June 8, 2022
Today, the market offers a large selection of steel pipes used in different areas of life. Steel pipes are durable, wear-resistant and have a long service life. This is why steel is the best material for making pipes.
There are several approaches to classifying pipes. For example, according to the cross-sectional shape, they are round, oval, square, rectangular, teardrop-shaped and arbitrary shapes. According to the method of processing the ends, a distinction is made between threaded, cone-shaped, edge-planted and specially processed pipes.
During manufacturing, pipes are connected in different ways: seamless, with a straight seam, and with a spiral seam. The manufacturing technology of the pipe itself also differs . It can be deformed, pressed, forged, rolled or centrifugally cast. Depending on the chosen manufacturing method, hot or cold temperature molding can be used.
Pipes also differ in the quality of surface treatment . They come in ground, polished, turned, and galvanized for rust protection. Pipes are also divided according to the area of application: for general purposes, special, main, target, with special properties and made of stainless steel.
When choosing a pipe, you need to consider the grade of steel from which it is made. Experts distinguish several types of steel: boiling, semi-calm and calm. Boiling steel is considered the lowest quality material. Due to gas bubbles dissolved in it, the finished pipe may be partially deformed. Calm steel is very high quality and reliable. Products made from it are expensive, but in serious production it is irreplaceable. Semi-quiet steel is considered to be the golden mean, as it has good characteristics and an affordable price.
Classification of steel pipes
All steel pipes can be classified according to certain parameters.
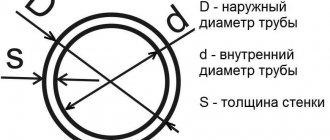
Pipe diameters are divided into:
- Small from 5-102 mm;
- Medium from 102-426 mm;
- Large – from 426 mm.
Also, when choosing products, you need to determine the throughput indicator, determined by the diameter of the pipe and the thickness of the walls.
Steel pipes can also be classified according to the following characteristics:
- Materials used to create the alloy;
- Cross-sectional shape;
- Dimensions;
- Connection technology;
- Method of performing insulation.
Galvanizing of steel pipes is carried out to maintain a sufficiently high resistance to corrosion.
There are two types of such products:
- Suture.
- Seamless.
Steel pipes can be classified according to the specifics of their manufacture:
- Galvanized;
- Hot rolled;
- Profile;
- Welded;
- Cold rolled;
- Cold drawn.
Installation of pipe structures involves certain difficulties due to the large mass of the constituent elements.
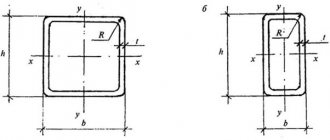
According to their cross-sectional shape, steel pipes are divided into:
- Square;
- Polygonal;
- Round;
- Rectangular.
Depending on the shape, the products are connected to each other using special couplings, welding or regular threads.
During the use of pipe structures, the quality characteristics of the materials gradually deteriorate and constantly lose capacity due to narrowing of the lumen. Steel pipes are also a good conductor of electric current. If there are problems with the electrical wiring, the likelihood of electric shock increases. The service life of steel pipes is approximately 25 years.
Features and Specifications
Steel water pipelines have the following characteristics. Some positive aspects have already been partially discussed above, but not everything is so rosy with this pipe rolling range.
It also has negative characteristics:
- Corrosive formations. Unfortunately, steel is susceptible to this effect. And the water supply system feels this with particular acuteness. In it, moisture is constantly combined with atmospheric oxygen. Such a combination is simply destructive for steel.
- Decrease in lumen over time. Such a highway tends to become overgrown over time. Her clearance can catastrophically decrease in just a couple of years.
- Labor-intensive installation and dismantling. Speaking about a steel pipeline, we must immediately make a reservation that assembling it is more difficult than tightening several nuts on fittings of a metal-plastic structure, or welding polypropylene pieces with a small welder. Connecting a steel water pipe will require the participation of a professional welder.
- Impressive weight. This characteristic feature of steel water supply pipe materials greatly complicates transportation and installation.
IMPORTANT! Steel networks can be protected from such a significant drawback as corrosion by priming and painting.
Advantages and disadvantages of equipped steel pipelines
Steel pipes have the following main performance characteristics:
- High strength;
- Corrosion resistance;
- Possibility of use under high operating pressure;
- A wide range of products differing in diameter and thickness of the metal layer;
- Resistance to temperatures up to 130 C˚;
- Sufficiently high thermal conductivity;
- The pipeline can be used for heating systems due to its low linear expansion;
- The operational period of pipe structures ranges from 5 to 15 years.
The possible duration of use of products can be increased due to high-quality anti-corrosion coating. Such performance characteristics make it possible to use steel products as materials for equipment for oil pipelines, gas pipelines, and water supply systems operating under high pressure conditions.
You should also take into account the disadvantages of pipe structures:
- Abrasive wear;
- Insufficient resistance to low temperatures;
- Relatively high roughness index;
- Steel pipelines are among the heaviest;
- Installing a pipeline requires a lot of effort and the use of special equipment;
- Since the material is very hard, in order to branch the network it is necessary to install specially made branches.
To prevent the lines from freezing, it is necessary to use good insulation.
What are the GOST standards for steel pipes?
The list of technical indicators of any type of steel pipe directly depends on which manufacturing method was used. All this is determined using GOST standards, knowledge of which will at least make it possible to take into account recommendations for the operation of a certain type of pipe.
Currently, the following regulatory documents for the production of steel pipes are most often used:
- GOST 30732-2006 . It was adopted in 2006: its provisions apply to pipes and fittings made of steel coated with a heat-insulating layer. Steel products that use polyurethane foam thermal insulation and a polyethylene shell, or a protective steel coating, are used in cases where it is necessary to lay underground heating networks. The coolant temperature should not exceed 140 degrees (an increase to 150 degrees is allowed only for a short time). In this case, the pressure in the system should not exceed 1.6 MPa.
- GOST 2591-2006 (88) . GOST, designed for hot-rolled steel, was adopted in 2006, although some sources allow the use of the old GOST - 2591-81. The document contains information relating to square rolled steel, for the production of which the “hot” method was used. This GOST applies to all products with side dimensions from 6 to 200 mm. Larger square pipes are produced if the manufacturer and the customer draw up a separate agreement.
- GOST 9567-75 . It specifies precision steel pipes for which high manufacturing precision is required. There are cold-formed and hot-rolled precision pipes of galvanized or chrome-plated type. The engineering industry especially needs the products of this increased GOST standard.
- GOST 52079-2003 . This document specifies standards for longitudinally welded and spiral-welded steel pipes with a diameter of 114 - 1420 mm. Main gas pipelines and pipelines through which oil and petroleum products are transported are constructed from such dimensional products. GOST 52079-2003 indicates that only products that are not corrosive can be transmitted through these pipes. Using steel pipes with large diameters, it is possible to transport substances with pressures of up to 9.8 MPa. The minimum temperature for the environment is -60 degrees. It is important to know that officially GOST 52079-2003 is no longer valid: from January 1, 2015, the new GOST 31447-2012 is in force.
- GOST 12336-66 . Its provisions concern closed products of a profile type, with a cross-section in the form of a square or rectangle. Starting from January 1, 1981, the powers of GOST 12336-66 were transferred to TU 14-2-361-79, but the relevance of its provisions has not been lost to this day.
- GOST 10705-91 (80) . Contains a list of technical conditions under which straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter from 10 to 630 mm are produced. To produce pipes according to this GOST, carbon or low-alloy steel is used. These products are used in many areas, but the priority is pipelines for pumping water. The provisions of the standard do not apply to steel pipes from which electric heaters are made.
- GOST 10706 76 (91) . Applies to straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes that have a general purpose. As follows from this document, the diameter of these products ranges from 426 to 1620 mm.
- GOST 10707 80 . Here are the standards according to which electric-welded cold-deformed pipes are produced, having varying degrees of accuracy: normal, increased and precision. The diameter of products whose production is oriented towards this document can be from 5 to 110 mm: in this case, unalloyed carbon steel is used. Sometimes electric-welded straight-seam products have references to GOST 10707 80 in the accompanying documentation: this is explained by the fact that in 1991 it was decided to extend the validity of this document.
Where are steel pipes used?
Steel pipes are considered one of the most widely used materials. Various industrial and construction facilities are equipped with products made from these components. Pipe structures are used in everyday life and in the agricultural sector.
Electric-welded structures are in most cases used to equip heat-conducting mains, gas pipelines, etc.
In most examples, profile pipes are used to equip metal frames of furniture products to increase stability during operation. Pipes with a high temperature resistance are used in the installation of water and gas pipelines. The products have a fairly long service life.
The scope of pipes can be determined depending on their classification:
- There are no special requirements for pipes in the manufacture of materials for cable systems and equipment for local pipelines.
- For main pipelines, materials that can withstand high pressure are used.
- Other pipes must have sufficient heat resistance.
- Products of the fourth class relate to the oil production industry and well drilling.
- Products of the fifth class are necessary for the manufacture of sufficiently strong supporting structures.
- The mechanical engineering industry uses pipe structures that can withstand significant mechanical loads.
Steel pipes are characterized by high service life, strength and reliability, affordable cost and ease of installation.
Pipeline installation: useful information
Of course, no one assembles kilometer-long highways using one pipe, since this would take too much time. Yes, and organizing cutting, welding, and insulation in field conditions is not so easy. Therefore, specialized enterprises that install steel pipes for water supply assemble enlarged sections at their bases - or, as they are also called, pipe strings.
The finished sections are transported to the site by long vehicles, so that straight sections of the highway are installed at an accelerated pace.
Pipe carrier delivers finished sections to the site
How a pipe string is assembled
To assemble sections from individual pipes, special installations are used. The pipes laid on them are dried, cleaned of dirt, and the ends are welded. If there is no factory insulation, the outer surface of the section is primed and a protective coating is applied with heat-shrink tape, which we mentioned just above.
Each of these operations is carried out in its own zone, since the workshop has separate lines for welding and applying insulation. When performing this work, pipes or finished sections rotate around their own axis.
The types of installations used depend on the volume of work performed, the size of the pipes, the technology of their assembly and insulation. Shaped parts for large pipelines are also assembled in the workshop - on special assembly tables.
Table for assembly and welding of shaped parts of pipelines
Centralizer for joining pipe ends
Assembly of pipeline sections of complex configurations is also carried out in the workshop
So:
- Let us consider, as an example, the installation of a section on a type III installation - they assemble pipes with a diameter of 219 mm and above. They are placed using a lifting mechanism on a rack, from where they are moved to the alignment line. Sections of three lengths are assembled there: 18m, 24m, 36m. They are all multiples of 6, since this is the standard length of one pipe.
- Upon completion of assembly, a seam root is formed at all section joints. This is done either by semi-automatic welding or by installing a special gasket from the inside. Then, the “semi-finished product” of the section, through an intermediate rack, is fed to the automatic submerged arc welding line.
At the next stage, the finished whip is fed to the insulation line, where it is dried, coated with primer, and a protective coating is applied. All that remains is to load the whips onto a long transport vehicle, which is called a “lash carrier,” and deliver them to the installation site.
Learn more about the most popular products
Straight-seam pipes made using electric welding are in most cases used for transporting petroleum products and gas, and in the design and construction of various metal structures. Blanks for such pipes are called strips; they are ordinary steel sheets of a certain thickness. The strips are cut into separate strips, which are bent into pipes during processing.
Various types of seams are used for welding:
- Laser seam;
- Arc welding;
- Induction;
- Plasma.
The final stage of production involves calibrating and testing the weld for strength. There are cold-rolled and hot-rolled rolling technologies for this type of pipe structures. The cross-section of pipes made in this way can be round or square.
Spiral welded pipes made using electric welding are produced in a similar way with the only difference. The steel sheet is first twisted into a spiral, and then carefully welded. Thanks to this welding technology, the pipe's resistance to mechanical stress and high internal pressure increases greatly.
Area of operation of such pipe structures:
- Heating mains;
- Various oil and gas pipelines;
- Waterways.
In cold-formed products, the wall thickness is 0.3-24 mm. Therefore, pipes are used in the design of aircraft, shipbuilding, industry and other industries where high strength and relatively low weight are required.
Hot-formed pipes are created from a solid heated cylindrical billet that is easily deformed. This technology makes it possible to create pipes with wall thicknesses from 2.5 to 75 mm. This type of pipe is used in systems with the highest possible internal pressure, in technological processes in the chemical industry, where leakage through a seam is considered unacceptable.
Depending on the application, the service life of these pipes is 10-50 years.
Assortment of seamless steel pipes, according to GOST 8732-78 (91)
The production of hot-deformed seamless steel pipes in accordance with GOST 8732-78 (91) is characterized by the presence of lengthy and complex processes. This factor explains the rather high price of these products. The use of hot-deformed and cold-rolled seamless pipes is suitable for extreme conditions, where in the event of the slightest leak the consequences can be very serious.
The raw material for the production of hot-deformed pipes without seams are metal blanks: the piercing process and heating to high temperatures leads to the formation of hollow cylinders - sleeves. At first, their irregular shape becomes smooth due to the passage of the rollers. Segments 4-12.5 m long are cut from the sleeve (the length can be measured or unmeasured). For hot-rolled steel, according to GOST, a slight discrepancy in wall thickness is allowed. The same applies to deviations in diameter: the main thing is that these differences do not exceed special regulatory instructions. The list of permissible diameter deviations in accordance with GOST 8732-78 (91) is available in special documents.
For the production of round-shaped seamless steel pipes, a cold-deformed method can be used: however, in this case they fall under the regulation of GOST 8734-75 (91). The production process in this case is very similar to hot deformation: the only difference is the use of water cooling for a metal workpiece that has been pierced using a press. In GOST, the instructions for cold-rolled steel pipes without seams are duplicated as for hot-rolled seamless products. There is also an indication of permissible deviations in diameter dimensions.
Galvanizing of pipes
Galvanized pipes are highly reliable and reasonably priced. Thanks to a special protective zinc layer, resistance to corrosion increases. Damage to the protective layer may occur after deformation at the impact site, after which rust may form on the pipe. These products are used when equipment with a high-strength design is required, in which pressure and temperature changes will not occur. Zinc-coated steel pipes are excellent for temporary structures used in difficult environments.
Assortment and main GOST standards of round steel pipes
Using a round steel pipe, manufactured in accordance with GOST, systems for transporting water and gas are most often installed. Like profile structures, this type of metal pipes is manufactured using various methods.
There are suture and seamless products of this type. Round steel pipes that meet all GOST requirements constitute the largest group, which is characterized by a very complex systematization. These products are classified mainly based on the manufacturing method.
Technical characteristics in accordance with GOST
The quality characteristics of steel pipes are always determined by the approved GOST. Special standards that require compliance are developed for ordinary and galvanized products that are used in the installation of water supply systems, heating systems, gas pipelines, etc. The state quality standard also determines the technological process in accordance with which production should be carried out.
When manufacturing their products, manufacturers often indicate dimensions in inches or millimeters. Galvanized pipes weigh approximately 3% more than conventional steel products. This feature must be taken into account in the design process of pipe structures. The zinc layer has its impact on installation and operating requirements. The layer applied to the surface must exceed 30 microns.
Labeling requires attention when choosing a product. On the pipe, the manufacturer indicates the material from which it is made, the weight, diameter of the product, as well as the thickness of the metal layer, the manufacturing plant, the batch number, and the date of actual production. All information provided must comply with current state standards.
Electric-welded steel pipes with straight seams: assortment, according to GOST 10705-91
The list of technical conditions according to which longitudinally welded electric-welded pipes are made from steel contains GOST 10705-91.
Among the most important provisions of this document are the following:
- The size of the permissible curvature is indicated within 1.5 mm/linear meter for products that have undergone heat treatment, and 2 mm/linear meter for those that have not. If the customer wants it, in the first case the parameter can be reduced to 1 mm, in the second - to 1.5 mm.
- If the pipe is subjected to heat treatment, then, with appropriate recommendations from the customer, a special protective atmosphere can be created for this procedure.
- Along the edges of the straight-seam electric-welded tube, according to GOST 10707-91, it is cut off at an angle of 90 degrees, followed by cleaning of all irregularities and defects that have arisen.
Gas and oil pipes made of steel used in industry are subject to a separate GOST. As already mentioned, GOST 52079-2003 concerns electric-welded steel products with a straight seam and a large diameter. In addition, a special category includes a variety of welded and seamless steel pipes used by the motorcycle industry. Any section of these products should not have a curvature of more than 1.5 mm. Thanks to the regulatory document 12132-66, permission is given for the manufacture of products that have an exceptionally high or increased degree of accuracy.
Decoding of chemical elements
Ai (U) aluminum. B (P) boron. Mo (M) molybdenum. C (U) carbon. Cr (X) chromium. Ni (N) nickel. V (B) tungsten. Cu (D) copper. Si (C) silicon. Co (K) cobalt. Pb (AC) lead. Ti (T) titanium. Se (E) selenium. Mn (G) manganese. Ga (Gl) gallium.
It should be noted that some chemical elements enhance corrosion resistance, these primarily include nickel, chromium, titanium and copper. Some chemical elements enhance plasticity and the ability of pipes to withstand high hydraulic pressure. These elements include nickel and vanadium. The following elements are responsible for the heat resistance indicators: cobalt, tungsten, molybdenum. And niobium and titanium enhance the acid resistance of steel products.
Manufacturing technology and production
The manufacturing process is strictly regulated. It includes several steps:
- Metal cutting. Special equipment makes it possible to cut strips of the same width.
- Editing stripes. The slightest roughness is eliminated thanks to horizontal rollers. The waviness of the material is thereby reduced to a minimum or eliminated altogether.
- Molding of the workpiece. Rolls are used again: vertical and horizontal. The goal of this step is to minimize the radius of the workpiece by bringing the edges closer together.
- High frequency seam welding. The task of this stage is to connect the edges of the workpiece. The edges are heated to the melting temperature and joined using special equipment.
- Treatment of external weld seam (burr removal).
- Calibration This operation allows you to achieve the desired geometric parameters. The sizing rolls are activated.
- Profiling. This step is only relevant for profiled samples.
- Cutting. Using a cutting machine, the product is cut into the required fragments.
12X18Н10Т (GOST 9941-81)
The technological cycle is completed by a system of measures aimed at identifying quality control. It includes: non-destructive testing of the weld, hydrotesting, flattening. Only after this the product receives a quality certificate. Without it, it is impossible to obtain a certificate of compliance with GOST.
Sometimes you hear the opinion that galvanized samples cannot be welded. The skeptics' arguments boil down to the fact that in this case it is difficult to guarantee tightness. However, welding work in this case is carried out at a high quality level.
They are completely identical to those practiced when working with ferrous metals. But special technological requirements are imposed on working with this particular material:
- Avoid overheating during welding. Otherwise, the zinc layer may begin to deteriorate.
- Carry out work in a room with good air circulation. In the absence of good ventilation, zinc vapor can have a negative impact on workers.
- Upon completion of welding, the seam is thoroughly cleaned. After the stripping process, a special coupling is installed in the center of the seam. It is boiled on both sides and painted when the temperature allows (after complete cooling).
The technology is relevant for the manufacture of products of any diameter. But if the diameter is increased, then a more complex coupling is used. It may consist of two or more parts.
Permissible deviations from dimensions and lengths
The production of such products requires maximum precision.
Deviations in length of multiple models are allowed:
- Accuracy class I: no more than +15 mm;
- Accuracy class II: +100 mm.
Maximum deviations in the length of measured products. Table No. 1
At the request of the consumer (customer), the ends of measured and multiple products of class II accuracy can be trimmed. This operation is performed either on one side only, or on both.
The deviation of the outer diameter from the nominal value should be as minimal as possible.
Limit deviations in outer diameter Table No. 2
Sometimes, at the request of the customer, a displacement in the outer diameter is allowed. These assumptions should not exceed the sum of the established deviations.
Deviations in wall thickness are allowed (external diameter, mm):
- up to 152: ±10%.
- from 152 to 1020: ±10%.
- from 1020: according to the Table.
Maximum deviations for wall thickness Table No. 3
| Maximum deviations for wall thickness Table No. 3 | Tolerance |
| 8–15 | Based on wall thickness ±10% |
| Over 15 | ±1.5 mm |
It is considered normal if there is a special agreement between the manufacturer and the customer allowing unilateral admission. It must match the wall thickness. But in general, the deviation should not exceed the sum of the tolerances indicated in Table No. 3.
Round welded (630x7.0mm)
As for curvature, the standard allows deviations of 1.5 mm (no more!) per 1 meter .
Important! The strictness of the technologists’ requirements is explained by the fact that rolled steel is used, among other things, in the construction of oil and gas pipelines. The slightest deviation from the technology approved by the standard is fraught with the most unpredictable consequences.
Basic requirements for transportation, storage and packaging
Rolled metal retains its original qualities under almost any conditions. But thin-walled products (1.5 mm) must be stored in a dry warehouse. Moisture is detrimental to it. Thin-walled samples can also be stored in special boxes. In this case, a canopy is required.
Storage of thick-walled samples is allowed in open space. The main thing is that a special platform be prepared for them.
Electric welded products are shipped in batches. There are no special requirements for its packaging. But a prerequisite is to secure the shipment during transportation. This will ensure overall safety during transportation.
Transportation of products is carried out:
- covered large-capacity cargo carriers;
- gondola cars;
- open vehicles.
Important! The basic condition for transportation is the possibility of vertical loading. As for unloading, it can only be done with crane equipment.
As a rule, welded metal products are stored in bundles. In most cases, one such bundle weighs 5 tons. If a minimum quantity is sold, then shipment of a bundle weighing 1 ton is allowed.
Sometimes shipment is carried out without packaging (bundles). This is explained by the need to increase the volume of the shipped batch. In addition, this method significantly saves time during unloading work directly on site.
Types of steel grades
- High-speed tool steel grades. They are usually designated by the letter “P” and indicate the tungsten content. For example, it could be P12.
- Structural alloy steels. Here the alloying elements are designated Cr (chromium), Si (nickel), Mo (molybdenum), Ti (titanium). The listed chemical elements increase corrosion resistance and, accordingly, ensure uninterrupted operation.
- Structural quality carbon steels.
- Standard quality steel. Usually has the St. badge. For example, Art.10, Art.30. In the first case, the carbon content is 0.10%, in the second 0.30%.
- Cast structural steels. They are usually marked with the index “L”.
- Stainless steel.
It should also be noted that there are the following categories: Sp - calm steel, Kp - boiling steel and Ps - semi-quiet steel.