Advantages of galvanized profile
Galvanized sheet is a type of metal product coated with a zinc layer to prevent corrosion. Rolled metal is produced by coating special grades of sheet steel with grade zinc. Thanks to this production and processing method, the products have the following technical features:
- High resistance to mechanical loads.
- Light weight.
- Economical.
- Corrosion resistance.
Steel structures are easy to transport and install due to their low weight, which is why they are preferable in many areas, for example, when installing communications and lighting. The zinc coating eliminates the only significant drawback of steel - susceptibility to corrosion. Galvanized sheet has an increased service life. Protective coatings are applied to metal workpieces and structures using the galvanic method, hot-dip galvanizing and other methods.
This is what a galvanized profile sheet looks like
According to purpose, galvanized sheets are divided into:
- ХШ - for cold stamping;
- HP - for cold profiling;
- PC - for painting (trained);
- OH - general purpose.
Galvanized sheet for cold stamping is divided into:
N - normal hood;
G - deep drawing;
VG - very deep drawing;
Based on the uniformity of the coating thickness, galvanized sheets are divided into:
NR - with normal thickness variation;
UR - with reduced thickness variation.
By agreement between the consumer and the manufacturer, galvanized steel can be produced:
KR - with a crystallization pattern;
MT - without crystallization pattern.
Features of manufacturing galvanized steel profiles
The steel sheet is covered with a protective layer on both sides. Depending on the scope of application of the metal workpiece, humidity and other operating conditions, the thickness of the coating may vary.
There are several production methods:
- Hot galvanizing is the most common method. Special industrial containers are used for galvanizing. Used to protect lighting poles.
- The galvanic method is the application of a layer of zinc through electrolytic dissociation. The metal structure is immersed in a container with electrolyte and becomes the cathode, and the zinc plate becomes the anode. The fastest method, the disadvantages of which are the low mechanical stability of the layer, small thickness of the zinc coating, and weak adhesion to the metal. The galvanic method is most often used for decorative purposes.
- Thermal diffusion method - the metal product is calcined in an oven at 400 degrees, covered with zinc powder. As a result of diffuse processes, the top layer of metal is saturated with zinc atoms, and the coating is extremely durable. But due to the complexity and energy consumption of the process, it is used only in the manufacture of specialized parts.
- Gas-thermal method - the metal is coated with a protective layer using gas-flame spraying. The procedure is simple and can be used even in field conditions, but the coating is uneven and subject to mechanical stress.
- Cold method - zinc is applied with a brush, spray or paint sprayer as in conventional painting. The method is economical, but the zinc layer is destroyed under the influence of mechanical loads.
The production of sheet profiles requires modern equipment and qualified personnel
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
3.1. Galvanized steel must be manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard technical documentation approved in the prescribed manner.
3.2. Galvanized steel is made from carbon cold-rolled coiled steel with a surface quality in accordance with GOST 16523-97. Steel grades must correspond to those given in table. 1a.
Table 1a
| Cink Steel | Cold rolled steel grade for making galvanized steel | ||
| Group | Hood category | first quality category | highest quality category |
| XSh | N, G | Steel grades with chemical composition according to GOST 380-94, GOST 9045-93 and GOST 1050-88 | Steel grades with a chemical composition in accordance with GOST 9045-93, as well as GOST 1050-88 with a sulfur content of no more than 0.035% and phosphorus - no more than 0.020% and GOST 380-94 with a mass fraction of sulfur no more than 0.035% and phosphorus - no more than 0.025 % |
| XSh | VG | 08ps, 08kp, 08Yu according to GOST 9045-93 | 08ps, 08kp, 08Yu according to GOST 9045-93 |
| 08ps, 08kp, 10 cl according to GOST 1050-88 | 08ps, 08kp, 10kp according to GOST 1050-88 with a mass fraction of sulfur no more than 0.030% and phosphorus no more than 0.020% | ||
| HP, PC | — | 08ps according to GOST 9045-93 | 08ps according to GOST 9045-93 |
| 08, 08ps according to GOST 1050-88 | 08, 08pa according to GOST 1050-88 | ||
| BSt0, BSt1, BSt2, BStZ of all degrees of deoxidation according to GOST 380-94 | BSt0, BSt1, BSt2, BSt3 of all degrees of deoxidation according to GOST 380-94 with a mass fraction of sulfur no more than 0.04% and phosphorus no more than 0.035% | ||
| HE | — | Steel grades with chemical composition according to GOST 380-94, GOST 9045-93 and GOST 1050-88 | Steel grades with a chemical composition in accordance with GOST 9045-93, GOST 1050-88, GOST 380-94 with a mass fraction of sulfur no more than 0.045% and phosphorus no more than 0.040% |
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
3.3. For galvanizing, zinc of grades Ts0 and Ts1 according to GOST 3640-94 is used with the addition of aluminum, lead and other metals to the bath. Alloying with lead is allowed by introducing zinc of grade Ts2.
3.4. The surface of galvanized steel must be clean and completely coated.
3.4.1. Violations of the continuity of the coating in the form of cracking on small beads located on defects in the steel base, the classification and dimensions of which are provided for by GOST 16523-97, are not allowed.
3.4.2. On sheets and strips with unedged edges, edge flaws with a depth exceeding the maximum deviations in width are not allowed.
3.4 — 3.4.2. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2)
.
3.5. For galvanized steel of groups ХШ, ХП and ОН, small sagging (sagging, layering), grains and uneven crystallization of zinc, traces from bends of the strip and control rollers, local roughness of the coating (rash), light scratches and abrasions that do not violate the continuity of the zinc coating, light and matte spots are allowed , uneven coloring of the passive film.
3.6. For galvanized steel of the PC group, dark dots and tracks (traces) from deformed small beads (sagging, layering), grains and local roughness of the coating (rash), a matte and blurred pattern of zinc crystallization, traces from strip bends, light scratches and abrasions that do not violate the continuity of the zinc are allowed. coatings, light matte spots, uneven coloring of the passive film.
3.7. At the request of the consumer, the passive film must have a uniform color.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
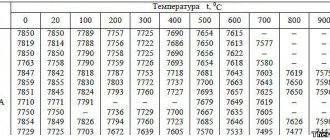
3.8. The reduced thickness difference of the UR zinc coating should be no more than 16 for class P, no more than 10 for class 1, no more than 4 microns for class 2. Galvanized steel of normal thickness HP must have a coating thickness within the limits specified in the table. 1.
Galvanized steel of the highest quality category is manufactured with different thicknesses of the zinc coating for steel groups XSh, HP and PC of class P - no more than 12, class 1 - no more than 8 and class 2 - no more than 3 microns.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1,2).
3.9. In the place of bending of galvanized steel with a thickness of up to 1.0 mm inclusive, when testing the adhesion strength of the coating to the base metal when bending 180°, there should be no peeling of the zinc coating exposing the steel surface. A network of small cracks along the entire length of the bend and peeling of the coating at a distance of up to 6 mm from the edges of the sample are allowed.
3.10. The mechanical properties of galvanized steel must comply with the standards specified in Table 1b.
Table 1b
| Cink Steel | Temporary tensile strength sВ, MPa | Yield strength sT, MPa, not less | Relative elongation d4, %, not less, at l 0 = 80 mm for steel thickness, mm | ||||
| groups | hood categories | up to 0.7 | St. 0.7 to 1.5 | St. 1.5 to 2.0 | St. 2.0 | ||
| N | 300-490 | — | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | |
| XSh | G | 275-430 | — | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| VG | 255-410 | — | 26 | 28 | 29 | 30 | |
| HP, PC | — | — | 230 | 20 | 22 | — | — |
| HE | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Note
. The values of temporary tensile strength and relative elongation for galvanized steel of group XIII of drawing categories N and G, relative elongation for steel of groups KhP and PK were optional until 07/01/89.
When calculating the tensile strength and yield strength, the thickness of the zinc coating is not taken into account.
3.10.1. The depth of the spherical hole of galvanized steel of group XSh must comply with the standards given in table. 1st century
Table 1c
| Thickness of galvanized steel | Depth of spherical hole for hood categories, not less | ||
| VG | G | N | |
| 0,5 | 8,5 | 8,0 | 6,9 |
| 0,6 | 8,9 | 8,5 | 7,2 |
| 0,7 | 9,2 | 8,9 | 7,5 |
| 0,8 | 9,5 | 9,3 | 7,8 |
| 0,9 | 9,9 | 9,6 | 8,2 |
| 1,0 | 10,1 | 9,9 | 8,6 |
| 1,1 | 10,3 | 10,1 | 8,7 |
| 1,2 | 10,5 | 10,3 | 8,8 |
| 1,3 | 10,7 | 10,5 | 8,9 |
| 1,4 | 10,8 | 10,6 | 9,0 |
| 1,5 | 11,0 | 10,8 | 9,1 |
| 1,6 | 11,3 | 11,0 | 9,5 |
| 1,7 | 11,4 | 11,1 | 9,6 |
| 1,8 | 11,5 | 11,2 | 9,7 |
| 1,9 | 11,6 | 11,3 | 9,8 |
| 2,0 | 11,7 | 11,4 | 9,9 |
Notes:
1. For galvanized steel of intermediate thicknesses, the depth of the spherical hole must correspond to the standards established for the next smaller thickness.
2. The depth of the spherical hole for galvanized steel with a thickness of over 1.5 mm was optional until 07/01/89.
3. When tested on devices such as MTL-10 g, the norms for the depth of the spherical hole are reduced by 0.3 mm.
3.10.2. For galvanized steel of group XIII of the highest quality category, the relative elongation should be 1 unit. more than the norms of the table 1b, and the depth of the spherical hole is 0.2 mm greater than the norms in the table. 1st century
3.10 — 3.10.2. (Amended edition, Rev. No. 2).
3.11. Galvanized steel of the XSh group is manufactured with a ferrite grain size of points 7, 8,9, 10 according to GOST 5639-82 for exhaust category VG and not lower than point 6 for exhaust category G.
For galvanized steel of category VG, grain unevenness is allowed within two adjacent numbers, for sheets of category G - within three adjacent numbers.
3.12. For galvanized steel of group XIII, category hood VG, the presence of structurally free cementite is allowed within points 0, 1, 2 and 4 of scale 1 according to GOST 5640-68. For categories G and N, the presence of structurally free cementite is not standardized.
3.13. The number of bends without fracture of galvanized steel of the HP, PK, OH groups must comply with the standards established in table. 1 year
Table 1d
| Thickness of galvanized steel, mm | Number of bends |
| Up to 0.8 incl. | 8 |
| St. 0.8 "1.2" | 5 |
| » 1,2 » 2,0 » | 3 |
| » 2,0 | 2 |
Note
. The norms for bending galvanized steel with a thickness of more than 1.5 mm were optional until 07/01/89.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
3.14. (Deleted, Amendment No. 2).
Hot dip galvanizing method
The most profitable, practical and popular technology. To apply a protective layer to a metal workpiece, after preliminary degreasing, it is immersed in a bath of molten zinc, after which it is removed and dried. The temperature of the zinc in the container is 450–460 °C.
The quality of the resulting zinc coating is carefully controlled. The protective layer is assessed visually, its thickness is checked (magnetic or metallographic) and the strength of adhesion to the surface (by heating, hammering, scratching).
The hot-dip galvanizing method has the following advantages:
- High mechanical strength of the protective coating.
- Zinc covers the entire area of the metal structure, including hard-to-reach places.
- The service life of the coating is up to 60 years, even when interacting with aggressive environments.
After galvanizing, the steel sheet has all the advantages of stainless metal and lends itself well to various types of processing. To further protect the surface after galvanizing, it is painted with decorative powder paint.
Galvanized steel is used to create modern lighting lanterns
ASSORTMENT
2.1. Galvanized steel is manufactured with a width from 710 to 1800 mm inclusive, and a thickness from 0.5 to 2.5 mm inclusive.
2.2. Dimensions, maximum deviations and other requirements for the assortment must comply with the requirements of GOST 19904-90.
Galvanized steel of the highest quality category is produced:
with a crescent shape of rolled steel no more than 6 mm per 3 m length;
with flatness PV and PU and permissible thickness deviations according to the standards of increased rolling accuracy;
with telescopicity of rolls with a steel width of up to 1000 mm, no more than 30 mm.
Examples of symbols
Galvanized steel 0.8 thick, 1000 wide, 2000 mm long, normal rolling accuracy B, normal flatness PN, snow-edged edge NO group OH, with crystallization pattern KR, first class zinc coating according to GOST 14918-80:
Galvanized steel coils 1.2 thick, 1000 mm wide, increased rolling accuracy A, with cut edge O, grade 08kp, very deep drawing VG, without MT crystallization pattern, with reduced thickness variation UR, second class coating according to GOST 14918-80:
Galvanized rolled steel with a differentiated coating 0.5 thick, 710 mm wide, increased rolling accuracy A, with a cut edge O, grade BSt3kp, for PC painting, without a crystallization pattern MT with a reduced thickness difference UR, with a first-class coating on one side and a second-class coating on the other GOST 14918-80:
Note
. The steel category XSh is not indicated in the order, and the drawing ability index (N, G or VG) is indicated in the designation.
Chapter. 2. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
Quality checking
Galvanizing GOST provides indicators that transfer sheets to one or another quality category - this can be specified in the accompanying documents. It is important for the buyer that the appearance of the material does not contain surface flaws or integrity violations.
The surface of the steel should be smooth and even, without cracks in the zinc layer. Sometimes, for some brands of material, the formation of spots, thin sagging and roughness on the surface is allowed. It belongs:
- to galvanization obtained by cold stamping;
- profiled sheets made on bending devices;
- material belonging to the general purpose group.
For other categories of galvanized steel there should be no defects during visual inspection; defects in the form of nicks are especially unacceptable. If the material is intended for painting, then there should be no signs of defects on it. Any crack affects the quality of the final product.
ACCEPTANCE RULES
4.1. Galvanized steel is accepted in batches. The batch must consist of sheets or rolls of the same group of galvanized steel, the same size, one type and class of coating thickness, type of preservation, the same grade and melt (steel of the KhSh, KhP and PK groups) and drawing category (steel of the KhSh group), must be registered and accompanied by a document on quality according to GOST 7566-94 with the addition of values of optional quality indicators.
The batch weight should not exceed the shift production of the unit.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2).
4.2. In the quality document, test results and chemical composition data are indicated at the request of the consumer.
For galvanized steel that has been awarded the state Quality Mark, the designation of the state Quality Mark is affixed to the quality document.
4.3. To control the size and quality of the surface, 6% of sheets or one roll from the batch are selected.
4.4. To control the adhesion strength of the coating, mechanical properties, and microstructure, one sheet or one roll from the batch is selected.
4.5. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, a re-check is carried out in accordance with GOST 7566-94.