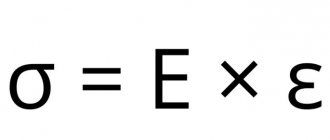| Brand: | R6M5K5 |
| Class: | High-speed tool steel |
| Used for rental: | Sections and shapes: GOST 19265-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006 Calibrated rod: GOST 19265-73, GOST 7417-75 Ground rod and silver: GOST 19265-73, GOST 14955-77 Strip: GOST 1926 5- 73, GOST 4405-75 Forgings and forged blanks: GOST 19265-73, GOST 1133-71 |
| Industrial use: | For processing high-strength stainless and heat-resistant steels and alloys under conditions of increased heating of the cutting edge. |
| Material hardness: | HB 10-1 = 269 MPa |
| Critical point temperature: | Ac1 = 840, Ac3(Acm) = 875, Ar3(Arcm) = 805, Ar1 = 765 |
| Forging temperature, °C: | Start 1160, end 850. Cooling in wells at 750-780 °C |
| Cutting ability: | — |
| Weldability of material: | Not applicable for welded structures |
| Flock Sensitivity: | Not sensitive |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | Less inclined |
| Analogues: | R9K5, R18, R6M5 |
Decoding
- The letter P indicates that the steel is high-speed;
- Number 6 - indicates the presence of Tungsten (W) and its average% in the steel (in this steel the Tungsten value is 5.70–6.70%);
- The letter M indicates the presence of Molybdenum (Mo);
- Number 5 - indicates the average% Molybdenum content (in this steel the Molybdenum value is 4.8–5.3%);
- The letter K indicates the presence of Cobalt (Co);
- Number 5 - indicates the average% Cobalt content (in this steel the Cobalt value is 4.7–5.2%).
Main characteristics
Rapid steels include metal alloys to which additional substances have been added that improve their chemical and physical properties. Thanks to this, the metal alloy becomes strong, wear-resistant, unable to come into contact with oxygen and become covered with rust. R6M5 high-speed steel differs from conventional carbon alloys in that it can process any hard material at high speed, while having good wear resistance.
Microstructure of R6M5 steel
It has unique properties that make it possible to produce tools such as cutters, taps or reamers. Made from this alloy, they will serve the owner faithfully for a very long time.
And the most famous and characteristics of steel grade R6M5 include:
- The hardness of steel grade R6M5 when heated. Typically, other alloys, during long-term and non-stop drilling, begin to heat up, and with increasing temperature, as is known, the metal begins to soften. And the drill loses its abilities and becomes fragile. The same high-speed steel can heat up to 6000 °C, maintaining its initial properties and without losing strength.
- Increased resistance to incandescence at fairly high temperatures.
- Holds an edge very well.
- Has high viscosity.
- Excellent processing on grinding equipment.
- Holds impact loads perfectly.
The characteristics of R6M5 steel listed above make the metal alloy indispensable in construction.
Chemical composition of steel R6M5K5
| Chemical element | % |
| Carbon (C) | 0,84 – 0,92 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0,2 – 0,5 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0,2 – 0,5 |
| Nickel (Ni) | up to 0.6 |
| Phosphorus (P) | up to 0.03 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 3,8 – 4,3 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 4,8 – 5,3 |
| Tungsten (W) | 5,7 – 6,7 |
| Vanadium (V) | 1,7 – 2,1 |
| Cobalt (Co) | 4,7 – 5,2 |
| Sulfur (S) | up to 0.03 |
| Copper (Cu) | up to 0.25 |
| Iron (Fe) | ~75 |
Features of steel sharpening
Items obtained from a quick cutter are subject to frequent dulling. And ordinary sharpening wheels, which are made of electrocorundum, will not help improve the quality of sharpening.
Sharpening a knife made of steel R6M5
In order to properly sharpen the tool, cup wheels and flat profiles are used. But, usually, such sharpening has its disadvantages. Therefore, in order to qualitatively sharpen a tool made from this type of metal alloy, two passes are used.
- first, preliminary sharpening is done, for which a wheel with an abrasive surface of grade 40 grain is used;
- for finishing, for which grade zero is used from 25 to 16.
Mechanical properties of R6M5K5 steel in a heat-treated state at elevated °C
| Test temperature, °C | 200 | 400 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 650 |
| Bending strength, MPa | 3820 | 3980 | 3040 | 2980 | 2790 | 2500 |
| H.V. | 833 | 769 | 726 | 686 | 626 | 528 |
| HRC ∂ (HB) | 64 | 62 | 61 | 59 | 57 | 52 |
Heat treatment of R6M5 steel
Heat treatment of the R6M5 alloy has a number of subtleties that relate to its properties. The fact is that it is capable of decarbonization during heating. To prevent this from happening, it is usually heated using a slow simmer.
R6M5 high-speed steel heats up to 1230 degrees. During heating, steel mill workers closely monitor the process. During the first warm-up, the temperature rises to two hundred degrees and the heating stops for an hour, then another additional heating is performed to thirty degrees. And again a vacation for an hour. After this, it is continued to be heated to 690 degrees and stopped again for an hour. And the last two heatings are brought to temperatures of 860 and 1230, respectively.
Physical properties of R6M5K5
| Test temperature, °C | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity E, GPa | 2,2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Density, pn, kg/cm3 | 8200 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient W/(m °C) | — | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 32 | 36 | 34 | 36 | 29 |
| Electrical resistivity (p, NΩ m) | 458 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
R6M5K5 high-speed tool steel
Decoding
- According to GOST 19265-73, the letter P means that the steel is high-speed.
- The number 6 following the letter P indicates the average mass fraction of tungsten in %, i.e. The average mass fraction of tungsten in steel is 6%.
- The letter M means that the steel is alloyed with molybdenum, the number 5 following the letter indicates the mass fraction of molybdenum in the steel in %, i.e. The molybdenum content in steel is about 5%.
- The letter K means that the steel is alloyed with cobalt, the number 5 following the letter indicates the mass fraction of cobalt in the steel in %, i.e. The cobalt content in steel is about 5%.
- According to GOST 19265-73, the designation of steel grade R6M5K5 does not indicate the mass fraction of chromium and vanadium.
Foreign analogues [1]
| Steel grade (Country) | Standard |
| 2723 (Sweden) | SS |
| 3243 (UK) | GB-03 |
| BM 35 (UK) | BS 4659 |
| 6-5-2-5 (Spain) | UNE 36073 (75) |
| F.550.C (Spain) | |
| EM 35 (Brazil) | ACO |
| VK-5E (Brazil) | Villares |
| HS 6-5-2-5 (Euronorms) | EN 96-79 |
| HS 6-5-2-5 (Germany) | DIN 17350 |
| HS 6-5-2-5 HC (France) | AFNOR NF NF A35-590 (92) |
| R8 (Hungary) | MSZ 4351 |
| SK5M (Poland) | PN/H 85022 |
| SKH 55 (Japan) | JIS G4403 |
| W6Mo5Cr4V2Co5 (China) | GB 9943-88 |
| R6M5K5 (Bulgaria) | BDS 7008 |
Type of delivery
- Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 19265-73, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88.
- Calibrated rod GOST 19265-73, GOST 7417-75.
- Polished rod and silver steel GOST 19265-73, GOST 14955-77.
- Strip GOST 19265-73, GOST 4405-75.
- Forgings and forged blanks GOST 19265-73, GOST 1133-71.
Characteristics and Application
Tungsten-molybdenum steel R6M5K5 is used for processing high-strength stainless and heat-resistant steels and alloys under conditions of increased heating of the cutting edge. This steel is the main grade of high-speed steel with increased productivity, used for the manufacture of various roughing and semi-finishing tools (mills, cutters, countersinks, thread-cutting tools, etc.) intended for processing carbon and alloy structural steels at high cutting conditions, as well as stainless steels and heat-resistant alloys. It is recommended instead of R18K5F steel, as it is more economical, and instead of R9K5 steel, as having higher (25-30%) cutting properties [2].
The cobalt content in steel improves heat resistance up to 645 °C due to an increase in the temperatures of the α → γ transformation, difficulty in carbide coagulation and its effect on the formation of the θ phase. The positive effect of cobalt on the heat resistance and thermal conductivity of steels with 0.7-0.9% C should increase with increasing its content (up to 10-15% and higher). At the same time, mechanical properties deteriorate. An increase in the tungsten (molybdenum) content at a constant cobalt content has the same effect.
R6M5K5 steel has a heat resistance of 630 °C, which is lower than that of R12F4K5 steel; the secondary hardness of R6M5K5 steel is also lower and is 65-65.5 HRC. This is due to the need to assign lower quenching temperatures, and consequently, to the difficulty of saturating the solid solution to the level obtained with R12F4K5 steel. The wear resistance of R6M5K5 steel is lower due to lower hardness and the absence of MC carbides in its structure. The mechanical properties of R6M5K5 steel are 20-30% higher than those of R12F4K5 steel.
The technological disadvantage of R6M5K5 steel is increased sensitivity to decarbonization. Its sandability is good.
This determines the scope of application of R6M5K5 steel [3].
Temperature of critical points, °C [2]
| Ac1 | Acm | Arm | Ar1 |
| 840 | 875 | 805 | 765 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 19265-73)
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | W | V | Co | Mo | N | S | R |
| no more | no more | |||||||||
| 0,84-0,92 | 0,50 | 0,50 | 3,80-4,30 | 5,70-6,70 | 1,70-2,10 | 4,70-5,20 | 4,80-5,30 | 0,40 | 0,030 | 0,030 |
Final heat treatment modes
| Hardening | Vacation | |||||
| tп, °C | tа, °C | Wednesday | t, °C | τ, h | Wednesday | H.R.C. |
| 800-850 | 1210-1240 | Oil, molten salts or alkalis | 540-560 | Two-three times an hour | Air | 64-66 |
Hardness (GOST 19265-73)
| Delivery status | Hardness |
| Annealed rod and strip | Up to HB 269 |
| Samples. Hardening at 1230 °C in oil; tempering (2- or 3-fold) at 550 °C, 1 hour | St. HRСе 65 |
Mechanical properties of steel as delivered (after annealing) at 20 °C [4]
| σ0.05, MPa | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, , % | ψ, % MPa | σcom 0.2, MPa | σcom, MPa | ε, % | tk, MPa | γ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 240 (5) | 510 (20) | 850 (30) | 12 (1) | 14 (1) | 520 (13) | 2720 (80) | 54 (1,5) | 590 (18) | 60 (1,4) | 18 (1) |
NOTE
- σ0.05 — Elastic limit
- σ0.2 — Yield strength
- σв — Temporary resistance
- δ — Elongation
- ψ — Relative narrowing of the cross section
- σсж 0.2 — Compressive yield strength
- σсж — Compressive strength
- ε — Relative settlement at the appearance of the first crack
- τк — Torsional strength — maximum shear stress
- γ — Relative shift
Mechanical properties of steel as received (after annealing) at elevated temperatures [4]
| tsp, °C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | σcom, MPa | tk, MPa | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB |
| 200 | 500 (50) | 870 (60) | 10 (2) | 11 (2) | 1100 (50) | 570 (30) | — | 258 (6) |
| 400 | 470 (50) | 770 (60) | 12 (2) | 11 (2) | 950 (50) | 500 (30) | — | 240 (6) |
| 600 | 330 (40) | 620 (50) | 28 (3) | 48 (5) | 730 (40) | 340 (20) | — | 165 (6) |
| 800 | 130 (20) | 270 (20) | 55 (4) | 60 (5) | 130 (20) | 120 (20) | — | 38 (4) |
| 1000 | 110 (20) | 130 (20) | 57 (4) | 50 (5) | 100 (20) | 60 (10) | 140 (15) | 26 (4) |
| 1100 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 170 (15) | — |
| 1200 | 40 (10) | 40 (10) | 87 (2) | 15 (2) | 70 (10) | 40 (10) | 75 (10) | 5 (1) |
Mechanical properties of steel as delivered at 20 °C [4]
| σ0.05, MPa | σв, MPa | σcom 0.2, MPa | σcom, MPa | tk, MPa | σben, MPa | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 2340 | 2050 | 3100 | 3750 | 1820 | 3000 | 25 |
Mechanical properties of steel in a heat-treated state at elevated temperatures [4]
| tsp, °С | σben, MPa | Hardness | |
| H.V. | HRСе | ||
| 200 | 3820 | 833 | 64 |
| 400 | 3980 | 769 | 62 |
| 500 | 3040 | 726 | 61 |
| 550 | 2980 | 686 | 59 |
| 600 | 2790 | 626 | 57 |
| 650 | 2500 | 528 | 52 |
Steel hardness depending on tempering temperature [2]
| tsp, °С | Hardness HRCе |
| 500 | 67 |
| 540 | 68 |
| 580 | 67 |
| 620 | 63 |
| 660 | 57 |
NOTE. Hardening at 1220 °C in oil; vacation three times for 1 hour.
Technological properties [2]
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1160, end 850.
Cooling in wells at 750-780 °C.
Forging and annealing temperature [2]
- forging temperature ranges 1160-850 °C;
- cooling after forging in wells at 750-800 °C;
- annealing at 840-860 °C, cooling 40 degrees/hour to 730-740 °C, holding for at least 4 hours, cooling 50 degrees/hour to 600 °C, in air;
- hardness after annealing no more than HB 269
Red resistance (GOST 19265-73)
| Temperature, °C | Time, h | Hardness HRCе |
| 630 | 4 | 59 |
NOTE. Sandability is good (GOST 19265-73).
Density ρп kg/cm3 at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20°C |
| R6M5K5 | 8200 |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 900 | |
| R6M5K5 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 32 | 36 | 34 | 29 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C |
| 20 | |
| R6M5K5 | 220 |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa
| steel grade | At test temperature, °C |
| 20 | |
| R6M5K5 | 83 |
Electrical resistivity ρ nom*m
| steel grade | ρ nom*m, at test temperature, °C |
| 20 | |
| R6M5K5 | 458 |
Bibliography
- Shishkov M.M. Brand of steels and alloys. 2000
- Poznyak L.A. Tool steels. Directory. 1977
- Geller Yu.A. Tool steels. 1983
- GSSSD 9-79 – State service of standard reference data
Find out more
Steel 12Х18Н12Т is corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant,...
Structural alloy steel 30ХГС…
HVG alloy tool steel…
Steel 6ХВГ tool stamping…
Cost of metal in products
It is not difficult to buy R6M5 in finished products, but the cost of the alloy is quite high. Here is a small price list of steel products of this brand. So a tool circle, depending on the thickness: 2, 5 or 16 mm, costs 1350, 1200, 600 rubles per kilogram, respectively. The cost of an instrumental strip is slightly lower and amounts to 620 rubles per kilogram.
Undoubtedly, prices for R6M5 grade metal in products may vary, so the given figures should be taken relatively, only to determine the level of cost of the alloy. On the other hand, high prices for high-speed cutting make the metal quite popular in the sale of scrap metal. The cost of secondary high-speed steel is significantly higher than that of conventional metal grades. Alternatively, products made from R6M5 alloy, which have served their service life, can be used as business scrap, with a higher value.
Decoding - what the marking symbols mean
Elements of equipment and devices have a high strength index, the material has excellent viscosity. Steel ensures long-term performance, both in product components and in blades or finished tools.
Such markings are a legacy of the Soviet era:
- The letter "P" is an indicator of high-speed steels. The expression comes from the translation of the English “rapid” - “swift”.
- The sign after “P” indicates the presence of tungsten in the composition as a percentage. For this particular metal it is in the range of 6% with minor deviations.
- This is followed by the letter “M”, meaning cash in the molybdenum mark. The next indicator is the percentage of presence of the element in the total mass.
- In addition to M, high-speed steels can include the following designations in their markings: “K” - cobalt, “T” - titanium, “F” - vanadium, “C” - zirconium.
Considering the designation “P6M5”, decoding can also include other letters. If the steel was smelted by electroslag remelting, an addition appears in the form of “Ш” (Р6М5-Ш). With the introduction of the latest technologies into the production process, the following wording now appears - P6AM5. This means adding nitrogen to the overall composition.
Products that have found a place in everyday life and in production
R6M5 steel, its characteristics and application for knives. This is a fairly common household item; there are a number of its manufacturers with a global brand, for example, Rapid. There are many videos on the Internet with experiments using knives made of R6M5 steel. Indeed, they are good at cutting such things: ropes, wood, meat and bones, etc. The most striking experiment involved an attempt to cut a metal plate several mm thick with a R6M5 knife, and it worked.
It should be added that high-speed steel R6M5 does not have a tendency for easy turning. Therefore, quite often knife owners complain about the inability to sharpen them. In any case, this cannot be done with household sharpeners. Apparently, this is why products made from P6M5 are rarely found in everyday life; they can more often be seen as an auxiliary tool among plumbing equipment or among avid fishermen and hunters.
In almost every home you can find household power tools. Auxiliary elements (equipment) for it can be made from quick cutters.
The P6M5 drill is used in the production of household tools intended for repair work. Additionally, there is an opinion that it is better to drill hardened iron using the R6M5K5 brand. In addition, there are the following types of drills:
- simple with one-sided sharpening;
- crown (for drywall);
- stepped;
- spear-shaped for glass and porcelain stoneware;
- on stone, brick, wood.
Despite the above comment, the P6M5 metal drill is also a fairly common tool. R6M5 is used to make countersinks, crowns, conical machine reamers, drills, slotting cutters, and hacksaw blades.
Video - How to make a knife from P6M5 with your own hands
Difficulties in hardening high-speed steel
Heat treatment of P6M5 contains a number of specific features associated with the characteristics of this brand, as well as a long heating time for hardening. To reach 1230 degrees Celsius (hardening temperature according to GOST), 25 percent more working time is spent than for a similar grade P18. First, a vacation period is made at 200 and 300 degrees for an hour. Further processing is carried out in 3 stages:
- 690 degrees -3 minutes;
- 860 - also 3 minutes;
- 1230 - 1.5 minutes.
Then the steel is cooled. In further processing, a three-time vacation period at 560 degrees for 1.5 hours is used. During tempering periods, the alloy is supplemented with alloying additives that form carbides, which increases the strength of the final metal. Previous annealing of steel helps eliminate high brittleness with a high strength index.