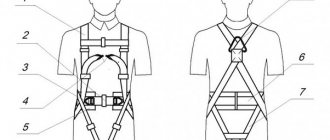
Workers falling from heights and falling objects when working at heights are one of the leading causes of serious injury or fatality in the workplace. Therefore, it is extremely important to be able to correctly select the necessary models of personal protective equipment against falls from a height and correctly assemble them into full-fledged safety systems.
In Russia, there are several documents that describe personal protection systems against falls from a height (safety systems). This is order 155 N dated March 28, 2014 on the approval of the Rules on labor protection when working at height (as amended on December 20, 2022)
and
GOST R 58208-2018/EN 363:2008 “System of occupational safety standards (SSBT).
Personal protective equipment against falls from height. Personal fall protection systems. General technical requirements" . It is worth noting that the Rules are a mandatory document for compliance by the employer and employee, while GOST is more of an advisory nature, however, the recommendations and examples given in the standard are based on generally accepted practice in the use of personal fall protection systems. We will focus on both documents, since the standard is a more recent document, and many points are described in more detail.
Here are some excerpts from the Labor Safety Rules when working at height, where requirements or descriptions of safety systems for working at height are found:
- clause 48: If it is impossible to use protective fences, it is allowed to work at height using safety systems.
- clause 86: Systems for ensuring the safety of work at height are divided into the following types:
- restraining systems - positioning systems - safety systems - rescue and evacuation systems. — rope access systems are distinguished separately.- clause 87: Systems for ensuring safety of work at height must:
a) correspond to the existing conditions in the workplace, the nature and type of work performed; b) take into account the ergonomic requirements and health status of the employee; c) after the necessary adjustment, correspond to the gender, height and size of the employee.- clause 88: Safety systems for working at height are designed:
a) to hold a worker in such a way that a fall from a height is prevented (retention or positioning systems); b) to safely stop a fall (safety system) and reduce the severity of the consequences of stopping a fall; c) for rescue and evacuation.- clause 89: The employer, in accordance with standard standards for issuing PPE and based on the results of an assessment of working conditions, provides the employee with a system for ensuring the safety of work at height, combining compatible PPE against falls from a height as elements, components or subsystems.
- clause 98: Safety systems for working at height consist of:
a) anchor device; b) harness (safety, for holding, for positioning, for sitting); c) connecting and shock-absorbing subsystem (slings, ropes, carabiners, shock absorbers, retractable type protection device, slider type fall protection device on a flexible or rigid anchor line).
When connecting components to form a personal fall protection system, the following aspects should be considered, among other things:
- suitability of the components for their intended use in the system, taking into account all phases of use (e.g. reaching a working position, working process);
- features of the workplace (for example, the tilt of the workplace, the location of the anchor device);
- characteristics of the user for whom the system is intended (for example, his qualifications);
- compatibility of components (for example, interaction of anchor devices with other components);
- ergonomic considerations (eg, proper selection of harness or attachment device to minimize discomfort and stress on the body).
Let's look at each system in more detail.
Restraint system
A restraint system is a personal fall protection system that prevents falls from heights by limiting the user's range of motion.
In restraint systems, the loads are insignificant, and any suitable harnesses (safety harnesses, for a sitting position, etc.) can act as components. Both safety and restraint lanyards can be used to connect the worker's harness to the anchor device. The use of slings with a length adjuster simplifies the organization of the system.
When is it used?
In the risk management hierarchy, priority is given to preventing a fall. Therefore, the use of a restraint system is always preferable to the use of a fall arrest system.
In many cases, when the amount of free space under the work site is minimal (low building height, running machinery, etc.), a restraint system may be the only option available.
It is important to remember that the restraint system is not designed to support the worker's body and therefore should not be used when working on sloped surfaces or vertical supports.
Unlike a safety system, a restraint system does not involve complex plans for the rescue and evacuation of the victim, since a fall is impossible.
Restrictions
At first glance, this type of security system is the simplest, but organizing such a system often requires complex preparation. The holding system is extremely difficult to organize on roofs of complex shapes with many bends. When organizing a restraint system, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a worker getting on fragile and fragile surfaces, in areas with open hatches, openings, etc. When organizing work on the corner of the roof, the worker should be kept from falling to any side by using two or more slings of the restraint system.
Layout examples
Using a fixed length lanyard:
Components:
- Safety harness
- Sling without shock absorber
- Temporary horizontal anchor line
Advantages:
Easy to use.
Disadvantages:
Requires suitable elements to install the anchor device at the required distance from the work area.
Safety system
A fall arrest system is a personal fall protection system that stops a fall and limits the force on the user's body to stop the fall.
Only safety (or combined) harnesses are used, in which there is an element for connection marked A (or two elements marked A/2). The use of belts in fall arrest systems is strictly prohibited due to the risk of injury or death from impact on the worker's spine when stopping a fall, or the worker falling out of the safety belt. Safety systems must include an energy-absorbing component (the Occupational Safety and Health Regulations for Working at Height indicate that a shock absorber is required), which reduces the fall energy transmitted to the worker to 6 kN.
When is it used?
Safety systems are used when there is a risk of falling below the support point of a worker who has lost contact with the supporting surface, and when it is impossible to eliminate or minimize this risk in other ways (for example, installing collective protective equipment).
The safety system must eliminate not only the risk of the worker hitting the ground, but also structural elements, mechanisms, etc. After a fall, the worker must be kept in an upright position.
When using a safety system, it is necessary to consider a plan for evacuating the employee from the suspended state.
Restrictions
The main limitation to the use of a fall arrest system is the available space under the worker. Depending on the components of the fall arrest system, up to 6 meters of headroom under the worker may be required to safely stop a fall. The distance of free space under the user is calculated based on the location of the anchor device, the height of the worker, the length of the shock absorber opening, etc.
In addition, when organizing a safety system, one should take into account the possible pendulum effect (if the anchor device is located away from the worker), various sharp edges of the support (damage to personal protective equipment during a fall), and the tools used (damage to textile personal protective equipment during hot work).
Layout examples
Using a double leg lanyard:
Components:
- Safety harness
- Double shoulder lanyard with shock absorber and anchor carabiners at the end
Advantages:
Easy to assemble and low cost.
Disadvantages:
Requires a large supply of free space under the user (large fall depth). Depending on the sling model, a minimum of 4-6 meters is required. Can only be used on supports with horizontal elements corresponding to the opening width of the carabiners on the sling. Slow movement of the worker. Highly qualified worker is required (admission group 2).
Using retractable PPE attached to the worker:
Components:
- Safety harness
- Double-arm retractable PPE with anchor carabiners at the ends and an integrated shock absorber
Advantages:
Easy to assemble.
Allows you to significantly reduce the depth of the fall, thanks to the automatic retraction of the lanyard. Disadvantages:
Can only be used on structures with suitable parts size for installing an anchor carabiner. Not all models are suitable for use with fall factor 2, or when falling over an inflection point. Slow movement of the worker. A highly qualified worker is required. (2nd admission group).
Using a clamp on a vertical flexible anchor line
Components:
- Safety harness
- Slider type clamp with integrated shock absorber
- Flexible anchor line fixed to an anchor device
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Small depth of the worker's fall. Does not require highly qualified workers. Higher travel speed. Disadvantages:
Pre-installation of the GAL is required, which requires additional time and additional PPE.
Using a clamp on a vertical rigid anchor line
Components:
- Safety harness
- Slider type clamp with integrated shock absorber
- Rigid anchor line
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Small depth of the worker's fall. Does not require highly qualified workers. Extremely high speed of access to the work area and descent from the workplace. Does not require preparation before use. Disadvantages:
High installation cost.
Using retractable type PPE mounted on a support
Components:
- Safety harness
- Retractable PPE
- Anchor device (horizontal anchor line)
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Small depth of the worker's fall. Does not require highly qualified workers. Extremely high speed of access to the work area and descent from the workplace. Ability to work over a large area (long length) along a horizontal anchor line. Disadvantages:
High installation cost.
General requirements
All harnesses must fully comply with accepted standards. For their manufacture, a material is selected that can withstand large mechanical loads exceeding the weight of the person working at height. At the same time, the product itself should be light.
Regardless of the type of harness, they are made of contrasting materials. For example, the threads should be clearly visible on the straps so that it is possible to visually monitor the condition of the loops and promptly identify defects in the integrity of the structure.
Additionally, the harness must be adjustable and tailored to the individual worker’s body shape. The fastenings of the product are made in such a way that the possibility of spontaneous weakening of the straps and safety belt is excluded.
Positioning system
A work positioning system is a personal fall protection system that allows the user to work in a position in which he or she is supported by the elements of the system.
When is it used?
It is used in cases where the worker has support for his feet, but to maintain balance he needs to hold onto the support with his hands. The positioning system allows you to free your hands to perform work, keeping the worker in a comfortable supported position. Typically, when performing work, all components of the positioning system are loaded by the worker and have no slack.
Restrictions
Can only be used in conjunction with a safety harness.
As with the use of a fall arrest system, consideration must be given to the type of work being performed and the use of suitable lanyards and harnesses. For example, when performing hot work, use slings and harnesses made of non-flammable materials.
Layout examples
Using a positioning lanyard installed around the support
Components:
- Combined harness (with positioning capability)
- Lanyard with length adjuster
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Convenient location in the work area. Disadvantages:
It is necessary to monitor the integrity of the sling and, if necessary, install protectors. The support surface may be sharp. Inability to move vertically.
Using a positioning lanyard installed at one end
Components:
- Combined harness (with positioning capability)
- Lanyard with length adjuster
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Ease of use.
Convenient location in the work area. Possibility of adjusting the working position in height. Disadvantages:
Less mobility in the horizontal plane.
"Height 016" "Vento"
In seventh place is the safety model “Height 016” “Vento”. It is produced in Russia. Has an average price.
The model includes five attachment points that allow it to be used as a safety, restraint and positioning harness. The product is complemented by a wide sash. The design ensures uniform distribution of the load on the waist and leg girths. It is possible to integrate a working seat. Product weight – 1.6 kg.
Pros:
- Suitable for working in unsupported spaces.
- LED strips.
- Large belt range – 70-130 cm.
- Complies with GOST.
- Withstands loads up to 150 kg.
- Material – polyamide, steel.
Minuses:
- None.
Rescue and evacuation system
A rescue system is a personal fall protection system that allows a worker to save himself or other workers.
Before performing any work at height, it is necessary to think through a rescue plan and prepare additional PPE for evacuation. Rescue and evacuation systems may include both PPE already used by workers and additional devices. If the evacuation requires the use of the same anchor devices as those used for the work, then they must be designed for a higher load.
In evacuation systems, knives or other cutting tools should not be used to cut the worker’s connecting and shock-absorbing subsystem!
When is it used?
In accordance with paragraph 108 of the Labor Safety Rules when working at height, in order to reduce the risk of injury to a worker who remains in the safety system after stopping a fall in a suspended state, the evacuation plan must include measures and means (for example, self-rescue systems) that allow (no more than 10 minutes) free the employee from being stuck. Evacuation is also carried out in cases where an employee cannot independently descend from the workplace or ascend to the surface (when working in tanks, mines, wells) due to poor health, injury, etc., or when standard descent routes are not available. Also, evacuation systems must be provided at all workplaces above 5 meters if standard escape routes from the workplace can be blocked (fire, smoke, etc.).
Layout examples
Using a pulley and lowering device
Components:
- Safety harness
- Pull block, lowering device, flexible anchor line
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Ease of use.
A 4:1 multiplier pulley makes it easy to relieve the victim’s connection and shock-absorbing system. Can be used by 1 worker. Disadvantages:
Often, access to the victim and connection of the end of the HAL to the harness is difficult. Application is possible only if there are no obstacles on the descent path.
Using a pre-installed evacuation system
Components:
- Safety harness
- Flexible anchor line, lowering device
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Very fast evacuation of the victim.
Does not require the installation of additional devices after the emergency station, the ability to immediately evacuate the employee. Disadvantages:
A large length of the GAL is required (usually 3 support lengths). Rapid evacuation is only possible if the employee did not use an additional positioning system.
Use of specialized devices such as Vento Sapsan and Tractel Derope UP
Components:
- Safety harness
- Evacuation device
- Anchor device
Advantages:
Automatic control of the victim's descent speed.
Possibility of lifting and lowering the victim on one device. Possibility of evacuation of the victim with escort. Disadvantages:
High cost of the device. Factory limited depth of descent (the rope is installed at the factory). Difficulty in replacing components when worn out.