labor protection in the organization is obliged to check the maintenance of records in different departments.
- There should not be more than two people in the hanging cradle at the same time. It is also prohibited to combine two cradles into one during work at heights, to use barrels as ballast, or to perform production tasks in low visibility conditions or in strong winds with a speed of more than 10 m/s. The enterprise's occupational safety specialist is obliged to make these changes to the labor protection instructions and conduct training at the workplace.
- In places where people climb onto scaffolding or scaffolding, the slope of the stairs cannot be more than 75 degrees to the horizontal, and the slope of the ladder cannot be more than 1/3.
Making changes to the enterprise's OSMS
After the new changes come into force, occupational safety specialists are expected to finalize all the necessary documentation, and this must be done in a short time. Part of the production processes associated with work at height now require the presence of PPR or TC; an assessment of professional risks when performing certain tasks may also be required.
If the risks of falling and causing significant injury are great enough, management may decide to train a group of employees to improve their skills. Internships are carried out in specialized centers.
After making amendments to the occupational safety documentation, the occupational safety specialist must instruct the personnel on site. A set of new measures may also be required to reduce the danger of working at height.
Harness testing
Whatever the level of professionalism of the person using the harness, before directly using the harness, you should study the instructions from the manufacturer, conduct a thorough inspection of the equipment, check the characteristics, and conduct practical tests.
The frequency of scheduled checks of the harness is regulated by GOST requirements; before each use it must undergo a visual inspection. If there are damaged areas, incompatibility of components and structural elements, or the potential for any of the buckles to self-unlock, use of the harness is prohibited.
Each unit of the safety product must be accompanied by instructions defining the procedure for preparing, checking and using the harness. The general rules are:
- Before use, the harness is put on: the belt is located at the waist, the leg loops and shoulder straps are located on the corresponding parts of the body.
- The position of the dorsal point is adjusted and the shoulder straps are tightened.
- The shoulder straps are connected to the belt using buckles and carabiners.
- The safety harness is tested under the conditions specified by the manufacturer: it is important to observe the recommended temperature conditions and exclude the possibility of damage to individual components and elements by chemically aggressive substances and sharp objects.
Safety equipment is stored in dry rooms, protected from direct sunlight, with air that is non-aggressive in composition and without obvious dust contamination. During storage, it is necessary to exclude the presence of harnesses near heating devices, flammable and chemically aggressive substances (gasoline, kerosene, acids, etc.), which can lead to changes in the properties and characteristics of equipment materials. Only natural drying of products free of contaminants is allowed. After completion of the warranty period, the product is taken out of service and destroyed so that third parties cannot accidentally use it.